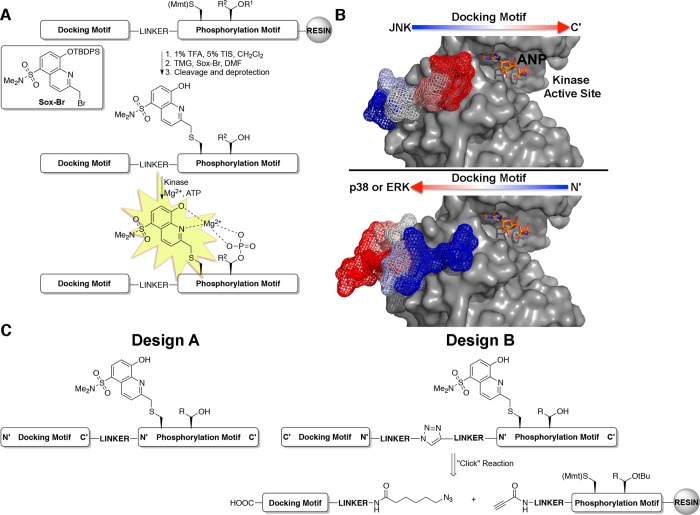
Figure 1.
Design of MAP kinase activity sensors. (A) MAP kinase activity sensors are comprised of three domains: a docking motif to impart selectivity, a Sox-containing phosphorylation motif that provides fluorescence readout, and a linker between the two motifs (TMG = tetramethyl guanidine; R1 = tBu; R2 = H or CH3). (B) Co-crystal structures of JNK1 (top, gray surface) and p38α (bottom, gray surface) with substrate docking motifs, NFAT4 (mesh) and MK2 (mesh) respectively (PDB 2XS0(23) and 2OKR(41)). Arrows indicate the orientation that the docking motifs of each MAP kinase subfamily bind. The ATP derivative, phosphoaminophosphonic acid-adenylate ester (ANP), is shown in orange sticks for clarity. (C) Design strategies for MAP kinase activity sensors that have docking motifs in forward (Design A) and reversed (Design B) directions.