Summary
Background
Advances in hepatitis C therapies have led to increasing numbers of patients seeking treatment. As a result, logistical and financial concerns regarding how treatment can be provided to all patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) have emerged.
Aim
The aim of this review was to evaluate predictors and predictive models of histologic progression and clinical outcomes for patients with CHC.
Methods
MEDLINE via PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science and Scopus were searched for studies published between January 2003 and June 2014.Two authors independently reviewed articles to select eligible studies and performed data abstraction.
Results
Twenty-nine studies representing 5817 patients from 20 unique cohorts were included. The outcome incidence rates were widely variable: 16-61% during median follow-up of 2.5-10 years for fibrosis progression; 13-40% over 2.3-14.4 years for hepatic decompensation; and 8-47% over 3.9-14.4 years for overall mortality. Multivariate analyses showed that baseline steatosis and baseline fibrosis score were the most consistent predictors of fibrosis progression (significant in 6/21 and 5/21, studies, respectively) while baseline platelet count (significant in 6/13 studies), aspartate and alanine aminotransferase (AST/ALT) ratio, albumin, bilirubin, and age (each significant in 4/13 studies) were the most consistent predictors of clinical outcomes. Five studies developed predictive models but none were externally validated.
Conclusions
Our review identified the variables that most consistently predict outcomes of patients with CHC allowing the application of risk based approaches to identify patients in need of early treatment and intensive monitoring. This approach maximizes effective use of resources and costly new direct-acting antiviral agents.
Keywords: antiviral therapy, cirrhosis, fibrosis progression, hepatic decompensation, viral hepatitis
Introduction
With the introduction of more efficacious and less toxic drugs, treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is evolving at a rapid pace. The two new direct-acting antiviral agents (DAA), simeprevir and sofosbuvir, increase rates of sustained virologic response (SVR) with shorter treatment durations compared to prior therapies.1, 2 Along with advances in therapy, there has been a focus on the public health impact of CHC. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Institute of Medicine, and the United States Preventative Services Task Force, have prioritized hepatitis C awareness, screening and diagnosis.3-5 Treatment is also being advocated as a means to prevent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. As a result of these processes, the pool of potential treatment candidates is expected to balloon. This has caused the conundrum in HCV treatment to shift from “Can we improve the efficacy and tolerability of HCV treatment?” to “Can we afford to treat all patients with CHC?”
At the core of the dilemma is the high cost of these new drugs. The estimated wholesale price of a 12-week course of sofosbuvir in the United States (US) is $84,000 and of simeprevir $66,000.6, 7 These staggering costs exclude retail markup, and associated cost of pegylated interferon (IFN), ribavirin, physician visits, and laboratory tests. While these new treatment regimens have SVR rates of 80-90%, and SVR has been shown to decrease cirrhosis complications, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and liver-related mortality, even resource-replete countries like the US cannot afford to treat all those who are infected.1, 2, 8 The logistical and financial barriers are much higher in resource-limited countries, many of which have higher prevalence of HCV infection than western countries. Clinicians and health policy makers will need to determine an optimal yet practical approach to provide these highly efficacious but extremely costly therapies to this burgeoning patient population.
One solution is to adopt a risk-stratified approach that targets therapy to those at the greatest risk of disease progression. There have been many studies investigating risk factors for disease progression in patients with CHC, but few have employed a longitudinal study design in generalizable patient populations using data that are routinely available in clinical practice. Results of the existing studies have also not been systematically summarized in a single document. Therefore, we performed a systematic review of the literature to (a) identify factors predictive of disease progression (fibrosis progression and clinical outcomes) in patients with CHC and (b) assess existing predictive models.
Methods
Data Sources and Search Strategy
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations in conducting this systematic review.9 With the assistance of a medical research librarian, we performed serial literature searches for English and non-English articles. MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE, Web of Science and Scopus were searched using the following keywords: “cirrhosis” or “liver cirrhosis” or “fibrosis”, “hepatitis C” or “hepatitis C, chronic” or “chronic hepatitis C”, “disease progression” or “progression” or “decompensation”. Boolean operators and medical subject heading terms as well as other controlled vocabulary were used to enhance electronic searches. An example of specific search strategy details is shown in Supplement Table 1.
All human subject studies published in full-text or abstract were eligible for inclusion. The search was limited to publications from 2003-2014 as this 10-year period contained the most contemporary and relevant data with respect to treatment and current practice. Additional studies of interest were identified by hand searches of bibliographies and cited reference tracking and consultation with clinical experts on the topic. The initial search was performed in October 2013 and the search was last updated on June 2, 2014.
Study Eligibility and Selection Criteria
Two authors (M.A.K. and A.S.L.) sequentially determined study eligibility. Studies were initially screened by the first author; decisions about study inclusion were made independently by both authors (M.A.K and A.S.L). Differences in opinion regarding study inclusion were resolved through consensus. Studies were included if they: (1) included human studies with participants 18 years of age or older; (2) systematically evaluated predictors of fibrosis progression and/or clinical outcomes for patients with CHC; and (3) used a longitudinal cohort study design. We focused on studies of untreated patients but also included studies with a mix of treated and untreated patients provided that <20% of the study population achieved SVR and results were stratified by treatment outcomes. For studies evaluating predictors of fibrosis progression, we selected studies only when paired biopsy was used to assess progression.
We excluded studies that enrolled (1) patients co-infected with hepatitis B (HBV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); (2) patients with additional causes of chronic liver disease; (3) patients with prior liver transplantation; and (4) specific groups of patients e.g. thalassemia patients only;.These patient populations were excluded because they likely have different rates and risk factors for disease progression compared to the general population of patients with CHC. In addition, studies that evaluated HCC as the only outcome of interest were excluded as we were interested in broad clinical outcomes for patients with CHC, and predictors of HCC development alone may not be the same as predictors of disease progression in CHC in general. Lastly, studies that focused on predictors that are not readily available clinically (e.g. genetic or other serum markers for which commercial assays are not available, and experimental imaging techniques) were excluded given that they would not be relevant to current clinical practice.
Definition of Variables and Outcomes
Patients with CHC were defined as those with detectable HCV ribonucleic acid (RNA). We were interested in two outcomes: histologic progression and clinical progression. The definition of histologic progression was an increase of ≥1 METAVIR (range 0-4) or Ishak (range 0-6) fibrosis stage on follow-up liver biopsy. The definition of clinical progression encompassed the progression from compensated to decompensated cirrhosis, and liver-related or overall mortality. The definition of compensated cirrhosis was based on histology when available (Ishak fibrosis score ≥5 or METAVIR 4) or on the combined results of other non-invasive testing including laboratory tests and imaging. Decompensated cirrhosis was defined by the presence of any of the following: ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), variceal bleeding, or hepatic encephalopathy (HE). The presence of HCC as defined by histology or American Association for Study of Liver Diseases radiologic criteria was variably included as a clinical outcome.10
Data Abstraction and Validity Assessment
Data from eligible studies were abstracted by two authors (M.A.K. and S.Y.) using a standardized template adapted from the Cochrane Collaboration.11 For all studies, we recorded: study design, sample size, patient population characteristics, duration of follow-up, predictor variables studied, outcomes measured, criteria used to define these outcomes, and measures of association/predictiveness of risk for these outcomes. We accepted the outcome definitions as stated by each study without independently validating or reviewing their data. Study authors were directly contacted for additional, unpublished data.
Assessment of Risk of Bias and Study Quality
Two authors (M.A.K and S.Y.) independently assessed the risk of study bias and study quality. Since all the included studies were non-randomized cohort studies, the Newcastle-Ottawa scale was used to judge study quality as recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration.12 This scale uses a star system to assess the quality of a study based on three domains: selection of the study population, comparability of the study groups, and method of outcomes assessment. For our review, given that no study had a comparison group, we excluded comparability components of the scale across all studies. Studies which received stars in every domain were assessed as being of high quality.
Data Synthesis and Analysis
Given the substantial variation in the design, methods and inclusion/exclusion criteria within our included studies, meta-analysis was not performed. Two authors (M.A.K. and S.Y.) qualitatively synthesized the results of the included studies, focusing on the risk factors evaluated and their independent predictiveness in terms of the outcomes measured and patient populations studied. Studies were categorized according to the outcome of interest: predictors of histologic progression, predictors of clinical outcomes, or studies investigating both clinical and histologic outcomes. All authors had access to the study data and had reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Results
Studies Included in the Systematic Review
After removal of duplicate entries, 2257 unique articles were identified by our systematic literature search (Figure 1). On the basis of abstract review, 69 were selected for full-text review. Two study authors classified 29 articles as meeting the predefined criteria for analysis. In total, these 29 studies included 5817 unique patients from 20 separate patient cohorts. Sixteen of these studies investigated predictors of histologic progression, eight studies evaluated predictors of clinical outcomes, and the remaining five studies investigated both histologic and clinical outcomes.13-41 Fourteen studies included treatment-naïve patients only, 5 included both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients, 8 included treatment-experienced patients only, and 2 studies did not describe the treatment status of the patients. We contacted four authors to obtain additional unpublished data.
Figure 1. Flow diagram of studies included in the systematic review.
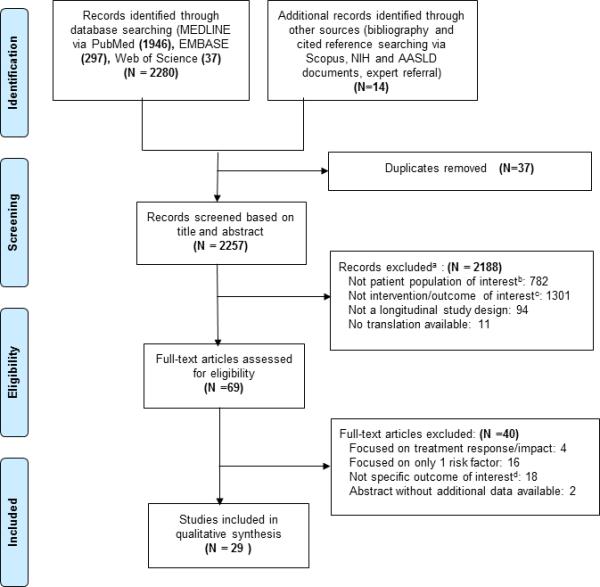
aMany studies met multiple exclusion criteria. Each study was coded under a single criterion only.
bIncludes animal models, pediatric populations, patients who had previously undergone liver transplant, patients with chronic liver disease other than HCV monoinfection, evaluation of only specific subsets of populations with CHC.
cIncludes studies that were descriptive papers only, studies that did not specifically evaluate for predictors of histologic or clinical progression, and studies that evaluated predictors that are not readily clinically available.
dIncludes studies that focused on risk factors for the development of HCC only, and studies where some patients achieved SVR and the results were not stratified based on response to treatment.
Characteristics of Studies on Histologic Progression
A total of 21 studies evaluated predictors of histologic progression. The studies included populations from Europe (n=10), Asia (n=2), and North (n=8) and South America (n=1). Only one study was prospective with the remaining 20 being retrospective analyses of previously collected data. The sample size for included studies varied (range 36 to 622 patients) with the majority having <200 patients (n=14). A number of studies had overlapping cohorts. Four studies were derived from the Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-term Treatment Against Cirrhosis (HALT-C) cohort, a US multi-center randomized controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of low dose pegylated IFN in CHC patients with advanced fibrosis who failed to respond to prior IFN therapy. Four other pairs of studies drew from the same cohort of patients.17, 21, 25, 29, 33, 35, 38, 41 These studies were included in the review despite overlapping cohorts given differences in predictors examined, outcomes evaluated and criteria for selection of subsets of patients analyzed within the overall larger cohort. The average duration of follow-up ranged from a median of 2.5 years to 10 years.
The studies had varied inclusion and exclusion criteria as detailed in Table 1. Among the non-HALT-C studies, 11 studies had explicit requirements for baseline Ishak/METAVIR fibrosis stage. Five studies required minimal or no fibrosis at baseline and the remaining 6 studies required lack of cirrhosis on initial biopsy. Only 14 studies described criteria used to determine adequacy of biopsy specimens. The majority of the studies had a single pathologist blinded to clinical data score the biopsies while the HALT-C study had a panel of pathologists review the biopsies and consensus staging was recorded. Exclusionary alcohol intake was described in 9 studies though the cutoff amounts and methods for ascertaining alcohol intake varied across the studies. The studies were predominately comprised of male patients in their late 30's to early 50's.
Table 1.
General Characteristics of Included Studies*
| Study and Country | Sample Size (n) | % Genotype 1 | Age | % Male | Study Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria/Patient characteristics | Exclusion criteria | |||||
| Predictors of Histologic Progression | ||||||
| Baran 2014 Turkey |
125 | 95 | Mean 45 |
38 | Ishak <4 on initial biopsy >9 portal tracts on liver biopsy Treatment naïve or non-SVR with prior treatment |
HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease HCC History of immunosuppressive therapy |
| Boccato 2006 Italy |
106 | 62 | Mean 41.6 |
56 | METAVIR F0 or F1 on initial biopsy Biopsy length >15mm and ≥7 portal tracts Minimum 4 yr follow-up Treatment naïve |
|
| Castera 2003 France |
96 | 62 | Mean 41 |
61 | No cirrhosis on initial biopsy Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected |
| Colletta 2005 Italy |
40 | 30 | Median 43.5 |
55 | Ishak ≤2 on initial biopsy Serial ALT values < 1.2 times ULN Treatment naïve |
|
| Cross 2009 United Kingdom |
112 | 58 | Median 44 |
66 | Biopsy length >10mm Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease Prior liver transplant ETOH intake ≥ 80g/d (male), ≥ 60g/d (female) |
| Fabris 2012 Italy |
93 | 52 | Median 38 |
46 | Ishak ≤1 on initial biopsy Persistently normal or near normal ALT Treatment naïve |
|
| Fartoux 2005 France |
135 | 60 | Mean 38.5 |
59 | METAVIR ≤1 on initial biopsy Biopsy length >10mm Only one known risk factor for HCV infection Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease Prothrombin time > 80% Platelets >150,000/mL Hyaluronic acid < 85ug/L |
| Ghany 2003 United States |
123 | 70 | Mean 41 |
63 | Treatment naïve | |
| Khouri 2003 Brazil |
55 | NR | Mean 38 |
58 | Biopsy length >15mm Minimum of 1 year interval between biopsies 18-75 years old Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected Immunosuppressed patients Chronic renal failure Using “potentially hepatotoxic drugs” |
| Kurosaki 2008 Japan |
97 | 88 | Median 52 |
51 | No cirrhosis on initial biopsy Treatment with IFN between biopsies without SVR |
HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease ETOH consumption >20g/d |
| Levine 2006 Ireland |
167 | 100 | Mean 53 |
0 | Women infected from contaminated immunoglobulin Biopsy length >15mm and ≥5 portal tracts Treatment naïve |
|
| Mummadi 2010 United States |
36 | NR | Median 47 |
75 | No cirrhosis on initial biopsy Minimum of 1 year interval between biopsies |
HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease Prior organ transplant ETOH intake >30g/d HCC |
| Perumalswami 2006 United States |
136 | 76 | Mean 44 |
58 | >10 portal tracts on liver biopsy Treatment naïve |
Decompensated cirrhosis HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease ETOH ≥60g/d (male), ≥40g/d (female) Malignancy Steroid therapy |
| Ryder 2004 United Kingdom |
214 | 34 | Median 36 |
59 | No cirrhosis on initial biopsy >5 portal tracts on liver biopsy Treatment naïve |
HIV co-infected Coagulation disorder Hemodialysis |
| Tamaki 2013 Japan |
314 | NR | Mean 53.7 |
47 | Minimum of 1.5 year interval between biopsies Biopsy length >15mm IFN between biopsies, without SVR |
HBV or HIV co-infected ETOH ≥40g/d HCC NASH |
| Williams 2011 United Kingdom |
282 | 44 | Mean 37 |
61 | Ishak 0 or 1 on initial biopsy >5 portal tracts on liver biopsy Minimum of 2 year interval between biopsies No treatment during study |
HIV co-infected Coagulation disorder Hemodialysis |
| Predictors of Clinical Outcomes | ||||||
| Bruno 2009 Italy |
324 | 63 | Median 59 |
51.1 | Compensated cirrhosis (Child A) ≤ 70 years old IFN based treatment (55%) without SVR |
HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease HCC “unable to attend regular follow-up visits” |
| Ghany 2011 United States |
470 | 94 | Mean 49.8 |
71.3 | HALT-C cohort: Ishak ≥3 on initial biopsy Prior treatment with IFN based therapy without SVR Evaluated control patients without further treatment |
HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease ETOH abuse within past year CTP score ≥7 History of hepatic decompensation Platelets <75,000 Neutrophil count <1500 Hematocrit <33% HCC or AFP>300 ng/ml Bilirubin >2.5 mg/dl Creatinine >1.5 mg/dl “Serious medical disorder” Use of illicit drugs within past 2 years |
| Giannini 2003 Italy |
63 | NR | Mean 52 |
73 | HBV or HIV co-infected Other chronic liver disease ETOH >40g/d |
|
| Rincon 2013 Spain |
145 | NR | Median 51 |
77 | Compensated cirrhosis Treatment naïve or non-SVR |
Other chronic liver disease Prior liver transplant HCC >3cm or multilobular or vascular invasion |
| Sinn 2008 South Korea |
647 | 71 | Mean 58.2 |
49 | Compensated cirrhosis Minimum of 1 year follow-up Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected CTP score >5 HCC |
| Sinn 2013 South Korea |
232 | 62 | Mean 57.2 |
38 | Compensated cirrhosis Minimum of 1 year follow-up ALT< 40 IU/l at baseline Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected CTP score >5 HCC |
| VanDerMeer 2012 Europe and Canada |
405 | 76 | Median 48 |
68 | Ishak ≥4 at baseline Prior treatment with IFN based therapy without SVR |
HBV or HIV co-infected |
| Vergniol 2011 France |
1457 | 58 | Mean 51.2 |
53.4 | 52% patients with prior treatment; 38% without SVR 14% SVR with results adjusted for treatment response |
HBV co-infected Other chronic liver disease |
| Predictors of Histologic Progression and Clinical Outcomes | ||||||
| Dienstag 2011 United States |
1050 clinical 622 histologic |
94 | Mean 51 |
71 | HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) 517 patients in IFN arm and 533 control arm |
HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) |
| Everhart 2009 United States |
985 clinical 557 histologic |
94 | Mean 50.2 |
71 | HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) 488 patients from IFN arm and 497 control arm |
HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) |
| Fontana 2010 United States |
462 clinical 209 histologic |
94 | Mean 49.5 |
70.3 | HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) 49.4% patients in IFN arm |
HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) |
| Ghany 2010 United States |
1050 clinical 547 histologic |
94 | Mean 50 |
71 | HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) 517 in IFN arm and 533 in control arm |
HALT-C cohort (See Ghany 2011 above) |
| Livingston 2010 United States |
52 | 67 | Median 41 |
51 | Alaska Native and American Indian persons Ishak ≤4 on initial biopsy Treatment naïve |
HBV or HIV co-infected |
AFP= alpha-fetoprotein; ALT= alanine aminotransferase; CTP= Child-Turcotte-Pugh; ETOH= alcohol; HALT-C= hepatitis c antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis; HBV=hepatitis B virus; HCC= hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV= hepatitis C virus; HIV= human immunodeficiency virus; IFN= interferon; NASH= non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; PC= analysis of prospectively designed cohort study; RC= retrospective analysis of cohort; SVR= sustained virologic response; ULN= upper limit of normal;
For select studies, reported data here reflects only a subset of the total study population based on the patient population and outcome of interest for this systematic review.
aAll studies of histologic progression required patients to undergo at least 2 liver biopsies as the method to evaluate fibrosis progression.
Characteristics of Studies of Clinical Outcomes
A total of 13 studies evaluated predictors of clinical outcomes. Six studies were conducted in the US (including 5 HALT-C studies), five in Europe and two in Asia. Only two studies were prospective with the remaining 11 being retrospective analyses. Sample size in each study varied from 52 to 1457 patients. Aside from the HALT-C studies, there was only one additional overlapping cohort.36, 37 The average duration of follow-up ranged from a median of 2.3 to a maximum of 14.4 years. Compared to studies on histologic progression, the on clinical outcomes consisted of patients who were older, had more advanced fibrosis at baseline, and were more likely to be treatment experienced.
Incidence of Histologic Progression
A summary of the specific outcomes evaluated and incidence of these outcomes in each study is displayed in Tables 2-4. For studies where the outcome was defined as ≥1 fibrosis stage increase on follow-up biopsy (n=13), the incidence of that outcome ranged from 21-61% over a range of follow-up of 2.5-10 years. 14, 16, 18, 21, 25, 28-33, 35, 41 Studies applying a stricter definition of fibrosis progression (≥2 stage increase on follow-up biopsy, n=3) had less variability in range of incidence of outcome, reporting 22-34% over a range of follow-up of 3.5-5.8 years.13, 23, 26 Studies with higher rates of fibrosis progression tended to have longer follow-up durations (>6 years), though there were several studies with follow-up of ≥6 years that had low rates of fibrosis progression. No identifiable differences in patient characteristics between studies with high vs. low incidence of fibrosis progression were noted.
Table 2.
Outcomes and Predictors Evaluated and Summary of Results: Histologic Progression
| Study | Outcomes Evaluated | % with Outcome | Years Follow-up (SD; range) | Predictors Significant on Multivariate Analysis | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Only Patients with Minimal Fibrosis at Baseline | |||||
| Boccato 2006 | ≥1 METAVIR stage increase | 60 | Mean 7.8 (1.51; 5-10) | ETOH intake (>40g/d) Baseline steatosis |
NR |
| Colletta 2005 | METAVIR ≥2 on follow-up biopsy | 35 | Median 6.5 (NR;2.25-5.5) | HCV RNA >8.0 ×106 copies/ml ETOH intake >20g/d |
NR |
| Fabris 2012 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 61 | Median 10 (NR;5.1-10) | HCV RNA >400,000 IU/ml ETOH intake >30g/d IL28B T/*x chol ≤175 mg/dl Follow-up >8yr |
4.3 (1.4-13) 100 (8-1300) 4.1(1.5-11) 4.9 (1.8-13) |
| Fartoux 2005 | METAVIR 3 or 4 on follow-up biopsy | 16 | Mean 5.2 (2.3;1.5-13.1) | Baseline steatosis | 4.8 (1.3-18.3) |
| Williams 2011 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 42 | Median 4.4 (NR;2-16) | Age (older) Median ALT per 10 IU/L |
1.34 (1.03-1.74) 1.07 (1.01-1.13) |
| Includes Patients with more Advanced Fibrosis at Baseline | |||||
| Baran 2014 | ≥2 Ishak stage increase | 22 | Mean 5.8 (NR; 1.25-18) | Baseline GGT Follow-up ALT (<40 IU/L) Treatment experience (failed) |
1.03 (1.01-1.5) 0.16 (0.03-0.93) 5.97 (1.81-19.7) |
| Castera 2003 | ≥1 METAVIR stage increase | 31 | Mean 4 (2.6; 0.8-14.6) | Worsening steatosis | 4.7 (1.3-10.8) |
| Cross 2009 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 21 | Median 4.2 (NR; 2.8-6.1) | Baseline steatosis | 14.3 (2.1-111.1) |
| Ghany 2003 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 39 | Mean 3.7 (NR; 0.25-17.6) | Baseline Ishak (low) Baseline HAI Baseline ALT (elevated) |
NR |
| Khouri 2003 | ≥1 Ludwig stage increase | 27 | Mean 3.25 (1.1;1-6.8) | None | NR |
| Kurosaki 2008 | ≥1 METAVIR stage increase | 23 | Mean 5.9 (NR;1.2-11.6) | Baseline steatosis Average ALT ≥100 IU/l |
5.14 (1.6-15.7) 5.21 (1.4-18.2) |
| Levine 2006 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 27 | Mean 5 (NR;NR) | Baseline Ishak Baseline ALT (elevated) |
NR |
| Mummadi 2010 | ≥1 stage increase on 0-4 scale | 53 | Median 4 (NR; 2-9) | ΔAPRI ΔFIB-4 |
NR |
| Perumalswami 2006 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 40 | Mean 3.6 (NR; 0.5-17) | Age (older) Baseline ALT (elevated) Baseline Ishak (low) Baseline HAI (higher severity) |
NR |
| Ryder 2004 | ≥1 Ishak stage increase | 33 | Median 2.5 (NR;1.9-9.4) | Age (older) Baseline Ishak (+fibrosis) |
1.08a (1.03-1.11) 1.93a (1.3-9.0) |
| Tamaki 2013 | Not defined | 23 | Mean 4.9 (2.9; NR) | ΔFIB-4 index/yr | 3.7 (1.07-12.5) |
ALT= alanine aminotransferase; APRI= aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index; ETOH= alcohol; GGT= gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; HAI= histologic activity index; HCV= hepatitis C virus; NR= not reported; RNA= ribonucleic acid;
Represents adjusted relative risk (RR) instead of OR.
Table 4.
Outcomes and Predictors Evaluated and Summary of Results: Histologic Progression and Clinical Outcomes
| Study | Outcomes Evaluated | % with Outcome | Years Follow-up (SD; range) | Predictors Significant on Multivariate Analysis | HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dienstaga 2011 | 1.Progression to cirrhosis | 1.29% | Median 6 (NR;0.8-7) | Not performed | |
| 2.Any clinical outcome: a) hepatic decompensation: ascites/variceal bleeding/ HE/SBP b)transplant c)HCC d)≥7 CTP score e)hepatic mortality f)overall mortality |
2.31% | ||||
| Everhart 2009 | Combined outcome: ≥2 Increase in Ishak, hepatic mortality or hepatic decompensation (≥7 CTP score, ascites, variceal bleed, HE) | 28% | Mean 3.5 (NR;NR) | Baseline Ishak (cirrhosis) HOMA2-IR (quartiles) Baseline steatosis (if cirrhosis) Mallory bodies |
1.92 (1.12-3.28) 1.25 (1.08-1.45) 0.49 (0.35-0.70) 1.59 (1.10-2.31) |
| Fontana 2010 | 1.≥2 Increase in Ishak | 1.34 | Mean 4.25 (NR; NR) | 1. Histologic progression Baseline platelet (per 50K, low) Baseline log HA |
0.72 (0.57-0.91) 2.42 (0.27-4.47) |
| 2. Clinical Outcomes: a)Hepatic decompensation: ascites/variceal bleeding/HE/SBP b)HCC c)≥7 CTP score or d) overall mortality |
2.15 | 2.Any clinical outcome Baseline bilirubin (elevated) Baseline INR (>1.0) Baseline albumin (low) Baseline logYKL-40 |
2.42 (1.42-4.13) 2.25 (1.30-3.89) 0.20 (0.10-0.38) 2.44 (1.28-4.63) |
||
| Ghany 2010 | 1.≥2 Increase in Ishak | 1.28 | Mean 3.5 (NR;NR) | 1. Histologic progression Baseline BMI (high) Baseline platelets (low) Baseline steatosis |
N R |
| 2.Clinical Outcomes: a)Hepatic decompensation: ascites/variceal bleeding/HE/SBP b) >7 CTP score or c)hepatic mortality |
2.13 | 2.Any clinical outcome Baseline Log AST/ALT (high) Baseline bilirubin (elevated) Baseline albumin (low) Baseline platelets/ 50K (low) |
3.34 (1.84-6.06) 1.82 (1.37-2.42) 0.20 (0.13-0.32) 0.59 (0.49-0.72) |
||
| Livingston 2010 | 1.≥1 Increase in Ishak 2.Hepatic Decompensation: ascites/esophageal varices/ HE/ coagulopathy |
1.60 2.17 |
Mean 6.2 (NR;2.3-13.3) | Not performed |
ALT= alanine aminotransferase; AST= aspartate aminotransferase; BMI= body mass index; CTP= Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CI= confidence interval; HA= hyaluronic acid; HE= hepatic encephalopathy; HCC= hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV= hepatitis C virus; HR= hazard ratio; INR= international normalized ratio; NR= not reported; RNA= ribonucleic acid; SBP= spontaneous bacterial peritonitis;
Univariate significance not reported.
Incidence of Clinical Progression
Studies assessing risk factors for clinical progression (n=13) included several distinct outcomes. Four studies evaluating progression from compensated to decompensated cirrhosis reported an incidence between 13-40% over a range of follow-up of 2.3-14.4 years. 15, 24, 31, 34 No clear pattern was identified between length of follow-up or patient characteristics and rate of outcomes. Notably, the definition of decompensation varied across studies. Four studies evaluating the incidence of overall mortality reported incidences between 8-47%. The range of follow-up for these studies was 3.9-14.4 years, with a higher rate of outcomes reported in studies with longer duration of follow-up. 15, 27, 39, 40 The remaining studies used an aggregate outcome encompassing a broad range of clinical end points including decompensation, increase in Child-Turcotte-Pugh score, development of HCC, liver transplant, and liver related as well as overall mortality. The reported incidence of this aggregate outcome was 13-31% over a range of follow-up of 3.5-6.3 years. 19, 20, 23, 26, 36, 37
Predictors of Histologic Progression
A detailed list of the predictors evaluated and the results of univariate analysis is provided in Supplement Tables 3, 4 and 5. For each study, the predictor variables were categorized as follows: 1) baseline clinical characteristics including demographics and relevant co-morbidities; 2) baseline laboratory results; 3) baseline histologic features; or 4) longitudinal laboratory and histology results.
All studies investigating predictors of histologic progression evaluated baseline clinical characteristics, baseline laboratory results and baseline histology results except for Tamaki et al who did not evaluate baseline histologic features.38 Only half of the studies evaluated longitudinal variables which were predominantly serial aminotransferase levels. Longitudinal biopsy results such as changes in steatosis score or histologic activity index (HAI) were assessed in only five studies.16, 22, 28-30 The predictors that were most consistently evaluated are listed in Figure 2A. The most common clinical characteristics assessed were age, gender, HCV genotype, alcohol intake, body mass index (BMI) and biopsy interval, and the most common laboratory values evaluated were platelet count and ALT levels. Baseline histologic features were also frequently investigated predictors and were included in >70% of studies.
Figure 2.

List of variables identified to have significant predictive value for (A) histologic and (B) clinical progression
Multivariable analysis was performed in all but two studies.19, 31 Variables found to be independently predictive of histologic progression are listed in Tables 2 and 4. Among all the variables assessed, baseline steatosis was most consistently reported as independently predictive of subsequent fibrosis progression (significant on multivariate analysis in 6 of 21 studies) with an odds ratio (OR) [(95% confidence interval (CI)] of 4.8 (1.3-18.3) to 14.3 (2.1-111.1).12, 16, 18, 20, 24, 27 Notably, one study found that effect of baseline steatosis on fibrosis progression was dependent on baseline fibrosis stage.20 Baseline Ishak/METAVIR fibrosis stage was the next most consistently identified independent predictor of histologic progression (significant on multivariable analyses in 5 of 21 studies).20, 25, 30, 33, 35 Only one of these studies reported the effect size, with adjusted relative risk of 1.93 (95% CI 1.3-9.0).35 Figure 2A depicts the number of studies in which individual variables were significantly or not significantly predictive of histologic progression on multivariate analyses.
Predictors of Clinical Outcomes
All 13 studies examining predictors of clinical outcomes included baseline clinical characteristics and laboratory results (Supplement Tables 4 and 5). Baseline histology was assessed in only 8 studies though biopsies were performed in every study. Only 3 studies incorporated longitudinal data which consisted of serial laboratory values only.23, 24, 36 The predictors that were most consistently evaluated are listed in Figure 2B. The most common clinical characteristics assessed were age, gender, and BMI; the most common laboratory values evaluated were platelet count and ALT level.
Multivariable analysis was performed in all but two studies.19, 31 The variables found to be independently predictive of clinical progression are listed in Tables 3 and 4. Among the variables assessed, baseline platelet count was the most consistent independent predictor of clinical outcomes (significant on multivariate analysis in 6 of 13 studies) followed by age, baseline AST/ALT ratio, albumin and bilirubin (each significant in 4 studies).15, 24, 26, 36, 37, 39 Figure 2B depicts the number of studies in which individual variables were significantly or not significantly predictive of clinical outcomes in multivariate analyses.
Table 3.
Outcomes and Predictors Evaluated and Summary of Results: Clinical Outcomes
| Study | Outcomes Evaluated | % with Outcome | Years Follow-up (SD; range) | Predictors Significant on Multivariate Analysis | HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohorts with Patients with a Broader Range of Fibrosis | |||||
| Ghany 2011 | 1.Decompensation: a)ascites b)variceal bleeding c)HE or d)SBP |
1.13 | Median 6.3 (NR; 1.4-8.7) | 1.Decompensation Baseline Platelets ≤150 Baseline Bilirubin ≤0.8mg/dL Baseline AST/ALT ≤0.8 >15% decrease in platelets >15% increase in bilirubin >15% decrease in albumin |
2.76(1.47-5.19) 0.37(0.18-0.75) 0.50(0.27-0.92) 2.29 (1.26-4.14) 2.62(1.37-5.00) 3.85(1.81-8.18) |
| 2. Hepatic mortality/ liver transplant | 2.17 | 2.Hepatic Mortality/Transplant Baseline platelets ≤150 Baseline albumin ≤3.9 >15% increase in albumin 5-15% increase in AST/ALT |
4.14 (2.29-7.47) 2.32 (1.33-4.06) 3.56 (1.82-6.97) 2.14 (1.16-3.96) |
||
| Giannini 2003 | 1 year overall mortality | 25 | ≥ 1 (NR;NR) | Baseline AST/ALT >1.16 Baseline MELD >9 Baseline CTP score >7 |
NR |
| VanDerMeera 2012 | Overall mortality | 25 | Median 8.1 (NR;NR) | Age (per year) Gender (male) Baseline Platelets per 10×109/L Log Baseline AST/ALT (per 0.1) |
1.06 (1.03-1.09) 1.90 (1.10-3.29) 0.90 (0.86-0.95) 1.29 (1.11-1.50) |
| Vergniol 2011 | Overall 5 year mortality | 8 | Median 3.9 (NR;NR) | Age (older) Treatment Liver stiffness FibroTest ActiTest |
1.03 (1.01-1.04) 0.28 (0.19-0.42) 2.9 (2.0-4.3) 60 (14-255) 0.19 (0.07-0.53) |
| Cohorts Restricted to Patients with Cirrhosis | |||||
| Bruno 2009 | 1.Decompensation: a)ascites b)variceal bleeding or c)HE |
1.40 | Median 14.4 (NR;0.9-19.5) | 1.Decompensation HCV Genotype(1b vs. 2a/c) Esophageal varices Baseline Platelets <80 Baseline Bilirubin ≥1.2ml/dL AFP ≥10ng/ml HCC development |
2.17 (1.31-3.59) 2.09 (1.33-3.30) 1.95 (1.08-3.51) 1.79 (1.16-2.76) 1.59 (1.09-2.32) 5.52 (3.77-8.09) |
| 2. Hepatic mortality | 2.33 | 2.Hepatic Mortality Age (10 yr increase) Gender (Male) HCV Genotype(1b vs. 2a/c) Esophageal varices Creatinine (≥1.2mg/dl) MELD >10 Decompensation HCC development |
1.61( 1.21-2.13) 1.87 (1.23-2.84) 2.37(1.33-4.22) 2.27 (1.41-3.66) 3.07 (1.65-5.73) 2.43 (1.57-3.76) 16.9 (9.97-28.6) 8.62 (5.57-13.3) |
||
| 3. Overall mortality | 3.47 | 3. Overall Mortality Age (10 yr increase) Gender (male) HCV Genotype(1b vs. 2a/c) Esophageal varices MELD >10 AFP ≥1ng/ml Decompensation HCC development |
1.63 (1.28-2.06) 1.88 (1.33-2.66) 1.83 (1.18-2.86) 2.19 (1.47-3.27) 2.15 (1.50-3.09) 1.62 (1.15-2.29) 7.08 (4.88-10.2) 3.80 (2.67-5.42) |
||
| Rincon 2013 | Decompensation: a)ascites b)variceal bleeding or c)HE |
29 | Median 2.3 (NR; 0.2-9.2) | HVPG Baseline albumin |
1.11 (1.05-1.17) 0.42 (0.22-0.82) |
| Sinn 2008 | First occurrence of : a) ≥ 2 increase CTP score b)HCC c)SBP d)variceal bleed, e)HE or f)hepatic mortality |
22 | Median 4.6 (NR;1-12.6) | Age>55 Gender (Male) Diabetes Baseline Platelets <140 Baseline APRI>1 |
2.2 (1.4-3.6) 1.7(1.2-2.3) 1.8(1.3-2.7) 4.9(3.4-7.2) 5.4 (3.5-8.3) |
| Sinn 2013 | Disease progression using same 2008 definition | 14 | Median 4.5 (NR;1-12.6) | Baseline ALT >26 (male) Baseline ALT> 23 (female) Baseline platelets (low, male) Baseline platelets (low, female) |
5.35 (1.05-27.3) 4.40 (1.12-15.8) 0.98 (0.96-0.99) 0.97(0.96-0.98) |
AFP= alpha-fetoprotein; ALT= alanine aminotransferase; APRI= aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index; AST= aspartate aminotransferase; CTP= Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CI= confidence interval; HE= hepatic encephalopathy; HCC= hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV= hepatitis C virus; HVPG= hepatic vein pressure gradient; HR= hazard ratio; MELD= model for end-stage liver disease; NR= not reported; SBP= spontaneous bacterial peritonitis;
Univariate significance not reported
Mathematical Prediction Models
Five studies provided prediction models, three for fibrosis progression and four for clinical outcomes (Supplement Table 6).23, 26, 32, 39, 40 Four of the models were derived from the HALT-C study. All the prediction models are primarily comprised of baseline laboratory results. Only one of the models incorporated longitudinal data. None of the models had been validated in external CHC cohorts and only two models reported the associated area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.23, 40
Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
Studies evaluating predictors of histologic progression were of varying quality, whereas studies investigating predictors of clinical outcomes or studies investigating combined outcomes were all of high quality except for one study.31 Six studies on histologic progression included a small number of patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis on initial biopsy who were not able to progress according to the author's definition.17,18, 25, 28, 33, 38 Two studies evaluated select cohorts (Levine et al evaluated untreated Irish women who acquired HCV infection during pregnancy only, and Livingston et al evaluated only treatment naïve Alaska Native and American Indian persons) and were scored as having limited representativeness. 30, 31 The remaining studies were scored as being at least somewhat representative of the average patient with CHC in the community (Supplement Table 2).
Discussion
Although there is abundant literature on the topic of predictors of histologic and clinical outcomes for patients with CHC, only 29 studies met our inclusion criteria which captured studies with a longitudinal study design in broad patient populations. Within the 29 studies included, the incidence of outcomes varied widely: 16-61% during a median follow-up of 2.5-10 years for fibrosis progression; 13-40% over 2.3-14.4 years for hepatic decompensation; and 8-47% over 3.9-14.4 years follow-up for overall mortality. The wide range in incidence of outcomes highlights the heterogeneity in patient population evaluated, stage of liver disease at enrollment, duration of follow-up, and definition of outcomes. Interestingly, higher rates of outcomes did not clearly correlate with longer durations of follow-up or more advanced disease at baseline across studies, pointing to more complex underlying interactions driving outcomes. Although the incidence data were not conducive to providing consensus outcome rates, we were able to identify risk factors that have most consistently been associated with outcomes of interest. Baseline steatosis and fibrosis score were the most consistent predictors of fibrosis progression and baseline platelet count, AST/ALT ratio, albumin, bilirubin and patient age were the most consistent predictors of clinical outcomes.
The variables identified as being most predictive of outcomes were not unexpectedly markers of more advanced liver disease. Though the overall finding that patients with more advanced disease are at higher risk for adverse outcomes is not novel, our study is the first to systematically identify the specific risk factors from among the many markers of advanced liver disease that portends worse prognosis. For example, among the laboratory markers of more advanced liver disease, platelet count, bilirubin, albumin and AST/ALT ratio conveyed meaningful risk information whereas INR, AST, ALT and MELD score did not. Differences in study design made it difficult to identify clear cut-off values for each predictor aside from platelet count with values ≤150,000/uL consistently associated with worse prognosis. Furthermore, individual laboratory markers may be less reliable in predicting outcomes than panels of markers such as aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI), FIB-4, Fibrotest and/or measurements of liver stiffness. The finding that patients with more advanced disease have greater risk of disease progression suggests there may be subsets of patients who are rapid progressors.Understanding whether some patients are destined to be rapid progressors and being able to identify these patients at an early stage will help target limited resources to treat those patients who will derive the most benefit. Though none of the existing predictive models have been externally validated, the model developed by Ghany and colleagues is most readily applicable in clinical practice as it is based on routinely available data and evaluates important liver-related clinical outcomes.26
Examining the results in more detail yielded several useful insights. First, the finding of steatosis as a predictor of outcomes highlights a potential modifiable risk factor associated with disease progression. This is particularly relevant given the evolving obesity epidemic. Our data suggests that patients may benefit from aggressive lifestyle interventions in addition to other standard of care treatment for patients with CHC. The prognostic information gained from baseline liver biopsy results suggests that liver biopsies not only provide information regarding current staging of liver disease but also useful prognostic information. As performance of liver biopsies continue to decline, evaluating whether non-invasive assessment of fibrosis and steatosis will provide the same prognostic information would be important. Though only one study included in our review used an additional modality to assess liver fibrosis in conjunction with biopsy, this study showed that liver stiffness measurements were associated with overall mortality.40
Our review also highlights several areas for improvement for future studies on predictors of disease progression in CHC. Analysis of the individual predictive value of each risk factor found that there was a notable lack of incorporation of longitudinal variables. In the few studies that did assess longitudinal data, these variables were usually restricted to laboratory values, predominantly AST and ALT levels. These models do not mirror clinical practice where assessments of risk of disease progression are based on the pattern of a patient's test results over time. Models restricted to only baseline data also cannot distinguish between patients with similar initial data but who go on to have distinct disease courses and outcomes. Future studies can also benefit from implementing standardized definitions and criteria for outcomes and employing a panel of investigators to adjudicate outcomes as the variability in definition of predictor and outcome variables was one of the biggest challenges.
There are other limitations to our review such as sample selection bias, sampling error, and misclassification bias in studies requiring paired biopsies. In the majority of studies biopsies were assessed by a single pathologist criteria for adequacy of biopsies was described in only 14 of 21 studies. Finally, the variability in duration of follow-up impacts not only incidence rates of outcomes, but also predictiveness of variables examined.
In summary, this systematic review demonstrated that while there is an abundance of literature on factors associated with histologic and/or clinical progression in CHC, there is a lack of longitudinal studies of representative, untreated, well characterized patients followed for a sufficiently long duration to allow the development of simple prediction models. Despite the limitations inherent to the existing literature, we were able to identify specific risk factors that have been consistently identified as being independently predictive of disease progression. By selecting studies consisting of broad patient populations and those that evaluated routinely obtained clinical data, our findings can be generalized to and applied in many clinical settings. From a policy standpoint, we have highlighted that it is possible to identify patients at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Policies that target costly new HCV therapies to these patients who would derive the most benefit will maximize their cost effectiveness. The availability of risk prediction tools that can be applied in the clinic will help physicians and patients decide whether to embark on HCV treatment now or to wait for more affordable treatment. These types of tools will be particularly important in resource-limited countries and must therefore be validated in broad patient populations.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
All authors approved the final version of the article, including the authorship list. The authors acknowledge Marisa Conte (University of Michigan Health System) for assistance with serial literature searches. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Michael Volk and Dr. Robert Fontana for their input and expertise regarding the existing literature; and Dr. Vineet Chopra, Dr. Michael Volk and Dr. Robert Fontana for critique and editing of the manuscript. We would also like to thank Dr. VanderMeer for providing additional unpublished data for this review.
This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health T32DK062708 training grant (MAK), the Turkish Association for the Study of the Liver (SY) and the Tuktawa Foundation (ASL and SY).
Abbreviations
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- APRI
aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index
- ARR
adjusted relative risk
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- BMI
body mass index
- CHC
Chronic hepatitis C
- CI
confidence interval
- DAA
direct-acting antiviral agents
- HAI
histologic activity index
- HALT-C
Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-term Treatment Against Cirrhosis
- HBV
hepatitis B virus
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV
hepatitis C virus
- HE
hepatic encephalopathy
- HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
- HR
hazard ratio
- IFN
interferon
- OR
odds ratio
- RNA
ribonucleic acid
- SBP
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- SVR
sustained virologic response
Footnotes
Specific Author Contributions: Monica A. Konerman: study concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting and revision of the manuscript. Suna Yapali: data abstraction; analysis and interpretation of data; revision of the manuscript. Anna S. Lok: study concept and design; analysis and interpretation of data; critical revision of the manuscript.
Statement of Interests
No personal interested relevant to this study.
REFERENCES
- 1.Lawitz E, Mangia A, Wyles D, et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. The New England journal of medicine. 2013;368(20):1878–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Therapeutics J. Olysio (simeprevir): Full prescribing information. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Medicine Io. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. 2010 Jan;11:2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moyer VA. Screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Annals of internal medicine. 2013;159(5):349–57. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-5-201309030-00672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Smith BD, Morgan RL, Beckett GA, et al. MMWR. Recommendations and reports : Morbidity and mortality weekly report. RR-4. Vol. 61. Recommendations and reports / Centers for Disease Control; 2012. Recommendations for the identification of chronic hepatitis C virus infection among persons born during 1945-1965. pp. 1–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gilead U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Gildead's Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Therapeutics J. Olysio: There are affordable options available. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- 8.Murphy EL. The increasing burden of mortality from viral hepatitis in the United States. Annals of internal medicine. 2012;157(2):149–50. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-2-201207170-00021. author reply 150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. International journal of surgery (London, England) 2010;8(5):336–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2011;53(3):1020–2. doi: 10.1002/hep.24199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Higgins JGR. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.0.2. 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wells GSB, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baran B, Gulluoglu M, Soyer OM, et al. Treatment failure may lead to accelerated fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2014;21(2):111–20. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Boccato S, Pistis R, Noventa F, Guido M, Benvegnu L, Alberti A. Fibrosis progression in initially mild chronic hepatitis C. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2006;13(5):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bruno S, Zuin M, Crosignani A, et al. Predicting mortality risk in patients with compensated HCV-induced cirrhosis: a long-term prospective study. The American journal of gastroenterology. 2009;104(5):1147–58. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Castera L, Hezode C, Roudot-Thoraval F, et al. Worsening of steatosis is an independent factor of fibrosis progression in untreated patients with chronic hepatitis C and paired liver biopsies. Gut. 2003;52(2):288–92. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Colletta C, Smirne C, Fabris C, et al. Value of two noninvasive methods to detect progression of fibrosis among HCV carriers with normal aminotransferases. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005;42(4):838–45. doi: 10.1002/hep.20814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cross TJ, Quaglia A, Hughes S, Joshi D, Harrison PM. The impact of hepatic steatosis on the natural history of chronic hepatitis C infection. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2009;16(7):492–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dienstag JL, Ghany MG, Morgan TR, et al. A prospective study of the rate of progression in compensated, histologically advanced chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2011;54(2):396–405. doi: 10.1002/hep.24370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Everhart JE, Lok AS, Kim HY, et al. Weight-related effects on disease progression in the hepatitis C antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis trial. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(2):549–57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fabris C, Falleti E, Cussigh A, et al. The interleukin 28B rs12979860 C/T polymorphism and serum cholesterol as predictors of fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C and persistently normal transaminases. Journal of medical virology. 2012;84(5):747–55. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fartoux L, Chazouilleres O, Wendum D, Poupon R, Serfaty L. Impact of steatosis on progression of fibrosis in patients with mild hepatitis C. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005;41(1):82–7. doi: 10.1002/hep.20519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fontana RJ, Dienstag JL, Bonkovsky HL, et al. Serum fibrosis markers are associated with liver disease progression in non-responder patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 2010;59(10):1401–9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.207423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ghany MG, Kim HY, Stoddard A, Wright EC, Seeff LB, Lok AS. Predicting clinical outcomes using baseline and follow-up laboratory data from the hepatitis C long-term treatment against cirrhosis trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2011;54(5):1527–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.24550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ghany MG, Kleiner DE, Alter H, et al. Progression of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2003;124(1):97–104. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ghany MG, Lok AS, Everhart JE, et al. Predicting clinical and histologic outcomes based on standard laboratory tests in advanced chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(1):136–46. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Giannini E, Risso D, Botta F, et al. Validity and clinical utility of the aspartate aminotransferase-alanine aminotransferase ratio in assessing disease severity and prognosis in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. Archives of internal medicine. 2003;163(2):218–24. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khouri ST, Perez RM, de Oliveira PM, et al. Rebiopsy in patients with untreated hepatitis C: a useful procedure. Journal of clinical gastroenterology. 2006;40(4):347–52. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000210100.36500.3f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kurosaki M, Matsunaga K, Hirayama I, et al. The presence of steatosis and elevation of alanine aminotransferase levels are associated with fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C with non-response to interferon therapy. Journal of hepatology. 2008;48(5):736–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.12.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Levine RA, Sanderson SO, Ploutz-Snyder R, et al. Assessment of fibrosis progression in untreated irish women with chronic hepatitis C contracted from immunoglobulin anti-D. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2006;4(10):1271–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Livingston SE, Deubner H, Bruden DL, et al. Factors associated with the progression of fibrosis on liver biopsy in Alaska Native and American Indian persons with chronic hepatitis C. Canadian journal of gastroenterology = Journal canadien de gastroenterologie. 2010;24(7):445–51. doi: 10.1155/2010/692036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mummadi RR, Petersen JR, Xiao SY, Snyder N. Role of simple biomarkers in predicting fibrosis progression in HCV infection. World journal of gastroenterology : WJG. 2010;16(45):5710–5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Perumalswami P, Kleiner DE, Lutchman G, et al. Steatosis and progression of fibrosis in untreated patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2006;43(4):780–7. doi: 10.1002/hep.21078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rincon D, Lo Iacono O, Tejedor M, et al. Prognostic value of hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients with compensated chronic hepatitis C-related cirrhosis. Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology. 2013;48(4):487–95. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2012.711848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ryder SD, Irving WL, Jones DA, Neal KR, Underwood JC. Progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C: a prospective repeat liver biopsy study. Gut. 2004;53(3):451–5. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.021691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Shin JU, et al. Disease progression in chronic hepatitis C patients with normal alanine aminotransferase levels. World journal of gastroenterology : WJG. 2013;19(14):2256–61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sinn DH, Paik SW, Kang P, et al. Disease progression and the risk factor analysis for chronic hepatitis C. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2008;28(10):1363–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tamaki N, Kurosaki M, Tanaka K, et al. Noninvasive estimation of fibrosis progression overtime using the FIB-4 index in chronic hepatitis C. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2013;20(1):72–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Van Der Meer AJP, Hansen BE, Feld JJ, et al. Prediction of long-term survival in chronic Hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis using standard laboratory tests. Journal of hepatology. 2012;56:S363. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vergniol J, Foucher J, Terrebonne E, et al. Noninvasive tests for fibrosis and liver stiffness predict 5-year outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(7):1970–9. 1979, e1–3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Williams MJ, Lang-Lenton M. Progression of initially mild hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2011;18(1):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


