Abstract
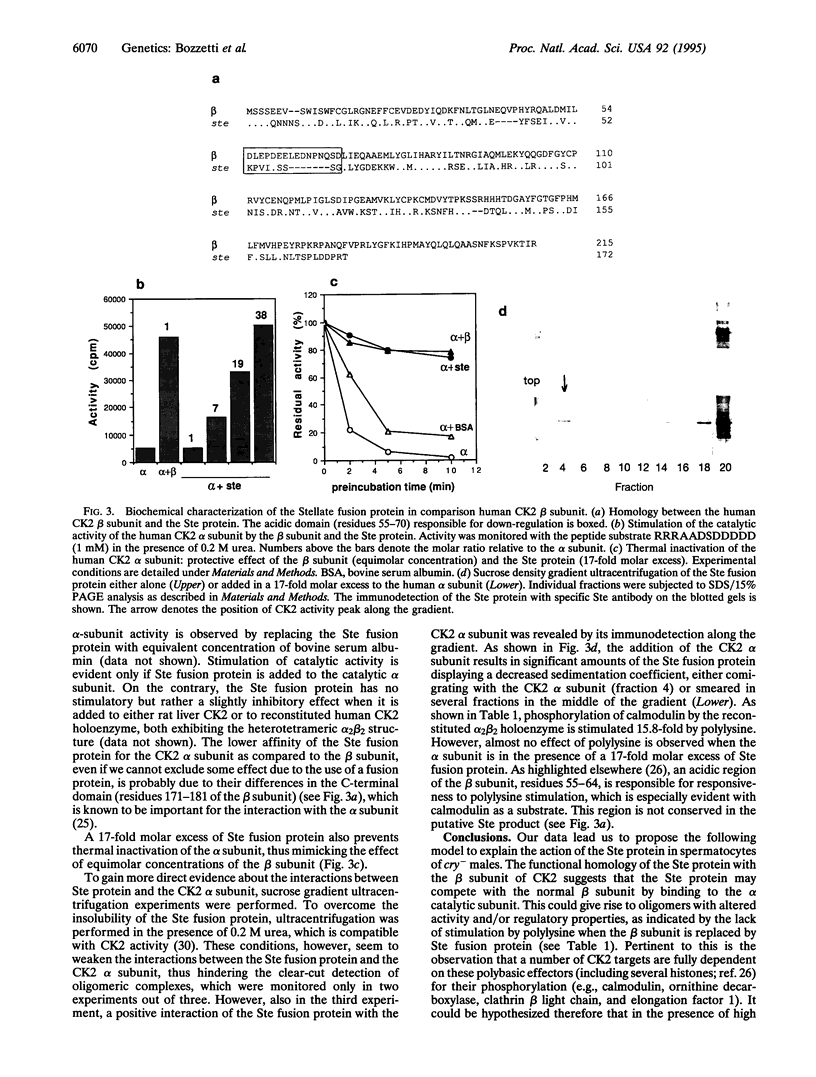
Males of Drosophila melanogaster lacking the Y chromosome-linked crystal locus show multiple meiotic alterations including chromosome disorganization and prominent crystal formation in primary spermatocytes. These alterations are due to the derepression of the X chromosome-linked Stellate sequences. To understand how the derepression of the Stellate elements gives rise to these abnormalities, we have expressed the protein encoded by the Stellate sequences in bacteria and produced an antibody against the fusion protein. Immunostaining of crystal- testes has clearly shown that the Stellate protein is a major component of the crystals. Moreover, in vitro experiments have shown that this protein can interact with the catalytic alpha subunit of casein kinase 2 enzyme, altering its activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II by casein kinase II: modulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi Y., Luke M., Laemmli U. K. Chromosome assembly in vitro: topoisomerase II is required for condensation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90215-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Wu J., O'Reilly D. R., Rivera-Marrero C. A., Hanna D. E., Miller L. K., Glover C. V. Expression and purification of the alpha and beta subunits of Drosophila casein kinase II using a baculovirus vector. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Apr;3(2):142–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldyreff B., Meggio F., Pinna L. A., Issinger O. G. Reconstitution of normal and hyperactivated forms of casein kinase-2 by variably mutated beta-subunits. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12672–12677. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. B. Non-Disjunction as Proof of the Chromosome Theory of Heredity (Concluded). Genetics. 1916 Mar;1(2):107–163. doi: 10.1093/genetics/1.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Gasser S. M. Regulation of topoisomerase II by phosphorylation: a role for casein kinase II. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):219–225. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Oligomeric structure and catalytic activity of G type casein kinase. Isolation of the two subunits and renaturation experiments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filhol O., Cochet C., Wedegaertner P., Gill G. N., Chambaz E. M. Coexpression of both alpha and beta subunits is required for assembly of regulated casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11133–11140. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. A filamentous form of Drosophila casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14349–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grankowski N., Boldyreff B., Issinger O. G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant human casein kinase II subunits alpha and beta from bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Lindsley D. L., Livak K. J., Lewis B., Siversten A. L., Joslyn G. L., Edwards J., Bonaccorsi S. Cytogenetic analysis of a segment of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1984 Aug;107(4):591–610. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G. Casein kinases: pleiotropic mediators of cellular regulation. Pharmacol Ther. 1993;59(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90039-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Hareven D. Gene expression and the control of spermatid morphogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):276–294. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J. Detailed structure of the Drosophila melanogaster stellate genes and their transcripts. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):303–316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J. Organization and mapping of a sequence on the Drosophila melanogaster X and Y chromosomes that is transcribed during spermatogenesis. Genetics. 1984 Aug;107(4):611–634. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER G. F., HESS O., BEERMANN W. [Phase specific function structure in spermatocyte nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster and their dependence of Y chromosomes]. Chromosoma. 1961;12:676–716. doi: 10.1007/BF00328946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Boldyreff B., Issinger O. G., Pińna L. A. Casein kinase 2 down-regulation and activation by polybasic peptides are mediated by acidic residues in the 55-64 region of the beta-subunit. A study with calmodulin as phosphorylatable substrate. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 12;33(14):4336–4342. doi: 10.1021/bi00180a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Boldyreff B., Marin O., Pinna L. A., Issinger O. G. Role of the beta subunit of casein kinase-2 on the stability and specificity of the recombinant reconstituted holoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):293–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Deana A. D., Pinna L. A. Endogenous phosphate acceptor proteins for rat liver cytosolic casein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11958–11961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo G., Bonaccorsi S., Robbins L. G., Pimpinelli S. Genetic analysis of Stellate elements of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1994 Dec;138(4):1181–1197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.4.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano C., Bonaccorsi S., Gatti M. The kl-3 loop of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster binds a tektin-like protein. Genetics. 1993 Mar;133(3):569–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Thomas W., Holm C. Segregation of recombined chromosomes in meiosis I requires DNA topoisomerase II. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90349-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E., Strohmaier K., Schaller H. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus gene products with antisera against bacterially synthesized fusion proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.983-991.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]