Abstract
Analogs of the immunosuppressive cyclic undecapeptide cyclosporin A (CsA) with substitutions in positions 1, 4, 6, and/or 11 were rationally designed to possess substantially diminished or no immunosuppressive activity. When these compounds were assayed for their capacity to interfere with the replication of human immunodeficiency virus, some displayed a potent antiviral activity in newly infected cells. However, only CsA could interfere with virus replication in persistently infected cells. One CsA analog with antiviral activity costimulated the phytohemagglutinin-induced production of interleukin 2 by human lymphocytes. Human immunodeficiency virus particles from drug-exposed cells showed lower infectivity than virions from untreated cells. Thus, these nonimmunosuppressive analogs of CsA constitute a promising class of lead compounds to develop drugs for effective treatment of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi J. D., Deyo D. T., Sun C. Q., Guillaume D., Dunlap B., Rich D. H. Synthesis, conformation, and immunosuppressive activities of three analogues of cyclosporin A modified in the 1-position. J Med Chem. 1990 Mar;33(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1021/jm00165a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alizon M., Sonigo P., Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Tiollais P., Montagnier L., Wain-Hobson S. Molecular cloning of lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):757–760. doi: 10.1038/312757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell K. D., Ramilo O., Vitetta E. S. Combined use of an immunotoxin and cyclosporine to prevent both activated and quiescent peripheral blood T cells from producing type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabletz T., Pietrowski I., Serfling E. The immunosuppressives FK 506 and cyclosporin A inhibit the generation of protein factors binding to the two purine boxes of the interleukin 2 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):61–67. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durette P. L., Boger J., Dumont F., Firestone R., Frankshun R. A., Koprak S. L., Lin C. S., Melino M. R., Pessolano A. A., Pisano J. A study of the correlation between cyclophilin binding and in vitro immunosuppressive activity of cyclosporine A and analogues. Transplant Proc. 1988 Apr;20(2 Suppl 2):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmel E. A., Verweij C. L., Durand D. B., Higgins K. M., Lacy E., Crabtree G. R. Cyclosporin A specifically inhibits function of nuclear proteins involved in T cell activation. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1617–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.2595372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber V., Dalgleish A. G., Newell A., Malkovsky M. Inhibition of HIV replication in vitro by fusidic acid. Lancet. 1987 Oct 10;2(8563):827–828. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch P., Malkovsky M., Kovats S., Sturm E., Braakman E., Klein B. S., Voss S. D., Morrissey L. W., DeMars R., Welch W. J. Recognition by human V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cells of a GroEL homolog on Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1269–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.1978758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Wittmann-Liebold B., Lang K., Kiefhaber T., Schmid F. X. Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):476–478. doi: 10.1038/337476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke E. K., Yuan H. E., Luban J. Specific incorporation of cyclophilin A into HIV-1 virions. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):359–362. doi: 10.1038/372359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Weissman I. Two cytoplasmic candidates for immunophilin action are revealed by affinity for a new cyclophilin: one in the presence and one in the absence of CsA. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschumacher R. E., Harding M. W., Rice J., Drugge R. J., Speicher D. W. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6238408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. W., Handschumacher R. E., Speicher D. W. Isolation and amino acid sequence of cyclophilin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8547–8555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., D'Aquila R. T. Therapy for human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 10;328(23):1686–1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306103282307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Haggarty B. S., Bonser S. E., Rackowski J. L., Shan H., Kanki P. J. Biological characterization of a simian immunodeficiency virus-like retrovirus (HTLV-IV): evidence for CD4-associated molecules required for infection. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2557–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2557-2568.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Miner Z., Kerppola T. K., Lambert J. N., Verdine G. L., Curran T., Rao A. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):352–355. doi: 10.1038/365352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B. D. Cyclosporine. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1725–1738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpas A., Lowdell M., Jacobson S. K., Hill F. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus and growth of infected T cells by the immunosuppressive drugs cyclosporin A and FK 506. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8351–8355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H., Mayrose D., Belshaw P. J., Alberg D. G., Schreiber S. L., Chang Z. Y., Etzkorn F. A., Ho S., Walsh C. T. Crystal structures of cyclophilin A complexed with cyclosporin A and N-methyl-4-[(E)-2-butenyl]-4,4-dimethylthreonine cyclosporin A. Structure. 1994 Jan 15;2(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofron J. L., Kuzmic P., Kishore V., Colón-Bonilla E., Rich D. H. Determination of kinetic constants for peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases by an improved spectrophotometric assay. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6127–6134. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Albers M. W., Wandless T. J., Luan S., Alberg D. G., Belshaw P. J., Cohen P., MacKintosh C., Klee C. B., Schreiber S. L. Inhibition of T cell signaling by immunophilin-ligand complexes correlates with loss of calcineurin phosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3896–3901. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Bossolt K. L., Franke E. K., Kalpana G. V., Goff S. P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein binds to cyclophilins A and B. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1067–1078. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90637-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovsky M., Asherson G. L., Stockinger B., Watkins M. C. Nonspecific inhibitor released by T acceptor cells reduces the production of interleukin-2. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):652–655. doi: 10.1038/300652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Loveland B., North M., Asherson G. L., Gao L., Ward P., Fiers W. Recombinant interleukin-2 directly augments the cytotoxicity of human monocytes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):262–265. doi: 10.1038/325262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Medawar P. B., Thatcher D. R., Toy J., Hunt R., Rayfield L. S., Doré C. Acquired immunological tolerance of foreign cells is impaired by recombinant interleukin 2 or vitamin A acetate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):536–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P. S., Ullman K. S., Fiering S., Emmel E. A., McCutcheon M., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4425–4433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol V., Kallen J., Pflügl G., Walkinshaw M. D. X-ray structure of a monomeric cyclophilin A-cyclosporin A crystal complex at 2.1 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):1119–1130. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
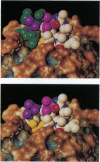
- Newell A. L., Malkovsky M., Orr D., Taylor-Robinson D., Dalgleish A. G. Antigen test versus reverse transcriptase assay for detecting HIV. Lancet. 1987 Nov 14;2(8568):1146–1147. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Galindo J. Persistent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of monoblastoid cells leads to accumulation of self-integrated viral DNA and to production of defective virions. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3700–3707. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3700-3707.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Dhaon M. K., Dunlap B., Miller S. P. Synthesis and antimitogenic activities of four analogues of cyclosporin A modified in the 1-position. J Med Chem. 1986 Jun;29(6):978–984. doi: 10.1021/jm00156a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Billich A., Datema R., Donatsch P., Hammerschmid F., Harrison R., Hiestand P., Jaksche H., Mayer P., Peichl P. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by SDZ NIM 811, a nonimmunosuppressive cyclosporine analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Aug;38(8):1763–1772. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.8.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hennighausen L., Siebenlist U. Inducible nuclear factor binding to the kappa B elements of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells can be blocked by cyclosporin A in a signal-dependent manner. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4037–4041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4037-4041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Sigal N. H. FK-506 and cyclosporin A: immunosuppressive mechanism of action and beyond. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Oct;4(5):548–552. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Dumont F., Durette P., Siekierka J. J., Peterson L., Rich D. H., Dunlap B. E., Staruch M. J., Melino M. R., Koprak S. L. Is cyclophilin involved in the immunosuppressive and nephrotoxic mechanism of action of cyclosporin A? J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):619–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Hayano T., Suzuki M. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase is the cyclosporin A-binding protein cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):473–475. doi: 10.1038/337473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Bukovsky A., Kondo E., Rosenwirth B., Walsh C. T., Sodroski J., Göttlinger H. G. Functional association of cyclophilin A with HIV-1 virions. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):363–365. doi: 10.1038/372363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg M. A., Dascal A., Blain N., Fitz-Gibbon L., Boulerice F., Numazaki K., Tremblay M. The effect of cyclosporine A on infection of susceptible cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1904–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]