Abstract
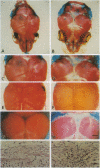
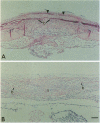
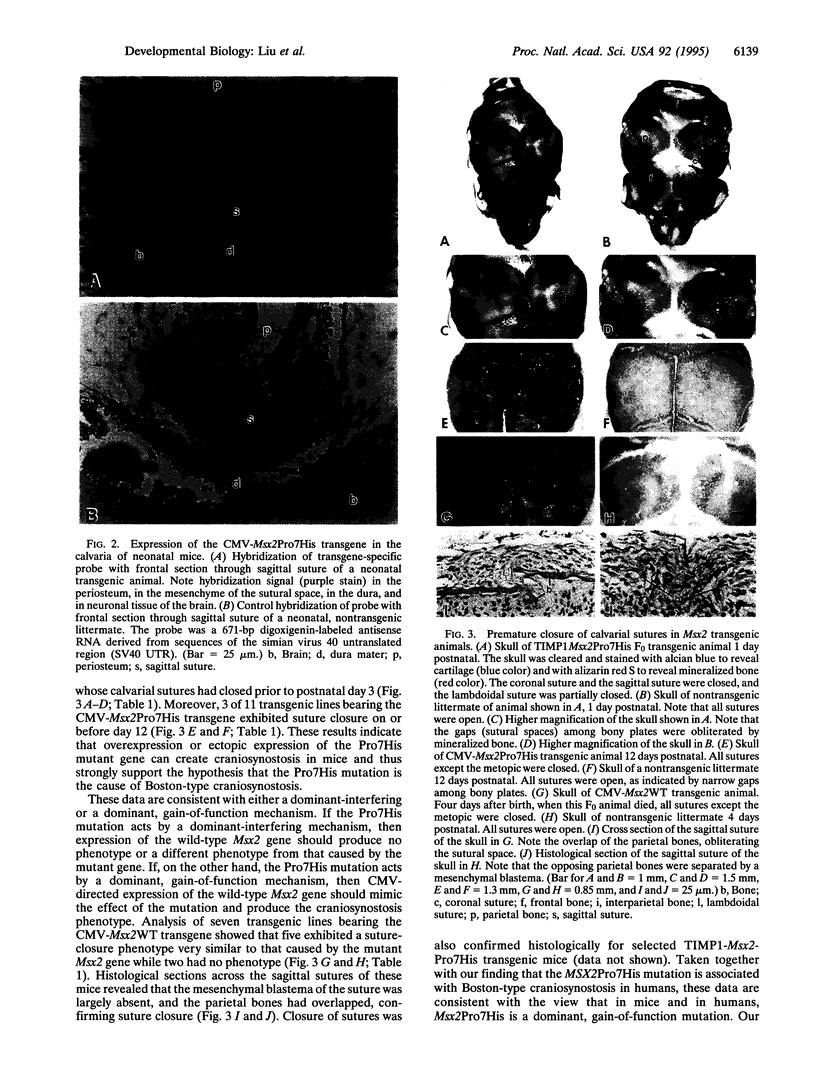
The coordinate growth of the brain and skull is achieved through a series of interactions between the developing brain, the growing bones of the skull, and the fibrous joints, or sutures, that unite the bones. These interactions couple the expansion of the brain to the growth of the bony plates at the sutures. Craniosynostosis, the premature fusion of the bones of the skull, is a common birth defect (1 in 3000 live births) that disrupts coordinate growth and often results in profoundly abnormal skull shape. Individuals affected with Boston-type craniosynostosis, an autosomal dominant disorder, bear a mutated copy of MSX2, a homeobox gene thought to function in tissue interactions. Here we show that expression of the mouse counterpart of this mutant gene in the developing skulls of transgenic mice causes craniosynostosis and ectopic cranial bone. These mice provide a transgenic model of craniosynostosis as well as a point of entry into the molecular mechanisms that coordinate the growth of the brain and skull.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. R., Noveen A., Liu Y. H., Ma L., Dobias S., Kundu R., Luo W., Xia Y., Lusis A. J., Snead M. L. Genomic structure, chromosomal location, and evolution of the mouse Hox 8 gene. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):123–131. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho C. N., Krabbenhoft K. M., Upholt W. B., Fallon J. F., Kosher R. A. Altered expression of the chicken homeobox-containing genes GHox-7 and GHox-8 in the limb buds of limbless mutant chick embryos. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1487–1493. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho C. N., Sumoy L., Rodgers B. J., Davidson D. R., Hill R. E., Upholt W. B., Kosher R. A. Expression of the chicken homeobox-containing gene GHox-8 during embryonic chick limb development. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Craniosynostosis update 1987. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1988;4:99–148. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Sutural biology and the correlates of craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Oct 1;47(5):581–616. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couly G. F., Coltey P. M., Le Douarin N. M. The triple origin of skull in higher vertebrates: a study in quail-chick chimeras. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):409–429. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. R., Crawley A., Hill R. E., Tickle C. Position-dependent expression of two related homeobox genes in developing vertebrate limbs. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):429–431. doi: 10.1038/352429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H. How embryos work: a comparative view of diverse modes of cell fate specification. Development. 1990 Mar;108(3):365–389. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Wilkinson J. E., Rothenpieler U. W., Patterson L. T., Williams-Simons L., Westphal H. Deregulation of Pax-2 expression in transgenic mice generates severe kidney abnormalities. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):65–67. doi: 10.1038/362065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R. Developmental expression of the endogenous TIMP gene and a TIMP-lacZ fusion gene in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1094–1106. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Francis-West P., Brickell P., Lumsden A. The signalling molecule BMP4 mediates apoptosis in the rhombencephalic neural crest. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):684–686. doi: 10.1038/372684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W. Cloning and evolutionary analysis of msh-like homeobox genes from mouse, zebrafish and ascidian. Gene. 1991 Feb 15;98(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90182-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Li X., Scott A. F., Meyers G., Chen W., Eccles M., Mao J. I., Charnas L. R., Jackson C. E., Jaye M. Jackson-Weiss and Crouzon syndromes are allelic with mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):275–279. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Müller U., Li X., Ma L., Luo W., Haworth I. S., Klisak I., Sparkes R., Warman M. L., Mulliken J. B. A mutation in the homeodomain of the human MSX2 gene in a family affected with autosomal dominant craniosynostosis. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90379-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett A. K., Vainio S., Ferguson M. W., Sharpe P. T., Thesleff I. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions are required for msx 1 and msx 2 gene expression in the developing murine molar tooth. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):461–470. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Homeotic transformations of murine vertebrae and concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoic acid. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):89–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90574-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. H., Ma L., Wu L. Y., Luo W., Kundu R., Sangiorgi F., Snead M. L., Maxson R. Regulation of the Msx2 homeobox gene during mouse embryogenesis: a transgene with 439 bp of 5' flanking sequence is expressed exclusively in the apical ectodermal ridge of the developing limb. Mech Dev. 1994 Dec;48(3):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie A., Ferguson M. W., Sharpe P. T. Expression patterns of the homeobox gene, Hox-8, in the mouse embryo suggest a role in specifying tooth initiation and shape. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):403–420. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan A. P., Davidson D. R., Sime C., Graham E., Baldock R., Bhattacharya S. S., Hill R. E. The Msh-like homeobox genes define domains in the developing vertebrate eye. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Warman M. L., Mulliken J. B., Weber J. L. Assignment of a gene locus involved in craniosynostosis to chromosome 5qter. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):119–122. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opperman L. A., Sweeney T. M., Redmon J., Persing J. A., Ogle R. C. Tissue interactions with underlying dura mater inhibit osseous obliteration of developing cranial sutures. Dev Dyn. 1993 Dec;198(4):312–322. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001980408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Bedford M. T., Burakova T., Arman E., Zimmer Y., Yayon A., Givol D., Lonai P. Developmental localization of the splicing alternatives of fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (FGFR2). Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):475–486. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Givol D., Yayon A., Yarden Y., Lonai P. Developmental expression of two murine fibroblast growth factor receptors, flg and bek. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1419–1434. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasleau F., Tocci M. J., Leung F., Kopchick J. J. Growth hormone gene expression in eukaryotic cells directed by the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat or cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patapoutian A., Miner J. H., Lyons G. E., Wold B. Isolated sequences from the linked Myf-5 and MRF4 genes drive distinct patterns of muscle-specific expression in transgenic mice. Development. 1993 May;118(1):61–69. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Winter R. M., Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Jones B. M., Malcolm S. Mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 gene cause Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):98–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Lyons G., Simandl B. K., Kuroiwa A., Buckingham M. The apical ectodermal ridge regulates Hox-7 and Hox-8 gene expression in developing chick limb buds. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2363–2374. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen V., Thies R. S. The BMP proteins in bone formation and repair. Trends Genet. 1992 Mar;8(3):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90197-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Reardon W., Baraitser M., Hayward R., Jones B., Malcolm S., Winter R. M., Oldridge M., Slaney S. F. Identical mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause both Pfeiffer and Crouzon syndrome phenotypes. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):173–176. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Monsoro-Burq A. H., Bontoux M., Le Douarin N. M. A role for Quox-8 in the establishment of the dorsoventral pattern during vertebrate development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10237–10241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Karavanova I., Jowett A., Thesleff I. Identification of BMP-4 as a signal mediating secondary induction between epithelial and mesenchymal tissues during early tooth development. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vershon A. K., Johnson A. D. A short, disordered protein region mediates interactions between the homeodomain of the yeast alpha 2 protein and the MCM1 protein. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90054-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warman M. L., Mulliken J. B., Hayward P. G., Müller U. Newly recognized autosomal dominant disorder with craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 1;46(4):444–449. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Slaney S. F., Oldridge M., Poole M. D., Ashworth G. J., Hockley A. D., Hayward R. D., David D. J., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P. Apert syndrome results from localized mutations of FGFR2 and is allelic with Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):165–172. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]