Abstract
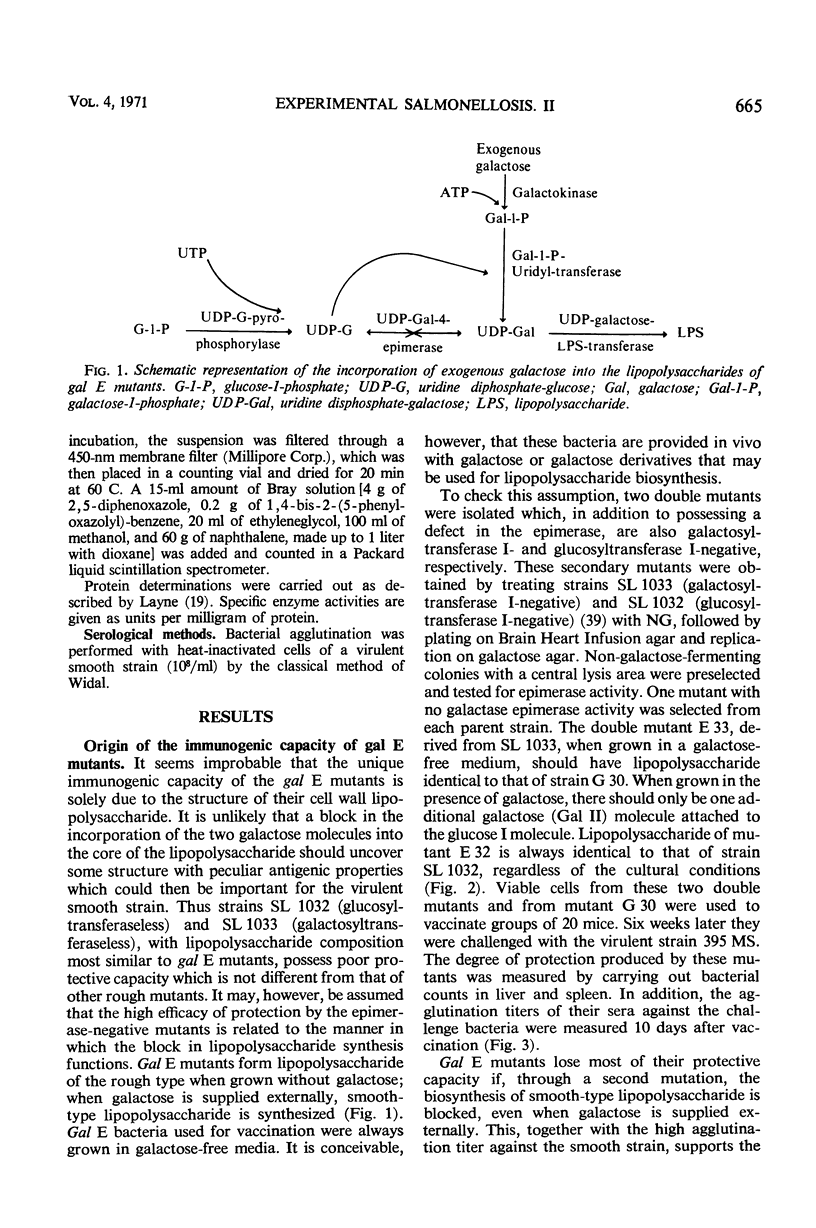
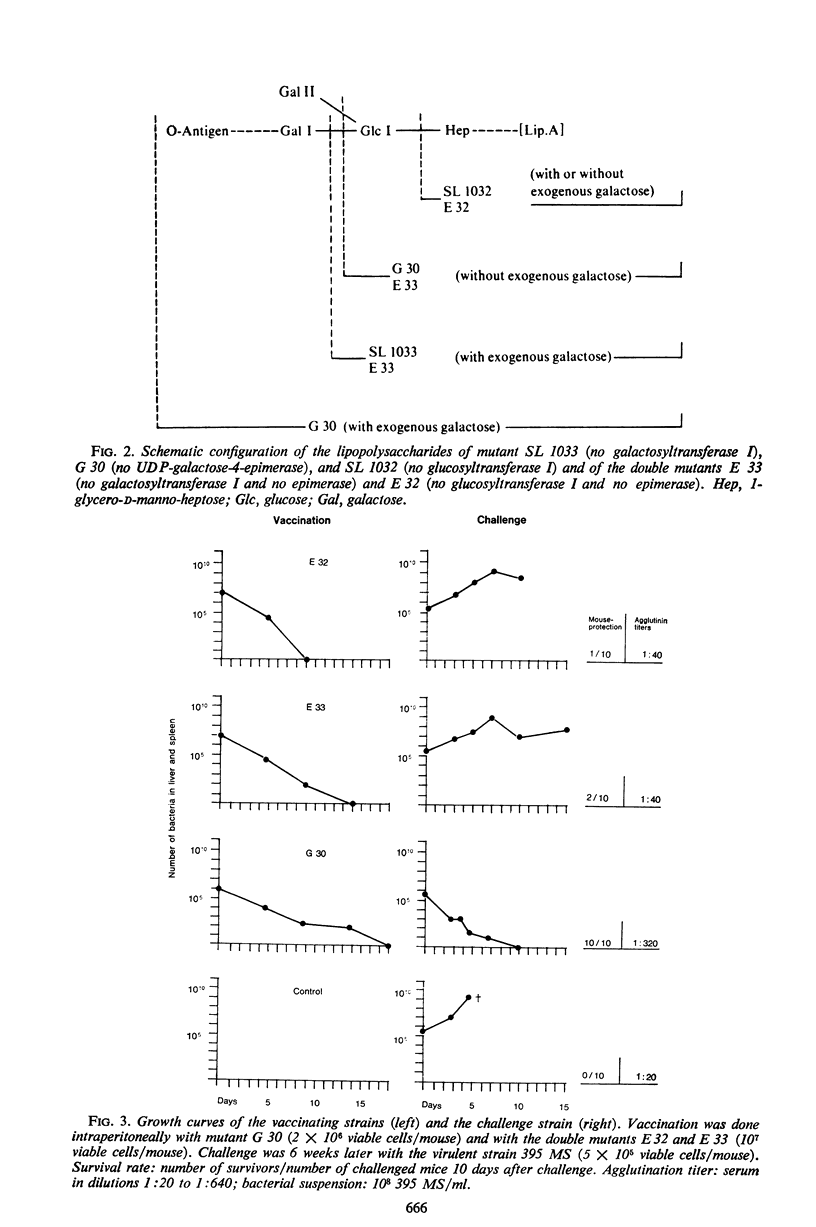
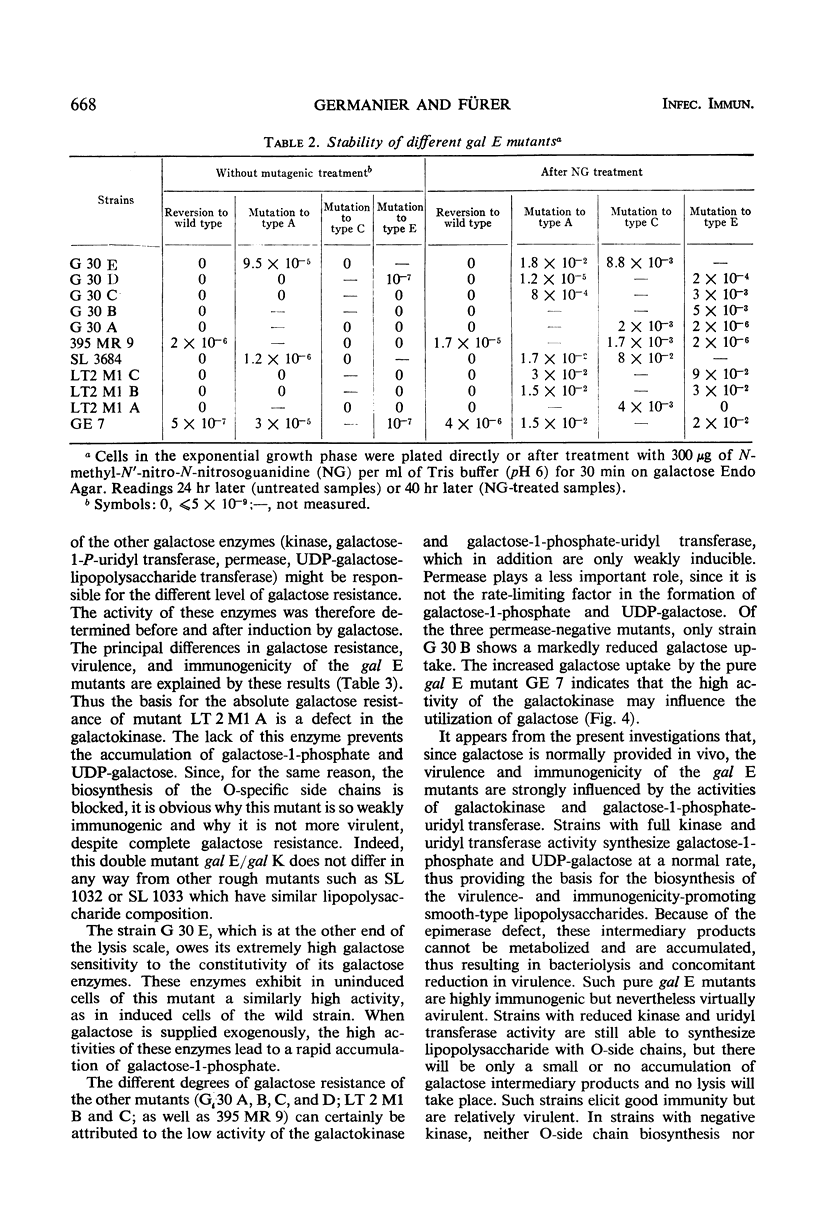
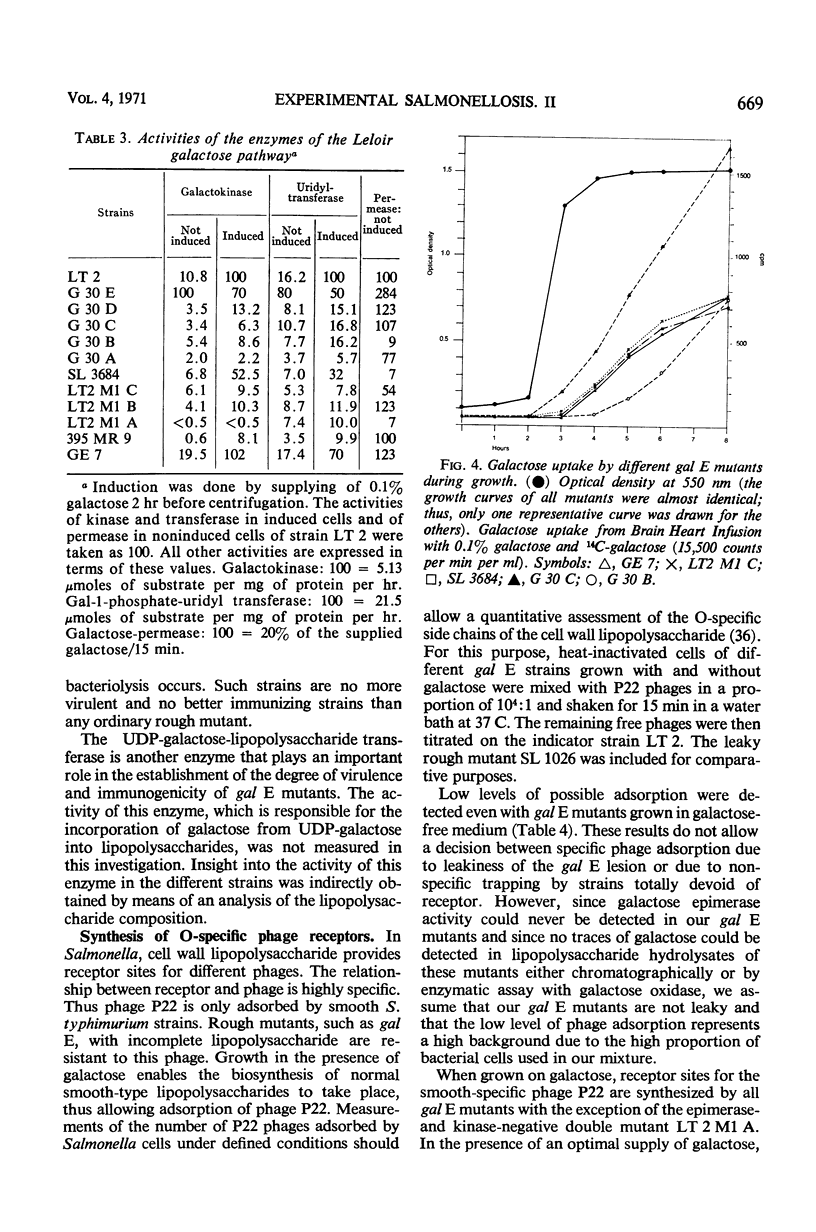
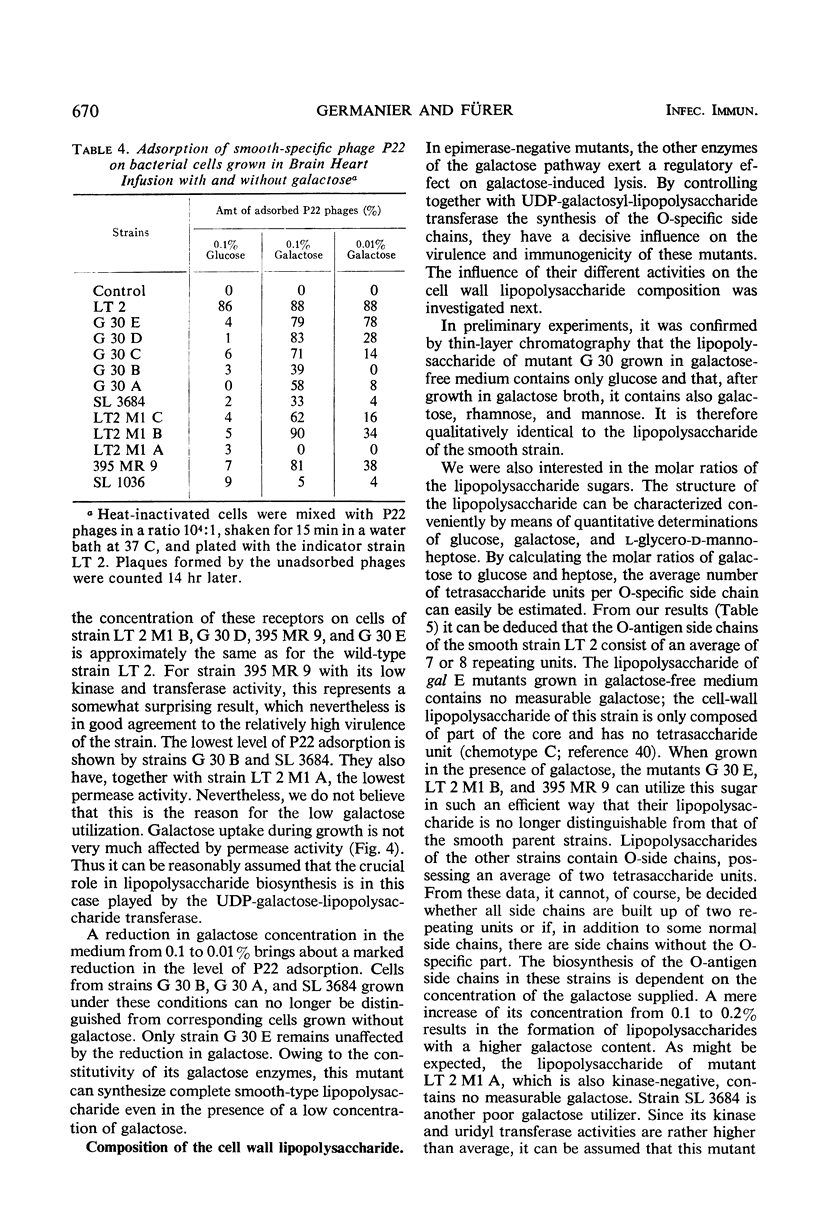
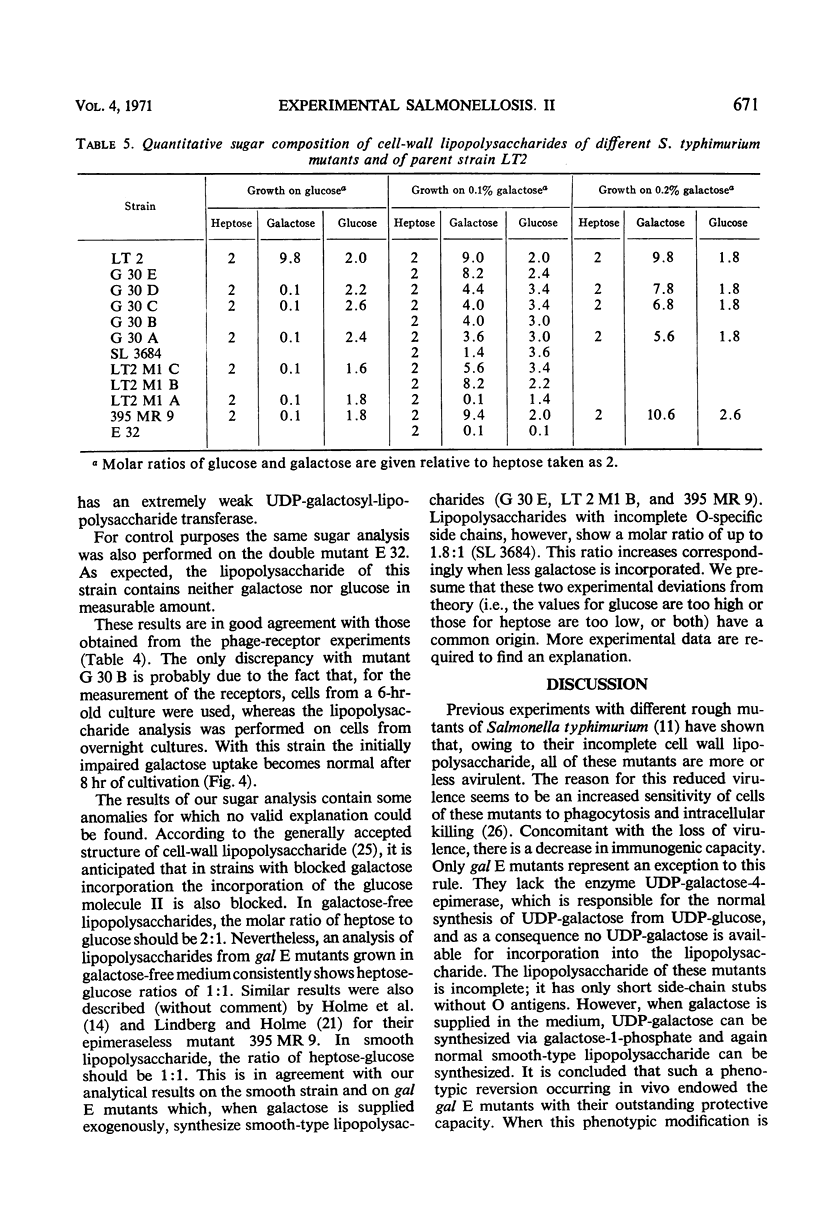
Salmonella typhimurium strains which are deficient in uridine diphosphate (UDP)-galactose-4-epimerase (gal E mutants) owe their outstanding protective capacity when used as live vaccine to the fact that when galactose is supplied exogenously, such as occurs in vivo, smooth cell wall lipopolysaccharides are synthesized. The mutants lose most of their protective capacity when this phenotypic curing is prevented by a second mutation of the kind found in strains LT2M1A (deficient in galactokinase) or E32 (deficient in UDP-galactose-lipopolysaccharide transferase). Despite such phenotypic reversion, the gal E mutants are rendered avirulent as a result of galactose-induced bacteriolysis. Secondary mutants have been isolated which differ from each other with respect to the extent of galactose-induced lysis. The differences in galactose sensitivity are attributable to different activities of the other Leoloir pathway enzymes, namely, galactokinase and galactose-1-phosphate-uridyl transferase. The influence of these enzymes on lipopolysaccharide composition and galactose sensitivity and thus on virulence and immunogenicity of gal E mutants has been studied.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTIN G. M'ECANISMES R'EGULATEURS DANS LA BIOSYNTH'ESE DES ENZYMES DU M'ETABOLISME DU GALACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. I. LA BIOSYNTH'ESE INDUITE DE LA GALACTOKINASE ET L'INDUCTION SIMULTAN'EE DE LA S'EQUENCE ENZYMATIQUE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:164–182. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Formation of protoplasts' in mutant strains of Salmonella induced by galactose. Nature. 1959 Apr 18;183(4668):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/1831131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. II. Bacteriolysis induced by galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. Nature. 1959 Oct 10;184(Suppl 15):1168–1169. doi: 10.1038/1841168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Shilo M. Role of cell wall structure of salmonella in the interaction with phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):279–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.279-285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Transduction by bacteriophage P22 in nonsmooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1588–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1588-1597.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in Experimental Salmonellosis I. Protection Induced by Rough Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.309-315.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO H., HONDA T., KAWAKAMI M., MITSUHASHI S. Studies on the experimental salmonellosis. VI. Longlasting immunity of mouse immunized with live vaccine of Salmonella enteritidis. Jpn J Exp Med. 1961 Jun;31:187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO TYPHOID IN MICE AND THE QUESTION OF "CELLULAR IMMUNITY". Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:391–404. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.391-404.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Antibody response and protection induced by immunization with smooth and rough strains in experimental salmonellosis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):406–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.406-417.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent J. L., Osborn M. J. Further studies on enzymatic synthesis of O-antigen in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4409–4419. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., MacPhee D. G., Stocker B. A. Properties of a Salmonella typhimurium mutant with an incomplete deficiency of uridinediphosphogalactose-4-epimerase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.155-161.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Hellerqvist C. G. Bacteriophage attachment sites, serological specificity, and chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharides of semirough and rough mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.57-64.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Sarvas M., Mäkelä P. H. Bacteriophage attachment to the somatic antigen of salmonella: effect of o-specific structures in leaky R mutants and s, t1 hybrids. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.88-97.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. I. Metabolism of galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito K. Antibody formation in mice infected with Salmonella typhimurium by primary immunization with sheep erythrocytes or bacterial cells. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito K. The chemical compositions in the cell wall of Salmonella typhimurium affecting the clearance-rate in mouse. Jpn J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;12(4):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1968.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in gram-negative enteric bacteria. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1968;31:77–124. doi: 10.1002/9780470122761.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., HORECKER B. L. Biosynthesis of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. I. Enzymatic incorporation of galactose in a mutant strain of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1831–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., ZELEZNICK L. D., HORECKER B. L. LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):783–789. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster C. W., Rundell K. Resistance of Salmonella typhimurium mutants to galactose death. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):103–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.103-109.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiba D. Two types of immunity in experimental typhoid; "cellular immunity" and "humoral immunity". Keio J Med. 1965 Jun;14(2):45–61. doi: 10.2302/kjm.14.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Stocker B. A. Genetics and cultural properties of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium lacking glucosyl or galactosyl lipopolysaccharide transferases. Nature. 1968 Mar 9;217(5132):955–957. doi: 10.1038/217955a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



