Figure 4.
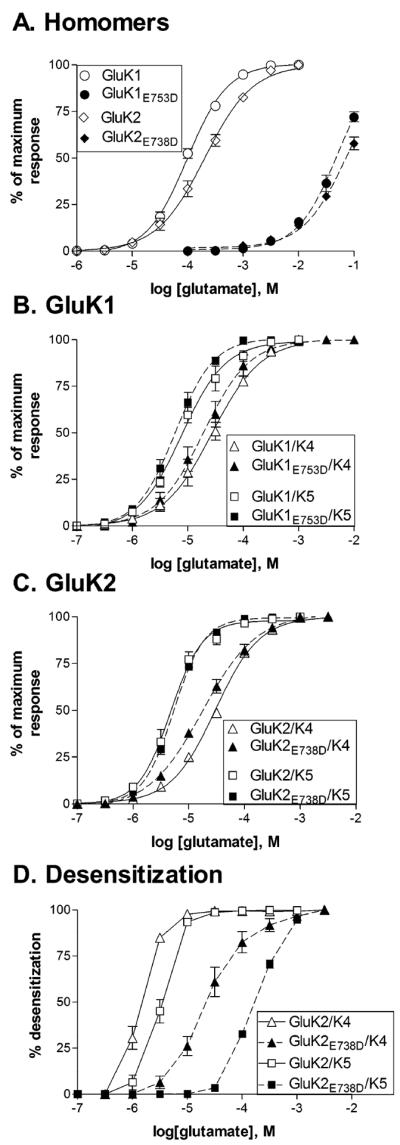
Mutations that reduce glutamate binding to GluK1 and GluK2 subunit alter desensitization, but not activation of heteromeric receptors.
A., B., C. Concentration-response relationships for glutamate were constructed by measuring the peak current amplitude and normalizing to the maximal peak response to a saturating concentration of glutamate for each cell. A saturating glutamate concentration could not be reached for mutated homomeric receptors, and therefore the peak current was estimated by fitting the current amplitudes for each cell with a logistic equation with a fixed Hill slope taken from the fit of the wild-type data. The maximum current from this fit was then used for normalization. Symbols represent mean ± SEM (n=3–8 cells) and solid (wild-type) or dashed (mutated) lines show the fit of a four-parameter logistic equation to the averaged data.
D. Effect of glutamate concentration on the extent of whole-cell desensitization. The steady state current measured at the end of the 5 second glutamate application was divided by the peak current. This steady state/peak ratio was then subtracted from 1 and multiplied by 100 to give the % desensitization.
