Abstract
Histone deacetylase-3 (HDAC3) is involved in cellular proliferation, apoptosis and transcriptional repression. However, the role of HDAC3 in angiogenesis remains unknown. HDAC3 negatively regulated the expression of angiogenic factors, such as VEGF and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). HDAC3 showed binding to promoter sequences of PAI-1. HDAC3 activity was necessary for the expression regulation of PAI-1 by HDAC3. VEGF decreased the expression of HDAC3, and the down-regulation of HDAC3 enhanced endothelial cell tube formation. HDAC3 negatively regulated tumor-induced angiogenic potential. We show the novel role of HDAC3 as a negative regulator of angiogenesis. [BMB Reports 2014; 47(4): 227-232]
Keywords: Angiogenesis, Angiogenic factors, Anti cancer drug-resistance, Histone deacetylase-3, Tumor-induced angiogenesis
INTRODUCTION
Among the numerous HDACs, HDAC3 is conserved in a wide range of species (1). HDAC3 forms large corepressor complexes containing N-CoR/SMRT (2). The overexpression of HDAC3 has been observed in colon cancer cells, in which it has an anti-apoptotic effect (3). HDAC3 confers resistance to TSA-induced apoptosis (4). HDAC3 induces death of otherwise healthy rat cerebella granule neurons (5).
HDAC inhibitors target HIF1 alpha, leading to anti-angiogenic effects (6). HDAC3 is critical in endothelial cell survival and atherosclerosis development in response to disturbed flow (7). We previously reported that hyaluronic acid promotes angiogenesis and decreases the expression of HDAC3 in HUVECs (8). HDAC3 acts as a corepressor of NF-κB, and negatively regulates HIF-1- alpha in breast carcinoma cells (9). Given the fact that HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of HIF-1-alpha, it is reasonable that HDAC3 may act as a negative regulator of angiogenesis.
In this study, we explored the possibility of HDAC3 as a regulator of angiogenesis. We found that HDAC3 negatively regulated the expression of VEGF and PAI-1. We examined the binding of HDAC3 to PAI-1 promoter sequences, as well as the effect of HDAC3 on tumor-induced angiogenesis, and the invasion potential of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) towards tumor cells. The novel role of HDAC3 as a negative regulator of angiogenesis is demonstrated.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
HDAC3 negatively regulates expression of PAI-1 and VEGF
We previously reported that SNU387R and Malme3MR cells showed resistance to microtubule-disrupting drugs such as celastrol and taxol (10). HDAC2 is increased in these cancer cell lines, and represses the expression of p53, through interaction with cancer/testis antigen CAGE (10). We found that the expression of HDAC3 in SNU387R and Malme3MR cells was lower than in their counterparts (Fig. 1A). The down-regulation of HDAC3 in SNU387 and Malme3M cells induced the expression of MDR1 (Fig. 1A), suggesting that HDAC3 regulates the response to anti-cancer drugs. It is generally believed that drug-resistance is accompanied by an enhanced angiogenic potential (11). This led us to hypothesize that HDAC3 may regulate angiogenic potential.
Fig. 1. HDAC3 negatively regulates the expression of PAI-1 and VEGF. (A) Cell lysates isolated from the indicated cancer cells were subjected to Western blot analysis (upper panel). At 48 h after transfection with the indicated siRNA (10 nM each), cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis. (B) At 48 h after transfection with the indicated siRNA (10 nM each), cell lysates were prepared, and subjected to cytokine array analysis. (C) At 48 h after transfection, Western blot analysis was performed. (D) Cell lysates isolated from the indicated cancer cells were subjected to Western blot analysis. (E) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. (F) Cells were transiently transfected with the indicated construct. At 48 h after transfection, Western blot analysis was performed. Cell lyastes prepared from SNU387 or Malme3M cells were also subjected to Western blot analysis. (G) Promoter sequences of PAI-1. (H) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibody (2 μg/ml), followed by ChIP assays.
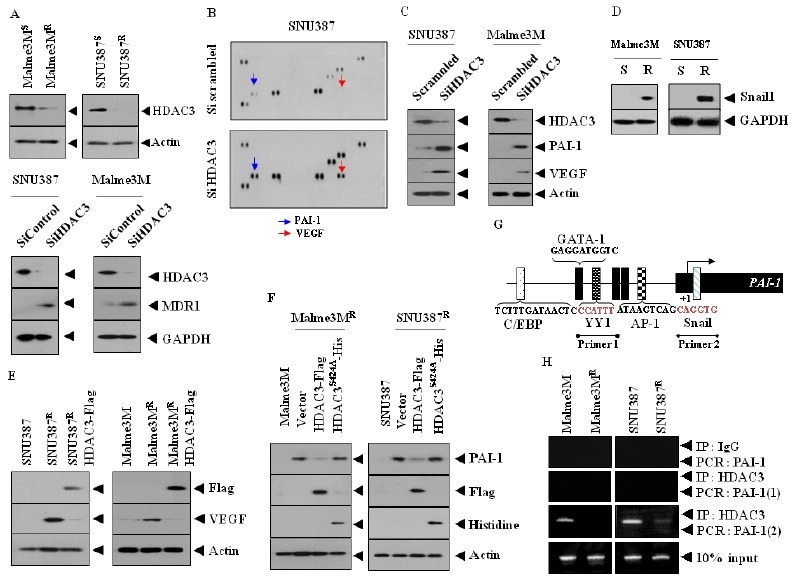
In order to explore the possibility of HDAC3 as a negative regulator of angiogenesis, we examined the effect of HDAC3 on the expression of angiogenic factor(s). Human angio antibody array analysis showed that the down regulation of HDAC3 in hepatic cancer cell line SNU387 induced the expression of angiogenic factors such as VEGF and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) (Fig. 1B). HDAC3 negatively regulated the expression of PAI-1 and VEGF (Fig. 1C). PAI-1 protects endothelial cells from Fas-mediated apoptosis (12). It is probable that PAI-1 is necessary for the resistance of SNU387R and Malme3MR cells to anti-cancer drugs. PAI-1 facilitates retinal angiogenesis (13), and is regulated by TGFβ (14). It will be necessary to examine whether HDAC3 affects TGFβ receptor signaling. Snail is required for TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (15). The functional blockade of Snail decreases the expression of PAI-1 in breast cancer cells and exerts a negative effect on cancer cell migration (16). We found that the expression of Snail was higher in SNU387R and Malme3MR cells than in their counterparts (Fig. 1D). It is reasonable that HDAC3 may regulate the expression of Snail, which in turn affects the expression of PAI-1. SNU387R and Malme3MR cells, which are cancer cells selected for resistance to anti-cancer drug celastrol, expressed a higher level of VEGF than did their counterparts, and HDAC3 negatively regulated the expression of VEGF in these drug-resistant cancer cell lines (Fig. 1E).
Hepatocyte growth factor and inducible nitric oxide synthase are involved in MDR-induced angiogenesis in hepatoma cell lines (17). In this study, we found that the down- regulation of HDAC3 in HUVECs led to the increased production of reactive oxygen species (personal observation). It will be necessary to examine the effect of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on the expression of VEGF.
Wild type HDAC3, but not mutant HDAC3S4242A, decreased the expression of PAI-1 in SNU387R and Malme3MR (Fig. 1F), suggesting that HDAC3 activity is necessary for the regulation of PAI-1 expression. Because HDAC3 regulates the expression of PAI-1, we examined the binding of HDAC3 to promoter sequences of PAI-1. PAI-1 promoter shows the binding sites for various transcription factors, such as YY1, Snail, and AP-1 (Fig. 1G). HDAC3 showed binding to site 2 of the PAI-1 promoter sequences in SNU387 and Malme3M cells (Fig. 1H). It would be necessary to examine the effect of HDAC3 on the expression of YY1, Snail, or AP-1.
These results show that HDAC3 regulates the expression of PAI-1, and VEGF and may act as a negative regulator of angiogenesis.
HDAC3 negatively regulates angiogenic and invasion potential
Because HDAC3 regulates the expression of PAI-1 and VEGF, we examined the effect of HDAC3 on angiogenic potential. Based on intravital microscopy, Malme3M cells transiently transfected with HDAC3 siRNA showed higher angiogenic potential than Malme3M cells (Fig. 2A). The conditioned medium of Malme3M cells transiently transfected with HDAC3 siRNA induced blood vessel formation, but this was not observed with Malme3M cells transfected with control siRNA, (Fig. 2A). Malme3MR cells transiently transfected with HDAC3-Flag showed lower angiogenic potential than did Malme3MR cells (Fig. 2A). The conditioned medium of Malme3MR cells transiently transfected with HDAC3-Flag also showed lower angiogenic potential than that of Malme3MR cells (Fig. 2A).
Fig. 2. HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of angiogenic potential. (A) Intravital microscopy analysis was conducted, as described. Malme3M cell lines were transfected with scrambled siRNA (10 nM) or HDAC3 siRNA (10 nM). Malme3MR cells were transfected with control vector (1 μg) or HDAC3-Flag (1 μg). At 48 h after transfection, cells or conditioned medium were mixed with matrigel. Four days later, FITC-dextran was injected via tail vein, to visualize blood vessel formation. (B) Paraffin section of tumor tissue derived from each indicated hepatoma cell line was subjected to H&E staining (upper panel), or immunofluorescence staining, employing anti-PECAM-1 antibody (lower panel). Representative images from five animals of each experimental group are shown (magnification, 200X for immunohistochemistry, and 100X for H&E staining; Olympus). DAPI staining was also performed. (C) HUVECs (3 × 104) were seeded in M199 containing 1% FBS, in the upper chamber of the transwell. The trypsinized cancer cells (2 × 104) were added to the lower chamber, and incubation continued at 37℃ for 14 h. The invaded cells were fixed with cold 4% paraformaldehyde, and stained with 1% crystal violet. Images were taken using an inverted microscope (Olympus), and migrated cells were quantified by manual counting. SNU387R or Malme3MR cells were pre-incubated with AVASTIN (4 μg/ml) or isotype-matched IgG (4 μg/ml), for 12 h prior to trypsinization. The columns represent the mean of triplicate experiments; bars indicate S.D.; *indicates P < 0.05, statistically different from controls. **indicates P < 0.0005, statistically different from controls.
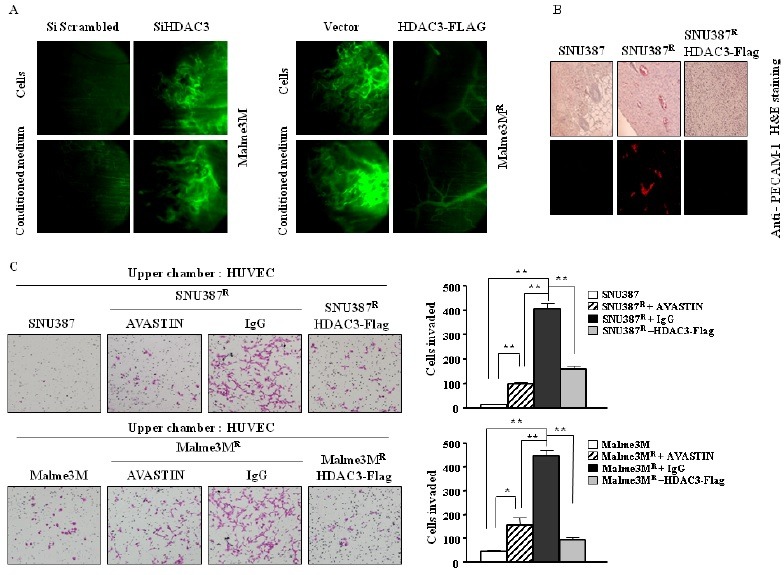
The decreased expression of PECAM-1, an angiogenic marker protein, was seen in tumors derived from SNU387R or Malme3MR cell lines stably expressing HDAC3 (data not shown). Immunofluorescence staining of paraffin section showed more blood vessels expressing PECAM-1 in tumor tissue derived from SNU387R cells than did tumor tissue derived from SNU387 cells (Fig. 2B). Tumor tissue derived from SNU387R cells stably expressing HDAC3-Flag showed a lower expression level of PECAM-1 than tumor tissue derived from SNU387R cells (Fig. 2B). PECAM-1 is necessary for the progression of tumor metastases (18). The down-regulation of PECAM-1 renders endothelial cells more prone to mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis (19). It will be interesting to examine whether the in vivo down-regulation of PECAM-1 regulates the response to microtubule-dis-rupting drugs. H&E staining showed more blood vessel in tumor tissue derived from SNU387R cells, than in tumor tissue derived from SNU387 cells (Fig. 2B). H&E staining showed more blood vessel in tumor tissue derived from SNU387R cells, than in tumor tissue derived from SNU387 cells stably expressing HDAC3 (Fig. 2B). Chemoinvasion assays were performed, to examine the interaction between cancer cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). SNU387R and Malme3MR cells enhanced the invasion potential of HUVECs, while their counterparts did not (Fig. 2C). AVASTIN, a VEGF-neutralizing antibody, prevented enhancement of the invasion potential of HUVECs by SNU387R or Malme3MR cells (Fig. 2C), suggesting that the VEGF secreted by these drug-resistant cancer cells mediates the interaction between cancer cells and HUVECs. The overexpression of HDAC3 in SNU387R or Malme3MR cells also prevented the enhanced invasion potential of HUVECs (Fig. 2C). These results suggest that HDAC3 plays a role in tumor-induced angiogenesis, and in the invasion potential of HUVECs.
HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of VEGF-promoted angiogenesis by regulating expression of PAI-1
Because HDAC3 negatively regulated angiogenic potential, we hypothesized that HDAC3 could be regulated by VEGF. VEGF increased the expression of PAI-1 (Fig. 3A), and decreased the expression of HDAC3, while increasing the expression of HDAC1 and HDAC2, but not HDAC5 or HDAC6, in HUVECs (Fig. 3A). This suggests that HDAC1 and HDAC2 may also be involved in VEGF-promoted angiogenesis. Because the expression of HDAC3 is inversely related to HDAC2 in HUVECs, it would be interesting to examine whether HDAC3 would regulate the expression of HDAC2 in HUVECs. The down-regulation of HDAC3 increased endothelial cell tube formation (Fig. 3B). VEGF induced the expression of PAI-1 in HUVECs (Fig. 3C). Wild type, but not mutant HDAC3 (S424A), prevented VEGF from inducing the expression of PAI-1 in HUVECs (Fig. 3C). VEGF induced the displacement of HDAC3 from site 2 of the promoter sequences of PAI-1 in HUVECs (Fig. 3D). VEGF decreased the expression of HDAC3 in SNU387 and Malme3M cells (Fig. 3E).
Fig. 3. HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of VEGF-promoted angiogenesis, by regulating expression of PAI-1. (A) HUVECs were treated with VEGF for various time intervals. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. (B) HUVECs were transiently transfected with control siRNA (10 nM) or HDAC3 siRNA (10 nM). At 48 h transfection, endothelial cell tube formation assays were performed. (C) HUVECs were transiently transfected with the indicated construct. At 48 h after transfections, cells were then treated with VEGF (20 ng/ml) for 2 h, followed by Western blot analysis. (D) HUVECs were treated with or without VEGF (20 ng/ml) for 2 h, and ChIP assays were followed. (E) SNU387 or Malme3M cells were treated with VEGF, for various time intervals.
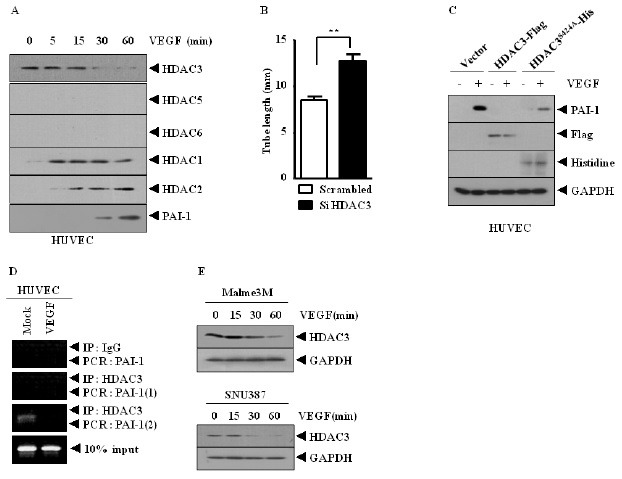
These results show that HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of VEGF-promoted angiogenesis.
HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of tumor-induced changes in endothelial cell signaling
Because HDAC3 regulates the expression of VEGF in SNU387R and Malme3MR cells (Fig. 1C), we examined the effect of HDAC3 on tumor-induced changes in endothelial cell signaling. The conditioned medium of SNU387R or Malme3MR cells, when added to HUVECs, enhanced endothelial cell tube formation (Fig. 4A). The overexpression of HDAC3 prevented SNU387R or Malme3MR cells from enhancing endothelial cell tube formation (Fig. 4A). AVASTIN prevented SNU387R or Malme3MR cells from enhancing endothelial cell tube formation (Fig. 4A). The conditioned medium of SNU387R or Malme3MR cells, but not those cancer cells expressing HDAC3, induced the activation of VEGFR2 in HUVEC (Fig. 4B). The conditioned medium of SNU387R or Malme3MR cells pre-incubated with AVASTIN did not influence the activation of VEGFR2 in HUVEC (Fig. 4B). AVASTIN sensitized SNU387R and Malme3MR cells to the apoptotic effects of taxol (Fig. 4C and D).
Fig. 4. HDAC3 acts as a negative regulator of tumor-induced angiogenic potential and apoptosis, in relation to VEGF. (A) Conditioned medium of the indicated cell line was add to HUVEC. SNU387R or Malme3MR cells were pre-incubated with AVASTIN (4 μg/ml) or isotype-matched IgG (4 μg/ml) for 12 h, prior to addition to HUVEC. 6-8 hours after addition, endothelial cell tube formation assays were performed, as described. (B) Conditioned medium of each cell line was added to HUVECs for 1 h. Cell lysates from HUVEC were prepared, and immunoprecipitated with anti-VEGFR2 antibody (2 μg/ml), followed by Western blot analysis. SNU387R or Malme3MR cells were pre-incubated with AVASTIN (4 μg/ml) or isotype-matched IgG (4 μg/ml), for 12 h prior to addition to HUVEC. One hour after addition to HUVEC, cell lysates prepared from HUVEC treated with conditioned medium of SNU387R or Malme3MR cells were also immunoprecipitated with anti-actin antibody (2 μg/ml), followed by Western blot analysis. (C) SNU387R or Malme3MR cells were pre-incubated with AVASTIN (4 μg/ml) or isotype-matched IgG (4 μg/ml), for 12 h. Cells were then treated with or without taxol (1 μM) for 24 h, followed by Western blot analysis. (D) is the same as (C), except that MTT assays were performed. *P < 0.005. P value was determined in comparison with value obtained from SNU387R or Malme3MR cells, pre-incubated with IgG.
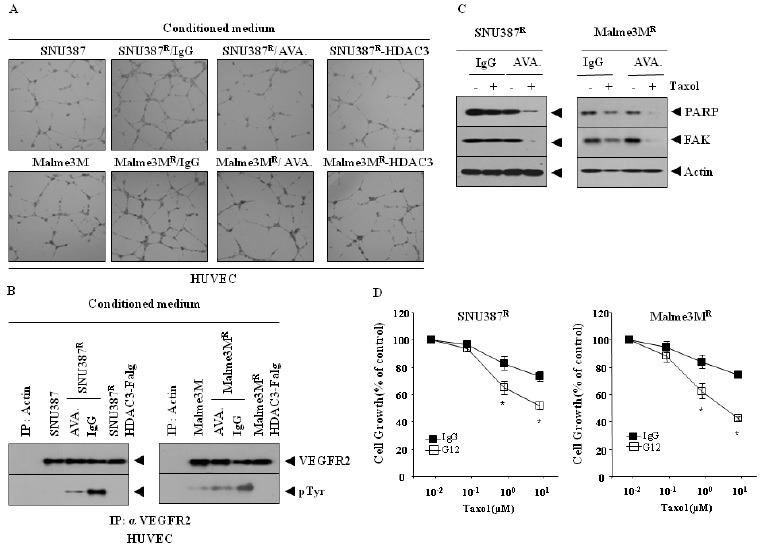
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are differentiated cells that form blood vessel walls. MicroRNAs have been shown to regulate VSMC phenotype in response to growth factor signaling (20). miR-15b, induced by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), is required for VSMC proliferation (21). These reports suggest a potential role of miR-15b in angiognesis. It would be interesting to examine whether HDAC3 would exert a regulation on the expression of miR-15b. Taken together, these results suggest that HDAC3 negatively regulates tumor-induced signaling changes in endothelial cells, and resistance to anti-cancer drugs, by regulating VEGF expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines and cell culture
The cancer cell lines used in this study were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified minimal essential medium (DMEM; Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) supplemented with heat-inactivated 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and antibiotics at 37℃ in a humidified incubator with a mixture of 95% air and 5% CO2. Drug-resistant SNU387R and Malme3MR cells were established, as described (10). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were isolated from human umbilical cord veins by collagenase treatment, and used in passages 3-6. The cells were grown in M199 medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin G, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 3 ng/ml bFGF (Upstate, MA, USA.), and 5 U/ml heparin, at 37℃, under 5% CO2/95% air.
Materials
All antibodies used in this study were purchased from Santa Cruz Company. All chemicals used in this study were purchased from Sigma Company. An ECL (enhanced chemiluminiscence) kit was purchased from Amersham. Lipofectamin and PlusTM reagent were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA USA).
Immunohistochemistry
We performed immunofluorescence staining, employing paraffin sections. Non-specific binding of antibodies was blocked by incubation with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 1 h before incubation with primary antibodies. The following primary antibodies were used: Anti-Flag (1:100, Santa Cruz, CA), anti-PECAM-1 (1:100, Santa Cruz) and anti-USP7 (1:50, Abcam, England). The sections were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4℃. After washing, secondary antibodies were applied at 1:100 or 1:200 dilutions for 1 h. We used goat anti-mouse IgG-Alexa 546 for PECAM-1 (Molecular Probes, USA). DAPI (Molecular Probes, USA), was added to stain nuclei. Confocal images were acquired, using a confocal laser scanning microscope (FV-1000, Olympus). DAPI staining was performed to stain nuclei. H&E staining was performed, to examine the extent of blood vessel formation in tumor tissues.
Cell viability determination
The cells were assayed for their growth activity, using 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma). Viable cell number counting was carried out by trypan blue exclusion assays.
Human angiogenesis antibody array
Expression levels of angiogenic factors were determined by using a Proteom ProfilerTM Human Angiogenesis Antibody Array Kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
ChIP assays
Assays were performed, according to standard procedures (22). The immunoprecipitates were reverse cross-linked. PCR was done on the phenol-chloroform-extracted DNA. PCR was done on the phenol-chloroform-extracted DNA, with specific primers of PAI-1 promoter-1 [5’-CCTTCACCAGCCCTCTTTCCATTGC-3’ (sense)], and [5’-ACCGAGGCCACCCCATAGGGT-3’ (antisense)]; and PAI-1 promoter-2 [5’-CGGGCTTAAGGCAGAGAACT-3’ (sense)], and [5’-TTTTTGGGAGAGCAGGGTT T-3’ (antisense)] sequences were used.
Preparation of SiRNA duplexes
The SiRNA duplexes were constructed with the following target sequences. HDAC3, sense (5'-AATAAGACTCTTGGTGAAGCC CCTGTCTC-3'); antisense (5'-AAGGCTTCACCAAGAGTCTTA CCTGTCTC-3'); HDAC3 (scrambled), sense (5'-GCGAAACTG ACCGGATATATTCCTGTCTC-3'); antisense (5'-GGGTATTAC AACGCCAACTATCCTGTCTC-3'). The construction of siRNA was carried out according to the instruction manual provided by the manufacturer (Ambion, Austin, TX).
Intravial microscope angiogenesis assays
Male BALB/c mice (6-8 week old) were obtained from Daehan Biolink (Seoul, Korea). The mice were maintained at the specific pathogen-free housing facility at the School of Medicine, Kangwon National University. The mice were anesthetized with 2.5% avertin (v/v) via intraperitoneal injection (Surgivet, Waukesha, WI, USA.), and abdominal wall windows were implanted. Next, a titanium circular mount with eight holes on the edge was inserted between the skin and the abdominal wall. Growth factor-reduced Matrigel containing VEGF (100 ng/ml) was applied to the space between the windows, and a circular glass cover slip was placed on top, and fixed with a snap ring. After four days, the animals were anesthetized, and injected intravenously with 50 μl of 25 ng/ml fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled dextran (molecular weight, Mr ∼2,000,000) via the tail vein. The mice were then placed on a Zeiss Axiovert 200 M microscope. The epi-illumination microscopy setup included a 100-W mercury lamp, and filter set for blue light. Fluorescence images were recorded at random locations of each window, using an electron-multiplying chargecoupled device camera (Photo Max 512, Princeton Instruments, Trenton, NJ, USA.), and digitalized for subsequent analysis, using the Metamorph program (Universal Imaging, Downingtown, PA, USA). The assay was scored from 0 (negative) to 5 (most positive) in a double-blinded manner.
Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as mean value ± standard deviation (S.D.), and differences between groups were analyzed using Student’s t-test. Mean values were considered significantly different, when P < 0.05.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation (2010-0021357, 2011-0010867, 2012H1B8A202 5495, C1008749-01-01). This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (1320160). This work was also supported by a grant from Kangwon National University (120131363).
References
- 1.Mahlknecht U., Emiliani S., Najfeld V., Young S., Verdin E. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the human histone deacetylase 3 gene. Genomics. (1999);56:197–202. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li J., Wang J., Wang J., Nawaz Z., Liu J. M., Qin J., Wong J. Both corepressor proteins SMRT and N-CoR exist in large protein complexes containing HDAC3. EMBO J. (2000);19:4342–4350. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.16.4342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Weichert Z. W., Röske A., Niesporek S., Noske A., Buckendahl A. C., Dietel M., Gekeler V., Boehm M., Beckers T., Denkert C. Class I histone deacetylase expression has independent prognostic impact in human colorectal cancer: specific role of class I histone deacetylases in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. (2008);14:1669–1677. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhang F., Shi Y., Wang L., Sriram S. Role of HDAC3 on p53 expression and apoptosis in T cells of patients with multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. (2011);6:e16795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bardai F. H., D'Mello S. R. Selective toxicity by HDAC3 in neurons: regulation by Akt and GSK3beta. J. Neurosci. (2011);31:1746–1751. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5704-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dai J., Peng L., Fan K., Wang H., Wei R., Ji G., Cai J., Lu B., Li B., Zhang D., Kang Y., Tan M., Qian W., Guo Y. Osteopontin induces angiogenesis through activation of PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 in endothelial cells. Oncogene. (2009);28:3412–3422. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zampetaki A., Zeng L., Margariti A., Xiao Q., Li H., Zhang Z., Pepe A. E., Wang G., Habi O., deFalco E., Cockerill G., Mason J. C., Hu Y., Xu Q. Histone Deacetylase 3 Is Critical in Endothelial Survival and Atherosclerosis Development in Response to Disturbed Flow. Circulation. (2010);121:132–142. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.890491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park D., Kim Y., Kim H., Kim K., Lee Y. S., Choe J., Hahn J. H., Lee H., Jeon J., Choi C., Kim Y. M., Jeoung D. Hyaluronic acid promotes angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFβ receptor interaction via CD44-PKCδ. Mol. Cells. (2012);33:563–574. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-2294-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bendinelli P., Matteucci E., Maroni P., Desiderio M. A. NF-kappaB activation, dependent on acetylation/deacetylation, contributes to HIF-1 activity and migration of bone metastatic breast carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Res. (2009);8:1328–1341. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim Y., Park H., Park D., Lee Y. S., Choe J., Hahn J. H., Lee H., Kim Y. M., Jeoung D. Cancer/testis antigen CAGE exerts negative regulation on p53 expression through HDAC2 and confers resistance to anti-cancer drugs. J. Biol. Chem. (2010);285:25957–25968. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.095950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin S. C., Chien C. W., Lee J. C., Yeh Y. C., Hsu K. F., Lai Y. Y., Lin S. C., Tsai S. J. Suppression of dual-specificity phosphatase-2 by hypoxia increases chemoresistance and malignancy in human cancer cells. J. Clin. Invest. (2011);121:1905–1916. doi: 10.1172/JCI44362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bajou K., Peng H., Laug W. E., Maillard C., Noel A., Foidart J. M., Martial J. A., DeClerck Y. A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protects endothelial cells from FasL-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Cell. (2008);14:324–334. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Basu A., Menicucci G., Maestas J., Das A., McGuire P. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) facilitates retinal angiogenesis in a model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. (2009);50:4974–4981. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu R. M., Choi J., Wu J. H., Gaston Pravia K. A., Lewis K. M., Brand J. D., Mochel N. S., Krzywanski D. M., Lambeth J. D., Hagood J. S., Forman H. J., Thannickal V. J., Postlethwait E. M. Transforming growth factor beta1-induced expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. (2010);285:16239–16247. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.111732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kokudo T., Suzuki Y., Yoshimatsu Y., Yamazaki T., Watabe T., Miyazono K. Snail is required for TGFbeta-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. (2008);121:3317–3324. doi: 10.1242/jcs.028282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fabre-Guillevin E., Malo M., Cartier-Michaud A., Peinado H., Moreno-Bueno G., Vallée B., Lawrence D. A., Palacios J., Cano A., Barlovatz-Meimon G., Charrière-Bertrand C. PAI-1 and functional blockade of SNAI1 in breast cancer cell migration. Breast Cancer Res. (2008);10:R100. doi: 10.1186/bcr2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lasagna N., Fantappiè O., Solazzo M., Morbidelli L., Marchetti S., Cipriani G., Ziche M., Mazzanti R. Hepatocyte growth factor and inducible nitric oxide synthase are involved in multidrug resistance-induced angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. (2006);66:2673–2682. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.DeLisser H., Liu Y., Desprez P. Y., Thor A., Briasouli P., Handumrongkul C., Wilfong J., Yount G., Nosrati M., Fong S., Shtivelman E., Fehrenbach M., Cao G., Moore D. H., Nayak S., Liggitt D., Kashani-Sabet M., Debs R. Vascular endothelial platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1) regulates advanced metastatic progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (2010);107:18616–18621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004654107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kitazume S., Imamaki R., Ogawa K., Komi Y., Futakawa S., Kojima S., Hashimoto Y., Marth J. D., Paulson J. C., Taniguchi N. Alpha2,6-sialic acid on platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM) regulates its homophilic interactions and downstream antiapoptotic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. (2010);285:6515–6521. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.073106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jost D., Nowojewski A., Levine E. Small RNA biology is systems biology. BMB Rep. (2011);44:11–21. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2011.44.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim S., Kang H. miR-15b induced by platelet- derived growth factor signaling is required for vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. BMB Rep. (2013);46:550–554. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2013.46.11.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Back S. S., Kim J., Choi D., Lee E. S., Choi S. Y., Han K. Cooperative transcriptional activation of ATP-binding cassette sterol transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes by nuclear receptors including Liver-X- Receptor. BMB Rep. (2013);46:322–327. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2013.46.6.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


