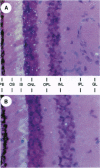
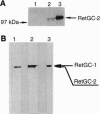
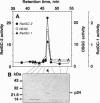
Abstract
One of the membrane guanylyl cyclases (GCs), RetGC, is expressed predominantly in photoreceptors. No extracellular ligand has been described for RetGC, but it is sensitive to activation by a soluble 24-kDa protein (p24) and is inhibited by Ca2+. This enzyme is, therefore, thought to play a role in resynthesizing cGMP for photoreceptor recovery or adaptation. By screening a human retinal cDNA library at low stringency with the cytoplasmic domains from four cyclases, we cloned cDNAs encoding a membrane CG that is most closely related to RetGC. We have named this GC RetGC-2, and now term the initially described RetGC RetGC-1. By in situ hybridization, mRNA encoding RetGC-2 is found only in the outer nuclear layer and inner segments of photoreceptor cells. By using synthetic peptide antiserum specific for each RetGC subtype, RetGC-2 can be distinguished from RetGC-1 as a slightly smaller protein in immunoblots of bovine rod outer segments. Membrane GC activity of recombinant RetGC-2 expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells is stimulated by the activator p24 and is inhibited by Ca2+ with an EC50 value of 50-100 nM. Our data reveal a previously unappreciated diversity of photoreceptor GCs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad I., Barnstable C. J. Differential laminar expression of particulate and soluble guanylate cyclase genes in rat retina. Exp Eye Res. 1993 Jan;56(1):51–62. doi: 10.1006/exer.1993.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. D., Bennett G. L., Vitangcol R. V., Jewett J. R., Burnier J., Henzel W., Lowe D. G. Extracellular domain-IgG fusion proteins for three human natriuretic peptide receptors. Hormone pharmacology and application to solid phase screening of synthetic peptide antisera. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23060–23067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bönigk W., Altenhofen W., Müller F., Dose A., Illing M., Molday R. S., Kaupp U. B. Rod and cone photoreceptor cells express distinct genes for cGMP-gated channels. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):865–877. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Lewis M., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Goeddel D. V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):68–72. doi: 10.1038/341068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Peng Y. W., Dhallan R. S., Ahamed B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W. A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):764–767. doi: 10.1038/362764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizhoor A. M., Lowe D. G., Olshevskaya E. V., Laura R. P., Hurley J. B. The human photoreceptor membrane guanylyl cyclase, RetGC, is present in outer segments and is regulated by calcium and a soluble activator. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1345–1352. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duda T., Goraczniak R. M., Sitaramayya A., Sharma R. K. Cloning and expression of an ATP-regulated human retina C-type natriuretic factor receptor guanylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 16;32(6):1391–1395. doi: 10.1021/bi00057a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L., Lowe D. G. Guanylyl cyclase receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30741–30744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goraczniak R. M., Duda T., Sitaramayya A., Sharma R. K. Structural and functional characterization of the rod outer segment membrane guanylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 1;302(Pt 2):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj3020455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorczyca W. A., Gray-Keller M. P., Detwiler P. B., Palczewski K. Purification and physiological evaluation of a guanylate cyclase activating protein from retinal rods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4014–4018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakki S., Sitaramayya A. Guanylate cyclase from bovine rod outer segments: solubilization, partial purification, and regulation by inorganic pyrophosphate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1088–1094. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. E., Hurley J. B. A phosphodiesterase inhibitor specific to a subset of bovine retinal cones. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11259–11264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Yamazaki A. Polymorphism in purified guanylate cyclase from vertebrate rod photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R. L., Bunt-Milam A. H., Chang M. L., Beavo J. A. cGMP phosphodiesterase in rod and cone outer segments of the retina. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):568–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;50(3):425–442. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90052-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Niidome T., Tanabe T., Terada S., Bönigk W., Stühmer W., Cook N. J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):762–766. doi: 10.1038/342762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Lambrecht H. G., Haberecht M., Redburn D., Schmidt H. H. Functional coupling of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent nitric oxide synthase and a soluble guanylyl cyclase in vertebrate photoreceptor cells. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3312–3320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W. Purification and identification of photoreceptor guanylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8634–8637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Stecher P., Kellner R. Bovine retinal rod guanyl cyclase represents a new N-glycosylated subtype of membrane-bound guanyl cyclases. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 1;222(2):589–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Stryer L. Highly cooperative feedback control of retinal rod guanylate cyclase by calcium ions. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):64–66. doi: 10.1038/334064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagnado L., Baylor D. Signal flow in visual transduction. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):995–1002. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90122-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Lieberman B. S., Yamane H. K., Bok D., Fung B. K. A third form of the G protein beta subunit. 1. Immunochemical identification and localization to cone photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24776–24781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea C. L., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B., Klock I. B., Bunt-Milam A. H. Identification of specific transducin alpha subunits in retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3529395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Seno K., Nishizawa Y., Hayashi F., Yamazaki A., Matsumoto H., Wakabayashi T., Usukura J. Ultrastructural localization of retinal guanylate cyclase in human and monkey retinas. Exp Eye Res. 1994 Dec;59(6):761–768. doi: 10.1006/exer.1994.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Chang M. S., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Singh S., Garbers D. L., Goeddel D. V. Human atrial natriuretic peptide receptor defines a new paradigm for second messenger signal transduction. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1377–1384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulis A., Goraczniak R. M., Duda T., Sharma R. K., Sitaramayya A. Structural and biochemical identity of retinal rod outer segment membrane guanylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 30;194(2):855–861. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Maxfield F. R. Preparation of solutions with free calcium concentration in the nanomolar range using 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 15;193(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90044-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. W., Robishaw J. D., Levine M. A., Yau K. W. Retinal rods and cones have distinct G protein beta and gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10882–10886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe I. M., Boero A., Vergani L., Panfoli I., Cugnoli C. Effect of light and calcium on cyclic GMP synthesis in rod outer segments of toad retina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe I. M., Panfoli I., Cugnoli C. Guanylate cyclase in rod outer segments of the toad retina. Effect of light and Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81439-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyjan A. W., de Sauvage F. J., Gillett N. A., Goeddel D. V., Lowe D. G. Molecular cloning of a retina-specific membrane guanylyl cyclase. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):727–737. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90035-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R., Pozzan T. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ with quin2. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:230–262. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R. B., Foster D. C., Garbers D. L., Fülle H. J. Two membrane forms of guanylyl cyclase found in the eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarfitz S., Hurley J. B. Transduction mechanisms of vertebrate and invertebrate photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14329–14332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sauvage F. J., Camerato T. R., Goeddel D. V. Primary structure and functional expression of the human receptor for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17912–17918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]