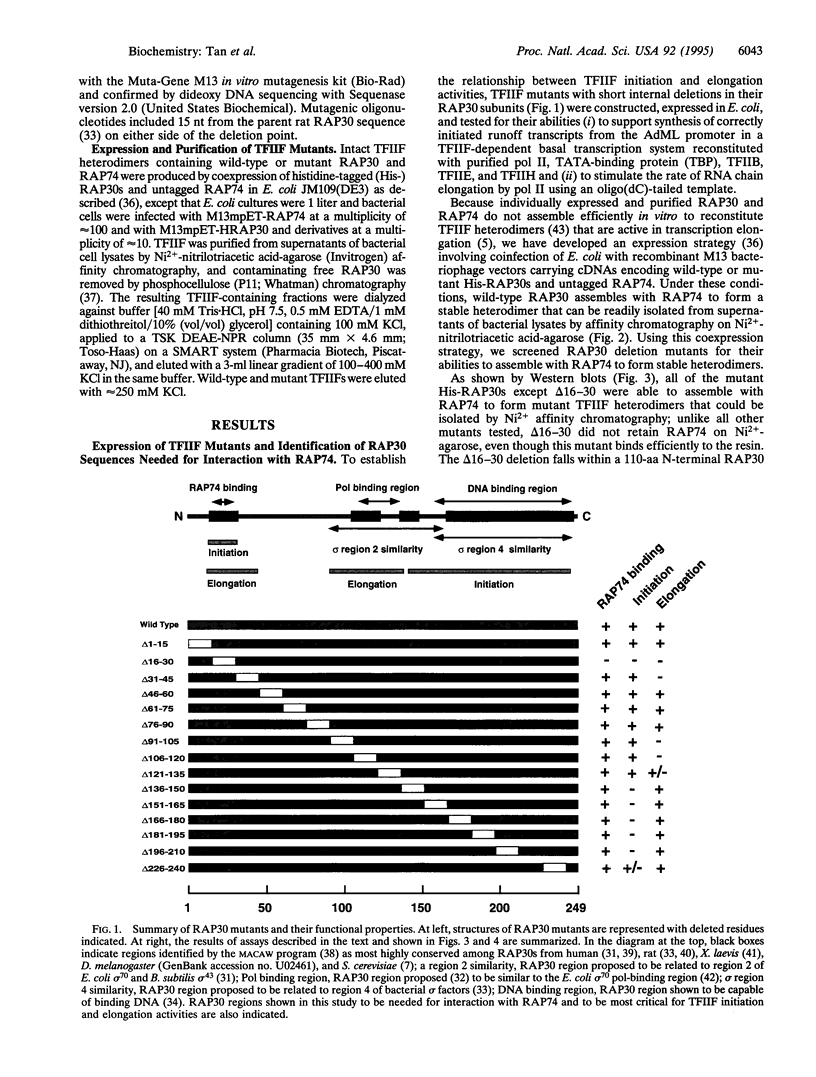
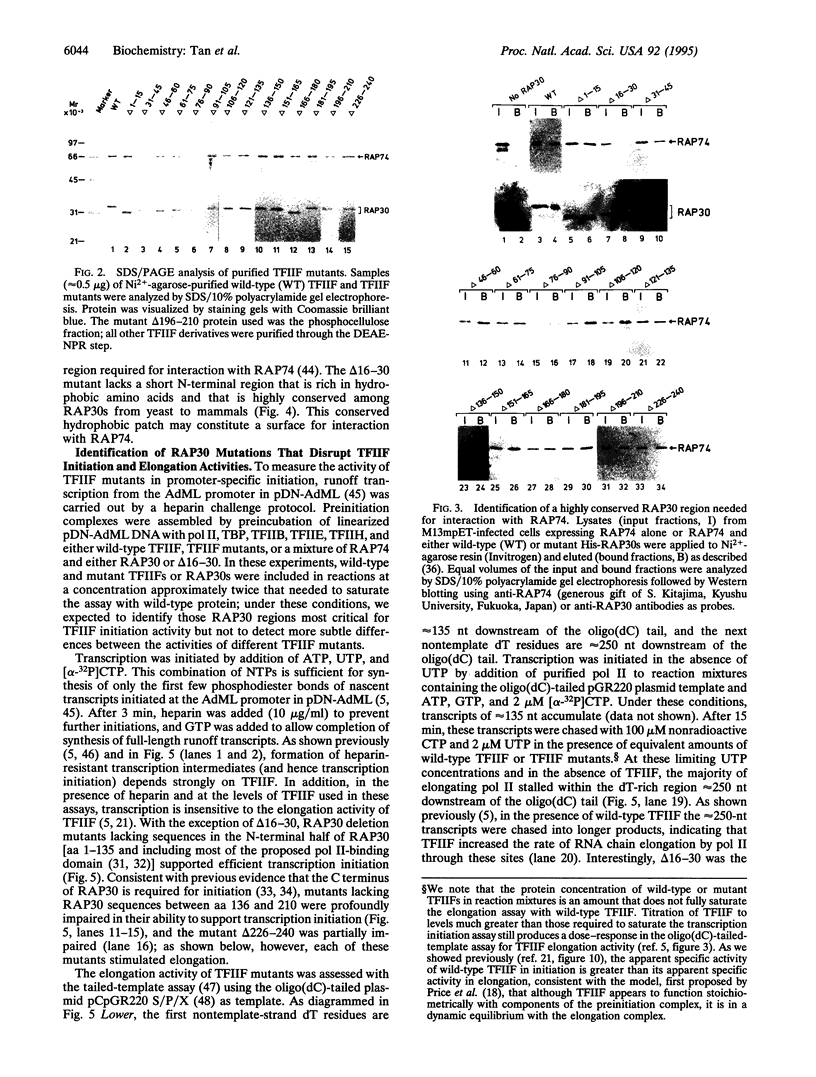
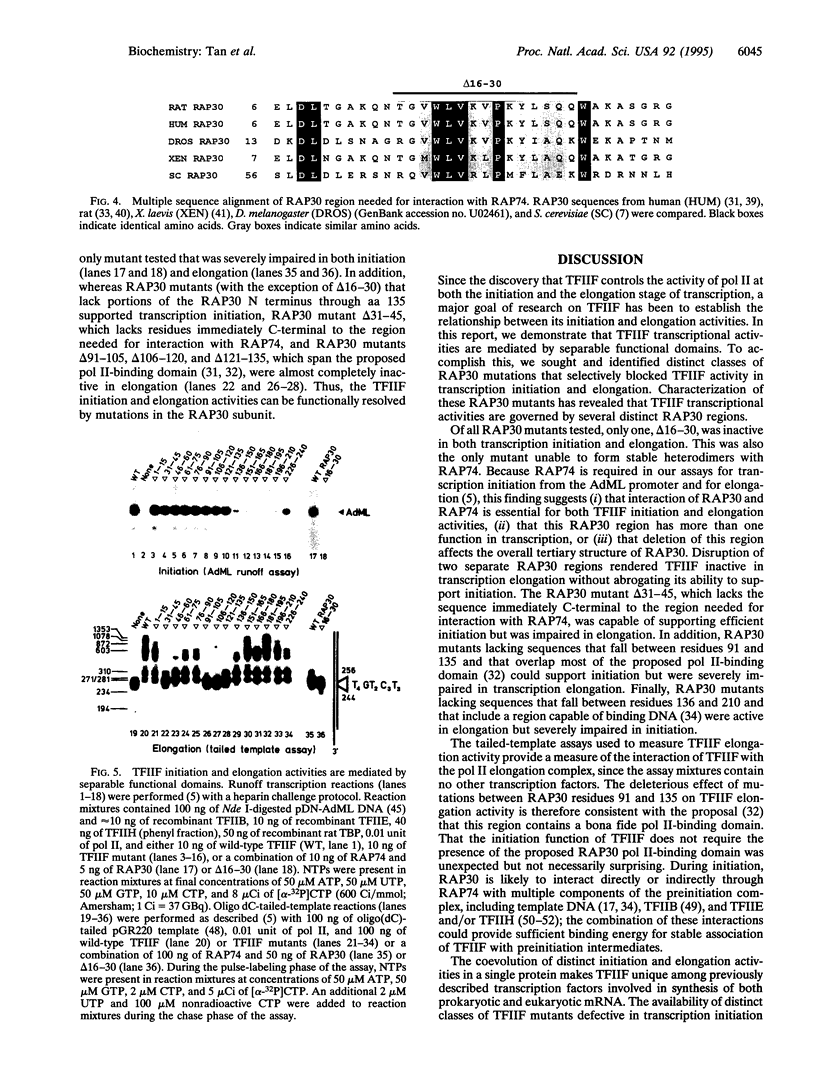
Abstract
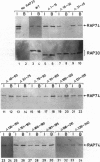
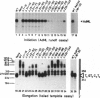
TFIIF is unique among the general transcription factors because of its ability to control the activity of RNA polymerase II at both the initiation and elongation stages of transcription. Mammalian TFIIF, a heterodimer of approximately 30-kDa (RAP30) and approximately 70-kDa (RAP74) subunits, assists TFIIB in recruiting RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex and activates the overall rate of RNA chain elongation by suppressing transient pausing by polymerase at many sites on DNA templates. A major objective of efforts to understand how TFIIF regulates transcription has been to establish the relationship between its initiation and elongation activities. Here we establish this relationship by demonstrating that TFIIF transcriptional activities are mediated by separable functional domains. To accomplish this, we sought and identified distinct classes of RAP30 mutations that selectively block TFIIF activity in transcription initiation and elongation. We propose that (i) TFIIF initiation activity is mediated at least in part by RAP30 C-terminal sequences that include a cryptic DNA-binding domain similar to conserved region 4 of bacterial sigma factors and (ii) TFIIF elongation activity is mediated in part by RAP30 sequences located immediately upstream of the C terminus in a region proposed to bind RNA polymerase II and by additional sequences located in the RAP30 N terminus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradsher J. N., Jackson K. W., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII. I. Identification, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25587–25593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradsher J. N., Tan S., McLaury H. J., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII. II. Functional properties and role in RNA chain elongation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25594–25603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Sopta M., Greenblatt J., Sharp P. A. RNA polymerase II-associated proteins are required for a DNA conformation change in the transcription initiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7509–7513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Bradsher J. N., Conaway R. C. Mechanism of assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. Transcription factors delta and epsilon promote stable binding of the transcription apparatus to the initiator element. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10142–10148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. General initiation factors for RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. Transcription initiated by RNA polymerase II and purified transcription factors from liver. Transcription factors alpha, beta gamma, and delta promote formation of intermediates in assembly of the functional preinitiation complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7559–7563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Garrett K. P., Hanley J. P., Conaway J. W. Mechanism of promoter selection by RNA polymerase II: mammalian transcription factors alpha and beta gamma promote entry of polymerase into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6205–6209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe B., Li J., Greenblatt J. Topological localization of the human transcription factors IIA, IIB, TATA box-binding protein, and RNA polymerase II-associated protein 30 on a class II promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19962–19967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Killeen M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F., Reinberg D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9999–10003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett K. P., Serizawa H., Hanley J. P., Bradsher J. N., Tsuboi A., Arai N., Yokota T., Arai K., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. The carboxyl terminus of RAP30 is similar in sequence to region 4 of bacterial sigma factors and is required for function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23942–23949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong D. W., Hashimoto S., Wada K., Roeder R. G., Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M. Imperfect conservation of a sigma factor-like subregion in Xenopus general transcription factor RAP30. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6414–6414. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Transcription factors IIE and IIH and ATP hydrolysis direct promoter clearance by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Roberts S., Maldonado E., Sun X., Kim L. U., Green M., Reinberg D. Multiple functional domains of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1021–1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. L., Campbell A. M., Feaver W. J., Poon D., Weil P. A., Kornberg R. D. TFIIF-TAF-RNA polymerase II connection. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 1;8(23):2868–2878. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.23.2868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Fujita H., Wang J., Takada R., Roeder R. G. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence of RAP30. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5436–5436. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. Factor-stimulated RNA polymerase II transcribes at physiological elongation rates on naked DNA but very poorly on chromatin templates. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13647–13655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kash S. F., Kellems R. E. Control of transcription arrest in intron 1 of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6198–6207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kephart D. D., Wang B. Q., Burton Z. F., Price D. H. Functional analysis of Drosophila factor 5 (TFIIF), a general transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13536–13543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. RNA polymerase: regulation of transcript elongation and termination. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2833–2842. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.13.1916107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Björklund S., Li Y., Sayre M. H., Kornberg R. D. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kitajima S., Yasukochi Y. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a rat cDNA homologous to human RAP30. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1994–1994. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Young R. A. An RNA polymerase II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):466–469. doi: 10.1038/368466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley S. A., Burgess R. R. Characterization of the Escherichia coli transcription factor sigma 70: localization of a region involved in the interaction with core RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7728–7734. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxon M. E., Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Transcription factor IIE binds preferentially to RNA polymerase IIa and recruits TFIIH: a model for promoter clearance. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 1;8(5):515–524. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken S., Greenblatt J. Related RNA polymerase-binding regions in human RAP30/74 and Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):900–902. doi: 10.1126/science.1652156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mote J., Jr, Ghanouni P., Reines D. A DNA minor groove-binding ligand both potentiates and arrests transcription by RNA polymerase II. Elongation factor SII enables readthrough at arrest sites. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 25;236(3):725–737. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Sharp P. A. DNA topology and a minimal set of basal factors for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90140-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Shykind B. M., Meyers R. E., Kim J., Sharp P. A. Multiple sets of basal factors initiate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18414–18421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Mote J., Jr Elongation factor SII-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II through a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1917–1921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. A., Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Footprinting analysis of mammalian RNA polymerase II along its transcript: an alternative view of transcription elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. A workbench for multiple alignment construction and analysis. Proteins. 1991;9(3):180–190. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Kobayashi N., Mizuno D., Natori S. Purification of a factor from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells specifically stimulating RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5064–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Reines D., Kane C. M. Purified elongation factor SII is sufficient to promote read-through by purified RNA polymerase II at specific termination sites in the human histone H3.3 gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14554–14560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Aso T., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. Roles for both the RAP30 and RAP74 subunits of transcription factor IIF in transcription initiation and elongation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25684–25691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. A bacteriophage vector suitable for site-directed mutagenesis and high-level expression of multisubunit proteins in E. coli. Biotechniques. 1994 May;16(5):824-6, 828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Garrett K. P., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. Cryptic DNA-binding domain in the C terminus of RNA polymerase II general transcription factor RAP30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9808–9812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers H. T. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II does not require hydrolysis of the beta-gamma phosphoanhydride bond of ATP. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):391–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyree C. M., George C. P., Lira-DeVito L. M., Wampler S. L., Dahmus M. E., Zawel L., Kadonaga J. T. Identification of a minimal set of proteins that is sufficient for accurate initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1254–1265. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. Q., Kostrub C. F., Finkelstein A., Burton Z. F. Production of human RAP30 and RAP74 in bacterial cells. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Jun;4(3):207–214. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. K., Wang D., Hawley D. K. Mechanistic studies of transcription arrest at the adenovirus major late attenuation site. Comparison of purified RNA polymerase II and washed elongation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7733–7744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonaha M., Aso T., Kobayashi Y., Vasavada H., Yasukochi Y., Weissman S. M., Kitajima S. Domain structure of a human general transcription initiation factor, TFIIF. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):273–279. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]