Abstract
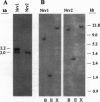
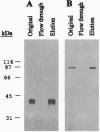
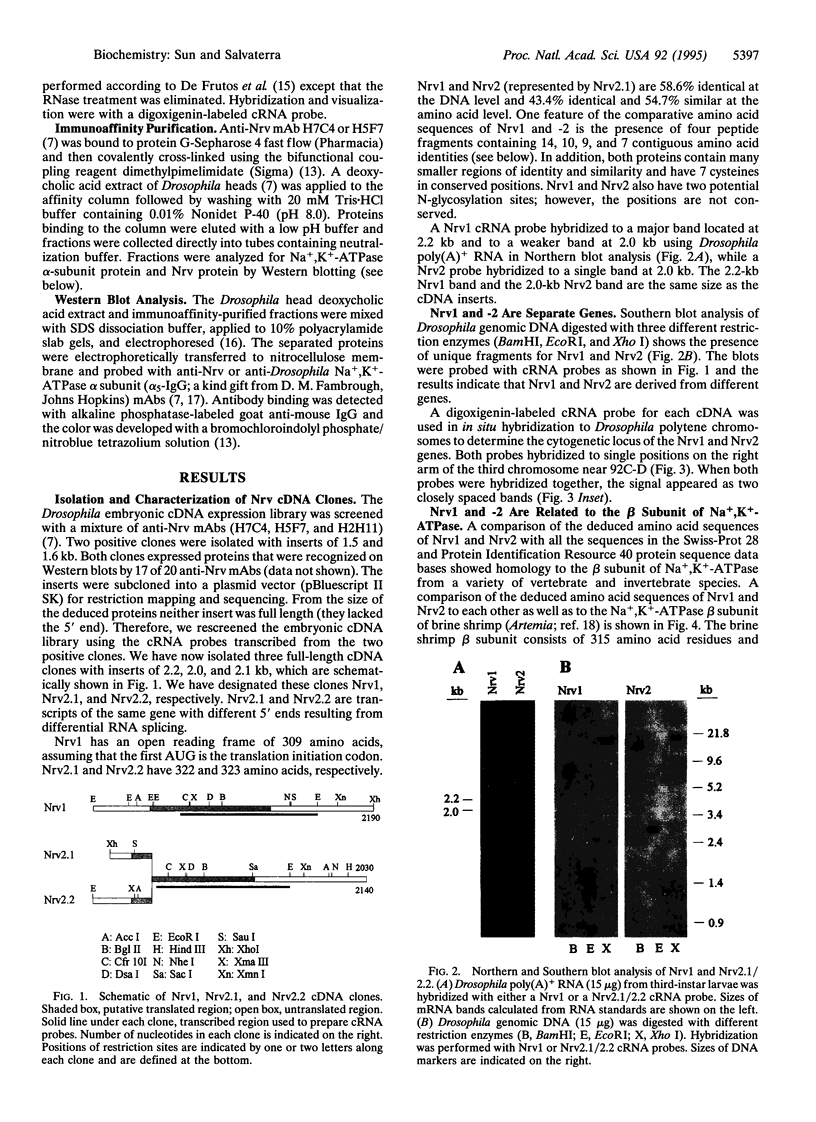
A nervous system-specific glycoprotein antigen from adult Drosophila heads, designated Nervana (Nrv), has been purified on the basis of reactivity of its carbohydrate epitope(s) with anti-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) antibodies that are specific markers for Drosophila neurons. Anti-Nrv monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), specific for the protein moiety of Nrv, were used to screen a Drosophila embryo cDNA expression library. Three cDNA clones (designated Nrv1, Nrv2.1, and Nrv2.2) were isolated that code for proteins recognized by anti-Nrv mAbs on Western blots. DNA sequencing and Southern blot analyses established that the cDNA clones are derived from two different genes. In situ hybridization to Drosophila polytene chromosomes showed that the cDNA clones map to the third chromosome near 92C-D. Nrv1 and Nrv2.1/2.2 have open reading frames of 309 and 322/323 amino acids, respectively, and they are 43.4% identical at the amino acid level. The proteins deduced from these clones exhibit significant homology in both primary sequence and predicted topology to the beta subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase. Immunoaffinity-purified Nrv is associated with a protein (M(r) 100,000) recognized on Western blots by anti-ATPase alpha-subunit mAb. Our results suggest that the Drosophila nervous system-specific antigens Nrv1 and -2 are neuronal forms of the beta subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonicek H., Persohn E., Schachner M. Biochemical and functional characterization of a novel neuron-glia adhesion molecule that is involved in neuronal migration. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1587–1595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonicek H., Schachner M. The adhesion molecule on glia (AMOG) incorporated into lipid vesicles binds to subpopulations of neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2961–2966. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02961.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey G. K., Fitzgerald S. C., Schrier B. K., Nelson P. G. Neuronal maturation in mammalian cell culture is dependent on spontaneous electrical activity. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 23;207(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya K. K., Bergstrom E. E., Hokin L. E. Molecular cloning of the beta-subunit of the Na,K-ATPase in the brine shrimp, Artemia. The cDNA-derived amino acid sequence shows low homology with the beta-subunits of vertebrates except in the single transmembrane and the carboxy-terminal domains. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81162-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco G., DeTomaso A. W., Koster J., Xie Z. J., Mercer R. W. The alpha-subunit of the Na,K-ATPase has catalytic activity independent of the beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23420–23425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Horowitz B., Miller R. P., McDonough A. A., Farley R. A. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase beta subunit from dog kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 8;912(2):244–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Bentley D. Pioneer growth cone steering along a series of neuronal and non-neuronal cues of different affinities. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1781–1795. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01781.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Lemas M. V., Hamrick M., Emerick M., Renaud K. J., Inman E. M., Hwang B., Takeyasu K. Analysis of subunit assembly of the Na-K-ATPase. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 1):C579–C589. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.3.C579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K. The functional role of the beta-subunit in the maturation and intracellular transport of Na,K-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor S., Antonicek H., Sweadner K. J., Pagliusi S., Frank R., Moos M., Schachner M. The adhesion molecule on glia (AMOG) is a homologue of the beta subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):165–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good P. J., Richter K., Dawid I. B. A nervous system-specific isotype of the beta subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase expressed during early development of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9088–9092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Antibodies to horseradish peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and in grasshopper embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. VI. Differential tryptic modification of catalytic functions of the purified enzyme in presence of NaCl and KCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F., Moats W., Jan Y. N. A carbohydrate epitope expressed uniquely on the cell surface of Drosophila neurons is altered in the mutant nac (neurally altered carbohydrate). EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3471–3477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Nojima H., Ohta T., Nagano K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2833–2844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirley T. L. Determination of three disulfide bonds and one free sulfhydryl in the beta subunit of (Na,K)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7185–7192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magyar J. P., Bartsch U., Wang Z. Q., Howells N., Aguzzi A., Wagner E. F., Schachner M. Degeneration of neural cells in the central nervous system of mice deficient in the gene for the adhesion molecule on Glia, the beta 2 subunit of murine Na,K-ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):835–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Vasallo P., Dackowski W., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R. Identification of a putative isoform of the Na,K-ATPase beta subunit. Primary structure and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4613–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Modyanov N. N., Broude N. E., Petrukhin K. E., Grishin A. V., Arzamazova N. M., Aldanova N. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Sverdlov E. D. Pig kidney Na+,K+-ATPase. Primary structure and spatial organization. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliusi S., Antonicek H., Gloor S., Frank R., Moos M., Schachner M. Identification of a cDNA clone specific for the neural cell adhesion molecule AMOG. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Feb;22(2):113–119. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvaterra P. M., Bournias-Vardiabasis N., Nair T., Hou G., Lieu C. In vitro neuronal differentiation of Drosophila embryo cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):10–22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00010.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., Timson L., Kawasaki E. S., Clark S. S., Witte O. N., Champlin R. Molecular relapse in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation detected by polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers S. T., Khan T., Shahid R., Dauzvardis M. F., Siegel G. J. Distribution of alpha 1 subunit isoform of (Na,K)-ATPase in the rat spinal cord. Neurochem Res. 1994 May;19(5):597–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00971336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubiger M., Feng Y., Fambrough D. M., Palka J. A mutation of the Drosophila sodium pump alpha subunit gene results in bang-sensitive paralysis. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lane L. K., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the beta-subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a cDNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):429–431. doi: 10.1038/321429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyjan A. W., Levenson R. Antisera specific for the alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 3, and beta subunits of the Na,K-ATPase: differential expression of alpha and beta subunits in rat tissue membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4531–4535. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow P. M., Patel N. H., Harrelson A. L., Goodman C. S. Neural-specific carbohydrate moiety shared by many surface glycoproteins in Drosophila and grasshopper embryos. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4137–4144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Renaud K. J., Fambrough D. M. Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the alpha-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4347–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Siegel N. R., Fambrough D. M. Expression of hybrid (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules after transfection of mouse Ltk-cells with DNA encoding the beta-subunit of an avian brain sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10733–10740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taormino J. P., Fambrough D. M. Pre-translational regulation of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in response to demand for ion transport in cultured chicken skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4116–4123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrey F., Kairouz P., Schaerer E., Fuentes P., Geering K., Rossier B. C., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Primary sequence of Xenopus laevis Na+-K+-ATPase and its localization in A6 kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1034–F1043. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Sun B., Yasuyama K., Salvaterra P. M. Biochemical analysis of proteins recognized by anti-HRP antibodies in Drosophila melanogaster: identification and characterization of neuron specific and male specific glycoproteins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1994 Mar;24(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. G., Sanchez-Watts G., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R. Cell-specific expression of mRNAs encoding Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit isoforms within the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7425–7429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. M., Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Multiple mRNAs from rat kidney and brain encode a single Na+,K+-ATPase beta subunit protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4905–4910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]