Abstract
Candida albicans, administered by gastric intubation, persisted in the gastrointestinal tract of gnotobiotic mice for long periods but was eliminated within a relatively short period of time in pathogen-free mice. Oxytetracycline administered by mouth had no reproducible effect on the persistence of C. albicans in the gastrointestinal tract of either germ-free or pathogen-free mice. Prolonged administration of streptomycin extended the time that C. albicans could be recovered from feces of pathogen-free mice when compared to mice not receiving the antibiotic or those receiving a single large dose. There was a brief interval of time during which C. albicans could not be recovered from the feces of gnotobiotic mice contaminated with certain intestinal bacteria, but eventually all mice began to shed the fungus again. C. albicans administered by mouth was not pathogenic for germ-free or pathogen-free mice. It can be concluded from these findings that mice do not possess an innate resistance to C. albicans but that pathogen-free mice do possess some ecological mechanism which prevents establishment of the fungus in their gastrointestinal tract. The reason for the difference in colonization of C. albicans in germ-free or gnotobiotic mice and pathogen-free mice was not determined.
Full text
PDF

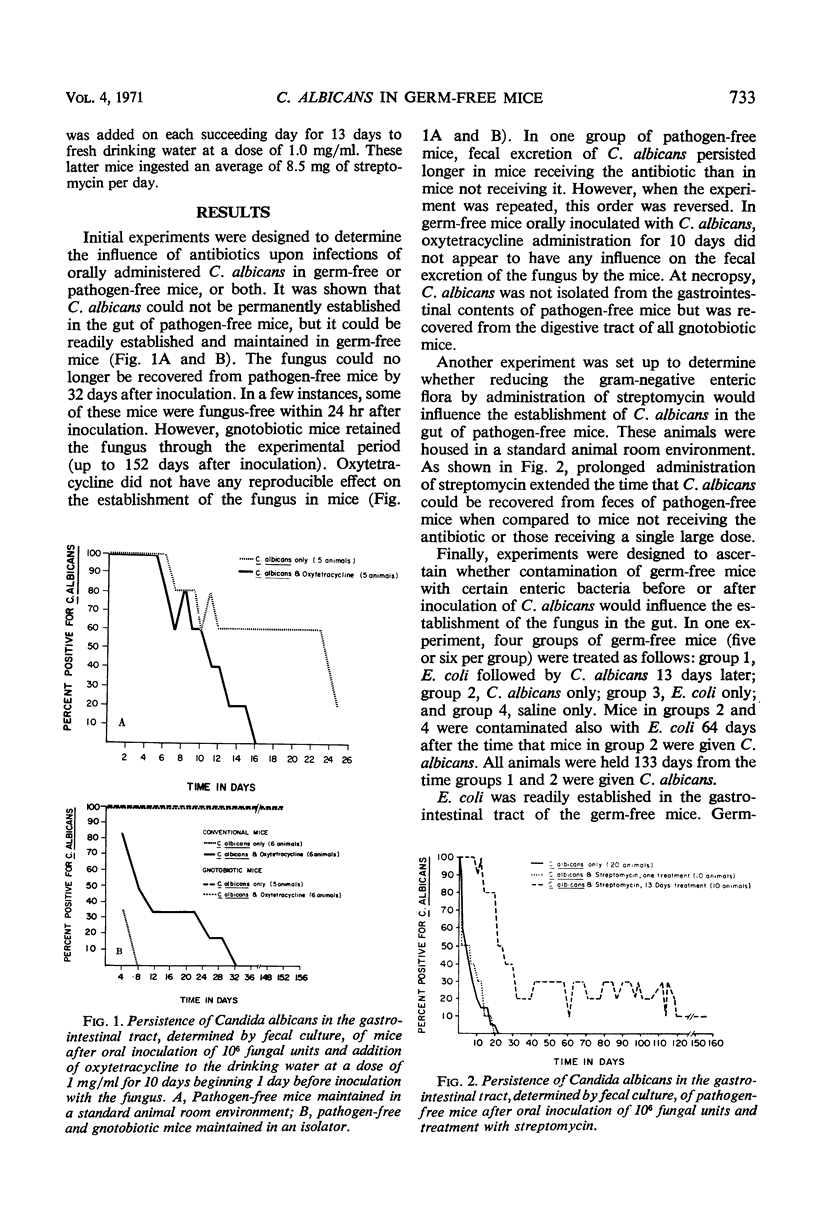
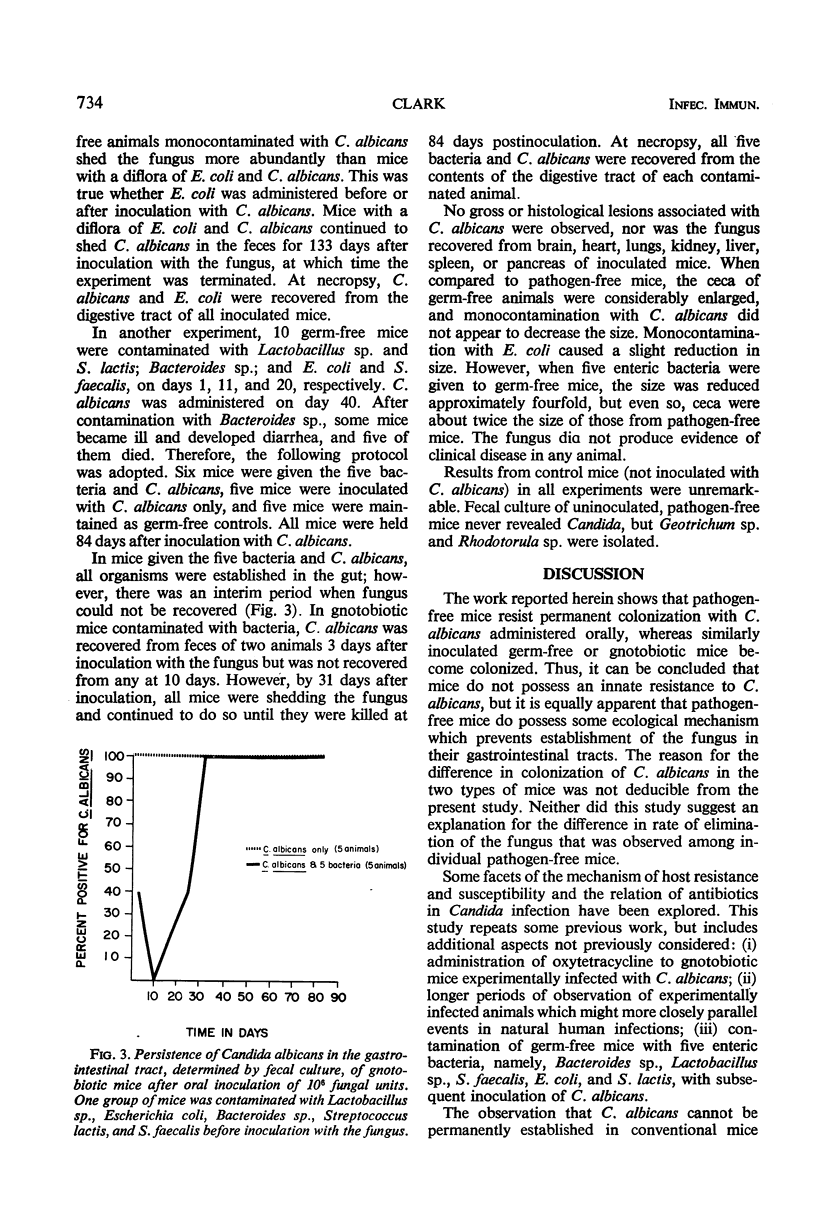



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on the resistance of the small intestine to infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1604-1608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P. Enhanced susceptibility to Salmonella infection in streptomycin-treated mice. J Infect Dis. 1962 Sep-Oct;111:117–127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. II. FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR ITS LOSS FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:817–828. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balish E., Phillips A. W. Growth and virulence of Candida albicans after oral inoculation in the chick with a monoflora of either Escherichia coli or Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1744–1749. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1744-1749.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balish E., Phillips A. W. Growth, morphogenesis, and virulence of Candida albicans after oral inoculation in the germ-free and conventional chick. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1736–1743. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1736-1743.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBIAS B. SPECIFIC AND NONSPECIFIC IMMUNITY IN CANDIDA INFECTIONS. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF CANDIDA CELL CONSTITUENTS AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE. Acta Med Scand. 1964;176:SUPPL 421–421:1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUOBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R. COMPOSITION, ALTERATION, AND EFFECTS OF THE INTESTINAL FLORA. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1322–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubos R. J., Savage D. C., Schaedler R. W. The indigenous flora of the gastrointestinal tract. Dis Colon Rectum. 1967 Jan-Feb;10(1):23–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02617382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. Experimental enteric Shigella and Vibrio infections in mice and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):411–418. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigellaflexneri. II. The inhibitory mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUPPERT M., CAZIN J., Jr, SMITH H., Jr Pathogenesis of Candida albicans infection following antibiotic therapy. III. The effect of antibiotics on the incidence of Candida albicans in the intestinal tract of mice. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):440–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.440-447.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPNIK M. J., KLIGMAN A. M., STRAUSS R. Antibiotics and fungous infections. J Invest Dermatol. 1952 Mar;18(3):247–260. doi: 10.1038/jid.1952.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., SUBBAIAH T. V. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. I. Kinetics of infection by Salmonella typhi-murium in normal and streptomycin-treated mice studied with abortive transductants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. P., BOHNHOFF M. CHANGES IN THE MOUSE'S ENTERIC MICROFLORA ASSOCIATED WITH ENHANCED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO SALMONELLA INFECTION FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jul-Aug;113:59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOURAD S., FRIEDMAN L. Pathogenicity of Candida. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:550–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.550-556.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Hatano H., Ohnishi N., Sasaki S., Nomura T. Establishment of Candida albicans in the alimentary tract of the germ-free mice and antagonism with Escherichia coli after oral inoculation. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Sep;13(3):263–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. W., Balish E. Growth and invasiveness of Candida albicans in the germ-free and conventional mouse after oral challenge. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):737–741. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.737-741.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAO G. R., SIRSI M. The pathogenicity of Candida albicans and the effect of nystatin on experimental candidiasis. Indian J Med Res. 1962 Jan;50:66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R., COSTELLO R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:59–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBS R., COSTELLO R. ASSOCIATION OF GERMFREE MICE WITH BACTERIA ISOLATED FROM NORMAL MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:77–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig M. S. Mechanisms by which antibiotics increase the incidence and severity of candidiasis and alter the immunological defenses. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):442–459. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.442-459.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig M. S. The role of antibiotics in the pathogenesis of Candidainfections. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):887–917. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



