| Title: | Azaheterobicyclic Compounds | ||
| Patent Application Number: | WO 2014/086453 Al | Publication Date: | 12 June 2014 |
| Priority Application: | EP 12008195.5 | Priority Date: | 7 December 2012 |
| Inventors: | Schiemann, K.; Stieber, F.; Esdar, C. | ||
| Assignee Company: | Merck Patent GMBH, Frankfurter Strasse 250, 64293 Darmstadt, DE | ||
| Cancer Research Technology Ltd.; Angel Building, 407 St. John Street, London ECl V 4AD, U.K. | |||
| Disease Area: | Inflammatory or hyperproliferative diseases, such as cancer | Biological Target: | Wnt pathway inhibitors |
| Summary: | The invention in this patent application relates to novel substituted azaheterobicyclic compounds, which are Wnt pathway inhibitors and may be useful in the treatment of inflammatory or hyperproliferative diseases such as cancer | ||
| Wnt proteins are a large family of cysteine-rich secreted ligands that bind to a receptor complex of the members of the Frizzled (Fz) family proteins. The Wnt signaling activates three different pathways: the canonical Wnt/β-catenin cascade, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway. The canonical pathway is the most understood and most relevant to cancer. The binding of the Wnt proteins to the Frizzled receptor allows β-catenin, the key mediator of Wnt signaling, to accumulate in the cytoplasm and then translocate into the nucleus. There, it regulates target gene expression in combination with members of the DNA-binding T cell factor I lymphoid enhancer factor (TCFILEF) family. However, if the Wnt ligands are absent, then β-catenin is phosphorylated by a protein complex made of Axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), and casein kinase 1 (CK1). The phosphorylation marks β-catenin for destruction via ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. The binding of Wnt to the Fz receptor inhibits the Axin–APC–GSK3J3 complex and stops the phosphorylation of β-catenin. | |||
| Several tumor types often contain over activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade. Some proteins of the pathway that are tumor suppressors can mutate and act as oncogenes. For example, the tumor suppressor APC is mutated in nearly 60% of all colon cancers. Many colon cancers express mutated stabilized β-catenin that cannot be phosphorylated. Also mutations of the tumor suppressor Axin were detected in hepatocellular, lung, and colon cancers. | |||
| Therefore, inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a possible and promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. While there are some reported Wnt pathway inhibitors, there exists a significant unmet medical need to identify new, more efficient Wnt pathway inhibitors. | |||
| Important Compound Classes: | 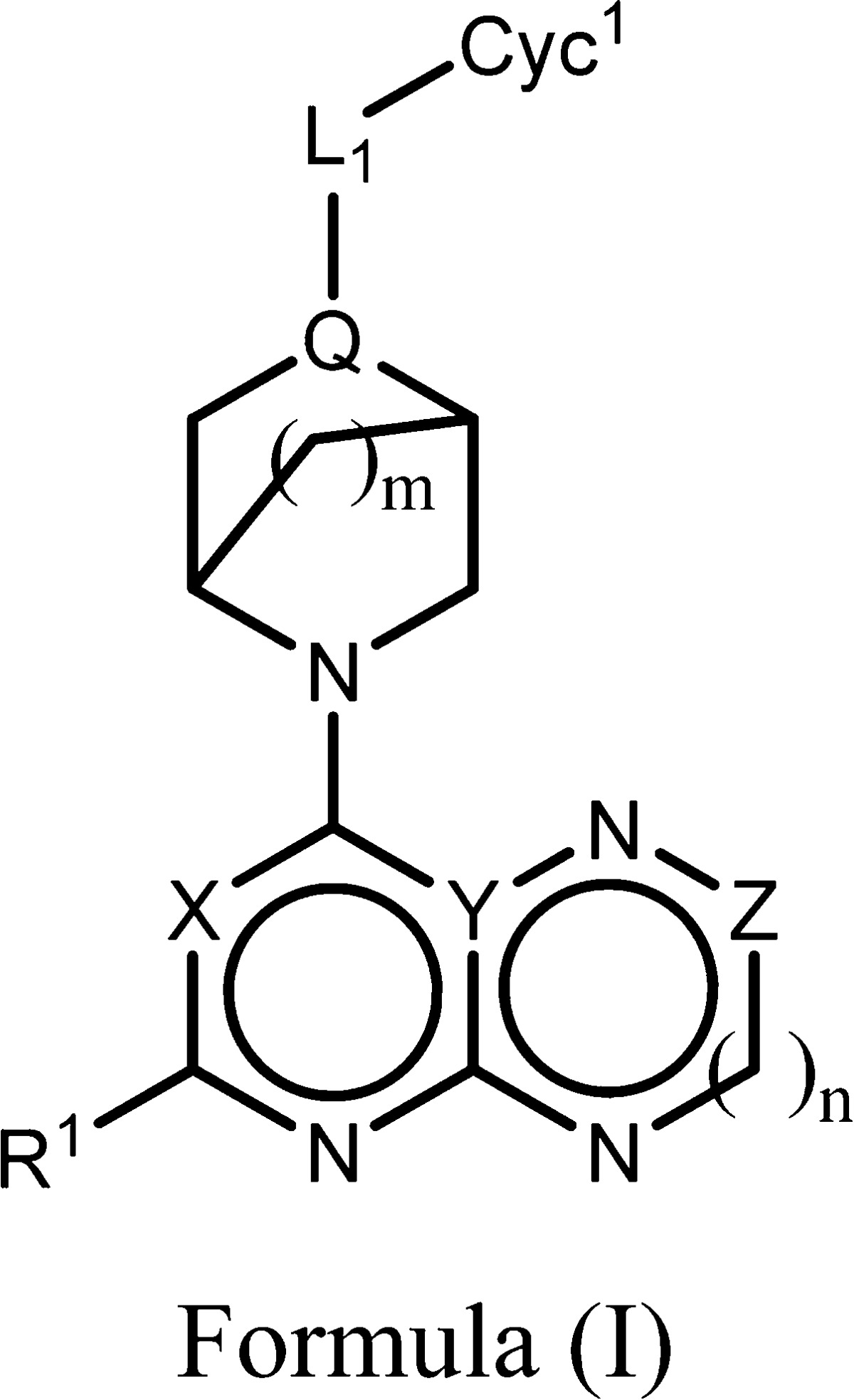 |
||
| Key Structures: | The inventors listed the structures of 300 examples of formula (I) including the following representative compounds: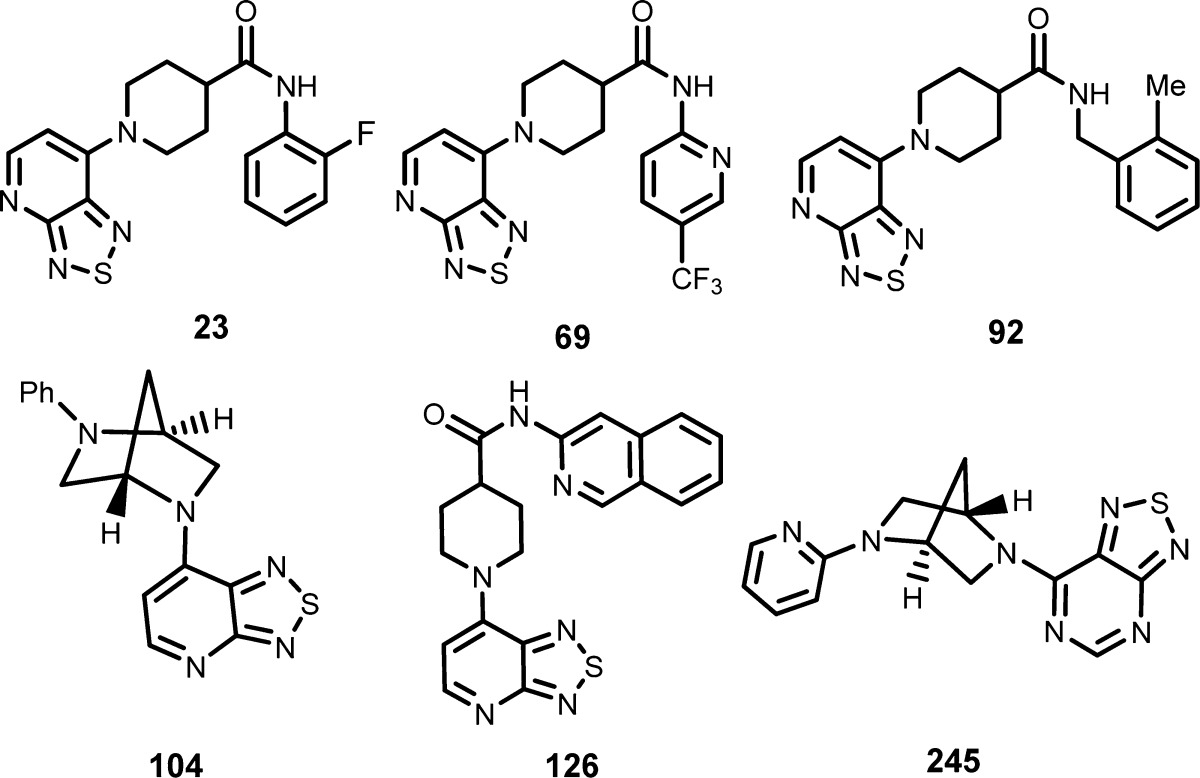
|
||
| Biological Assay: | Cellular Assay for Wnt Pathway Activity | ||
| Biological Data: | The IC50 values were determined for the compounds of the invention and ranged from <0.05 to 5.0 μM. The values for the above representative examples are listed in the following table: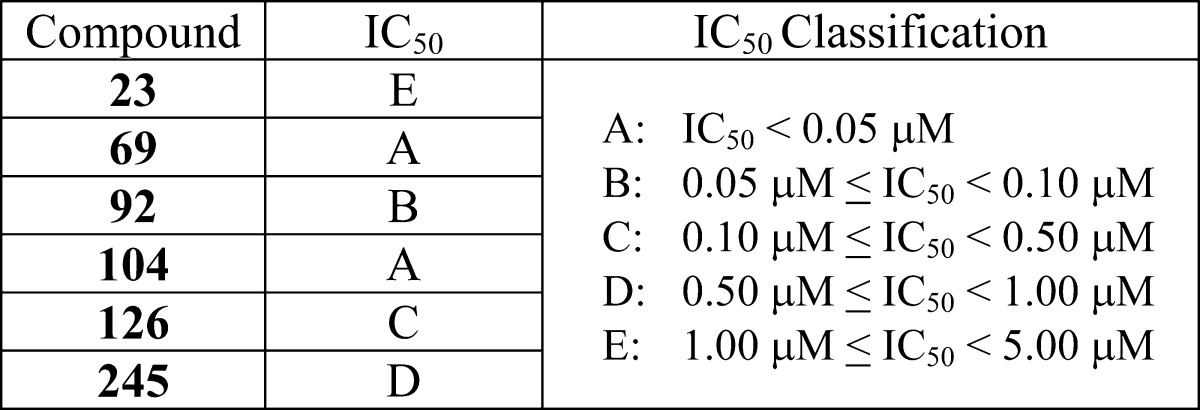
|
||
| Recent Review Articles: | Guo Y.; Xiao L.; Sun L.; Liu F.. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61(4), 337–346. | ||
| McQueen P.; Ghaffar S.; Guo Y.; Rubin E. M.; Zi X.; Hoang B. H.. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2011, 11(8), 1223–1232. | |||
| Elston M. S.; Clifton-Bligh R. J.. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 326(1–2), 48–54. | |||
| Macheda M. L.; Stacker S. A.. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8(6), 454–465. | |||
The authors declare no competing financial interest.


