Abstract
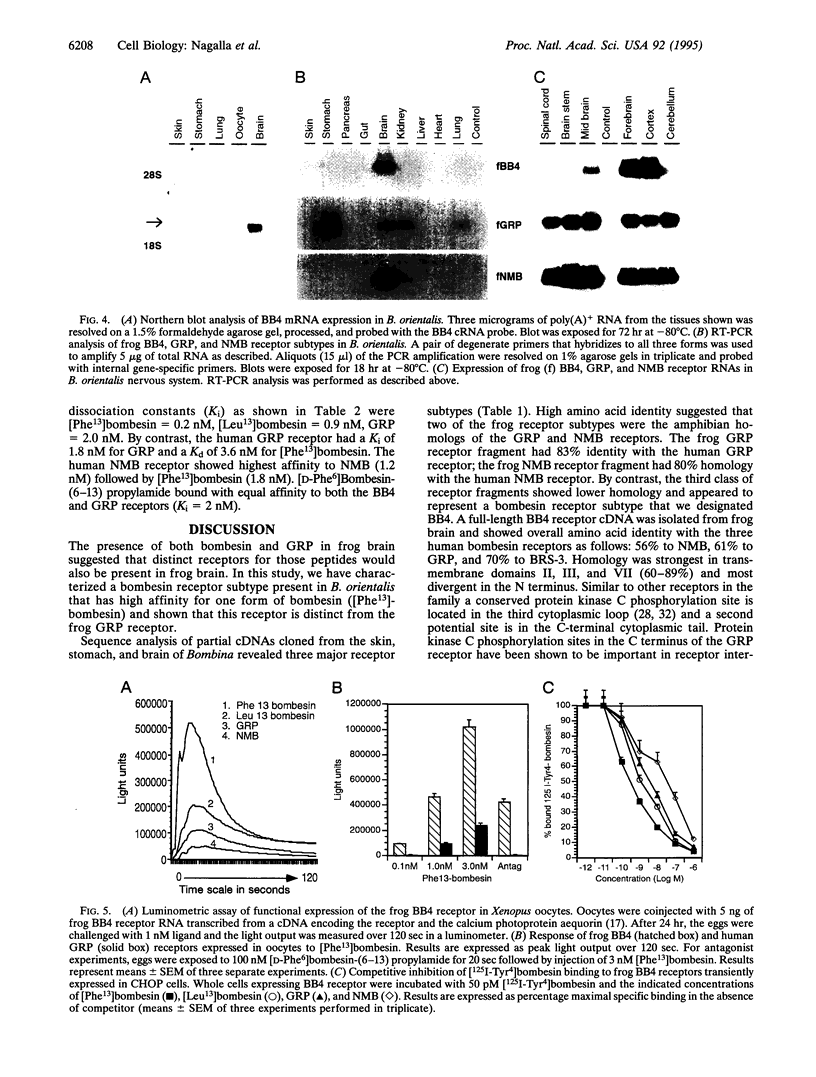
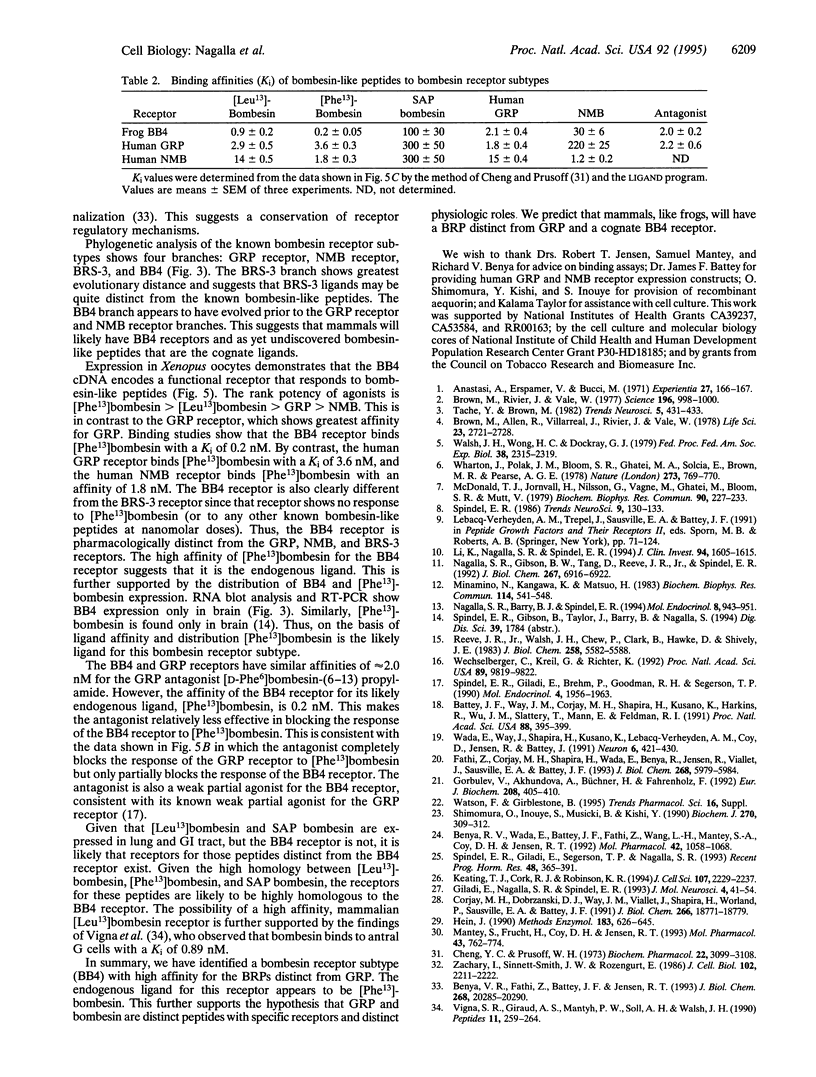
Bombesin is a tetradecapeptide originally isolated from frog skin and demonstrated to have a wide range of actions in mammals. Based on structural homology and similar biological activities, gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) has been considered the mammalian equivalent of bombesin. We previously reported that frogs have both GRP and bombesin, which therefore are distinct peptides. We now report the cloning of a bombesin receptor subtype (BB4) that has higher affinity for bombesin than GRP. PCR was used to amplify cDNAs related to the known bombesin receptors from frog brain. Sequence analysis of the amplified cDNAs revealed 3 classes of receptor subtypes. Based on amino acid homology, two classes were clearly the amphibian homologs of the GRP and neuromedin B receptors. The third class was unusual and a full-length clone was isolated from a Bombina orientalis brain cDNA library. Expression of the receptor in Xenopus oocytes demonstrated that the receptor responded to picomolar concentrations of [Phe13]-bombesin, the form of bombesin most prevalent in frog brain. The relative rank potency of bombesin-like peptides for this receptor was [Phe13]bombesin > [Leu13]bombesin > GRP > neuromedin B. In contrast, the rank potency for the GRP receptor is GRP > [Leu13]bombesin > [Phe13]bombesin > neuromedin B. Transient expression in CHOP cells gave a Ki for [Phe13]bombesin of 0.2 nM versus a Ki of 2.1 nM for GRP. Distribution analysis showed that this receptor was expressed only in brain, consistent with the distribution of [Phe13]-bombesin. Thus, based on distribution and affinity, this bombesin receptor is the receptor for [Phe13]bombesin. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that this receptor separated prior to separation of the GRP and neuromedin B receptors; thus, BB4 receptors and their cognate ligands may also exist in mammals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Bucci M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, 2 analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):166–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02145873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J. F., Way J. M., Corjay M. H., Shapira H., Kusano K., Harkins R., Wu J. M., Slattery T., Mann E., Feldman R. I. Molecular cloning of the bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptor from Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):395–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya R. V., Fathi Z., Battey J. F., Jensen R. T. Serines and threonines in the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor carboxyl terminus mediate internalization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20285–20290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Allen R., Villarreal J., Rivier J., Vale W. Bombesin-like activity: radioimmunologic assessment in biological tissues. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 31;23(27-28):2721–2728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90652-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Rivier J., Vale W. Bombesin:potent effects on thermoregulation in the rat. Science. 1977 May 27;196(4293):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.860130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corjay M. H., Dobrzanski D. J., Way J. M., Viallet J., Shapira H., Worland P., Sausville E. A., Battey J. F. Two distinct bombesin receptor subtypes are expressed and functional in human lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18771–18779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Corjay M. H., Shapira H., Wada E., Benya R., Jensen R., Viallet J., Sausville E. A., Battey J. F. BRS-3: a novel bombesin receptor subtype selectively expressed in testis and lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbulev V., Akhundova A., Büchner H., Fahrenholz F. Molecular cloning of a new bombesin receptor subtype expressed in uterus during pregnancy. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 1;208(2):405–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating T. J., Cork R. J., Robinson K. R. Intracellular free calcium oscillations in normal and cleavage-blocked embryos and artificially activated eggs of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Sci. 1994 Aug;107(Pt 8):2229–2237. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.8.2229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantey S., Frucht H., Coy D. H., Jensen R. T. Characterization of bombesin receptors using a novel, potent, radiolabeled antagonist that distinguishes bombesin receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):762–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Jörnvall H., Nilsson G., Vagne M., Ghatei M., Bloom S. R., Mutt V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin B: a novel bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90814-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagalla S. R., Barry B. J., Spindel E. R. Cloning of complementary DNAs encoding the amphibian bombesin-like peptides Phe8 and Leu8 phyllolitorin from Phyllomedusa sauvagei: potential role of U to C RNA editing in generating neuropeptide diversity. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Aug;8(8):943–951. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.8.7997236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagalla S. R., Gibson B. W., Tang D., Reeve J. R., Jr, Spindel E. R. Gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) is not mammalian bombesin. Identification and molecular cloning of a true amphibian GRP distinct from amphibian bombesin in Bombina orientalis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6916–6922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. R., Jr, Walsh J. H., Chew P., Clark B., Hawke D., Shively J. E. Amino acid sequences of three bombesin-like peptides from canine intestine extracts. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5582–5588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Inouye S., Musicki B., Kishi Y. Recombinant aequorin and recombinant semi-synthetic aequorins. Cellular Ca2+ ion indicators. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):309–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2700309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Giladi E., Brehm P., Goodman R. H., Segerson T. P. Cloning and functional characterization of a complementary DNA encoding the murine fibroblast bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1956–1963. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Giladi E., Segerson T. P., Nagalla S. Bombesin-like peptides: of ligands and receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1993;48:365–391. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571148-7.50017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigna S. R., Giraud A. S., Mantyh P. W., Soll A. H., Walsh J. H. Characterization of bombesin receptors on canine antral gastrin cells. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90079-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Wong H. C., Dockray G. J. Bombesin-like peptides in mammals. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2315–2319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechselberger C., Kreil G., Richter K. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of a bombesinlike peptide from brain and early embryos of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9819–9822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




