Abstract
Interleukin-12 is a heterodimeric, pro-inflammatory cytokine that is a key driver of cell-mediated immunity. Clinical interest in IL-12 is significant due to its potent anti-tumor activity and efficacy in controlling certain infectious diseases such as Leishmaniasis and Listeria infection. For clinical applications, the ease of production and purification of IL-12 and the associated cost continues to be a consideration. In this context, we report a simple and effective heparin-affinity based purification of recombinant human IL-12 (hIL-12) from the serum-free supernatants of stable IL-12-transduced HEK293 cells. Fractionation of culture supernatants on heparin Sepharose columns revealed that hIL-12 elutes as a single peak in 500 mM NaCl. Coomassie staining and Western blot analysis showed that hIL-12 eluted in 500 mM NaCl is homogeneous.Purity of hIL-12 was ascertained by RP-HPLC and ESI-MS analysis, and found to be ~98%. Western blot analysis, using monoclonal antibodies, demonstrated that the crucial inter-subunit disulfide bond linking the p35 and p40 subunits is intact in the purified hIL-12. Results of far UV circular dichrosim, steady-state tryptophan fluorescence, and differential scanning calorimetry experiments suggest that purified hIL-12 is in its stable native conformation. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and bioactivity studies demonstrate that hIL-12 is obtained in high yields (0.31 ± 0.05 mg/ mL of the culture medium) and is also fully bioactive. Isothermal titration calorimetry data show that IL-12 exhibits a moderate binding affinity (Kd(app) = 69 ± 1 μM) to heparin. The purification method described in this study is expected to provide greater impetus for research on the role of heparin in the regulation of the function of IL-12. In addition, the results of this study provide an avenue to obtain high amounts of IL-12 required for structural studies which are aimed at the development of novel IL-12-based therapeutics.
Keywords: Interleukin-12, Heparin Sepharose, HEK293, cytokine, purification, bioactivity
Introduction
Interleukin-12 (IL-12), previously known as natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF) and cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor (CLMF), is a heterodimeric cytokine comprised of p40 and p35 subunits linked by an inter-subunit disulfide bridge [1]. Among its many pleiotropic functions, IL-12 has been shown to induce: (i) IFNγ production; (ii) proliferation of activated T and NK cells; and (iii) TH1 differentiation [2]. These functions are mediated by binding of intact IL-12 to its heterodimeric transmembrane receptor complex consisting of two chains, IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2 [3].
In addition to bridging the innate and the adaptive branches of the immune system, IL-12 has demonstrated remarkable activity in controlling infectious diseases such as Leishmaniasis and Listeria infection as well as inhibiting tumor growth [4–6]. Regarding the latter, IL-12 has shown potent antitumor and antimetastatic activity in a range of preclinical tumor models [7–13]. Unfortunately, severe toxicities associated with repeated systemic delivery of IL-12 have dampened enthusiasm for its use in the clinic. Nevertheless, interest remains high for the development of novel delivery strategies to maintain IL-12’s bioactivity while mitigating toxicity. In addition, in a recent National Cancer Institute-sponsored workshop, a committee of cancer immunotherapy experts ranked IL-12 third among immunotherapeutic agents with high potential for use in treating cancer [14].
A significant obstacle to the continued exploration of IL-12 is the limited and expensive supply of recombinant IL-12 due to the lack of an efficient method for its overexpression and purification. Several attempts to produce recombinant IL-12 through a variety of host systems including bacteria, yeast, insect, and plants, have not met with much success [15–19]. Biologically active IL-12 is glycosylated and therefore methods using lower eukaryotes and prokaryotes, which lack complete post-translational modification machinery have proven to be largely inefficient [20]. In addition, attempts to overexpress recombinant IL-12, fused to purification tags, in mammalian cells have also been limited [21]. Relatively low protein expression yields, the potential for undesirable antigenic epitopes due to extra amino acids left behind after cleavage of the protein purification tag, and the risk of contamination of recombinant IL-12 samples with proteases used for removal of protein purification tag(s), has severely hampered interest in the production of affinity tag fused recombinant IL-12 in mammalian cells.
This study describes an effort to overcome the limitations of current IL-12 purification protocols using IL-12 producing HEK293 cells grown in serum-free media in a Hollow Fiber bioreactor that allows high-density growth without any animal components. After demonstrating that IL-12 is a strong intrinsic heparin binding protein, a simple one-step heparin affinity based purification method for IL-12 was developed. The simple method described in this study resulted in large yields of highly pure IL-12 that could be used to trigger intensive development of novel IL-12-based therapeutics.
Materials and methods
Materials
L-glutamine, HEPES buffer, trypsin-EDTA, G418 sulfate, Low molecular weight heparin (~3000Da) and 100 x stock of penicillin(10,000 Units/mL)/streptomycin (10mg/mL) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Cell culture media components, including FBS, horse serum, DMEM, and AMEM were purchased from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL). CDM-HD serum replacement was purchased from Fiber Cell Systems (Frederick, MD). Recombinant hIL-12 was purchased from Peprotech (Rocky Hill, NJ). Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kits were purchased from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL). All antibodies used for Western were purchased from eBiosciences (San Diego, CA). Heparin Sepharose columns were purchased from GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences (Piscataway, NJ).
Heparin string identification
The heparin binding segment search was performed using a recently developed heparin binding string search algorithm [22]. Amino acid sequences (in the FASTA format) corresponding to the p40 and p35 subunits were independently used to identify putative heparin binding segments. After completion of the search on the subject sequence (hIL-12), the string tool provides an output file detailing the amino acid sequence and the position of the potential heparin binding segments in hIL-12 [22]. Based on the information generated by the search algorithm, the surface electrostatic potential distribution map of hIL-12 was confirmed using the PBEQ solver available at CHARMM-GUI [23, 24]. Electrostatic potential map of hIL-12 was visualized using the surface view representation available in PyMol (a molecular visualization program) [25].
Generation of HEK293 cell lines overproducing human IL-12p70
The DNA vector (plasmid AG181) optimized for maximal production of human IL-12p70, expressing the p40 subunit from the hCMV promoter and the p35 subunit from the simian CMV promoter [26], was used for the generation of stable clonal HEK293-H cell lines. Highly purified, endotoxin-free DNA plasmid (Qiagen EndoFree Giga kit, Hilden, Germany) was linearized by restriction enzyme digestion and purified using the Nucleotide Removal Kit (Qiagen) and ethanol precipitated under sterile conditions. One million HEK293-H cells (Invitrogen, number 11631–017) were stably transfected by the calcium phosphate coprecipitation technique using 10 μg of HindIII-linearized hIL-12p70 (plasmid AG181) and 1 μg of EcoRI linearized pRSVneo used for selection. The cells were cultured in complete media consisting of DMEM with 10% v/v FCS, 1x penicillin/streptomycin (100Units/mL, 100μg/mL), and 500 μg/mL G418. Clone 293H/78 was among the highest producers with good growth properties. The cells were expanded and seeded in serum-free media (DMEM with 10% CDM-HD serum replacement, 1x penicillin/streptomycin, and 250 μg/mL G418) in a hollow fiber system (FiberCell Systems Inc., Frederick, MD) as described previously [27]. Cell supernatants (20 mL) were harvested daily and assayed for IL-12 levels by ELISA. IL-12 production was stable for up to 3 months. Supernatants collected between days 26 to 36 were used for the purification procedure.
Purification of hIL-12 using heparin Sepharose affinity chromatography
Cell culture supernatants (20mL) were loaded onto a pre-equilibrated heparin Sepharose (10mm*100 mm)column in 10 mM phosphate bùffer, pH 7.2. Protein elution was performed at 4° C in the same buffer using an increasing step-wise gradient of sodium chloride at a constant elution rate of 1 mL per minute. Protein elution was monitored at 280 nm with an Econo UV Monitor (BioRad, Inc., USA). The eluted protein was desalted and concentrated using a 10 kDa molecular weight cut-off at a rotor speed of 2500 x g. Protein concentration was estimated using the molar extinction coefficient value at A280 nm and also using the dye binding methods with BCA[28] and Bradford protein estimation assays using BSA as standard [29].
SDS-PAGE
Purified hIL-12 was resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE under both reduced and non-reduced conditions according to the method of Laemmli [30]. Gels were independently stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 and ProQ Emerald green specific for staining glycoproteins [31].
Western blot analysis
Purified hIL-12 was separated on 10% SDS-PAGE under both reduced and non-reduced conditions. The proteins were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and blocked using 5% skim milk in 1X Tris buffered saline with Tween-20 (TBS-T) (10mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20; pH 7.4) at room temperature for 1hr. Membranes were washed once with 0.2% BSA in 1X TBS-T. Mouse anti-hIL-12 antibodies specific for p70, p40 and p35 (eBiosciences Inc., San Diego, CA) were added at a 1:2000 dilution and incubated overnight. A secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase (Genescript Inc., Piscataway, NJ) was added to the membrane at a 1:2500 dilution and incubated at 4°C for 2 hours. Bands were visualized using NBT/BCIP as a substrate for the alkaline phosphatase.
Reversed-phase HPLC analysis
hIL-12 purity was assessed via reversed-phase HPLC analysis. Samples were loaded onto a reversed phase C-18 column with the mobile phase consisting of two solvents (A) 0.1% TFA in water and (B) 0.1% TFA in acetonitrile. Using two type of gradient conditions, one a linear gradient of 5–70% of B for 30minutes and two a step gradient of 0–15% of B for 15 minutes, 15–65% of B for 45 minutes and 65–100% of B for 15 minutes hIL-12 sample purified from heparin Sepharose was resolved on a two different C18 matrices, one Zorbax column with 300SB-CN column with 4.6 × 250mm dimension containing 5 μM porous particle with 300 Å pore size (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA) and two PRP-3 column with 2.1 × 150mm dimension containing 10 μM porous particle with 300 Å pore size (Hamilton, Reno, NV). The flow rate of the mobile phase was set at 1mL/min. The elution of protein (at 25 ° C) was monitored at 280 nm using a Hitachi L-74006 UV-Visible detector.
Measurement of hIL-12 concentration and bioactivity
hIL-12 concentration was determined via ELISA (Human IL-12 p70 ELISA Ready- SET-Go, Biosciences Inc., San Diego, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions [26]. Bioactivity of purified hIL-12 was determined by quantifying IFN-γ secretion by the IL-12-responsive NK-92MI cell line [32] (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) cultured in complete media consisting of AMEM supplemented with 12% FBS, 12% horse serum, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 0.2 mM inositol, 0.02 mM folic acid, and 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol. In brief, cultured NK-92MI cells were seeded in a 96 well plate at 20,000 cells/well. Purified hIL-12 was added to cells at final concentrations of 1 ng/mL, 0.2 ng/mL and 0.04 ng/mL. Recombinant hIL-12 from Peprotech (Rocky Hill, NJ) and cell culture media without IL-12 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. IFN-γ concentrations in NK92-MI supernatants after 24 hrs were quantified using an IFN-γELISA kit (Human IFN-γELISA Ready-SET-Go, eBiosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA) as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Isothermal titration calorimetry
Isothermal titration calorimetric experiments were performed using the iTC200 (MicroCal Inc., Northampton, MA) at 25°C. All protein samples were dialyzed in 1X PBS (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4 2mM KH2PO4) pH 7.4. Samples were subjected to centrifugation to remove any aggregated or precipitated material and were degassed before the titration. Concentration of heparin to hIL-12 was maintained at a molar ratio of 10:1. The contents of the syringe (heparin) were added sequentially in 1.3 μl aliquots to the cell (hIL-12) with a 12-second interval between injections. Using Origin Version 7.0 software, heats of reaction per injection (μcalories/second) were determined by the integration of peak areas. Thermodynamic values were derived after fitting the data using a one-site of binding model available in Origin 7.0. The fit provides values of the heat of binding (ΔH°), the stoichiometry of binding (n), and the dissociation constant (Kd) from plots of the heat evolved per mole of heparin injected versus the heparin/hIL-12 molar ratio [33].
Steady-state fluorescence
Intrinsic fluorescence spectra of hIL-12 were collected using a Hitachi F-2500 spectrofluorometer at 2.5 nm resolution, with an excitation wavelength of 280 nm at 25 °C. All fluorescence measurements were conducted at a protein concentration of 100 μg/mL in 1X PBS pH 7.4. Appropriate blank corrections were made to subtract for background noise.
Circular dichroism
CD analysis of hIL-12 was performed using a Jasco spectropolarimeter. Far-UV CD spectrum for hIL-12 (100 μM) was recorded in 1X PBS pH 7.4 using a quartz cell of 0.1 mm path length with a scan speed of 50 nm/second. Suitable blank corrections were made to obtain the final CD spectrum. CD data was expressed in molar ellipticity (deg. cm2.dmol−1).
Differential scanning calorimetry
Heat capacity of hIL-12 was measured as a function of temperature at pH 7.2 using a Differential Scanning Calorimeter (NANO DSCIII) with a ramping temperature of 1 °C/min from 10 °C to 90 °C. hIL-12 was subjected to degassing in 1X PBS pH 7.4 before the acquisition of DSC data. Thermal denaturation of hIL-12 was performed at a protein concentration of ~100 μM. Both the heating and cooling cycles were recorded to examine the reversibility of the thermal unfolding process.
ESI-MS analysis
Electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry was performed on a Bruker ESI-QTOF machine using a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Purified hIL-12 sample (0.1mg/mL) was subjected to desalting using ZipTip™, mixed with methanol (with 0.1% formic acid) and directly infused into the ESI source using a syringe pump. Mass spectra were obtained in a positive ion mode.
Results and discussion
Mammalian overexpression of hIL-12
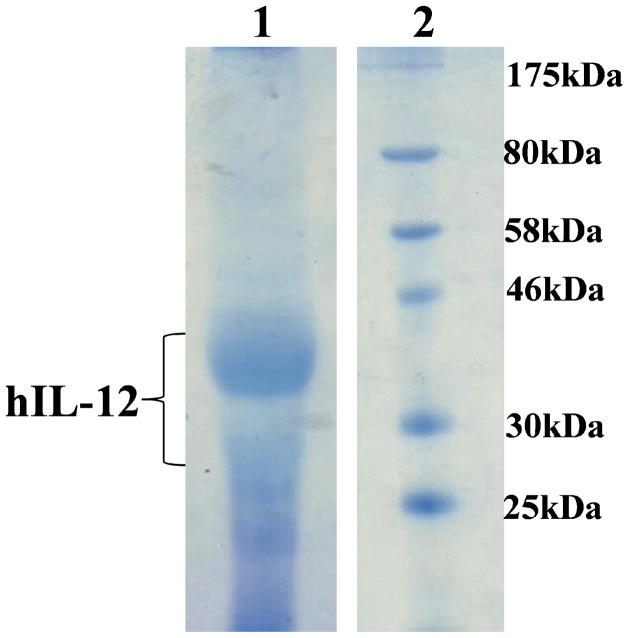
Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293-H) were previously transduced with the dual promoter plasmid (AG181, DPhuIL-12p70 ) expressing both subunits p40 and p35 from the same vector from 2 promoters arranged in counter-clockwise orientation [26]. The stable, high producing cell clone 293-H/78 was cultured in a hollow fiber bioreactor in serum-free medium. SDS-PAGE of culture supernatants showed two prominent closely moving bands corresponding to the p40 (Mw ~40 kDa) and p35 (Mw ~ 35 kDa) subunits of hIL-12 (Fig. 1). The band representing the 35 kDa subunit was observed to be quite diffuse compared to that of the 40 kDa subunit (Fig. 1). Similar observations, on the diffuse nature of the band corresponding to the p35 band, were previously made when the SDS PAGE gels of IL-12 were stained with Coomassie blue. Interestingly, the p35 band appears to be less diffuse when the SDS gels are stained with Emerald green stain which recognizes glycosylated proteins. The average concentration of hIL-12, as assessed by ELISA, in culture supernatants was 364 ± 62 μg/mL. In addition, the total amount of protein in culture supernatants was measured using the Bradford protein assay. Results indicated that hIL-12 accounts for ~25% of total proteins in culture supernatants.
Fig 1.
Overexpression of hIL-12. SDS-PAGE depicting the overexpression of hIL-12 secreted by IL-12-transduced HEK293 cells grown in serum-free medium in a hollow fiber system and analyzed in Coomassie Blue stained gel. Lane 1 - Cell Culture Supernatant; Lane 2 - Protein Marker.
Identification of heparin binding strings in hIL-12
Several cytokines such as, the fibroblast growth factors, vascular endothelial growth factors and interferon-γ, are known to specifically bind to heparin [34–37]. In silico analyses have shown that heparin binding proteins contain amino acid sequences characterized by special patterns of basic amino acids and other natural amino acids [38, 39]. The importance of the distribution of these patterns for heparin binding has been corroborated using three-dimensional crystal and solution structures of several heparin binding cytokines [36, 37, 40, 41]. In this context, the occurrence of such conspicuous amino acid patterns has been used to predict binding affinity of proteins to heparin [42–45]. In silico analysis of the cytokine amino acid sequence database, using the recently developed algorithm, revealed the presence of putative heparin binding amino acid segments in cytokines which, to date, had not previously been annotated as heparin binding proteins (data not shown). One among those cytokines is IL-12. In this context, it is important to mention that Hasan et al (1999), using an ELISA approach on IL-12-BSA fusion protein, suggested that IL-12 is a heparin binding protein [46]. However, the heparin binding specificity of IL-12 was ambiguous due to the presence of BSA in the fusion protein. BSA is known to non-specifically bind to various ligands including heparin [47].
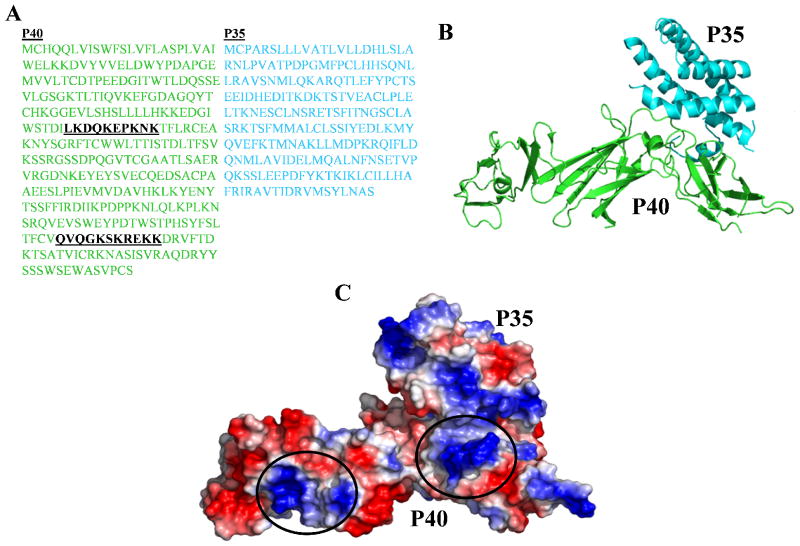
hIL-12 was found to contain two potential heparin binding sites located on the p40 subunit: LKDQKEPKNK (amino acid segment, 117–126) and QVQGKSKREKK (amino acid segment, 276–286) (Fig. 2A). Interestingly, the p35 subunit did not show the presence of any potential heparin-binding string(s) (Fig. 2A). Mapping these putative heparin binding segments on the three-dimensional structure of hIL-12 reveals that the basic residues within each segment are located in close spatial proximity, creating two positively charged clusters in the p40 subunit (Fig. 2B). The presence of these clusters creates a conducive microenvironment for binding of negatively charged molecules such as heparin. This led to the prediction that hIL-12 can potentially bind to polyanions like heparin (Fig. 2C).
Fig 2.
Amino acid sequence and three-dimensional structure of hIL-12. (A) Single letter coded amino acid sequence of the p40 (green) and p35 (cyan) subunits of hIL-12. The two potential heparin binding sites are highlighted in black. (B) Structure of the backbone of hIL-12, with the p40 and p35 subunits of hIL-12 depicted in green and cyan, respectively. (C) Electrostatic potential map of the structure of hIL-12. The potential heparin binding sites are circled..
Purification of hIL-12 using heparin affinity chromatography
Because hIL-12 contains putative heparin binding strings, it was hypothesized that its heparin binding affinity could be exploited for purification using heparin Sepharose affinity chromatography. Heparin is a highly sulfated molecule and is known to interact with its specific protein partners through electrostatic interactions [38, 45]. Therefore, purification of heparin binding proteins is achieved by heparin Sepharose affinity chromatography using a simple salt gradient [48–51].
Fractionation of proteins in culture supernatants using heparin Sepharose affinity chromatography, under a stepwise NaCl gradient, produced three prominent peaks (Fig. 3A). SDS-PAGE gels of the different fractions eluted in a NaCl gradient, detected independently by Coomassie blue staining, silver staining and polyclonal IL-12 antibodies, revealed that most of the contaminating proteins were eluted in the wash buffer and in 100 mM NaCl (Fig. 3A). Only, a very small peak was observed in 200 mM NaCl where no distinct band was observed in SDS-PAGE (Figs. 3A, 3B lane 3). A faint band corresponding to the p40 subunit was detected in the 300 mM NaCl fraction (Figs. 3A, 3B, lane 4) but the majority of the secreted IL-12 was eluted in the 500 mM NaCl fraction (Figs. 3A, 3B lane 5, and 3C). In addition, ProQ emerald green staining of the fraction eluted in 500 mM NaCl (Fig. 3C) suggests that purified IL-12 is glycosylated.
Fig 3.
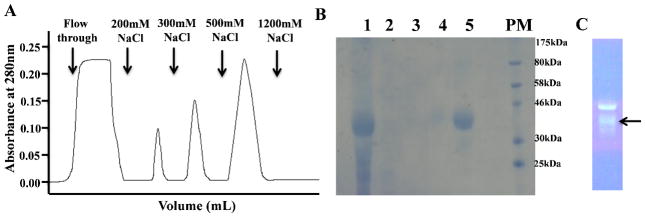
Purification of hIL-12 using heparin Sepharose chromatography. (A) Fractionation of proteins, secreted in the hollow fiber culture medium, on heparin Sepharose. (B ) SDS-PAGE of the different fractions, eluted under a NaCl gradient, as detected by Coomassie blue staining. Lane 1 - Cell Culture Supernatant; Lane 2 - Flow through (100 mM NaCl); Lane 3 – 200mM NaCl; Lane 4 – 300mM NaCl; Lane 5 – 500mM NaCl; PM-Protein Marker. (C) Lane showing the purified hIL-12 from 500mM NaCl fraction stained with ProQ emerald green stain and a distinct p35 subunit band(s) is highlighted by an arrow.
Bradford protein assay and ELISA measurements were carried out to assess if contaminants not detectable by Coomassie staining, were present in the 500 mM NaCl fraction. A disparity in the protein concentrations measured by Bradford assay and ELISA would indicate the presence of non-IL-12 protein contaminants in the 500 mM NaCl fraction. The Bradford assay calculated the concentration of protein in the 500 mM NaCl fraction as 0.31 ± 0.05 mg/ mL of the hollow fiber supernatant while hIL-12 ELISA in the same fraction yielded a concentration of 0.31 ± 0.05 mg/mL. The excellent agreement between the results of the Bradford assay and ELISA suggest that the protein fraction eluted in 500 mM NaCl is predominantly IL-12.
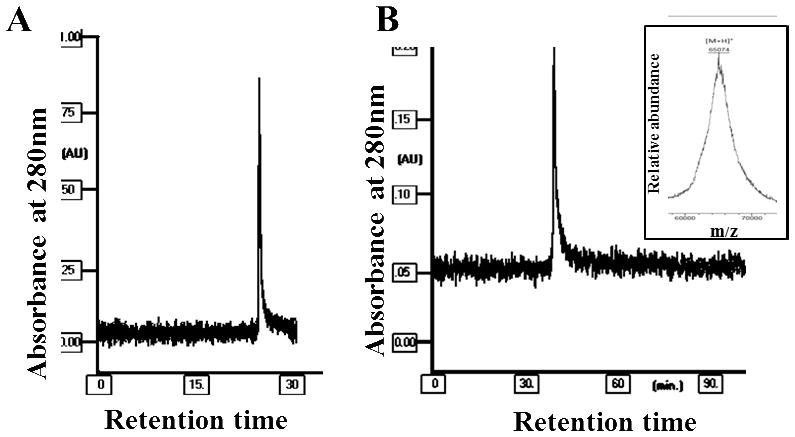
Reverse phase HPLC chromatography was used to quantitate the purity of hIL-12 isolated from heparin Sepharose column. Two different elution conditions were used to monitor any potential contaminants present in the sample. hIL-12 eluted as a single peak both under linear (Fig. 4A) and stepwise gradient conditions (Fig. 4B). Measurement of peak area in the reversed phase HPLC profile indicates that the purity of hIL-12 is greater than 98% (Fig. 4A and 4B). ESI-MS analysis of purified hIL-12 revealed a relatively broad peak corresponding to an average molecular mass of 65,074 Da. This value is higher than the expected molecular mass value of 62,024 Da calculated from the amino acid sequence of IL-12. The observed broadening of the ESI mass peak and the disparity between the experimental and theoretical molecular mass can be attributed to the reported glycosylation of hIL-12 [26, 52–54]. Several previous studies have reported the presence of p40 dimer as a contaminant in IL-12 heterodimer preparations. Interestingly, the ESI mass spectra of hIL-12 did not show the presence of p40 homodimer. It appears that the p40 homodimer, which if formed, could possibly have eluted from the heparin Sepharose column in lower concentrations of NaCl. The heparin binding pocket is possibly less accessible in the p40 dimer than in its monomeric form.
Fig 4.
Purity of hIL-12 was confirmed using RP-HPLC and ESI-MS Analysis. (A) Chromatogram showing the resolution of hIL-12 sample on a reverse phase C18 column (Zorbax) using a linear with mobile phase consisting of two solvents (A) 0.1% TFA in water and (B) 0.1% TFA in Acetonitrile. (B) Chromatogram showing the resolution of hIL-12 sample on a reverse phase C18 column (PRP-3) using a stepwise gradient with mobile phase consisting of two solvents (A) 0.1% TFA in water and (B) 0.1% TFA in acetonitrile. In the inset, mass spectrum showing the peak of hIL-12 molecule with average experimental molecular mass.
Integrity of the inter-subunit disulfide bond in the purified recombinant hIL-12
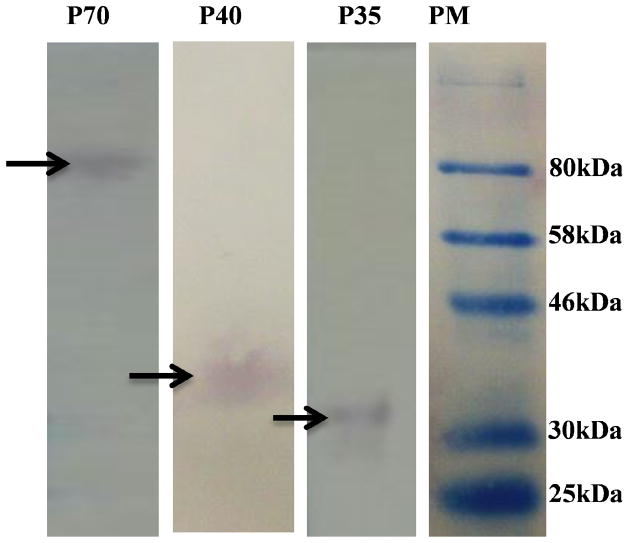
The p35 and p40 subunits in IL-12 are bridged by an inter-subunit disulfide bond [55–57]. This bond has been shown to be critical for the bioactivity of IL-12 as both p35 and p40 must bind to their respective receptor chains, i.e. IL-12Rβ2 and IL-12Rβ1, respectively, for activation of the receptor [55–57]. The presence of the intermolecular disulfide bond between the p35 and p40 subunits was examined using three different monoclonal antibodies specific for the intact heterodimer, the p40 subunit, or the p35 subunit (Fig. 5). SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions showed a single band corresponding to a molecular weight of ~75 kDa suggesting that the inter-subunit disulfide bond bridging the p35 and p40 subunit is intact in the purified hIL-12. As expected, the constituent p35 and p40 subunits were detected under reduced conditions, in the presence of 1% v/v β-mercaptoethanol, indicating that the inter-subunit disulfide bond is intact in the purified recombinant IL-12 (Fig. 5).
Fig 5.
Integrity of the inter-subunit disulfide bond between the p40 and p35 subunits of purified recombinant hIL-12. Western blot analysis of hIL-12, under non-reducing conditions (Lane-p70 - detected by a monoclonal antibody against intact hIL-12) and under disulfide bond reduced conditions Lane-p40 – detected by monoclonal antibodies against the p40 subunit and Lane-p35 - detected by monoclonal antibodies against the p35 subunit. Lane-PM is the protein molecular weight marker.
Conformation of purified hIL-12
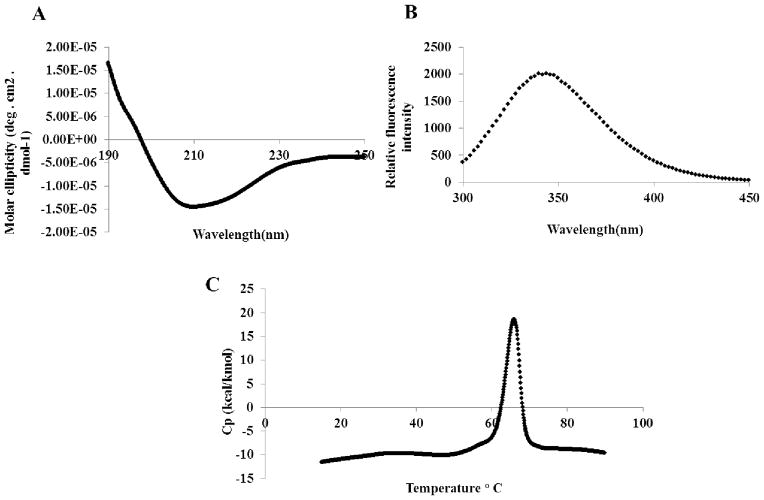
To verify that purified hIL-12 is in its native conformation [58], far UV circular dichroism (CD) was used to measure the secondary structural conformation. Far UV CD spectrum of purified hIL-12 (Fig. 6A) showed a minimum centered at around 210 nm and a broad shoulder in the 222 nm region signifying that the protein backbone contains both α-helix and β-sheet structural elements. This observation is consistent with the crystal structure of IL-12 which shows that the p40 and p35 subunits are predominantly in β-sheet and α-helical conformations, respectively [57].
Fig 6.
Biophysical characterization of purified recombinant hIL-12. (A) Far UV CD spectrum, (B) Intrinsic fluorescence spectrum, and (C) Differential scanning thermogram. For the DSC experiment, purified hIL-12 (1.0 mg/mL) was dissolved in 10 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) containing 100 mM NaCl. Thermograms were corrected for background noise. The experiments were performed at a scan rate of 1 °C/min.
Intrinsic steady state tryptophan fluorescence provides useful information on the tertiary structure of proteins [59, 60]. The steady state fluorescence spectrum of purified recombinant hIL-12 showed that the wavelength maximum is centered at 343 nm suggesting that the protein has a well-defined tertiary structure with the indole ring of the tryptophan residues buried in a partially hydrophobic environment of the protein (Fig. 6B).
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) directly measures the thermal stability of purified hIL-12 [61]. The DSC thermogram of purified hIL-12 shows a Tm, the temperature at which 50% of the protein population exists in denatured state(s), of 65 ± 0.3 °C, (Fig. 6C). The DSC data, in conjunction with the Far UV CD and steady state tryptophan fluorescence results, clearly suggest that the purified recombinant hIL-12 is in a structured and stable conformation.
Bioactivity of purified hIL-12
IFN-γ production by the IL-12-responsive NK-92MI cell line was used to compare the biological activities of purified hIL-12 and commercially available hIL-12. The bioactivity assay showed that IFN-γ levels induced by the purified IL-12 shows similar activity as the commercial hIL-12 (Fig. 7). This observation is quite encouraging considering the fact that, unlike commercial IL-12 samples, no protein stabilizing agent was added to our purified IL-12 preparations.
Fig 7.
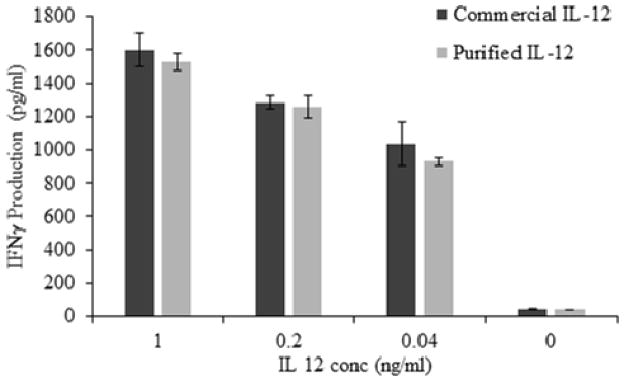
Bioactivity of purified hIL-12. IL-12-responsive NK 92MI cells were incubated with IL-12 samples (1 ng/mL, 0.2 ng/mL, 0.04 ng/mL) for 24 hrs. Secretion of IFN-γ was quantified via ELISA. Bioactivity of purified hIL-12 (grey bars) was compared with commercial hIL-12 (black bars). Bars show mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments.
IL-12 exhibits specific binding affinity to heparin
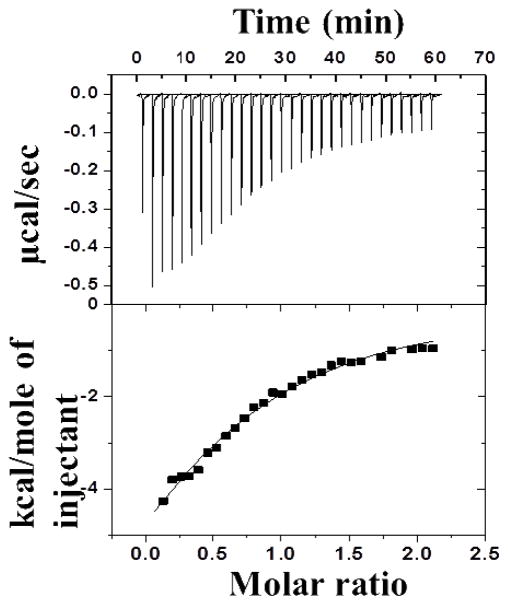
The heparin binding affinity of IL-12 predicted by in silico analysis and successfully exploited for heparin-affinity chromatography was measured quantitatively using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). This experimental technique is very versatile because it can provide a direct measure of the binding affinity, binding stoichiometry, and thermodynamics of protein-ligand interactions. The isothermogram characterizing the IL-12-heparin interaction at 25°C shows an exothermic hyperbolic curve suggesting that the interaction produced heat (Fig. 8). The binding isotherm characterizing the interaction between heparin and IL-12 fits best to the one-site binding model and yields a binding constant [Kd(app)] value of ~70 μM. The protein to glycosaminoglycan binding stoichiometry is calculated to be 1:1. The interaction between IL-12 and heparin occurs with a significant decrease in entropy, suggesting that electrostatic forces play a significant role in promoting the binding. ITC data conclusively demonstrate, for the first time, that IL-12 is a heparin binding protein.
Fig 8.
Isothermogram representing the binding of hIL-12 to heparin in 1X PBS (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 2mM KH2PO4) (pH 7.4). The upper panels show the raw data for the titration of approximately 1 mM heparin to 0.1 mM of hIL-12. The solid line in the bottom panel represents the best-fit of the experimental data, using a one-set of sites binding model from Microcal Origin. hIL-12 appears to bind to heparin with a strong affinity [ Kd(app) value of 69 ± 1.14 μM]. The hIL-12/heparin binding affinity is characterized by enthalpy and entropy values of −2.8 kcal.mol.−1 and 0.0094 kcal.mol.−1. K−1, respectively.
Conclusions
The results of this study indicate that the heparin binding affinity of IL-12 can be successfully exploited to purify bioactive recombinant IL-12 from mammalian cultures in a single step without the use of protein affinity tags. This simple and efficient purification method can be expected to serve as trigger for intensive research efforts to better understand the role of heparin on the structure-function relationship of IL-12. In this context, it may be of interest to note that glycosaminoglycans such as, heparin and heparin sulfate play a crucial role in activation of transmembrane kinase receptors of cytokines [62]. In addition, the high yields of pure IL-12 obtained using the method described in this study will provide an avenue to embark on structural studies aimed at the development of novel IL-12 based therapeutics for the treatment of cancers and infectious diseases.
Highlights.
Two potential heparin binding segments were detected in the amino acid sequence of the p40 subunit of interleukin-12 (IL-12).
Human IL-12 (hIL-12) is shown to exhibit strong binding affinity to heparin.
hIL-12 is purified to homogeneity in a single step using heparin Sepharose affinity chromatography.
Purified recombinant hIL-12 is well-folded and biologically active.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health [NCRR COBRE Grant 1 P20 RR15569 (TKSK), P30 GM103450 (TKSK), K22 CA131567 (DAZ), R01 CA172631 (DAZ), R15 CA176648, the Department of Energy (Grant DE-FG02-01ER15161 (TKSK), National Science Foundation and the Arkansas Biosciences Institute (TKSK and DAZ), by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health (NCI/NIH) (GNP and BKF). We thank C. Bergamaschi and JJS Cadwell for discussions, and B. Chowdhury for technical assistance.
Abbreviations
- hIL-12
Human Interleukin-12
- ITC
Isothermal Calorimetry
- CD
Circular Dichroism
- DSC
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
- NKSF
Natural Killer Cell Stimulatory Factor
- CLMF
Cytotoxic Lymphocyte Maturation Factor
- NK
Natural Killer
- IFN-γ
Interferon gamma
- HEK
Human Embryonic Kidney
- SDS-PAGE
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Poly Acrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
- TBS
Tris Buffered Saline
- PBS
Phosphate Buffered Saline
- BSA
Bovine Serum Albumin
- NBT/BCIP
Nitroblue Tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3′-indolylphosphate
- FBS
Fetal Bovine Serum
- FASTA
FAST Alignment
- HPLC
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- ESI-MS
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- ESI-QTOF
ESI-Quadrupole time of flight
Footnotes
Disclosure
GNP, MR and BKF are inventors on US Government-owned patents and patent applications related to IL-12. There are no further patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the policies on sharing data and materials.
Author contributions
SJ, BK, DZ & TKSK made substantial contributions to conception and design of the study. SJ and BK participated actively in execution of the study. SJ, BK, SS, DZ & TKSK analyzed and interpreted the data. SJ, DZ & TKSK wrote the manuscript. RJ, JB, MR, GNP, BKF generated IL-12 DNA and cell clone and produced IL-12 raw material.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Kobayashi M, Fitz L, Ryan M, Hewick RM, Clark SC, Chan S, Loudon R, Sherman F, Perussia B, Trinchieri G. Identification and purification of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF), a cytokine with multiple biologic effects on human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989;170:827–845. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:133–146. doi: 10.1038/nri1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Trinchieri G, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. The IL-12 family of heterodimeric cytokines: new players in the regulation of T cell responses. Immunity. 2003;19:641–644. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Afonso LC, Scharton TM, Vieira LQ, Wysocka M, Trinchieri G, Scott P. The adjuvant effect of interleukin-12 in a vaccine against Leishmania major. Science. 1994;263:235–237. doi: 10.1126/science.7904381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Roberts MT. Current understandings on the immunology of leishmaniasis and recent developments in prevention and treatment. Br Med Bull. 2005;75–76:115–130. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldl003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brombacher F, Dorfmuller A, Magram J, Dai WJ, Kohler G, Wunderlin A, Palmer-Lehmann K, Gately MK, Alber G. IL-12 is dispensable for innate and adaptive immunity against low doses of Listeria monocytogenes. Int Immunol. 1999;11:325–332. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Coughlin CM, Salhany KE, Wysocka M, Aruga E, Kurzawa H, Chang AE, Hunter CA, Fox JC, Trinchieri G, Lee WM. Interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 synergistically induce murine tumor regression which involves inhibition of angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:1441–1452. doi: 10.1172/JCI1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Del Vecchio M, Bajetta E, Canova S, Lotze MT, Wesa A, Parmiani G, Anichini A. Interleukin-12: biological properties and clinical application. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4677–4685. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hance KW, Rogers CJ, Zaharoff DA, Canter D, Schlom J, Greiner JW. The antitumor and immunoadjuvant effects of IFN-alpha in combination with recombinant poxvirus vaccines. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2387–2396. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hung K, Hayashi R, Lafond-Walker A, Lowenstein C, Pardoll D, Levitsky H. The central role of CD4(+) T cells in the antitumor immune response. J Exp Med. 1998;188:2357–2368. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Osaki T, Peron JM, Cai Q, Okamura H, Robbins PD, Kurimoto M, Lotze MT, Tahara H. IFN-gamma-inducing factor/IL-18 administration mediates IFN-gamma- and IL-12-independent antitumor effects. J Immunol. 1998;160:1742–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tatsumi T, Huang J, Gooding WE, Gambotto A, Robbins PD, Vujanovic NL, Alber SM, Watkins SC, Okada H, Storkus WJ. Intratumoral delivery of dendritic cells engineered to secrete both interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 effectively treats local and distant disease in association with broadly reactive Tc1-type immunity. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6378–6386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zaharoff DA, Hoffman BS, Hooper HB, Benjamin CJ, Jr, Khurana KK, Hance KW, Rogers CJ, Pinto PA, Schlom J, Greiner JW. Intravesical immunotherapy of superficial bladder cancer with chitosan/interleukin-12. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6192–6199. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cheever MA. Twelve immunotherapy drugs that could cure cancers. Immunol Rev. 2008;222:357–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Budzianowski J. Tobacco--a producer of recombinant interleukins. Przegl Lek. 2012;69:1060–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Foss DL, Moody MD, Murphy KP, Jr, Pazmany C, Zilliox MJ, Murtaugh MP. In vitro and in vivo bioactivity of single-chain interleukin-12. Scand J Immunol. 1999;50:596–604. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1999.00633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morris KR, Bruce MP, Janardhana V, Thomas JD, Bean AG, Strom DG. Expression of biologically active recombinant porcine interleukin-12 from Escherichia coli. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008;126:373–376. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Su BS, Chiu HH, Lin CC, Shien JH, Yin HS, Lee LH. Adjuvant activity of chicken interleukin-12 co-administered with infectious bursal disease virus recombinant VP2 antigen in chickens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2011;139:167–175. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thomas JD, Morris KR, Godfrey DI, Lowenthal JW, Bean AG. Expression, purification and characterisation of recombinant Escherichia coli derived chicken interleukin-12. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008;126:403–406. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aydin H, Azimi FC, Cook JD, Lee JE. A convenient and general expression platform for the production of secreted proteins from human cells. J Vis Exp. 2012 Jul 31;(65) doi: 10.3791/4041. pii: 4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jiao HY, Zhan MY, Guo MZ, Yi Y, Cong Y, Tian RG, Zhang WY, Bi SL. Expression of human IL-12 in mammalian cell and study on its biological activities. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2007;21:235–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chris D. In: Identification of Consensus Glycosaminoglycan Binding Strings in Proteins. Jacqueline M, Meghna C, Srinivas J, Thallapuranam KSK, Wing Ning L, editors. 2013. pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Im W, Beglov D, Roux B. Continuum Solvation Model: computation of electrostatic forces from numerical solutions to the Poisson-Boltzmann equation. Computer Physics Communications. 1998;111:59–75. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jo S, Vargyas M, Vasko-Szedlar J, Roux B, Im W. PBEQ-Solver for online visualization of electrostatic potential of biomolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W270–275. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.DeLano WL, Lam JW. PyMOL: A communications tool for computational models. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society. 2005;230:U1371–U1372. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jalah R, Rosati M, Ganneru B, Pilkington GR, Valentin A, Kulkarni V, Bergamaschi C, Chowdhury B, Zhang GM, Beach RK, Alicea C, Broderick KE, Sardesai NY, Pavlakis GN, Felber BK. The p40 subunit of interleukin (IL)-12 promotes stabilization and export of the p35 subunit: implications for improved IL-12 cytokine production. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:6763–6776. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.436675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chertova E, Bergamaschi C, Chertov O, Sowder R, Bear J, Roser JD, Beach RK, Lifson JD, Felber BK, Pavlakis GN. Characterization and favorable in vivo properties of heterodimeric soluble IL-15.IL-15Ralpha cytokine compared to IL-15 monomer. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:18093–18103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.461756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985;150:76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gallagher S, Chakavarti D. Staining proteins in gels. J Vis Exp. 2008 Jul 8;(17) doi: 10.3791/760. pii: 760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Luckay A, Sidhu MK, Kjeken R, Megati S, Chong SY, Roopchand V, Garcia-Hand D, Abdullah R, Braun R, Montefiori DC, Rosati M, Felber BK, Pavlakis GN, Mathiesen I, Israel ZR, Eldridge JH, Egan MA. Effect of plasmid DNA vaccine design and in vivo electroporation on the resulting vaccine-specific immune responses in rhesus macaques. J Virol. 2007;81:5257–5269. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00055-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wiseman T, Williston S, Brandts JF, Lin LN. Rapid measurement of binding constants and heats of binding using a new titration calorimeter. Anal Biochem. 1989;179:131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kenig M, Gaberc-Porekar V, Fonda I, Menart V. Identification of the heparin-binding domain of TNF-alpha and its use for efficient TNF-alpha purification by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008;867:119–125. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lortat-Jacob H, Grimaud JA. Interferon-gamma binds to heparan sulfate by a cluster of amino acids located in the C-terminal part of the molecule. FEBS Lett. 1991;280:152–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80225-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mummery RS, Rider CC. Characterization of the heparin-binding properties of IL-6. J Immunol. 2000;165:5671–5679. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.10.5671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Salek-Ardakani S, Arrand JR, Shaw D, Mackett M. Heparin and heparan sulfate bind interleukin-10 and modulate its activity. Blood. 2000;96:1879–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cardin AD, Weintraub HJ. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989;9:21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gandhi NS, Mancera RL. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008;72:455–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Murphy JW, Cho Y, Sachpatzidis A, Fan C, Hodsdon ME, Lolis E. Structural and functional basis of CXCL12 (stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha) binding to heparin. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:10018–10027. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608796200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pellegrini L, Burke DF, von Delft F, Mulloy B, Blundell TL. Crystal structure of fibroblast growth factor receptor ectodomain bound to ligand and heparin. Nature. 2000;407:1029–1034. doi: 10.1038/35039551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Delacoux F, Fichard A, Cogne S, Garrone R, Ruggiero F. Unraveling the amino acid sequence crucial for heparin binding to collagen V. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29377–29382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004724200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hileman RE, Fromm JR, Weiler JM, Linhardt RJ. Glycosaminoglycan-protein interactions: definition of consensus sites in glycosaminoglycan binding proteins. Bioessays. 1998;20:156–167. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199802)20:2<156::AID-BIES8>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schick BP, Maslow D, Moshinski A, San Antonio JD. Novel concatameric heparin-binding peptides reverse heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin anticoagulant activities in patient plasma in vitro and in rats in vivo. Blood. 2004;103:1356–1363. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-07-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Munoz EM, Linhardt RJ. Heparin-binding domains in vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:1549–1557. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000137189.22999.3f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hasan M, Najjam S, Gordon MY, Gibbs RV, Rider CC. IL-12 is a heparin-binding cytokine. J Immunol. 1999;162:1064–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hattori T, Kimura K, Seyrek E, Dubin PL. Binding of bovine serum albumin to heparin determined by turbidimetric titration and frontal analysis continuous capillary electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 2001;295:158–167. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Farooqui AA. Purification of enzymes by heparin-sepharose affinity chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980;184:335–345. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hung KW, Kumar TK, Kathir KM, Xu P, Ni F, Ji HH, Chen MC, Yang CC, Lin FP, Chiu IM, Yu C. Solution structure of the ligand binding domain of the fibroblast growth factor receptor: role of heparin in the activation of the receptor. Biochemistry. 2005;44:15787–15798. doi: 10.1021/bi051030n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rajalingam D, Kumar TK, Soldi R, Graziani I, Prudovsky I, Yu C. Molecular mechanism of inhibition of nonclassical FGF-1 export. Biochemistry. 2005;44:15472–15479. doi: 10.1021/bi0516071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sullivan R, Klagsbrun M. Purification of cartilage-derived growth factor by heparin affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:2399–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Carra G, Gerosa F, Trinchieri G. Biosynthesis and posttranslational regulation of human IL-12. J Immunol. 2000;164:4752–4761. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.9.4752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Murphy FJ, Hayes MP, Burd PR. Disparate intracellular processing of human IL-12 preprotein subunits: atypical processing of the P35 signal peptide. J Immunol. 2000;164:839–847. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Doucey MA, Hess D, Blommers MJ, Hofsteenge J. Recombinant human interleukin-12 is the second example of a C-mannosylated protein. Glycobiology. 1999;9:435–441. doi: 10.1093/glycob/9.5.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stern AS, Podlaski FJ, Hulmes JD, Pan YC, Quinn PM, Wolitzky AG, Familletti PC, Stremlo DL, Truitt T, Chizzonite R, et al. Purification to homogeneity and partial characterization of cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor from human B-lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:6808–6812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tsai JL, Jose Priya TA, Hu KY, Yan HY, Shen ST, Song YL. Grouper interleukin-12, linked by an ancient disulfide-bond architecture, exhibits cytokine and chemokine activities. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014;36:27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yoon C, Johnston SC, Tang J, Stahl M, Tobin JF, Somers WS. Charged residues dominate a unique interlocking topography in the heterodimeric cytokine interleukin-12. EMBO J. 2000;19:3530–3541. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.14.3530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Greenfield NJ. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:2876–2890. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sharma VK, Kalonia DS. Steady-state tryptophan fluorescence spectroscopy study to probe tertiary structure of proteins in solid powders. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92:890–899. doi: 10.1002/jps.10354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Li Z, Meighen EA. Steady-state fluorescence and phosphorescence spectroscopic studies of bacterial luciferase tryptophan mutants. J Fluoresc. 1994;4:209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01878453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Johnson CM. Differential scanning calorimetry as a tool for protein folding and stability. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013;531:100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Heldin CH, Ostman A. Ligand-induced dimerization of growth factor receptors: variations on the theme. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996;7:3–10. doi: 10.1016/1359-6101(96)00002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]