Abstract
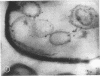
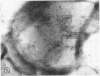
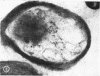
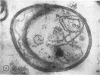
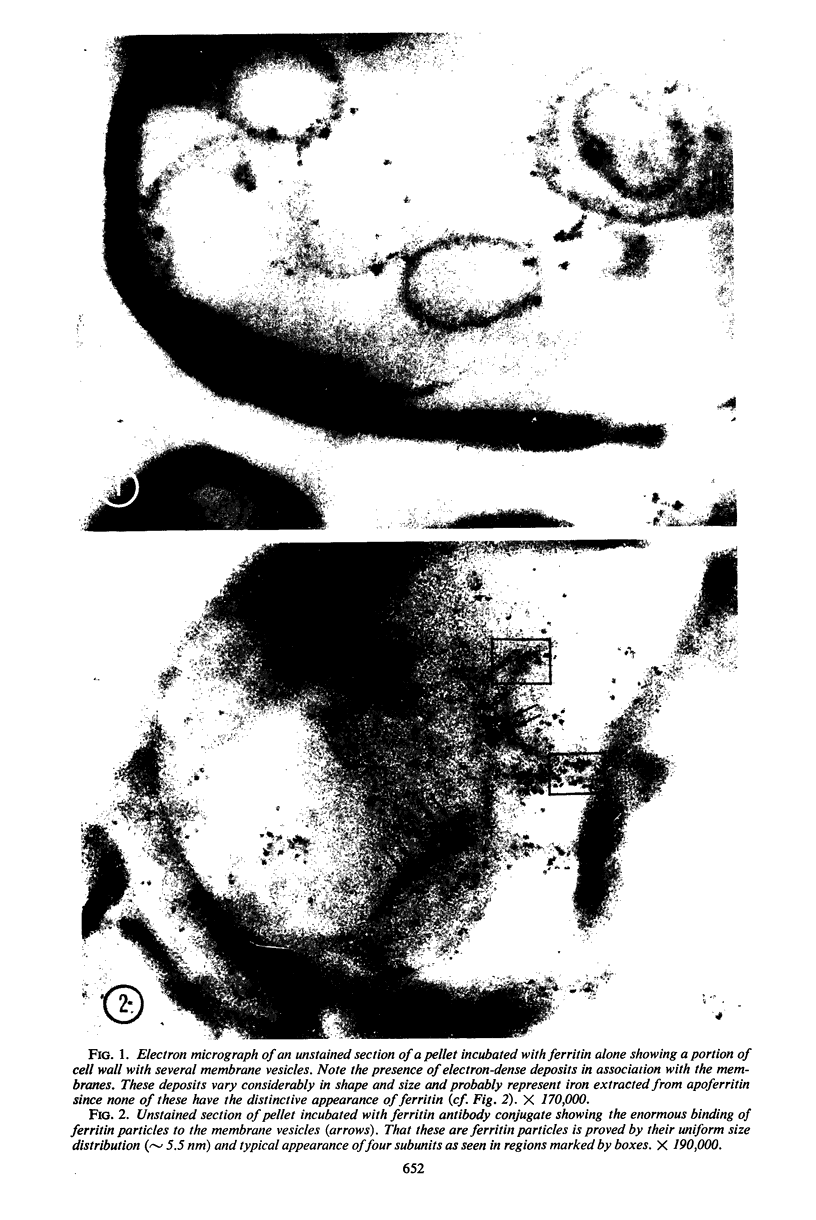
Highly purified staphylococcal alpha toxin has been used to produce monospecific anti-alpha antibody in rabbits. Gamma globulin prepared from the serum of these rabbits was coupled with ferritin by using toluene diisocyanate. Staphylococcal cells which had been disrupted by two passages through an LKB X-press were treated with this conjugate. Electron microscopic examination of this material showed alpha toxin or an antigenically mature precursor located on the cytoplasmic membrane. The possible function of alpha toxin in this situation is discussed.
Full text
PDF
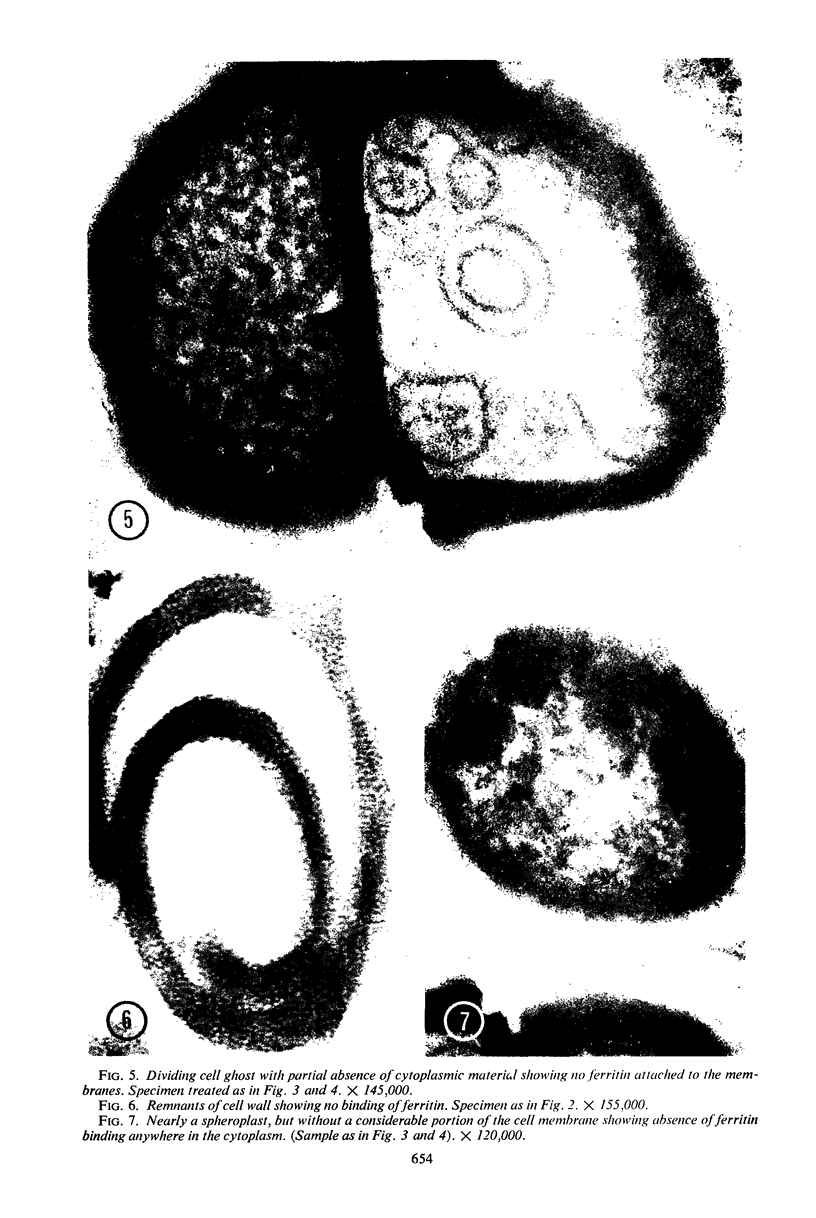

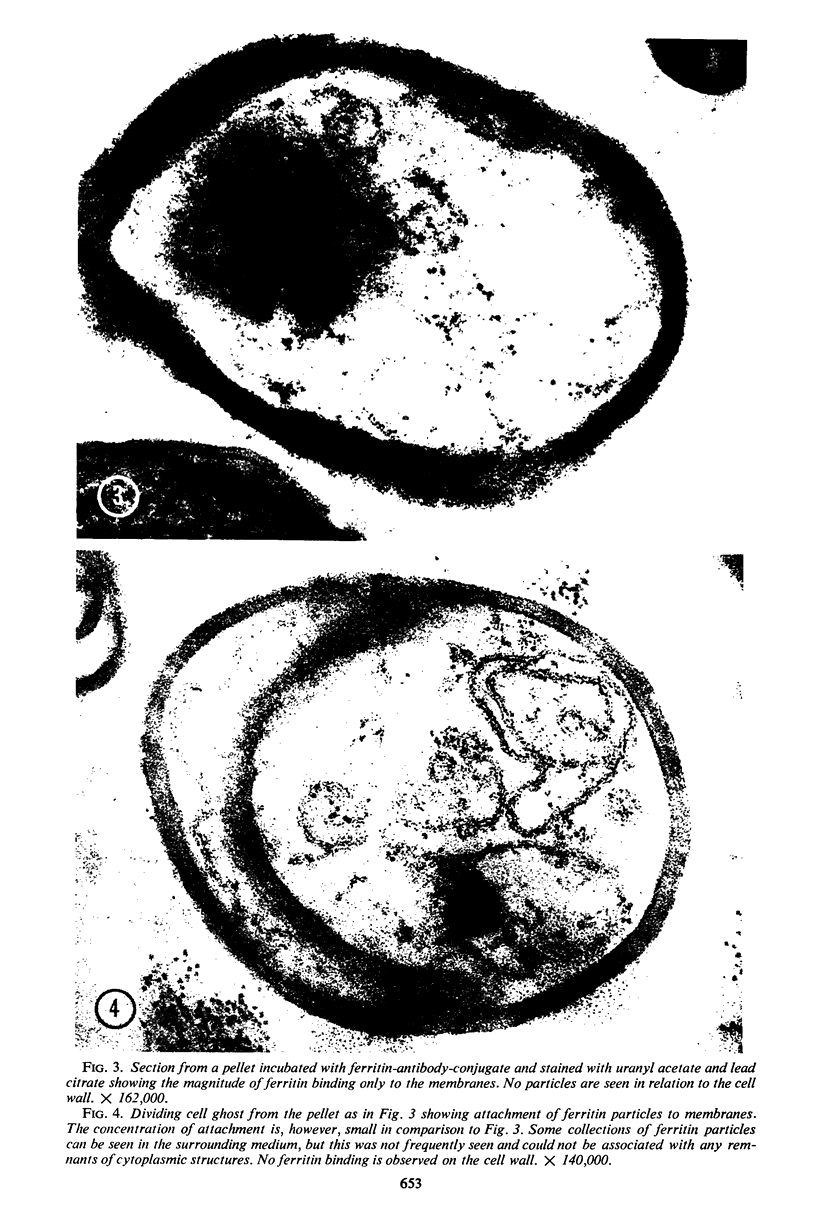


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti E. L., Emmelot P. Studies on plasma membranes. IV. The ultrastructural localization and content of sialic acid in plasma membranes isolated from rat liver and hepatoma. J Cell Sci. 1967 Dec;2(4):499–512. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter J. R. Production, purification, and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1655–1662. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1655-1662.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O., Laurell G., Löfström G. Stimulation of staphylococcal haemolysin production by low concentrations of penicillin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;68(1):142–148. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.68.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPRAL F. A., LI I. W. Virulence and coagulases of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:151–153. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPPER M. H., JACKSON G. G., DOWLING H. F. Characteristics of the micrococcal nasal carrier state among hospital personnel. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jun;45(6):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhardt V. T., Huber T. W., Pope L. M. Electron microscopy and viability of lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts, protoplast-like bodies, and protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):396–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.396-401.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]