Abstract
The GacS/GacA system in the root colonizer Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 is a key regulator of many traits relevant to the biocontrol function of this bacterium. Proteomic analysis revealed 12 proteins were down-regulated in a gacS mutant of P. chlororaphis O6. These GacS-regulated proteins functioned in combating oxidative stress, cell signaling, biosynthesis of secondary metabolism, and secretion. The extent of regulation was shown by real-time RT-PCR to vary between the genes. Mutants of P. chlororaphis O6 were generated in two GacS-regulated genes, trpE, encoding a protein involved in tryptophan synthesis, and prnA, required for conversion of tryptophan to the antimicrobial compound, pyrrolitrin. Failure of the trpE mutant to induce systemic resistance in tobacco against a foliar pathogen causing soft rot, Pectobacterium carotovorum SCCI, correlated with reduced colonization of root surfaces implying an inadequate supply of tryptophan to support growth. Although colonization was not affected by mutation in the prnA gene, induction of systemic resistance was reduced, suggesting that pyrrolnitrin was an activator of plant resistance as well as an antifungal agent. Study of mutants in the other GacS-regulated proteins will indicate further the features required for biocontrol-activity in this rhizobacterium.
Keywords: induced systemic resistance, proteomic analysis, tryptophan metabolism
Certain rhizobacteria stimulate plant growth and responses to stress (Bloemberg and Lugtenberg, 2001). Some beneficial bacteria inhibit growth of phytopathogenic fungi by production of antifungal metabolites, and/or exoenzymes. The antifungal agents include hydrogen cyanide (HCN), siderophores, biosurfactants and antibiotics, and enzymes including proteases, lipases, chitinases, and glucanases (Dubis et al., 2007; Haas and Defago, 2005; Raaijmakers et al., 2002). The root colonizer Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 produces several compounds with antifungal activity including a pyoverdine-like siderophore, phenazines, pyrrolnitrin and HCN (Kang et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2011; Park et al., 2011). Effective root colonization by P. chlororaphis O6 also protects plants from pathogens through induction of systemic resistance against various plant diseases as well as drought and salinity stress (Cho et al., 2008; 2012; Han et al., 2006).
The two component sensor kinase system involving GacS and GacA is conserved in plant-associated pseudomonads and regulates production of many of the biocontrol active components. The system involves activation of phosphorylation of GacS by an as yet unknown signal followed by phospho-transfer to the GacS regulator. Phosphorylated GacA activates changes expression from genes encoding small regulatory RNAs, such as RsmX, RsmY and RsmZ, which compete with translational repressors, RsmA and RsmB (Brencic et al., 2009). The GacS/GacA regulon is extensive, for example encompassing about 10% of the genes in P. fluorescens Pf-5 (Hassan et al., 2010).
The genome of P. chlororaphis O6 (Loper et al., 2012) possesses genes potentially encoding GacS, GacA, and the proteins, RsmA and RsmB interacting with rRNAs. However, findings with P. chlororaphis O6 and other pseudo-monads reveal that the GacS-regulated traits differ between strains. For example, a gacS mutant of P. chlororaphis O6 has increased swimming and swarming motilities (Kim et al., 2014a), whereas lack of GacS in P. fluorescens Pf-5 has no effect on swimming, and decreases swarming activity, due to mainly loss in production of a surfactant (Hassan et al., 2010).
This study employed a proteomic approach for better understanding the genes regulated by GacS in P. chlororaphis O6, and we compared proteomes from the wild type and gacS mutant strains. Proteins that were down regulated in the gacS mutant were identified and their potential functions deduced. The role of two of these proteins, one involved in pyrrolnitrin production and the second in tryptophan biosynthesis, was explored using mutants in the GacS-regulated genes, prnA and trpE. The abilities of the prnA and trpE mutants to colonize roots and induce systemic resistance were investigated.
Bacteria were stored at −70°C in 25% glycerol. The gacS mutant and the gacS-complemented strain of P. chlororaphis O6 were constructed previously (Kang et al., 2004) and grown at 28°C with shaking at 200 rpm in King’s medium B broth. A prnA mutant of P. chlororaphis O6 was constructed previously (Park et al., 2011). Cultures of Escherichia coli DH5α were grown at 37°C on Luria-Bertani (LB) broth.
Extracts were prepared from the wild type, the gacS mutant and the complemented mutant by sonication of cells grown to stationary phase in LB and harvested by centrifugation. Proteins were extracted by washing cells twice in ice-cold phosphate buffered saline before suspension in sample buffer containing 7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 4% (w/v) 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl dimethyammonio-1-propanesulfonate, 1% (w/v) dithiothreitol and 2% (v/v) pharmalyte and 1 mM benzamidine. After sonication for 10 seconds and incubation for one h at room temperature, the mixture was vortexed and centrifuged at 15,000 × g for one h at 15°C to obtain the soluble fraction used in gel analysis. Changes in protein profiles between the wild type, the gacS mutant, and the complemented gacS mutant were detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis using procedures described previously (Oh et al., 2013b). Protein spot intensities of wild type and gacS mutant on 2-D PAGE analyses were assessed by Student's t test. Three independent two dimensional protein analyses were performed, and significantly up- or down-regulated protein spots in the gacS mutant were selected and identified using Q-TOF analysis (Oh et al., 2013b).
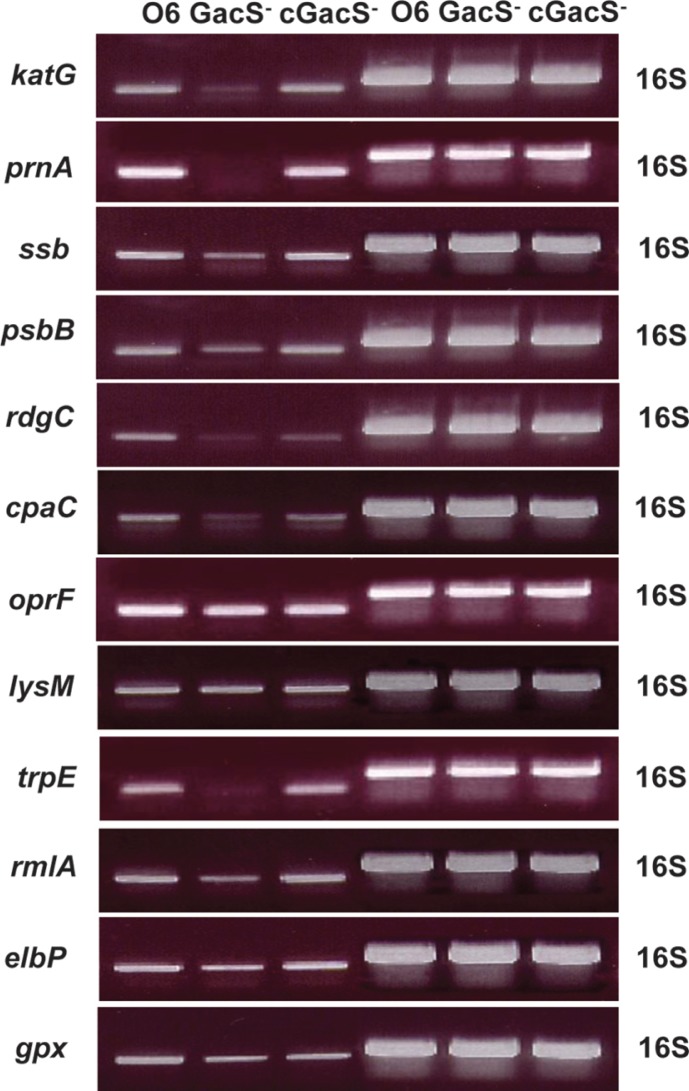
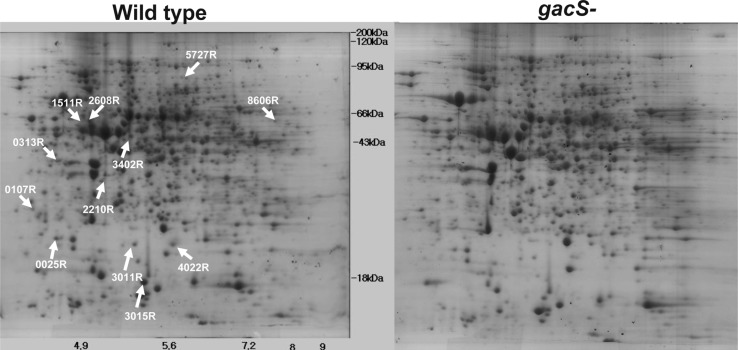
Twelve protein spots were observed in the gacS mutant at lesser intensities than in the gels from the wild type strain (Fig. 2A). Based on a cut-off value of twofold change, peptide identification revealed they were a catalase/peroxidase with homology to KatG from P. fluorescens Pf-01 (Table 1), a tryptophan halogenase (PrnA), catalyzing the first step in pyrrolnitrin synthesis, a single-strand DNA binding protein (Ssb), a serine protease (PspB), a recombination associated protein (RdgC), and a potential secretin (CpaC), involved in pilus synthesis, and an outer membrane protein (OprF) (Table 1). Proteins showing fold changes between two- and four- fold were: a protein with a LysM domain associated with binding peptidoglycan (LysM), the anthranilate/para-aminobenzoate synthase component I (TrpE), involved in tryptophan synthesis from chorismate, glucose 1-phosphate thymidilate transferase (RmlA) required for rhamnose synthesis, a protein functioning in isoprenoid biosynthesis (ElbP), and glutathione peroxidase (Gpx) (Table 1).
Fig. 2.
Transcript accumulations from selected genes in the wild type (O6), the gacS mutant (GacS-) and the complemented gacS mutant (cGacS-) were assessed by RT-PCR. Data are shown for RNA extracted from stationary phase cells from one of two independent studies showing the same results. PCR bands from RNA transcripts of the 16S rRNA genes are shown to confirm equal loading of the wells.
Table 1.
Identification of the down-regulated proteins by GacS from Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6
| Spot number | Observed migrationa
|
Identified protein
|
Fold change
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mr (kDa) | pI | Proteinb | Ion Score or Matching sequenced | Mr (kDa) | pI | Meanc | SEc | p-valued | ||
| 5727R | 81 | 6.12 | Catalase/peroxidase I, KatG (P. fluorescens Pf0-1 YP347933) | FLANPDQLADAFAR(84) FAPLNSWPDNVSLDK(51) DWWPNQLNLK(19) |
83 | 5.30 | >−100 | 0.001 | ||
| 8606R | 62 | 7.64 | Tryptophan halogenase, PrnA (P. chlororaphis ACN AAD46360) | IGVGEATIPSLQK(76) TSLPTNYDYLR(39) DQATADFLNLWGLSDNQPLNQIK(55) |
61 | 5.80 | >−100 | 0.001 | ||
| 4022R | 21 | 5.77 | Single-strand DNA-binding protein, Ssb (P. putida pWWO NP542825) | VAEIAGEYLR(28) VILVGTCGQDPEVR(53) |
21 | 6.13 | >−100 | 0.002 | ||
| 1511R | 50 | 4.99 | Serine protease, PspB (P. brassicaceaum AF286062) | VNLDYDGLLGSR SFSDVGLTPNQR |
107 | 5.19 | >−100 | 0.018 | ||
| 0313R | 37 | 4.59 | Recombination associated protein, RdgC (P. fluorescens Pf-5 AAY93657) | LTQDLPFDAEALET | 34 | 4.93 | >−100 | 0.029 | ||
| 3402R | 40 | 5.30 | Pilus assembly protein, CpaC (P. fluorescens Pf0-1 ABA723932) | LTLTPTLVGNDR | 44 | 8.46 | >−100 | 0.011 | ||
| 0025R | 21 | 4.71 | Outer membrane protein, OprF (P. chlrororaphis AAD24553) | QVLTSQYGVESSR(59) VQSVGYGESRPVADNATEAGR(36) VAPAPAPVPEPTPEPEAPVAEVVR(48) QYPQTTTVVEGHTDSVGPDAYNQK (36) |
34 | 5.59 | −56.6 | 3.65 | 0.012 | |
| 3015R | 17 | 5.44 | Peptidoglycan-binding LysM, LysM (P. fluorescens PfO-1 ABA72026) | LLDLLTPGNANASEQLK(52) | 15 | 5.25 | −4.2 | 0.60 | 0.020 | |
| 2608R | 56 | 5.10 | Anthranilate/para-aminobenzoate synthases component I, TrpE (P. fluorescens Pf0-1 YP 350846) | LADQPNSYLLESVQGGEK(56) EYILAGDCMQVVPSQR (20) |
55 | 5.02 | −2.7 | 0.61 | 0.028 | |
| 2210R | 30. | 5.11 | Glucose 1-phosphate thymidylate transferase, RmlA (P. stutzeri CAC44166) | GFAWLDTGTHDSLLEASQYVQTIEHR (80) | 28 | 4.83 | −2.6 | 0.17 | 0.004 | |
| 0107R | 25 | 4.41 | Isoprenoid biosynthesis protein, GATase1_ES1, ElbP (P. protegens Pf-5 YP263046) | LTQDLPFDAEALET(57) | 23 | 5.28 | −2.6 | 0.17 | 0.011 | |
| 3011R | 21 | 5.38 | Glutathione peroxidase, Gpx (P. fluorescens Pf-5 YP258072) | LLAGEGAEFPGDITWNFEK(80) | 18 | 5.35 | −2.3 | 0.3 | 0.017 | |
The Mr and pI values were estimated from 2-dimensional gels obtained in three independent experiments. Ions score is −10*Log(P), where P is the probability that the observed match is a random event. Individual ions scores > 49 indicate identity or extensive homology (p<0.05). Protein scores are derived from ions scores as a non-probabilistic basis for ranking protein hits. Amino acid sequences without ion scores were determined by Q-TOF analysis.
Annotation from NCBI databases using the MASCOT search program (www.matrixscience.com).
The mean and standard error (SE) of fold change of the selected spot was calculated by comparing spot intensities between wild type and gacS mutant of three independent gels using quantitative image analysis (PDQest 2-D analysis Software).
Student’s t-test.
The study was continued with a transcript analysis to determine the extents to which changes protein level in the gacS mutant correlated with altered gene expression. RNA accumulation from the genes predicted to encode the GacS-regulated proteins was evaluated by endpoint RTPCR. Cells grown in LB broth were harvested in stationary phase (OD600 nm = 2.4). Total RNA was isolated using the Trizol method following the user's manual (GIBCO BRL, Rockville, MD, USA). RT-PCR was performed using the QuantiTect SYBR Green reverse transcription-PCR kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, USA). A reaction mixture of 25 μl was incubated at 50ºC for 30 min for reverse transcription, followed by RT-PCR with each primer set (Supplementary Table 1). A Rotor-Gene 2000 Real Time Cycler machine (Corbett Research Inc., Australia) was used for 35 cycles with denaturation at 94ºC for 15 seconds, annealing at 55°C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72ºC for 30 seconds. PCR reactions were stop after 20 cycles and PCR products were loaded on 2% agarose gel. The results provided are typical of three independent studies. Findings shown in Fig. 2 are from stationary phase cells and comparable loading between samples was demonstrated from the consistency of the PCR products for the 16S rRNA genes (Fig. 2).
Transcripts in the gacS mutant compared to the wild type were most reduced for katG, prnA, rdgC, cpaC and trpE. For other genes, expression was impaired (psbB, ssb and rmlA) by the gacS mutation. However, for gpx, lysM, and oprF transcript levels were near wild type. These findings suggest that other mechanisms other than direct effects on transcription for control of protein levels may be operating.
We have prior evidence that genes, such as prnA and trpE, showing changes in transcript levels in the gacS mutant, were part of the RpoS regulon in P. chlororaphis O6 (Oh et al., 2013a; Park et al., 2011). These findings agree with control of pyrronitrin production by quorum sensing as shown in another P. chlororaphis isolate PA23 (Selin et al., 2012) and specifically by mutation in gacA in P. chlororaphis isolate 30–84 (Wang et al., 2013). Indeed, extraction and assay showed pyrrolinitrin formation was eliminated in an rpoS mutant (Park et al., 2011), as later confirmed for another isolate by Selin et al. (2012). We believe that the observations with the gacS mutant occurred because rpoS transcription and RpoS protein abundance are controlled by GacS (Kang et al. 2004: Oh et al., 2013a). Two other proteins also were regulated similarly, the catalase/peroxidase KatG and a potential glutathione peroxidase, Gpx. Both of these proteins have significant roles in cellular protection against oxidative stress. Identical changes in catalase/peroxidase and superoxide dismutase isozyme patterns were observed in rpoS and gacS mutants (Oh et al., 2013b). A recent report indicated that P. chlororaphis 30–84 expression from rpoS is under GacA control (Wang et al., 2013).
It is interesting that two of the other GacS-regulated proteins have roles in DNA repair: the single strand DNA binding protein Ssb could be associated with repair of DNA breaks caused by hydrogen peroxide (Ananthaswamy and Eisenstark, 1977) and the protein, RdgC, is proposed to act with RecA to aid in DNA repair when there is damage in replication forks or by double strand breaks (Briggs et al., 2010).
Two proteins down-regulated in the absence of GacS, OprF and LysM, were associated with cell wall functions. OprF is a major outer membrane protein with multiple potential roles that includes the formation of outer membrane vesicles (Wessel et al., 2012). Studies with other pseudomonads also linked oprF expression with quorum sensing and Gac regulation. Crespo and Valverde (2009) observed mutations in the oprF gene sequence in P. fluorescens CHA0 that affected activity of the repressor proteins RsmA/E which are involved in GacA regulation. Additionally an oprF mutant in P. aeruginosa showed reduced production of the quorum-sensing signals, acyl homoserine lactones (Fito-Boncompte et al., 2011). The second GacS-regulated protein has a LysM domain associated with peptidoglycan binding (Bateman and Bycroft, 2000). It is possible that changes in the peptidoglycan binding proteins in the gacS mutant were involved in the elongated growth of these cells observed by atomic force microscopy for cells grown in a biofilm (Anderson et al., 2005) and SEM analysis (Kim et al., 2014b). Additional cell surface changes also are implicated due to the control by GacS in isolate P. chlororaphis O6 of the enzyme, RmlA, involved in generating rhamnose (Zuccotti et al., 2001), and a potential secretin, CpaC, involved in pilus formation (Bitter, 2003). We note changes in colony surface morphology and in biofilm formation for the gacS mutant compared to the wild type strain (Anderson et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2014b).
To characterize the role of the GacS-regulated genes, trpE and prnA mutants were constructed. A trpE mutant was made by homologous marker exchange mutagenesis. A PCR product from the trpE gene was generated using genomic DNA and two specific primers based on the genome sequence of P. chlororaphis O6 (Loper et al., 2012); forward (5′-ATG ATC CGC GAA GAA TTC CT-3′) and reverse (5′-TCA GTC CGG GGT TTG CTC GG-3′) in polymerase chain reactions (PCR). The PCR fragment (about 1.5 kb) was cloned into cloning vector pGEM-7Z. The trpE sequence in the pGEM-7Z plasmid was disrupted by the insertion of a 0.9 kb KpnI fragment containing the kanamycin resistance gene from the plasmid pRL648 (Elhai and Wolk, 1988). The chromosomal trpE gene in P. chlororaphis O6 was mutated using the exchange vector pCPP54 (TcR) and pRK2073 helper plasmid strain as previously described (Miller et al., 1997). The mutants were selected on LB agar containing 5% sucrose based on their sensitivity to tetracycline and resistance to kanamycin. A prnA mutant of P. chlororaphis O6 was constructed previously (Park et al., 2011).
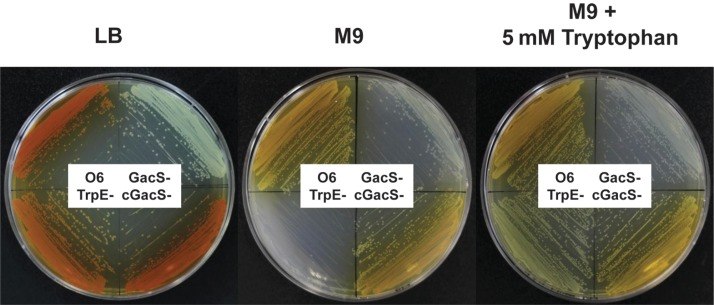
The effects of mutations in prnA and trpE mutants on the requirement for tryptophan for growth was studied (Fig. 3) using cells pre-grown on LB agar plates for 2 days at room temperature. The cells were washed several times by re-suspension in sterile distilled water, and the suspension adjusted to OD600nm = 0.1 before being applied to M9 minimal medium agar plates with or without a supplement of 5 mM tryptophan (Sigma Co., MO, USA) to assess growth. As anticipated, the trpE mutation rendered the mutant unable to grow on minimal medium without the addition of 5 mM tryptophan (Fig. 3). The prnA mutant grew well on the minimal medium with or without the tryptophan (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Auxotrophic phenotype of Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 trpE mutant under minimal growth conditions. Each bacterial strain O6 (wild type), the gacS mutant (GacS-), the complemented gacS mutant (cGacS-), and the trpE mutant (TrpE-) was applied to Luria Bertani agar (LB), M9 minimal agar (M9), or M9 minimal agar with 5 mM tryptophan. The growth images were photographed two days after inoculation on the plates. The images are representative of three independent experiments.
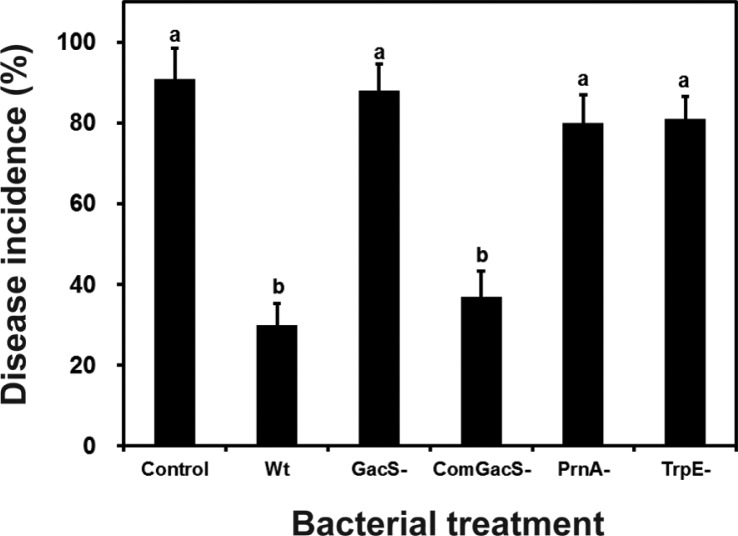
Induction of systemic resistance by colonization of roots with the mutants was measured in tobacco cv. Xanthi seedlings using a challenge of the soft rot bacterium, Pectobacterium carotovorum SCCI (Han et al., 2006). Briefly, sterilized seeds were placed on 1 ml of 0.5% (w/v) MS agar supplemented with 3% sucrose contained in the wells of a 12-well microtiter plate (SPL Inc., Korea). After growth for three weeks, the seedlings were inoculated with suspensions of cells of the wild type, the gacS mutant, the complemented gacS mutant, the trpE mutant and the prnA mutant. The cells for the inocula were grown to an OD600nm = 2.0 in LB broth, pelleted by centrifugation and suspended in sterile 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) to an OD600nm = 0.2. The inocula, 10 μl, of bacterial suspensions containing 1 × 108 colony forming units (cfu)/ml, were applied to the seedling roots. Sterile 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer was applied to control plants. One week after bacterial treatments, tobacco plants were challenged with P. carotovorum subsp. carotovora SCCI by pipetting 2 μl of pathogen inoculum onto a leaf (1× 108 cfu/ml) as described by Han et al. (2006). One to two days after pathogen challenge, the extent of soft-rot was rated visually and the disease severity assessed. The trpE and prnA mutants displayed less ability than the wild type or the complemented gacS mutant to protect the plants against the pathogen (Fig. 4). The extent of protection from the prnA and trpE mutants was low and similar to that displayed by the gacS mutant.
Fig. 4.
Effect of mutations in prnA and trpE of Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 on induced systemic resistance activity in tobacco against Pectobacterium carotovorum SCCI. Roots of three week-old tobacco grown in microtiter wells were inoculated with wild type (Wt), the gacS mutant (GacS-), the complemented gacS mutant (ComGacS-), the trp mutant (TrpE) and the prnA mutant (PrnA) or were treated with water as a negative control prior to pathogen challenge. After one week, leaves were challenged with P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum SCCI and soft rot symptomic leaves were scored after two days. Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments according to Duncan’s multiple range test (p< 0.05). Two independent experiments were performed with at least 21 plants/treatment.
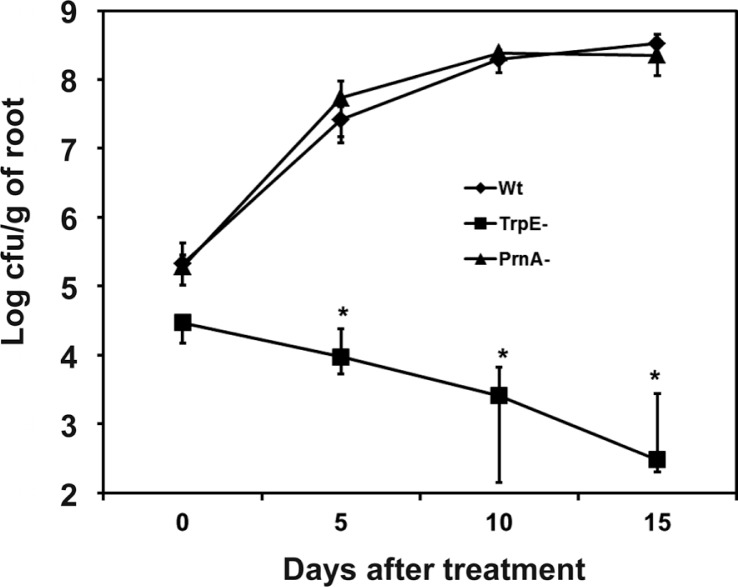
The efficacy of root colonization of the wild type, the trpE mutant and prnA mutant was compared on the tobacco cv. Xanthi seedlings using methods described previously with three week old seedlings raised in the well plates (Han et al., 2006). Roots were excised at defined times after inoculation, and the fresh weight was measured before transferred into 10 ml of sterile distilled water. After vigorous vortexing for 1 min, serial dilutions of these washings were plated onto LB-agar plates containing antibiotics appropriate to the strain. Colonies were scored after incubation at 28°C for two days. Studies were repeated two times with three plants/each treatment. Root colonization in terms of cfu/g fresh weight roots was calculated for each time point. Data were statistically analyzed by ANOVA with the IBM SPSS Statistics version 21 (IBM Corp., Somers, New York, USA). The lack of induced resistance for the trpE mutant correlated with loss of root colonization which declined with time over a 15-d trial (Fig. 5). In contrast both the wild type and the prnA mutant colonized the root surfaces with increases in cfu/root during the first 10 d of the 15 d assessment period (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Effect of mutations in prnA and trpE in Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 on colonization of roots of tobacco under sterile, non-competitive growth conditions. Three week-old tobacco roots in microtiter plates were inoculated with the wild type strain (Wt), the prnA mutant (PrnA-) and trpE mutant (TrpE-) of P. chlororaphis O6. At the defined days after inoculation, root colonization of each bacterial strain was measured based on culturable cells obtained from excised roots. Data are the means of three independent studies with three plants per treatment in each study. Vertical bars represent standard errors. * indicates differences between bacterial strains by Duncan’s multiple range test at p< 0.05.
The failure of the trpE mutant to colonize the plant roots suggested that the supply of tryptophan in the tobacco root exudates was inadequate to maintain wild type level of growth at the root surface. The ability of the prnA mutant to colonize but not to induce systemic resistance suggested that pyrronitrin was active as an effector. This suggestion indicated that pyrrolnitrin had a dual role for the biocontrol-active pseudomonad, both as a direct anti-microbial compound as well as an effector of induced resistance (Park et al., 2011). A similar role was determined for the phenazines produced by this bacterial isolate (Kang et al., 2007). However, our findings of impaired colonization with the trpE mutant emphasized that the formation of pyrrolnitrin in the rhizosphere would be influenced by the supply of tryptophan in the plant root exudates.
In summary, the proteomics analysis of control by GacS confirmed its role as a key regulator of proteins with anticipated roles not only in the formation of antimicrobials but also in oxidative stress, cell signaling, secretion and cell surface properties. Production of KatG and Gpx, involved in protection against oxidative stress, overlapped between the rpoS mutant and the gacS mutant. The newly identified GacS-regulated proteins in this paper, Ssb, PspB, RdgC, LysM, RmlA, and ElbP, indicate further the diverse role of this regulatory system in a rhizosphere-competent pseudomonad with biocontrol potential.
Fig. 1.
Representative images of two-dimensional electrophoresis gels showing proteins from the wild type Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 (wild type) and the gacS mutant (gacS-). Extracts were from cells grown to stationary phase in rich medium. The proteins were stained with silver. Locations of proteins that were present in extracts from the wild type but to a lesser extent in the extracts from the mutant are shown by arrows.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2011-0011555).
References
- Ananthaswamy HN, Eisenstark A. Repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced single-strand breaks in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1977;130:187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.187-191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson AJ, Britt DW, Johnson J, Narisimhan G, Rodriguez Physicochemical parameters influencing the formation of biofilms compared in mutant and wild-type cells of Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Water Sci Tech. 2005;52:21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman A, Bycroft M. The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglyosylate D (MltD) J Mol Biol. 2000;299:1113–1119. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter W. Secretins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: large holes in the outer membrane. Arch Microbiol. 2003;179:307–314. doi: 10.1007/s00203-003-0541-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemberg GV, Lugtenberg BJJ. Multiple basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2001;4:343–350. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brencic A, McFarland KA, McManus HR, Castang S, Mogno I, Dove SL, Lory S. The GacS/GacA signal transduction system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa acts exclusively through its control over the transcription of the RsmY and RsmZ regulatory small RNAs. Mol Microbiol. 2009;73:434–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs GS, Yu J, Mahdi AA, Lloyd RG. The RdgC protein employs a novel mechanism involving a finger domain to bind to circular DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:6433–6446. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho SM, Kang BR, Han SH, Anderson AJ, Park JY, Lee YH, Cho BH, Yang KY, Ryu CM, Kim YC. 2R,3R-butanediol, a bacterial volatile produced by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6, is involved in induction of systemic tolerance to drought in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008;21:1067–1075. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-8-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho SM, Kang BR, Kim JJ, Kim YC. Induced systemic drought and salt tolerance by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 root colonization is mediated by ABA-independent stomatal closure. Plant Pathol J. 2012;28:202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo MCA, Valverde C. A single mutation in the oprF mRNA leader confers strict translational control by the Gac/Rsm system in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Curr Microbiol. 2009;58:182–188. doi: 10.1007/s00284-008-9306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubis C, Keel C, Haas D. Dialogues of root-colonizing biocontrol pseudomonads. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2007;119:311–328. [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J, Wolk CP. A versatile class of positive-selection vectors based on the nonviability of palindrome-containing plasmids that allows cloning into long polylinkers. Gene. 1988;68:119–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fito-Boncompte L, Chapalain A, Bouffartigues E, Chaker H, Lesouhaitier O, Gicquel G, Bazire A, Madi A, Connil N, Veron W, Taupin L, Toussaint B, Cornelis P, Wei Q, Shioya K, Deziel E, Feuilloley MGJ, Orange N, Dufour A, Chevalier S. Full virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires OprF. Infect Immun. 2011;79:1176–1186. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00850-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D, Defago G. Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:307–319. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han SH, Anderson AJ, Yang KY, Cho BH, Kim KY, Lee MC, Kim YH, Kim YC. Multiple determinants influence root colonization and induction of induced systemic resistance by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Mol Plant Pathol. 2006;7:463–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan KA, Johnson A, Shaffer BT, Ren Q, Kidarsa TA, Elbourne LDH, Hartney S, Duboy R, Goebel NC, Zabriskie TM, Paulsen IT, Loper JE. Inactivation of the GacA response regulator in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 has far-reaching transcriptomic consequences. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:899–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang BR, Cho BH, Anderson AJ, Kim YC. The global regulator GacS of a biocontrol bacterium Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 regulates transcription from the rpoS gene encoding a stationary-phase sigma factor and affects survival in oxidative stress. Gene. 2004;325:137–143. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2003.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang BR, Han SH, Zdor RE, Anderson AJ, Spencer M, Yang KY, Kim YH, Lee MC, Cho BH, Kim Y C. Inhibition of seed germination and induction of systemic disease resistance by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 requires phenazine production regulated by the global regulator, GacS. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;17:586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JS, Kim YH, Anderson AJ, Kim YC. The sensor kinase GacS negatively regulates flagellar formation and motility in a biocontrol bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Plant Pathol J. 2014a;30:215–219. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.11.2013.0109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JS, Kim YH, Park JY, Anderson AJ, Kim YC. The global regulator GacS regulates biofilm formation in Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 differently with carbon source. Can J Microbiol. 2014b;60:133–138. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2013-0736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JH, Ma KC, Ko SJ, Kang BR, Kim IS, Kim YC. Nematicidal activity of nonpathogenic biocontrol bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Curr Microbiol. 2011;62:746–751. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9779-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loper JE, Hassan KA, Mavrodi DV, Davis EW, 2nd, Lim CK, Shaffer BT, Elbourne LD, Stockwell VO, Hartney SL, Breakwell K, Henkels MD, Tetu SG, Rangel LI, Kidarsa TA, Wilson NL, van de Mortel JE, Song C, Blumhagen R, Radune D, Hostetler JB, Brinkac LM, Durkin AS, Kluepfel DA, Wechter WP, Anderson AJ, Kim YC, Pierson LS, 3rd, Pierson EA, Lindow SE, Kobayashi DY, Raaijmakers JM, Weller DM, Thomashow LS, Allen AE, Paulsen IT. Comparative genomics of plant-associated Pseudomonas spp.: insights into diversity and inheritance of traits involved in multitrophic interactions. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CD, Kim YC, Anderson AJ. Cloning and mutational analysis of the gene for the stationary-phase inducible catalase (catC) from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:5241–5245. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.16.5241-5245.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SA, Kim JS, Han SH, Park JY, Dimkpa C, Edlund C, Anderson AJ, Kim YC. The GacS-regulated sigma factor RpoS governs production of several factors involved in biocontrol activity of the rhizobium Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Can J Microbiol. 2013a;59:556–562. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2013-0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SA, Kim JS, Park JY, Han SH, Dimkpa C, Anderson AJ, Kim YC. The RpoS sigma factor negatively regulates production of IAA and siderophore in a biocontrol rhizobacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Plant Pathol J. 2013b;29:323–329. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.01.2013.0013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park JY, Oh SA, Anderson AJ, Neiswender J, Kim JC, Kim YC. Production of the antifungal compounds phenazine and pyrrolnitrin from Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 is differentially regulated by glucose. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2011;52:532–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaijmakers JM, Vlami M, de Souza JT. Antibiotic production by bacterial biocontrol agents. Anton Leeuw Int J G. 2002;81:537–547. doi: 10.1023/a:1020501420831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selin C, Fernando WG, de Kievit T. The PhzI/PhzR quorum-sensing system is required for pyrrolnitrin and phenazine production, and exhibits cross-regulation with RpoS in Pseudomonas chlororaphis PA23. Microbiol. 2012;158:896–907. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.054254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Lee SH, Seeve C, Yu JM, Pierson LS, 3rd, Pierson EA. Roles of the Gac-Rsm pathway in the regulation of phenazine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas chlororaphis 30–84. MicrobiologyOpen. 2013;2:505–524. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel AK, Liew J, Kwon T, Marcotte EM, Whiteley M. Role of Pseuomonas aeruginosa peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane proteins in vesicle formation. J Bacteriol. 2013;195:213–219. doi: 10.1128/JB.01253-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuccotti S, Zanardi D, Rosano C, Sturla L, Tonetti M, Bolognesi M. Kinetic and crystallographic analyses support a sequential-ordered Bi Bi catalytic mechanism for Escherichia coli glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 2001;313:831–843. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]