Abstract
Introduction:
The efficient use of libraries can be an important factor in determining the educational quality of Universities. Therefore, investigation and identification of factors affecting library anxiety becomes increasingly necessary. The purpose of this research is to determine the factors effecting library anxiety of students in Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences.
Materials and Methods:
This was an applied survey research using Bostick's Library Anxiety questionnaire as data gathering tool. The statistical population consisted of all students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (15011 students) with the sample size of 375 using stratified random sampling. The validity of data gathering tool was confirmed by experts in the library and information science and its reliability was determined by Cronbach's alpha (r = 0.92). Descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation) and inferential statistics (t-test and ANOVA) were used for data analysis using SPSS 18 software.
Results:
Findings showed that the mean of library anxiety score was 2.68 and 2.66 for students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences respectively which is above average (2.5). Furthermore, age and gender had no meaningful effect on the library anxiety of students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, but gender had a meaningful effect on library anxiety of students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences while age had no such effect.
Conclusion:
The results showed that the mean of factors effecting library anxiety in students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences is higher than average and therefore not satisfactory and only factors relating to feeling comfortable in the library is lower than average and somewhat satisfactory.
Keywords: Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, library anxiety, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, students
INTRODUCTION
The effective use of library plays an important role in users’ ability in identification, retrieval and accessing of information.[1] Therefore today libraries are considered the foundation of education, research and development and effective use of academic libraries can greatly affect the quality of education and research of a university. The efficient use of libraries by students is only possible if students using the library are also provided with psychological peace and security along with necessary conditions and facilities.[2]
Newcomer students entering a university will encounter many new situations among which are the necessity of independence in research and finding the necessary resources in the libraries. This necessity is so unfamiliar to the students that it feels like entering another country with completely different environment and culture and this sudden change can sometimes even cause nervous reactions. This along with other factors can have complex psychological effects on students using academic libraries and thus affect the quality of using library facilities. The result of these reactions is creating fear and anxiety in students.[3]
Students need to make use of certain skills in order to conduct academic researches and therefore most universities hold workshops teaching students the necessary skills using classical and computer based education methods. One of the main objectives of these workshops is teaching students the effective use of libraries. However, even after all these workshops some students feel uncomfortable while using libraries. In professional articles, these uncomfortable feelings are referred to as “library fear” and “library anxiety”.[4]
Library anxiety has been investigated for a long time resulting in publication of numerous articles in various countries. Among the first studies was a biennial study conducted by Melon in which the feeling of students while using libraries was described as “fear”.[4,5] This unpleasant feeling while using a library was unofficially called library anxiety since before then but even after general acceptance of this term in the field of librarianship no great efforts were spent in its measurement or accurate study until four decades ago. In other words, Melon was the first person to propose the concept of library anxiety as an official theory and his research resulted in the realization of library anxiety theory.[5]
For some students, library is a safe haven for study and research, but in others it can cause nervousness and anxiety which can affect their use of library facilities. This initial anxiety can cause more anxiety for students and can lead to non-beneficial use of library.[5]
Library anxiety happens when a student looking for necessary resources in a library finds out that he's ill equipped for his search library anxiety is considered normal among students and is rarely considered important. The signs of library anxiety are negative feelings such as uncertainty, stress, fear and mental confusion.[1]
Due the growth and development of internet and communication and information technology which is able to provide students with a large quantity of information, electronic resources anxieties such as computer phobia, computer anxiety, technology anxiety and technology phobia which are affected by personal, racial, educational, gender and other differences between the users have also become important. These electronic resource anxieties can also affect library anxiety.[4]
Khadivi conducted a study titled “A study of library and electronic resources anxiety among students at the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences”. The findings showed that the familiarity of students with library and electronic resources were below average and that there was no meaningful difference between the library anxiety different genders, but age has a meaningful effect of library anxiety which increased with a decrease in students’ age.[6] Hariri and Nemati in their study called “Evaluation of Library anxiety among students: Collage Rehabilitation Science in Iran University of Medical Sciences” showed that library anxiety due to staff barriers, affective barriers, library knowledge and mechanical barriers were around average (average score = 3). Furthermore, male students experienced more anxiety.[2] Jokar and Taherian conducted a study called “A. Comparative study of library anxiety between students of educational science and psychology college in Shiraz University, based on the scale Bastyk library anxiety”. Their findings showed the library anxiety to be below average and that there was no meaningful difference between the library anxiety of male and female students and that of the students that had made use of libraries before entering the university compared to those who hadn’t. However, the library anxiety was significantly higher in librarianship students compared to students of other disciplines and also in masters students compared to bachelor students.[7] A study by Anwar et al. investigated library anxiety among university students in Kuwait. Results showed that library anxiety of the students was average and that there was no meaningful relation between gender and library anxiety.[8] In another work, Gross and Latham investigated the relation between library anxiety and information literacy. The findings showed a weak negative correlation between library literacy and library anxiety scores of the students which shows that library anxiety slightly decreases with the increase of library literacy. Also, the library anxiety among investigated students was average.[9] Jiao et al. in a study titled “Library anxiety: Characteristics of “at risk” college students” discovered that newcomer students have high levels of library anxiety and their anxiety decreases linearly with each academic year.[10]
Since library anxiety is a negative and unpleasant feeling while using libraries,[5] it can act as a psychological factor and harms the effective use of library facilities. The importance of libraries in the furthering of educational and research goals of universities makes the study of library anxiety a necessary endeavor. Although library anxiety had been the subject of various international studies in the past two decades, not many significant studies regarding the relation between library anxiety and psychological barriers such as barriers with staff, affective barriers, knowledge of the library, comfort in the library and mechanical barriers has been conducted in Iran. Also, the studies by Jokar and Taherian in Shiraz University of Medical Science[7] and Khadivi in Isfahan University of Medical Science[1] showed the library anxiety to be below average and different between these two universities. Therefore, the goal of this study is the investigation of factors affecting library anxiety in students of Isfahan University of Medical Science and Shiraz University of Medical Science in year 2011-2012 (1390) in order to identify the important factors and removal of these factors with the help of relevant authorities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study uses applied survey method. The statistical population consisted of the students of Isfahan University of Medical Science (6011 students) and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (9000 students) with the total of 15011 students. The sample size was determined to be 375 students using Krejcie and Morgan table[11]. The sampling method used was stratified random sampling with each university being considered one stratum, selecting the number of samples based on the number of students of each university. Using this method, 150 samples were chosen from Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and since this university consists of 7 departments, 22 samples were selected from each department. Similarly, 225 samples were selected from Shiraz University of Medical Sciences with 29 samples from each department (8 departments in total). The data gathering tool used was Bostick's Library Anxiety questionnaire which consists of 39 questions in 5 library anxiety issues: (1) Barriers with staff - Misconceptions of the students resulted from regarding librarians as unfriendly or unhelpful individuals or too busy to lend a helping hand that can cause anxiety (2) affective barriers-the feeling of insufficiency or helplessness while working in the library (3) knowledge of the library-unfamiliarity with library and information science skills, the library building and different resources and facilities provided in the library that can lead to fear and anxiety, (4) comfort in the library-lack of peace and comfort in the library resulted from poor special design of the library and lack of security and belonging in the library that can cause students to leave the library before finishing their research or refuse to go to library altogether and (5) mechanical barriers-anxiety resulted from working with machines such as copy machines, printers and computers.[12] This questionnaire was scored using 5 grades Likert scale (1) complete disagreement, (2) disagreement, (3) undecided, (4) agreement, (5) complete agreement and the closer the average score of a factor was to 5, the more effect it had on the library anxiety of the students. The mean score in this study was considered to be 2.5. The questionnaires were distributed to the students personally. Also, the researcher was present during answering questions and provided clarifications whenever needed. Furthermore in accordance to research ethics, special attention was paid in observance of actions such as an explanation to the responders and gaining Informed consent for participation in the study, impartiality of the researcher and avoiding certain biases, using the most recent information and scientific resources, complete honesty in presentation and analysis of data and avoiding alteration of data in order to reach the conclusion intended by the researcher and confidentiality of the results obtained from the questionnaires. In order to determine the reliability of the questionnaire, Cronbach's alpha (r = 0.92) was used. Data analysis was carried out using descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation) and inferential statistics (t-test and ANOVA) with the help of SPSS 18 software.
RESULTS
The demographic data analysis showed that 50% of the investigated students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (76 students) were male and 50% (76 students) were female. In Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, 49.3% of the investigated students were male (106 students) and 50.7% of them were female (109 students). Also, the response rate was 97%. In Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 22.4% of the students were between 21 and 22 years old, 74.3% were between 23 and 24 and 3.3% of the students were between 25 and 26 years old. On the other hand, in Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, 21.9% of the students were between 21 and 22 years old, 66.1% were between 23 and 24 and 13% of the students were between 25 and 26 years old. In both universities, most of the students were between 23 and 24 years old and very few of them were between 25 and 26 years old.
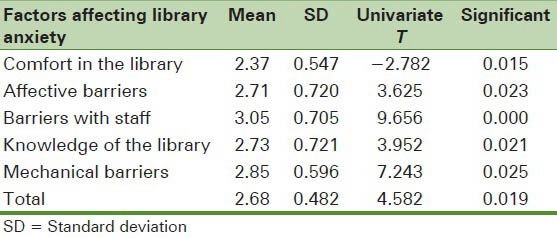
The findings regarding the factors affecting library anxiety of students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences showed that the meaningfulness level of this study is higher than 0.01 (0.019) therefore the factors affecting library anxiety had higher than average scores (2.5) according to the students. Among these factors, barriers with staff had the highest (3.052) and comfort in the library had the lowest (2.37) average score [Table 1].
Table 1.
Average and SD of the factors affecting library anxiety among the students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
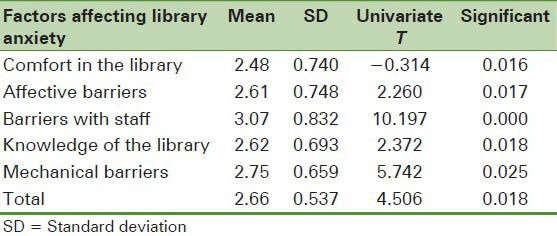
The findings regarding the factors affecting library anxiety of students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences showed that the meaningfulness level of this study is higher than 0.01 (0.018) therefore the factors affecting library anxiety had higher than average scores (2.5) according to the students. Among these factors, Barriers with staff had the highest (3.07) and Comfort in the library had the lowest (2.48) average score [Table 2].
Table 2.
Average and SD of the factors affecting library anxiety among the students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences
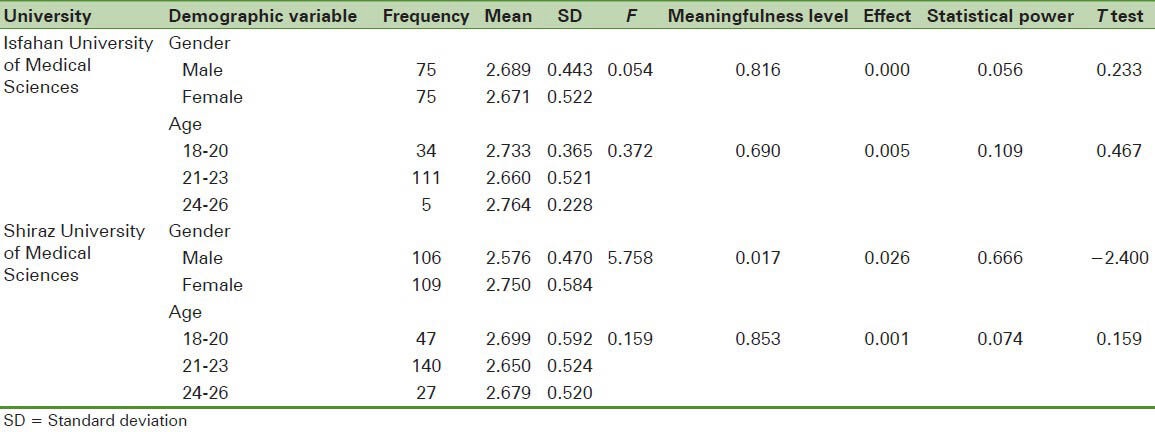
The findings regarding the relation between library anxiety and gender and age of the students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences showed that the observed F were not meaningful for age and gender and library anxiety (P < 0.05). Therefore, the average score of library anxiety had no meaningful relation with gender and age of the students. On the other hand, the observed F for gender and library anxiety of students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences was meaningful in P < 0.05 level, but the observed F for Library anxiety and the age of the students was not meaningful [Table 3].
Table 3.
The comparison of library anxiety between the students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences based on age and gender
DISCUSSION
Anxiety is part of a person's life and is considered by all societies to be a suitable form of adaptation. The importance of effective use of libraries in order to advance the educational and research goals of universities makes the study of factors such as library anxiety a necessity and helps identify the factors responsible for them. The goal of this study is identification of the factors affecting library anxiety from the view point of students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences. The results showed that the library anxiety in the students of both universities was a little above average. Khadivi et al.[4] in their study titled “Study of library anxiety and electronic resources among users of Isfahan University” reported that the library anxiety in students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences is average. Also, Hariri and Nemati have reported average library anxiety level in the student of the rehabilitation department of Iran University of Medical Sciences in their study called “Evaluation of Library anxiety among students: College Rehabilitation Science in Iran University of Medical Science”.[2] Jokar and Taherian also conducted a study called “Comparative study of library anxiety between students of educational science and psychology college in shiraz university, based on the scale Bastyk library anxiety” and reported above average library anxiety levels.[7] These results are consistent with the results obtained in the present study.
Jiao and Onwuegbuzie conducted a study regarding the relation between library anxiety and personality dimensions and reported that four of the seven personal cognition dimensions are related to tow of the factors causing library anxiety among which is feeling uncomfortable in the library. According to their study, students with negative personal perceptions are more prone to library anxiety.[3] They also conducted another study investigating the effects of information technology on library anxiety and reported that feeling uncomfortable in the library is among the most important factors causing anxiety among students[12] which isn’t consistent with the results of the present study since the results of this study shows that the score for feeling comfortable in the library is below average. Jiao and Onwuegbuzie also reported that affective factors are one of the most important factors causing anxiety among students[13] which is consistent with the results obtained from this study.
The results of the present study also showed that the most important factor affecting library anxiety in students of Isfahan University of Medical Science and Shiraz University of Medical Science is barriers with the staff which is in agreement with the results of the study by Jokar and Taherian.[7] In their study called “A Comparative study of library anxiety between students of educational science and psychology college in shiraz university, based on the scale Bastyk library anxiety” they reported that library anxiety was meaningfully higher in students of librarianship compared with other students and in Masters students compared to Bachelor students which was due the factors related to the staff and library trust which is the same as the results obtained from this study. Battle investigated the effect of library literacy on library anxiety and reported that the library literacy of the students and their understanding of academic libraries is poor and proper teaching of library literacy can help decrease library anxiety[14] and in another study Cleveland reported that visiting academic libraries prior to entering universities is necessary and can help reduce library anxiety. Therefore, development of new plans, training of the staff and changes in the library environment can help students achieve a full understanding of library environment.[15]
Another of the factors affecting library anxiety is mechanical barriers which had above average score in Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences. Jiao and Onwuegbuzie in their study titled “Dimensions of library anxiety and social interdependence” reported that mechanical barriers are among the most important factors affecting library anxiety.[3] In another study, they reported that the use of novel technologies in libraries can lead to negative effects and computer related anxieties which will lead to library anxiety due to mechanical barriers.[13] These results are consistent with the current study. Due to the growth of new technologies and familiarity of students with new software and hardware this mechanical barrier has been overcome and even in the cases when the familiarity with the new technologies is low, the possibility of learning these new technologies is available to students.
There was no meaningful relation between age and gender of the students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and their library anxiety, but the library anxiety in students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences were meaningfully affected by their gender while no meaningful difference due to age was observed. In their study, Jokar and Taherian reported that library anxiety wasn’t meaningfully different between male and female students.[7] Furthermore Cleaveland reported that library anxiety and the factors affecting it are not dependent on gender, age and academic year[15] which is in agreement with the results of the current study. Omran AB in a study called “library anxiety and internet anxiety among graduate students of a major research university” concluded that age is the only factor capable of predicting library anxiety and using that predicted library anxiety levels between students.[16] Also Hariri and Nemati in their study titled “Evaluation of Library anxiety among students: College Rehabilitation Science in Iran University of Medical Science” reported that men had more library anxiety compared to women only in subsidiary comparison of mechanical barriers.[2]
CONCLUSION
Using a library is possible only if the conditions are such that the user can concentrate and conduct the necessary researches. If a library fails to provide users with these conditions, it can cause them to suffer from library anxiety.[17] One must always keep in mind that library anxiety has behavioral, psychological, emotional and conceptual effects.[1] Also using the library for users suffering from library anxiety is a negative experience and causes them to spend less time and energy using libraries.[18] Therefore special attention must be paid to library anxiety and factors causing it.
The results of this study showed that the average score of factors affecting library anxiety in Isfahan University of Medical Science and Shiraz University of Medical Science was above average and therefore unsatisfactory. Only the factors related to feeling comfortable in the library is a little below average in both universities and therefore somewhat satisfactory. Based on these results and in order to reach a desirable situation (reduction of factors affecting library anxiety), it is necessary to familiarize high school students with academic libraries before entering college using periodical workshops and other methods. These methods can also be used to familiarize university students with academic libraries in order to reduce their library anxiety. Workshops training academic library staff and librarians in work ethics are also useful in reducing barriers with staff and library anxiety.
Footnotes
Source of Support: This article was extracted from research granted No 290229 by Health Information Technology Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Conflict of Interest: None declared
REFERENCES
- 1.Khadivi Sh. Overview of library anxiety in university libraries. Library and Information Studies. 2004;15:109–14. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hariri N, Nemati LS. Evaluation of library anxiety among students: Collage Rehabillation Science in Iran University of Medical Science. Libr Inf Sci Inf Technol. 2009;2:39–52. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jiao QG, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Dimensions of library anxiety and social interdependence; implications for library services. Libr Rev. 2002;51:71–8. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khadivi Sh, Shabani A, Abedi MR. Study of library anxiety and electronic resources among users of Isfahan University. Studies in Education and Psychology. 2004;30:115–6. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jiao QG, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Prevalence and reasons for university library usage. Libr Rev. 1997;46:411–42. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Khadivi Sh. A study of library and electeronic resources anxiety among students at the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. Studies in Education and Psychology. 2008;3:30–116. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jokar A, Taherian A. Comparative study of library anxity between students of educational science and Psychology College in Shiraz University, base on the scale Bastyk library anxity. Journal of Educational and Psychological Research. 2008;4:135–55. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Anwar M, Al-Kandari N, Al-Qallaf C. Use of Bostick's Library Anxiety Scale on Undergraduate Biological Sciences Students of Kuwait University. Libr Inf Sci Res. 2004;26:266–83. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gross M, Latham D. Attaining information literacy: An investigation of the relationship between skill level, self estimates of skill and library anxiety. Libr Inf Sci Res. 2007;29:332–53. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jiao QG, Onwuegbuzie AJ, Lichtenstein AA. Library anxiety: Characteristics of ‘at risk’ college students. Libr Inf Sci Res. 1996;18:151–63. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Powell Ronal R. Nadjla Hariri. Tehran: Islamic Azad University Scientific Publication Center; 2000. Basic Reasearch Methods for Librarians. Trans. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Erfanmanesh MA, Didgah F. Vol. 4. Ketabe Mah: Koliat; 2010. Library anxiety: Challeng for the effective use of library servises; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jiao QG, Onwuegbuzie AJ. The impact of information technology on library anxiety; the role of computer attitude. Proquest Nurs Allied Health Source. 2004;23:138–44. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Battle JC. Texas: University of North Texas; 2004. The effect of information literacy instruction on library anxiety among international students. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cleveland A. Library anxiety: A decade of empirical research. Libr Rev. 2004;53:177–85. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Omran AB. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh; 2001. Library anxiety and internet anxiety among graduate students of a major research university. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Derven B. Useful theory for librarianship. Drexel Libr Q. 1998;13:16–32. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Keefer J. The hungry rat's syndrome: Library anxiety, information literacy and the academic reference process. Ref Q. 1993;32:333–9. [Google Scholar]


