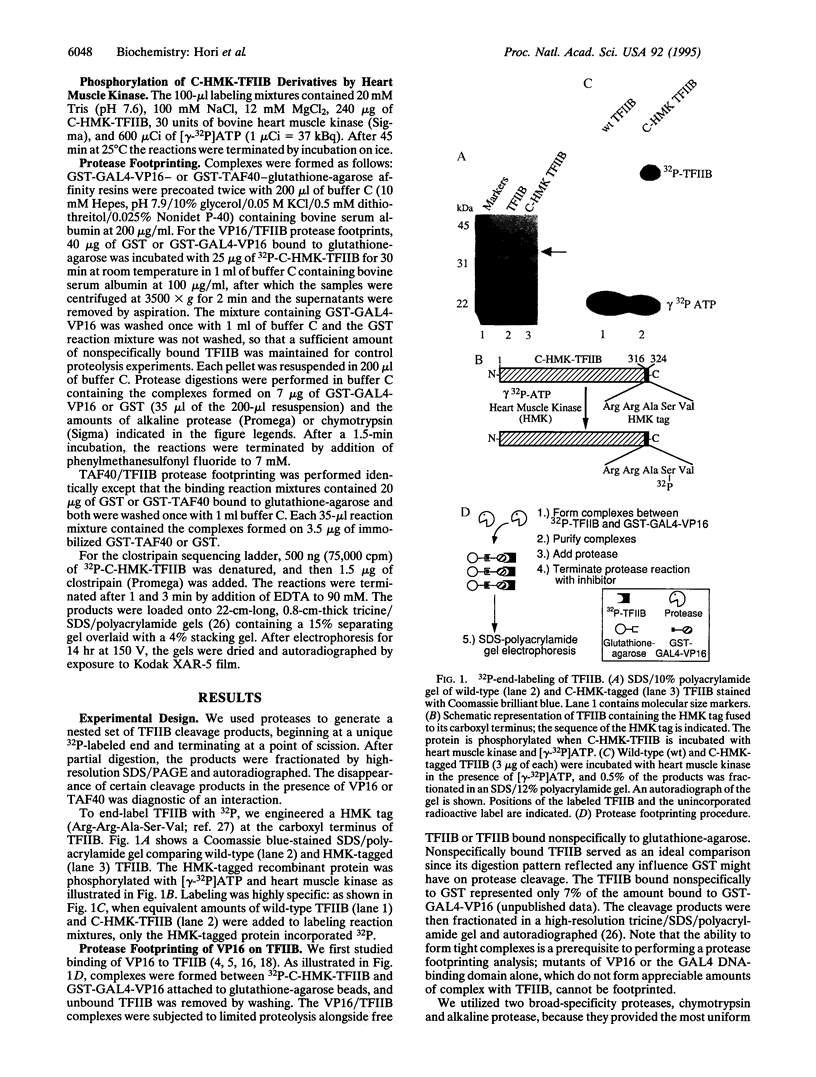
Abstract
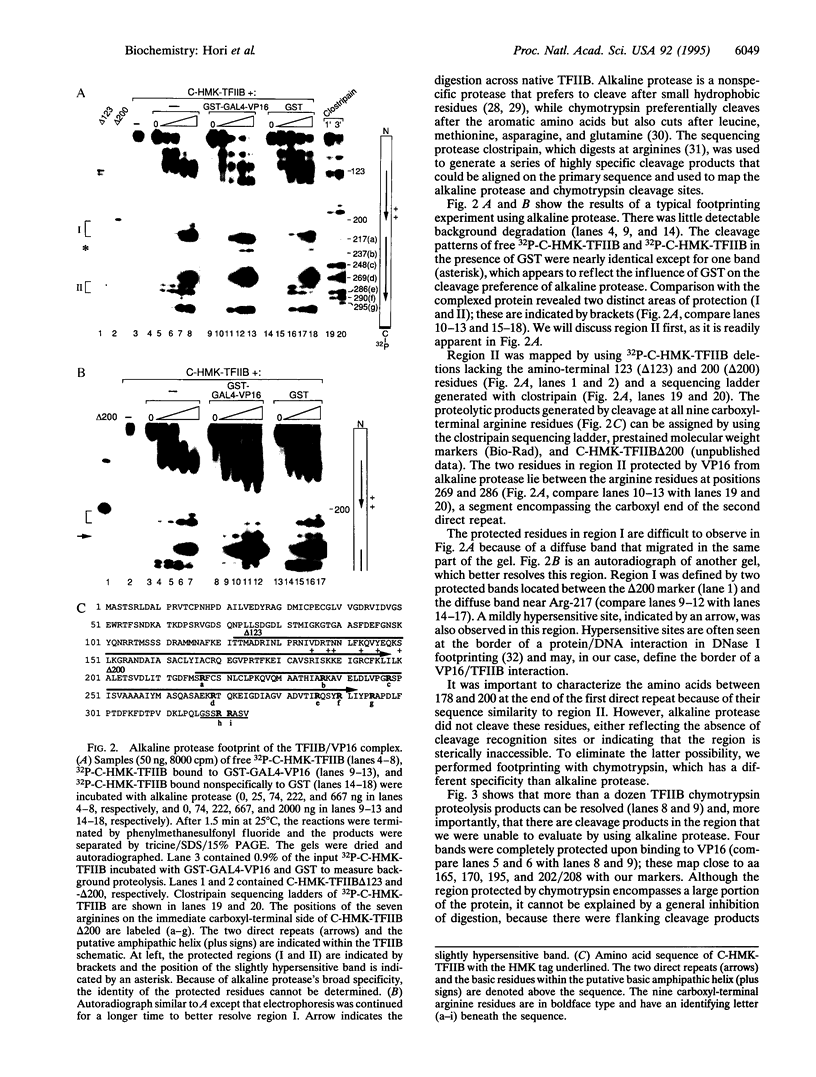
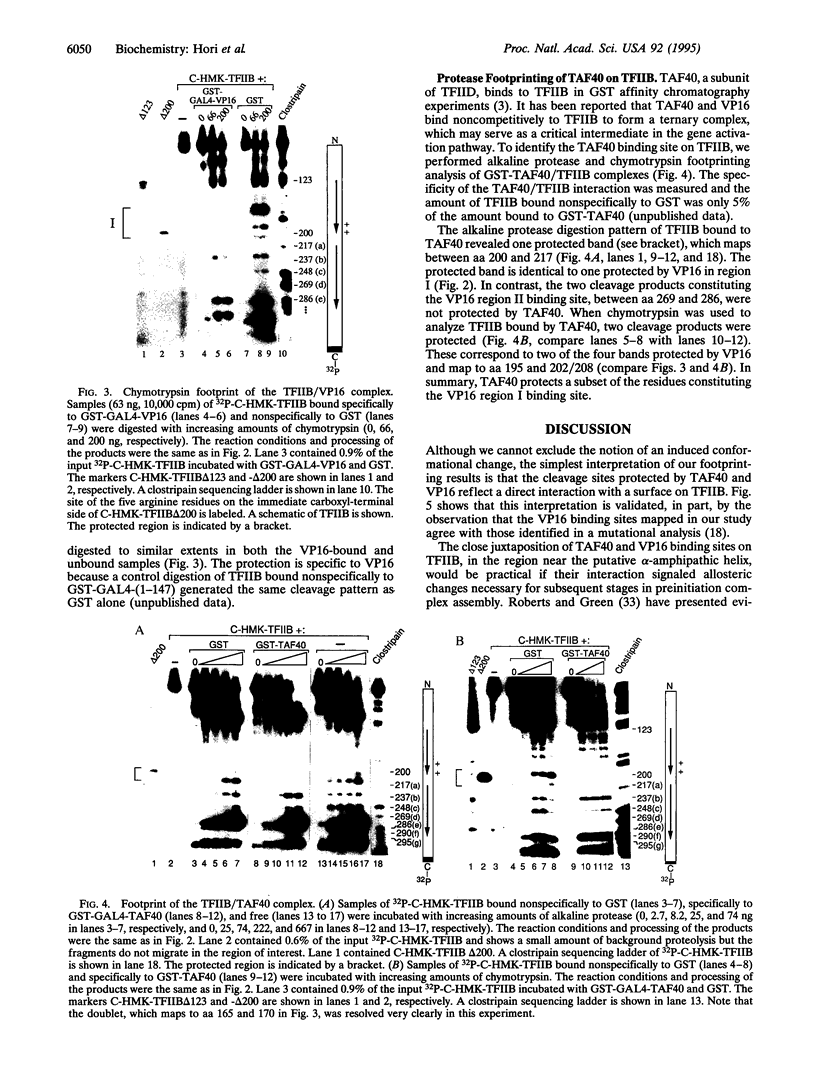
Transcriptional stimulation by the model activator GAL4-VP16 (a chimeric protein consisting of the DNA-binding domain of the yeast activator GAL4 and the acidic activation domain of the herpes simplex virus protein VP16) involves a series of poorly understood protein-protein interactions between the VP16 activation domain and components of the RNA polymerase II general transcription machinery. One of these interactions is the VP16-mediated binding and recruitment of transcription factor TFIIB. However, TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-associated factors (TAFs), or coactivators, are required for this interaction to culminate in productive transcription complex assembly, and one such TAF, Drosophila TAF40, reportedly forms a ternary complex with VP16 and TFIIB. Due to TFIIB's central role in gene activation, we sought to directly visualize the surfaces of this protein that mediate formation of the ternary complex. We developed an approach called protease footprinting in which the broad-specificity proteases chymotrypsin and alkaline protease were used to probe binding of 32P-end-labeled TFIIB to GAL4-VP16 or TAF40. Analysis of the cleavage products revealed two regions of TFIIB protected by VP16 from protease attack, one of which overlapped with a region protected by TAF40. The close proximity of the VP16 and TAF40 binding sites on the surface of TFIIB suggests that this region could act as a regulatory interface mediating the effects of activators and coactivators on transcription complex assembly.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogenhagen D. F. Proteolytic footprinting of transcription factor TFIIIA reveals different tightly binding sites for 5S RNA and 5S DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5149–5158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Kakidani H., Leatherwood J., Mostashari F., Ptashne M. An amino-terminal fragment of GAL4 binds DNA as a dimer. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Leatherwood J., Carey M., Ptashne M., Kornberg R. D. Activation of yeast polymerase II transcription by herpesvirus VP16 and GAL4 derivatives in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4746–4749. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy B., Green M. R. Eukaryotic activators function during multiple steps of preinitiation complex assembly. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):531–536. doi: 10.1038/366531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Roeder R. G. Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Hoey T., Thut C. J., Admon A., Tjian R. Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori R., Carey M. The role of activators in assembly of RNA polymerase II transcription complexes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Apr;4(2):236–244. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar M., Kaiser K., Lottspeich F., Meisterernst M. A novel mediator of class II gene transcription with homology to viral immediate-early transcriptional regulators. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Binding of general transcription factor TFIIB to an acidic activating region. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):569–571. doi: 10.1038/353569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. Study of allosteric communication between protomers by immunotagging. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):749–750. doi: 10.1038/361749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Hisatake K., Sumimoto H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Sequence of general transcription factor TFIIB and relationships to other initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9553–9557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. M. Cleavage at arginine residues by clostripain. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:165–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Characterization of receptors for immune interferon in U937 cells with 32P-labeled human recombinant immune interferon. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8514–8519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. L., Shen F., Triezenberg S. J. Pattern of aromatic and hydrophobic amino acids critical for one of two subdomains of the VP16 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):883–887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. G., Green M. R. Activator-induced conformational change in general transcription factor TFIIB. Nature. 1994 Oct 20;371(6499):717–720. doi: 10.1038/371717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. G., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Interaction between an acidic activator and transcription factor TFIIB is required for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):741–744. doi: 10.1038/363741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman J. D., Vinson C. R., McKnight S. L. Evidence of changes in protease sensitivity and subunit exchange rate on DNA binding by C/EBP. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):771–774. doi: 10.1126/science.2202050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S., Greaves R., O'Hare P. Transcriptional activation by the acidic domain of Vmw65 requires the integrity of the domain and involves additional determinants distinct from those necessary for TFIIB binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5233–5244. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Pearson A., Coulombe B., Truant R., Zhang S., Regier J. L., Triezenberg S. J., Reinberg D., Flores O., Ingles C. J. Binding of basal transcription factor TFIIH to the acidic activation domains of VP16 and p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):7013–7024. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]