Abstract
Recent perspectives forecast a new paradigm for future “third generation” vaccines based on commonalities found in diverse pathogens or convergent immune defenses to such pathogens. For Staphylococcus aureus, recurring infections and a limited success of vaccines containing S. aureus antigens imply that native antigens induce immune responses insufficient for optimal efficacy. These perspectives exemplify the need to apply novel vaccine strategies to high-priority pathogens. One such approach can be termed convergent immunity, where antigens from non-target organisms that contain epitope homologs found in the target organism are applied in vaccines. This approach aims to evoke atypical immune defenses via synergistic processes that (1) afford protective efficacy; (2) target an epitope from one organism that contributes to protective immunity against another; (3) cross-protect against multiple pathogens occupying a common anatomic or immunological niche; and/or (4) overcome immune subversion or avoidance strategies of target pathogens. Thus, convergent immunity has a potential to promote protective efficacy not usually elicited by native antigens from a target pathogen. Variations of this concept have been mainstays in the history of viral and bacterial vaccine development. A more far-reaching example is the pre-clinical evidence that specific fungal antigens can induce cross-kingdom protection against bacterial pathogens. This trans-kingdom protection has been demonstrated in pre-clinical studies of the recombinant Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence 3 protein (rAls3) where it was shown that a vaccine containing rAls3 provides homologous protection against C. albicans, heterologous protection against several other Candida species, and convergent protection against several strains of S. aureus. Convergent immunity reflects an intriguing new approach to designing and developing vaccine antigens and is considered here in the context of vaccines to target S. aureus.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, vaccines, NDV-3, Als3, convergent immunity, convergent antigen
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus infections are ubiquitous, potentially life-threatening, and a rising public health issue (1–3). On an individual basis, skin and skin structure infections (SSSI) due to S. aureus are among the most frequent of clinical complaints and often complicate unrelated medical procedures (4, 5). Based on 2005 data, over 14 million individuals sought clinical care for SSSI that year in the United States alone (6). More recent data estimate the actual incidence of S. aureus infections to be 600 per 100,000, projecting to exceed 1.5 million SSSI due to S. aureus each year in the United States (7). Of these, approximately 80,000 yield life-threatening invasive infections annually in the U.S (8–10). Moreover, nearly 15% of patients (roughly 12,000 per year) contracting invasive S. aureus succumb to this infection (11). From a broader perspective, the widespread use of antibiotics to treat SSSI is costly and raises the selection pressure favoring increasing drug resistance (12). Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains are now common agents of community-based outbreaks (1, 3, 13). Thus, despite a diminishment in MRSA infections in adults in recent years (9), the incidence of invasive infections due to MRSA remains unacceptably high. In contrast to adults, no significant reduction in healthcare-associated MRSA infections has been observed in children (14). To the contrary, populations vulnerable to S. aureus infections extend beyond the immune compromised, and increasingly include otherwise healthy populations for which no endogenous risk factors have been identified (15, 16).
Beyond SSSI, invasive infections due to S. aureus are life-threatening and increasingly impervious to even the most modern antibiotics. Infections of skin and skin structure, along with mucocutaneous colonization burden also impose significantly greater risk of invasive infections. Compared to non-carriers, elderly men with high-burden of MRSA nasal colonization develop infections at a fourfold greater frequency than non-colonized individuals (17). In addition, greater burden of skin and mucosal colonization imparts a greater risk for long-term readmission and mortality in MRSA-colonized veterans (18). Moreover, a history of MRSA-positive clinical culture is a significant positive predictor of risk for community-onset invasive MRSA infection following hospital discharge (19). Further, high density nasal colonization by MRSA also increases the risk of invasive disease (20). The incidence of invasive community-acquired MRSA infections in children increased significantly from 2005 to 2010 (14).
From these perspectives, vaccine-mediated protection against S. aureus disease overall, and MRSA infections in particular, holds promise to address significant unmet patient needs, leading to significant public health benefit. Beyond mitigating SSSI, vaccines that reduce nasal or mucocutaneous burden of MRSA are also likely to reduce the risk of life-threatening invasive infections. In addition, use of effective vaccines has the potential to enhance antibiotic efficacy or mitigate resistance, by reducing overall use and allowing more selective application of these drugs. Thus, efficacious vaccines targeting S. aureus are urgently needed.
Insights from Natural Host Defense Against S. aureus
A primary factor likely resulting in limited success to date in development of an efficacious vaccine against S. aureus is an incomplete understanding of key host-defense mechanisms responsible for natural protective immunity. Immunologic determinants relevant to host defense against S. aureus infection may be organized into recognition, regulation, or effector systems. Optimization of these systems, individually and synergistically, is necessary for efficacy in novel vaccines targeting this organism.
Mediation of immune recognition
Pattern recognition receptors [PRRs; e.g., toll-like receptors (TLRs) or nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain like receptors (NLRs)] and their ligation by cognate pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) trigger specific signal transduction pathways. These circuitries include myeloid differentiation factor-88 (MyD88), IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), inhibitor of κB kinase (IκBK), and nuclear factor κB (NFκB) activation cascades. Their activation yields up-regulation of host-defense peptide and cytokine expression (21–24). Deficient TLR-mediated responses (25) emphasize the importance of these circuits in rapid defense against S. aureus infection. Immune dysfunctions that render patients at increased risk of S. aureus infection (26–28) include deficient TLR or TLR-mediated response pathways [e.g., MyD88, IRAK-4, IL-1R (21, 25, 27)], and dysfunctions in IL-1β induction (29, 30). Insightful reviews of these topics can be found elsewhere (31–33).
Immune regulation
In 2008, Renner et al. (27) identified a dominant polymorphism in the gene encoding signal transduction/activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) that was associated with recurring infections due to S. aureus or other opportunistic pathogens. Because STAT3 is key to the differentiation of Th17-polarized T cells, this condition is associated with recurring infections often observed in Job’s Syndrome (also called Hyper-IgE syndrome or Buckley Syndrome). In response to IL-6 and TGFβ or IL-23 elaborated by antigen-presenting cells (APC), Janus-activated kinase-2 (JAK2) phosphorylates and activates STAT3. In turn, the phosphorylated STAT3 (STAT3P) activates the transcription factor RAR-related orphan receptor γτ (RORγτ), and to a lesser extent RORγα. These events lead to expression of IL-17A and other members of the Th17 cytokine circuitry, including IL-22. We and other groups have demonstrated that the IL-17 pathway (IL-17A, IL-22, host-defense peptides) is of particular relevance to immune defense against S. aureus infection. Interestingly, αβ and γδ CD4+ T cells may contribute differently to induce the Th17 pathway in distinct tissue contexts (34, 35). Excellent reviews of this concept can be found elsewhere (31, 36) As discussed below, it is important to note that both IL-17 and IL-22 significantly influence the function of innate immune effector systems against S. aureus, including neutrophils and host-defense peptides.
Resident γδ T cells are key to early containment and clearance of S. aureus at the interface of skin and mucosa (37). However, γδ T cells do not appear to induce IL-22 in relation to the IL-17 pathway in mouse models (38), and mice deficient in αβ T cells have dysfunctional abscess formation in S. aureus wound infection models (39). Moreover, IL-17A/F deficiency predisposes to spontaneous dermatologic infection, but not hematogenous infection by S. aureus in some mouse models (40). Thus, vaccines that induce protective CD4+ αβ and γδ T cell-mediated responses may optimize protective efficacy against S. aureus SSSI.
In addition to the Th17 response, a Th1 response may also play a role in defense against infection due to S. aureus. Our laboratory and others have shown that interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is actively induced in response to S. aureus infection (41). Further, Cho et al. showed that IL-1β is of special importance to effective host defense of the skin (42). Paralleling the activation of STAT3 in Th17 responses, Th1 responses are mediated by STAT4 activation in response to signaling by IFN-γ and IL-12. Phosphorylation of STAT4, largely via JAK1, induces expression of T-box protein expressed in T cells (Tbet), which then promotes interferon regulatory factor-9 (IRF9) to up-regulate type I (IFN-α and β) and type II (IFN-γ) interferons. Although the role of type I interferons in host defense against S. aureus is not well understood, IFN-γ is likely to play a role in cell-mediated immunity against this and other opportunistic pathogens. It is notable that infections due to S. aureus are significantly more common in individuals affected by HIV than in HIV-negative populations. This relationship supports the importance of cell-mediated adaptive immunity and T-cell regulation in effective host defense against this pathogen. Interestingly, in some models, neutralization of IFN-γ may actually enhance the host defense against recurrent S. aureus skin infection (43), potentially by de-repression of Th17 pathways.
It should also be emphasized that natural infection caused by S. aureus elicits a robust antibody response in immune competent individuals. In contrast to the Th17 or Th1 paradigms, a Th2 response plays a key role in the induction of antibodies in response to S. aureus. In this circuit, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 are the signature cytokines for CD4+ T-cell polarization to a Th2 response. The signaling pathway that mediates this response involves STAT6 activation of the GATA3 transcription factor (44). Importantly, colonization in the absence of frank infection may be insufficient to induce high Ab levels. Alternatively, even if baseline Ab levels are elevated in healthy individuals as a result of colonization, infection due to S. aureus induces a further rapid increase in Ab levels. Thus, the exposure and response of B cells to staphylococcal antigens is an acute aspect of the adaptive immune response to this organism. As will be discussed below, whether a protective or durable anamnestic response occurs in response to S. aureus infection remains a central question in natural infection, and is a key goal of novel S. aureus vaccines.
Immune effectors
In healthy individuals, S. aureus colonizes human skin and mucosa without causing overt disease, and without inflammatory host defenses. This fact suggests differences in fundamental aspects of host defense against S. aureus colonization versus invasion. Moreover, specific molecular or cellular effectors, and their coordination, likely differ in distinct tissues (e.g., mucocutaneous versus hematogenous), or in different stages of infection (acute versus chronic). Mindful of these caveats, effectors involved in anti-staphylococcal host defense of relevance to potential mechanisms of protective vaccines are reviewed below.
Mechanochemical barrier
Initial insights from the Human Microbiome Project (NIH) have affirmed that S. aureus is a predominant and common member of the human microbiome (45). The structure and chemical composition of intact skin are key features that normally ward off S. aureus opportunistic infection. From the continuous exfoliation of the epidermis, to its antimicrobial chemistry as reflected in sebum, salt, and pH conditions shaped by sebaceous, eccrine, and apocrine glands, the human skin imposes a mechanochemical barrier to S. aureus invasion (46). Additionally, ceramides, squalene, and wax esters likely contribute to cutaneous defense against S. aureus (47). Such factors have not been traditionally considered accessible to vaccines or anti-infective immunotherapies.
Host-defense peptides
Human skin and mucosa are perfused with a variety of host-defense peptides. Principal structural classes are the defensins, cathelicidins, and other molecules including S100A7 (psoriacin) and dermcidin (48). Prototypic α-defensin, β-defensin, and cathelicidin class molecules are human neutrophil peptide-1 (hNP-1), β-defensin-2 (hβD-2), and LL-37, respectively. Microbicidal chemokines (kinocidins) derived from platelets and other cells also defend against S. aureus and other infections (24, 49). The regulation, structural biology, and mechanisms of action of these and related molecules are the topics of other reviews (50–52). New evidence is emerging that host-defense peptides may be inducible by vaccination in protection against S. aureus SSSI (see below).
Humoral immunity
B lymphocytes and antibodies may contribute to protection against mucocutaneous colonization or invasive infection caused by S. aureus. First, functional antibodies can promote opsonophagocytosis (FcγRII equivalent receptor-mediated), neutralize extracellular virulence determinants (e.g., secreted exotoxins), or potentiate targeted complement fixation (e.g., IgG dimers or IgM via the classical pathway). For example, the anti-Panton–Valentine leukocidin antibody (anti-LukAB) emerges in transition from acute-phase to convalescent sera in children with invasive S. aureus infection (53). Second, B cells are now increasingly recognized as integral to antigen presentation (54, 55) and cytokine conditioning of T-cell responses (56). It should also be recognized that generation of IgG antibody subclasses 1 or 3 (IgG1 or IgG3) in humans is dependent upon CD4+ T-cell activation of B-cell subclass switching. Thus, such antibody responses are subordinate to T-cell regulation, emphasizing the essential roles of T cells in humoral and cell-mediated immunity to S. aureus.
The potential risks of inducing opsonophagocytic antibodies in patients having overt or cryptic granulocyte dysfunctions should also be recognized. S. aureus is a facultative intracellular pathogen capable of at least temporary survival in the harsh phagolysosome of the neutrophil. Thus, even if antibody targeting S. aureus is capable of promoting opsonophagocytosis in vitro, unless the granulocyte can rapidly kill the organism, opsonization could simply facilitate phagocytosis for immune avoidance and cryptic dissemination. This mechanism of immune subversion by S. aureus has been hypothesized in P47phox null mice by Pancari et al. (57).
Complement
Complement cascades afford molecular bridges between innate and adaptive immunity. Lectin and alternative-pathway complement fixation can both occur in response to PAMPs such as teichoic acid and peptidoglycan on the S. aureus surface (58). By comparison, classical complement fixation leverages the humoral response to guide complement targeting of S. aureus. Here, the C1qrs complex targets antigen-specific antibody on the organism surface. Complement fixation also yields opsonins such as C3b and C5b, which decorate the organism for opsonophagocytosis by professional leukocytes. Furthermore, anaphylatoxin products of complement protein cleavage (e.g., C3a and C5a) support leukocyte chemotaxis to sites of S. aureus infection. Activation of the antimicrobial mechanisms of these cells (reactive oxygen species, hypohalous reactants, cleavage of antimicrobial peptides, granule mobilization, etc.) occurs en route to sites of infection (59).
Neutrophils and other host cells
Neutrophils (or polymorphonuclear leukocytes) represent the predominant cellular effectors of host-defense against S. aureus. This fact is supported by numerous clinical conditions in which lack of functional neutrophils, or dysfunctions in neutrophils are associated with increased risks of S. aureus infection: (a) neutropenia (60–63); (b) dysfunctions in granulocyte oxidative burst [e.g., chronic granulomatous disease; (64, 65)]; (c) dysfunctions in Th17 polarization, which recruits/activates neutrophils [e.g., Job Syndrome; (66, 67)]; and (d) dysfunctions in leukocyte adhesion molecule expression or function as required for neutrophil margination and diapedesis to target sites of infection [e.g., LAD-1 and -2; (68, 69)]. Less clear are the roles of cells in protection against S. aureus infection. These include the monocyte/macrophage lineage, natural killer (NK), and perhaps even CD8+ T cells. For example, up to 50% of S. aureus organisms that are phagocytized by neutrophils survive intracellularly. Normally, macrophages in-turn efferocytose S. aureus-containing neutrophils, thereby enabling effective clearance. However, intra-neutrophil S. aureus appear to cause neutrophil up-regulation of CD47, preventing their effective efferocytosis by macrophages, thus facilitating survival and potential metastatic seeding of S. aureus (70). Efficacious vaccines will need to overcome such S. aureus survival mechanisms.
Other effectors
The direct antimicrobial activities of kinocidins (microbicidal chemokines) are likely to play important roles in defense against S. aureus infection (49). For example, through IL-12 elaboration, dendritic cells appear to induce and coordinate CXC, CC, and other kinocidins (71). Recent evidence has also uncovered previously unforeseen relationships that offer insights into host-defense against S. aureus on one hand, and polymicrobial host–pathogen relationships on another. For example, infection with influenza suppresses NADPH oxidase-dependent opsonophagocytic clearance of bacteria by macrophages and neutrophils in mouse models (72). In turn, susceptibility to secondary MRSA infection is significantly increased. On another front, invariant natural killer/T-cell (iNKT) receptor-expressing cells can produce IL-17A independently of IL-6 co-stimulation. Hence, iNKT cells also may promote protective inflammatory responses to S. aureus infection. Further, IL-1 and IL-23 elaboration is necessary for sustained IL-17A/F and IL-22 generation by iNKT cells in response to S. aureus (73). Moreover, IL-1 and IL-23 generated by PAMP-stimulated dendritic cells can also induce in vitro IL-1 and IL-23 secretion from NK1.1− cells, which are iNKT cells principally found in the skin and peripheral cutaneous lymph nodes. In parallel, CD8+ T cell-mediated clearance of S. aureus-infected host cells has been reported in a murine model (74). Mice exposed to heat-killed S. aureus generate robust CD8+ T-cell responses when CD40 ligand is co-stimulated with specific antibody, yielding protective efficacy in a mastitis model. Such examples suggest that historically unappreciated molecules and cells are likely integral to host defense against S. aureus, and may be integral to creating efficacious vaccines.
The Challenge of Normal Flora in Vaccine Development
Co-evolution with mammals has uniquely enabled S. aureus to occupy a specialized niche as a part of the normal bacterial microbiota (75). Thus, the human immune system is faced with a balancing act: hold the organism at bay, without evoking unnecessary inflammation. Yet, why S. aureus transitions from a harmless commensal to an opportunistic pathogen remains a mystery in many cases? For example, acquired deficits in host-defense mechanisms (e.g., neutropenia) are clearly associated with increased risk of invasive S. aureus infection. However, more subtle or even cryptic conditions, alone or in combination, may also render a host at increased risk of infection. Further, certain virulence factors of S. aureus may correlate with an increased propensity to cause an opportunistic infection, as might interactions with other normal flora. Some of the factors that could mitigate such an opportunistic infection are discussed below.
Influence of other vaccines on S. aureus colonization
Vaccines targeted to pathogens other than S. aureus have been observed to produce significant increases in colonization by S. aureus in vaccine recipients. Specifically, use of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, which reduces both nasopharyngeal colonization as well as disease due to serotypes included in the vaccine, can increase the frequency of S. aureus colonization in those receiving the vaccine versus unvaccinated controls (10.1 versus 5.0%, respectively) (76). Additionally, the use of live attenuated influenza vaccine has been shown to increase the carriage density of and duration of colonization by S. aureus, much like what has been observed with wild-type influenza virus (77). This phenomenon is most likely due to a reestablishment of the equilibrium of the microbiome, but could also be due to a deviation of the immunological profile of some individuals such that they become better hosts for S. aureus.
Impact of microbiome on immune polarization
The impact of the human microbiome on the immunological posture of individuals and their response to vaccines is a relatively new field. Explorations such as those by Eloe-Fadrosh et al. (78) provide insight that the microbiome can greatly influence polarization of the immune system. In their particular study, individuals harboring a more diverse and complex microbiome community exhibited a multiphasic cell-mediated immune response to an oral typhoid vaccine. In contrast, Ferreira et al. (79) speculated that the more diverse microbiome of individuals from developing countries may account for the suppressed immune response to several vaccines as is observed relative to more developed countries.
Observations that commensal bacterial and commensal pathogens leave an immunological “footprint” in the form of detectable humoral and cell-mediated immune response to some surface proteins are common [e.g., Ref. (80–82)] and not altogether unexpected. Combined, these observations suggest that the mere presence of S. aureus in the microbiome should not be expected to be sufficient to explain or predict the readiness of a given immune system to respond to a vaccine targeting S. aureus.
Impact of immunization on microbiome
It is well established that vaccines targeting select serotypes of bacterial pathogens (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis) are very successful at reducing or eliminating serotypes that are represented in the vaccine. However, it is also evident that such vaccination can result in serotype replacement with non-vaccine serotypes of the same or related organisms [e.g., Ref. (83, 84)]. Additionally, potential synergistic relationships between specific commensal pathogens, such as observed between S. aureus and Candida albicans (85), C. albicans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (86), and P. aeruginosa and S. aureus (87). These relationships suggest that altering the microbiome composition via immunization may have broader impact by creating a less favorable environment for synergistic pathogens.
Experience in prior use of native S. aureus antigens
To date, there have been at least 19 S. aureus vaccine clinical studies conducted in the US (see Table 1) that have evaluated over 20 different antigens (see Table 2). Although much of the data remain proprietary, all of these antigens had to have been successfully evaluated in one or more animal challenge studies and shown to be safe and immunogenic when evaluated in pre-clinical toxicity studies to be considered for clinical evaluation. Thus, insufficient immune response in humans may be one factor that has limited the number of these vaccine candidates advancing to Phase 2 studies. To date, no S. aureus vaccines have been demonstrated to have efficacy for any specific disease indication in humans. For example, two of the vaccines that were advanced to Phase 2b/3 studies did not demonstrate efficacy (88, 89) and one of those, using the IsdB antigen, revealed potentially significant safety issues in cardiothoracic surgery patients (89). All of these antigens induce antibodies in human vaccines, many of which have been shown to have functional activity against S. aureus isolates. Furthermore, several of these vaccines have been demonstrated to induce T-cell responses, including IL-17A and IFN-γ. Even so, there is still no clear evidence for or consensus on surrogate markers of protection against any S. aureus indication. Recently, a tetravalent S. aureus vaccine was advanced into a Phase 2/3 clinical trial (NCT01643941; see Table 1). Whether this vaccine will be more efficacious than its predecessors remains to be determined.
Table 1.
Vaccines containing S. aureus antigens that have been evaluated in human clinical trials as reported on clinicaltrials.gov.
| Sponsor | Vaccine | Antigens | Clinicaltrials.gov identifier | Clinical Study Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nabi | StaphVAXa | CP8 conjugate, CP5 conjugate | NCT00071214 | 3 |
| NCT00130260 | 3 | |||
| NCT00211900 | 3 | |||
| NCT00211913 | 3 | |||
| NCT00211926 | 3 | |||
| NCT00211965 | 3 | |||
| NCT00211991 | 3 | |||
| GSK | GSK2392 | 4-component | NCT01160172 | 1 |
| Pfizer | SA3Ag | CP8 conjugate, CP5 conjugate, clumping factor A | NCT01018641 | 1 |
| SA4Ag | Same as SA3Ag plus manganese transporter C | NCT01364571 | 1 | |
| SA4Ag and SA3Ag | NCT01643941 | 1, 2 | ||
| Merck | V710a | Iron surface determinant B | NCT00303069 | 1 |
| NCT01324440 | 1 | |||
| NCT00735839 | 1 | |||
| NCT00822757 | 1 | |||
| NCT00572910 | 2 | |||
| NCT00518687 | 2, 3 | |||
| NIAID | STEBvax | Enterotoxin B | NCT00974935 | 1 |
| Uniformed services | Monovalents | Alpha toxin | NCT01011335 | 1, 2 |
| University of the Health Sciences | Panton–Valentine leukocidin toxoid | |||
| Bivalent | Alpha toxin, Panton–Valentine leukocidin toxoid |
aDevelopment terminated.
CP, capsular polysaccharide.
Table 2.
Vaccine antigens targeting S. aureus that have been evaluated in human clinical trials.
| Antigen | Description | Sponsor | Clinical study phase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP8 conjugate CP5 conjugate PVL Hla | CP8 conjugated to rEpA CP5 conjugated to rEpA Panton-Valentine Leukocidin toxoid Alpha hemolysin | GSK | No public disclosure. GSK purchased the Nabi pentavalent S. aureus vaccine (PentaStaph) in 2011 (http://globenewswire.com/news-release/2011/04/27/445328/219830/en/Nabi-Biopharmaceuticals-Completes-Final-PentaStaph-TM-Milestone.html) | |
| SEB | Enterotoxin B | NIAID | (90, 91) | |
| Protein 1 Protein 2 Protein 3 Protein 4 | No public disclosure of the identity of the antigens. | Novartis | 1 | N/A |
| Cbp Clf Fbp Eap | Collagen-binding protein Clumping factor Fibronectin binding protein Extracellular adherence protein | Vaccine Research International | http://www.vri.org.uk/PhaseITrial.pdf | |
| IsdB | Iron surface determinant B | Mercka | (82, 89) | |
| CP5 conjugate | CP5 conjugated to CRM197 | Pfizer | 1, 2 | (92) |
| CP8 conjugate | CP8 conjugated to CRM197 | |||
| Mntc | Manganese transporter C | |||
| ClfA | Clumping factor A | |||
| rAT rLukS-PV | Alpha hemolysin Panton-Valentine Leukocidin toxoid | Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences | http://www.empr.com/bivalent-s-aureus-vaccine-demonstrates-good-immunogenicity-and-neutralizing-activity/article/314713/ | |
| CP8 conjugate | CP8 conjugated to rEpA | Nabia | 1, 2, 3 | (93, 94) |
| CP5 conjugate | CP5 conjugated to rEpA | |||
| CP336 conjugate | CP336 conjugated to rEpA |
aDevelopment terminated.
CP, capsular polysaccharide; rEpA, recombinant P. aeruginosa exoprotein A; CRM197, cross-reactive material 197; a non-toxic recombinant variant of diphtheria toxin (Corynebacterium diphtheriae).
The Paradox of Recurring S. aureus Infection
A mystery regarding human infections caused by S. aureus is the propensity of this organism to cause recurring infections due to poor efficacy of anamnestic response in a significant proportion of the overall population. There are several potential and non-exclusive explanations for this observation.
Immune subversion
Staphylococcus aureus is known to have a wide array of virulence factors and immune subversion mechanisms. These strategies include dysregulating T-cell responses via superantigens, disabling host-defense peptides via protease elaboration, avoidance of complement and antibody activities by capsular expression, and suppression of phagocyte chemotaxis and phagocytosis. The specific mechanisms of immune subversion by S. aureus are the topic of other excellent reviews (95–97). Interestingly, Skurnik et al. recently identified natural antibodies in normal human sera that inhibit antibody targeting the S. aureus capsule (98). This observation raises the possibility that anti-idiotypic or other auto-antibodies diminish otherwise protective humoral immunity versus S. aureus. Thus, even if a perfectly appropriate and otherwise efficacious natural immune response were to be induced by a vaccine, it may not be fully or even detectably effective due to direct or indirect immune subversion mediated by S. aureus.
Ineffective anamnestic response
An anamnestic response to infection requires the presence and function of long-term immune memory cells. Relevant to S. aureus infection, mucosal FCRL4+/CD27− B memory cells, as well as lymphoid FCRL4−/CD27+ B memory cells are likely required for sustained or rapidly inducible antibody formation (99). Beyond B cells, CD45RA−/CCR7+ memory T cells in lymph nodes, and CD45RA−/CCR7−effector memory T cells in mucocutaneous settings are believed to contribute to anamnestic responses (100, 101). In recurring infections due to S. aureus, it is likely that such anamnestic response mechanisms are either sub-optimal, or subverted by the pathogen. For example, a recent analysis by Fowler and Proctor (102) posits that antibody is not the primary mechanism of host defense against S. aureus disease. Their review of the literature yielded no causal relationship connecting IgG deficiency or hypogammaglobulinemia with increased propensity for S. aureus infection. Thus, vaccine strategies that solely induce anamnestic humoral responses targeting native antigens face challenges based on natural history of S. aureus infection in humans. In parallel, phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) toxins elaborated by S. aureus may cause dysfunctional antigen presentation by dendritic cells to memory lymphocytes (103). Moreover, S. aureus-induced dysregulation of monocyte responses, along with a decreased central memory CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell response, is associated with invasive infection due to S. aureus in pediatric populations (104). From these perspectives, efficacious vaccines targeting S. aureus must, by necessity, enhance anamnestic responses in ways that include cell-mediated mechanisms.
Exploitation of regulatory lymphocytes
In neonates, exposure to S. aureus polarizes naive CD4+ T cells to a FOXP3+/CD25+/CD127Low phenotype, corresponding to a modulated immune response (105). This response likely establishes tolerance to colonization early in life. While such tolerance may prevent a potentially harmful inflammatory response to commensal S. aureus, it may also impair effective immune responses to invasion or re-infection. Similarly, a regulatory subset of CD8+/CD11chiT cells has been shown to emerge in the setting of S. aureus infection (106). This regulatory subset may inhibit appropriate CD4+ T-cell polarization in response to the organism. As above, the capability to overcome exploitation or dysregulation of appropriate immune responses is likely necessary for efficacy in novel vaccines targeting S. aureus.
Applying Convergent Immunity to Innovative S. aureus Vaccines
The perspectives above offer broad insight into the multi-factorial and synergistic quality of natural host defense against S. aureus. It follows that vaccines affording protective efficacy against this organism will necessarily stimulate optimal immune defenses to target the organism and spare host tissues. To this end, a review of recent studies of vaccine development and evaluation in humans and experimental models is helpful.
The principle of convergent immunity
Over the span of evolutionary time, humans and microbes have developed highly specialized systems by which they may exploit and protect themselves from one another. A basic premise of protective immunity is that specific antigens in a given pathogen can induce protective immunity to that pathogen, referred to as homologous immunity, and in many cases can afford protection against various strains of the target pathogen, referred to as heterologous immunity [e.g., Ref. (107, 108)]. In a similar context, microbial pathogens have evolved to exploit specific host features for virulence (e.g., adherence and invasion of host cells to initiate the infection process). Thus, diverse pathogens with similar host targets and niches may use similar or identical pathogenesis strategies. The existence of such similar host–pathogen relationships would logically predict overlaps or even convergence in immunological defenses that may be targeted by convergent vaccine antigens. These antigens are structural and/or functional homologs from organisms that have convergent structural and/or functional characteristics to those found in the target pathogen. These concepts comprise the principle of convergent immunity.
As detailed in the discussion above, the human immune system relies upon an array of PRRs that have been optimized to sense and trigger rapid responses to cognate PAMPs (Figure 1). In turn, immune responses activated by these triggers have evolved to recruit, activate, and regulate immune effectors most capable of neutralizing that particular microbial threat. Even so, co-evolution of normal flora as well as obligate pathogens has allowed microbes the opportunity to evolve specialized strategies by which to avert host defenses, enabling colonization or pathogenesis. Thus, convergent immunogens induce immune processes surmounting those to which microbes have already become adapted or resistant and, in theory, afford protective efficacy.
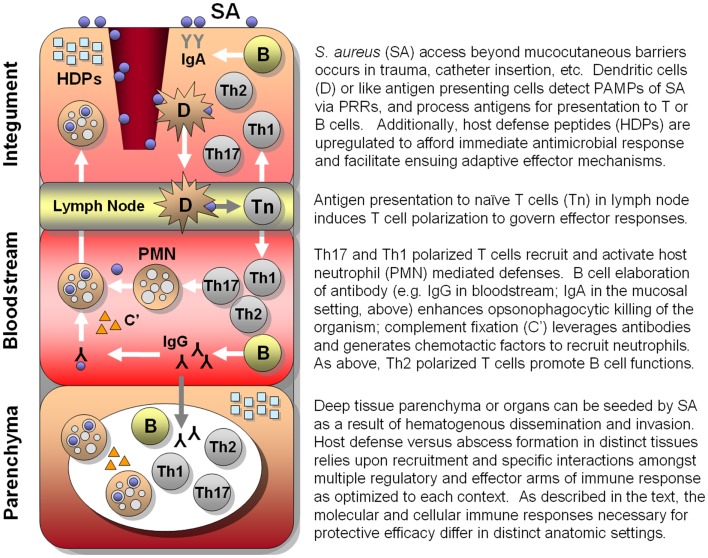
Figure 1.
Hypothesized integrated human immune circuitries in host defense against S. aureus infection. In this illustration, three distinct immunological compartments are shown. Note that lymphocytes, phagocytes, antibody, and molecular effectors (e.g., host-defense peptides, complement, antibody) may be present in each immunological compartment. However, specific profiles and roles of immune effectors may not be identical in each compartment. Vaccines that apply convergent immunity may be designed to optimize those defenses against S. aureus that best protect the host in context of specific compartments.
From this perspective, it follows that the generation of immunogens that stimulate host defenses not typically encountered by a given microbe may have advantages in development of novel vaccines. This concept of convergent immunity is similar to that termed “un-natural” immunity (109, 110). To this end, the era of molecular and cellular technologies has, in effect, accelerated evolution, such that mankind can now rapidly create strategic immunogens that are not known to be present naturally in any microbe. Moreover, novel adjuvants are emerging that provide opportunities to further shape immune responses to convergent antigens. As a result, it may be possible to use convergent immunity strategies to stimulate host defenses that would not be induced otherwise, and which are highly protective against S. aureus and other high-priority pathogens. The following discussion considers key concepts in this respect.
Insights from recent human S. aureus vaccine initiatives
Despite highly meritorious efforts, the development of a licensed, efficacious vaccine or immunotherapy targeting S. aureus has been elusive to date (see above). Multiple variables likely contribute to this situation, reflecting the complex host–pathogen relationship between S. aureus and human beings. Immunological insights from recent carefully designed vaccine clinical trials may aid in considering potentially improved strategies (Table 3). It should also be emphasized that even though efforts to-date have not yielded a licensed S. aureus vaccine, they have greatly contributed to our understanding of basic pathogenesis strategies of this pathogen, and the human immune responses to it. These advances cannot be overstated in terms of their positive contributions to the field and insights into design and development of efficacious vaccines.
Table 3.
Comparison of recent clinical trials of active vaccines and passive antibodies targeting S. aureus disease.
| Developer | Vaccine strategy | Target antigen(s) | Target patient(s) | Immunology | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nabi | Bivalent polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine | Capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8 | Chronic hemodialysis patients | Robust antibody response; durable for greaterthan year | Phase 3: trended but did not statistically reduce incidence of invasive infection (93) |
| Inhibitex | Passive antibody (no adjuvant) | Clumping factor A (ClfA) | Established staphylococcemia; neonatal staphylococcemia | Rapid, durable systemic levels of α−ClfA antibody | Phase 3: trended but did not statistically reduce risk of developing invasive infection (111) |
| Merck | Recombinant protein with or without aluminum hydroxide | Iron surface determinant B (IsdB) siderophore | Cardiothoracic sternotomy patients | Robust antibody response | Phase 2: vaccine potentially associated with serious post-operative complications (89) |
A prominent trend among the approaches exemplified above is an emphasis on robust antibody responses to the target antigen. While it is likely a contributing factor to human protection against the pathogen (43, 112–115), induction of humoral immunity alone may be insufficient to prevent S. aureus infections (116–118). Moreover, the observed efficacy of some vaccines in animal models of S. aureus infection may not entirely recapitulate human responses for several reasons. First, animal models often use adjuvants that are not applicable for use in humans, such as Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA). Such adjuvants may enhance immunity in animals that cannot be generated in humans using other adjuvants. Second, non-human mammals may defend against S. aureus via mechanisms that are not identical to human immunity (119–122). However, recent studies suggest that S. aureus organisms respond to human and other mammalian hosts (e.g., mice) in a nearly identical manner, suggesting consistent targets for vaccines and immune therapies (123, 124). Beyond these considerations, uncertainties in immune defenses, as well as fundamental host-pathogen relationships regarding normal flora status, may present special challenges to the development of an efficacious vaccine targeting S. aureus.
Thus, the experience to date in the development of vaccines targeting native S. aureus immunogens either in single or multi-antigen formats has provided only limited success. Even so, important new information has been gained from the many laudable efforts that have been made toward the development of S. aureus vaccines and immunotherapies (Tables 1–3). From these perspectives, innovative strategies such as vaccines applying convergent immunity that capitalize on emerging insights into efficacious host defense against this organism are needed.
Historical insights into convergent immunity in human vaccines
In the context of vaccine development, “natural” immunity can be defined as inducing an immune response to an antigen that is naturally present in or on the target pathogen. This is the fundamental basis of vaccine development for most of the 200-year history of modern vaccine use, which typically reflects the principles of homologous and/or heterologous immunity (see above). Moreover, aspects of convergent immunity have been important factors in past and present vaccine development. Strategic use of an antigen that is convergent in structure and/or function to that in a target pathogen intends the outcome of altering and enhancing the protective efficacy of the vaccine beyond what can be obtained using the “natural” antigen. This strategy encompasses the use of epitope homologs that can effectively serve as surrogates of those in the target antigen, even though the origins of such homologs may be unrelated to the target pathogen. Specific examples follow, and some of these concepts have also been reviewed elsewhere (109, 125).
Cross-protection between related viral pathogens
Early human trials to develop a vaccine against smallpox were in fact based on the cowpox virus (126). It was similar enough to the human smallpox virus that the immune response to the cowpox virus was sufficient to protect from disease due to the smallpox virus. This is an early example of using convergent immunity to successfully defend against a target pathogen.
Toxoid antigens
A critical evolution in the development of vaccines against specific bacterial pathogens, in particular Corynebacterium diphtheria and Clostridium tetani, was the recognition that disease due to critical toxin(s) could be ameliorated by formaldehyde-treatment or “toxoiding” of a native toxin protein [see Ref. (127)], This process also allows the purified toxoid protein to be used as a direct immunogen rather than having to use antiserum from toxin-tolerized animals. Though the main goal of toxoids has been to abrogate toxin activity, a side-result has been to also create convergent immunogens successful in generating a protective immune response against the target organism.
Attenuated live virus vaccines
Since the early days of viral vaccine development, attenuation of the virulence of the target viral pathogen has been successfully employed to develop vaccines. Polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella zoster are perhaps the most common examples of attenuated viruses used in human vaccines. Though the specific target of the attenuation may not be fully defined, these biological alterations, induced by imposing selection pressures on the virus under non-natural conditions in non-human viral propagation systems. These strategies include propagation in cells lines in which the virus had little or no pathogenic impact or reduced replication temperature, and are often directed to components of viral replication or intercellular translocation machinery, or to key viral immunogens responsible for protective immunity. Live viral vaccines are often attenuated by mutations favored during replication in non-natural hosts (e.g., influenza in embryonated chicken eggs). These permanent mutations make the attenuated viral antigen(s) distinct from those spread through human-to-human transmission. Ultimately, attenuated live virus vaccines ameliorate disease by interfering with the initiation or progression of target viral pathogenesis using immunogens and/or inducing immune responses not normally observed in nature. In addition, such approaches often aid in understanding pathogenesis of the target viral pathogen, and enhancement of immunogenicity to advance novel and more efficacious vaccines. Similar strategies of attenuation have also been used in some live bacterial vaccines, such as the BCG, typhoid, and typhus vaccines.
Consensus sequences in multi-clade HIV vaccines
Early in the efforts to develop a vaccine that would prevent HIV/AIDS, it was recognized that there were many clades of HIV and sequence variants of immunogens within each clade. One solution that has been attempted is the generation of “consensus sequence” protein antigens that would not align exactly with any one viral clade, but perhaps represent many or all [e.g., Ref. (128, 129)]. Though a clever concept, this approach has not yet resulted in protection against HIV disease in clinical trials required for evaluation. It remains to be seen whether such approaches will outpace more conventional strategies and lead to the efficacy and successful licensing of HIV/AIDS vaccines. That achievement will set the stage to evaluate the utility of natural versus convergent immunity in this vaccine target. In more recent times, this same concept is being adopted in the development of new influenza vaccines (130).
Use of recombinant protein antigens
Recombinant proteins can, but may not, mirror the composition and higher-order structure of their native template counterparts (see Designing Convergent Immunogens, below). Even though recombinant protein immunogens are intended to mimic a specific native protein, there are often modifications associated with the expression construct and/or manufacturing process to enhance productivity, optimize folding, reduce aggregation, or influence other molecular features. Such changes, the result of intentional or unintentional modifications in the new protein antigen, can produce antigens that are structurally and/or immunologically distinct from those found in the native antigen in the target pathogen. A simple example is found in the Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence 3 (Als3) protein, which contains a six-His affinity tag to facilitate purification, yet is successful in stimulating a robust immune response in humans, including those who have been primed by natural exposure to C. albicans (81). However, as detailed below, because of intentional truncation and expression in a heterologous organism (rendering a non-native structure and glycosylation pattern), the Als3 antigen is no longer native to C. albicans. Thus, beyond modifications of a native antigen, using such an immunogen to protect against an organism (e.g., S. aureus) other than its original source by exploiting convergent antigen(s) of the target pathogen illustrates one application of convergent immunity, i.e., cross-kingdom convergent immunity.
Cross-protection of polysaccharide serotypes in pneumococcal vaccines
The concept of convergent immunogens is not limited to protein antigens. A parallel approach is well established for bacterial capsular polysaccharide antigens. For example, there is some evidence indicating that serotype 6B conjugate vaccine can cross-protect against serotype 6A (131) and that serotype 9V conjugate vaccine can be effective in protecting against serotype 9A infection (132). However, cross-protection between serotypes within the same pneumococcal serogroup remains controversial. Likewise, previous speculation that serotype 19F conjugate vaccine can provide cross-protection against serotype 19A is still controversial (133, 134), with epidemiological data suggesting that the inclusion of a serotype 19A conjugate component in the second-generation pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is beneficial (135).
Deleterious immunity
Deleterious immunological consequences may also occur due to unintended alterations of key immunogenic epitopes, as in the development of a vaccine targeting respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). In one case, a formalin-inactivated viral vaccine was formulated with an aluminum hydroxide suspension, commonly used as an adjuvant for bacterial vaccines. This vaccine, evaluated in infants and children, led to an immune response that actually exacerbated the viral infection rather than mitigated it; 80% of trial participants had to be hospitalized and two infants died (136). The specific cause of this vaccine failure is still debated, but further work on this important vaccine target was delayed by more than 30 years before new vaccine candidates were pursued in clinical trials.
Central dogma of conventional vaccinology is to use native antigen(s) from the target organism to induce protective immune responses against that organism. By comparison, convergent immunity strategically leverages non-native antigen homologs (including from organisms other than the target pathogen) to drive antigen-restricted immune responses against a target organism. The above examples illustrate how convergent immunity applies non-native antigen homologs to induce vaccine efficacy. Variations of this theme have been employed throughout the history of human vaccine development. Many attenuated live virus, polysaccharide, and recombinant protein vaccines, where no intentional manipulation of native antigen primary structure or composition has occurred, can be considered native antigens. Further, the increasing use of chemical modification of antigens (e.g., toxoids, conjugation, etc.) or protein sequence alteration (e.g., fusion proteins or truncated protein antigens) in licensed vaccines shows the successful application of customized native antigens in human vaccines. However, convergent immunity takes this concept one step further: use of a native or customized native antigen relative to one pathogen, and apply it to antigen-restricted protection targeting a different pathogen containing structurally and/or functionally homologous antigen(s). Thus, native immunity and convergent immunity are distinct but complementary forces in the design of efficacious vaccines. With advances in technology and understanding of protective immune responses, convergent immunity will almost certainly be leveraged in some form for future vaccine development, including for development of vaccines targeting S. aureus.
Insights from use of convergent antigens in S. aureus vaccine studies
In 2008, it was shown that a recombinant protein based on the N-terminal region of a surface antigen, agglutinin-like sequence 3 protein from C. albicans (rAls3), which had previously been shown to be an adhesin (137) and an invasin (138), could protect mice from intravenous challenge with S. aureus (41). This predicted outcome was based on the discovery that Als3 had a high degree of structural homology with two surface proteins on S. aureus, clumping factor A (Clfa) and collagen-binding protein (Cna) (139). Moreover, the N-terminus of Als3 and other Als family members have close structural homology to adhesins and invasins from a number of microbial pathogens, including Yersinia spp. and other Gram-negative organisms, and hemagglutinin from influenza virus strains. Studies using rAls3 formulated with aluminum hydroxide (referred to as NDV-3; see below) and have now established a strong foundation for pursuing this antigen as an example of applying convergent immunity to contribute to the development of a successful S. aureus vaccine.
Murine bacteremia models
Prior studies from our group have demonstrated that immunization with the C. albicans rAls3 antigen induces protective efficacy against MRSA bacteremia in Balb/C mice (41). Further, in the specific conditions of this model, immunization with rAls3 evokes protective efficacy against hematogenously disseminated S. aureus infection in B cell but not T-cell knockout mice. Supporting a key role for T cells, non-immunized animals were protected by adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cells from NDV-3 immunized mice but not by transfer of B220+ B cells or serum from NDV-3 immunized mice. Further, NDV-3 protection against MRSA bacteremia was abrogated in IL-17A null mice (140). Collectively, this body of evidence is consistent with the emerging immunobiology of natural S. aureus antigens, in which Th17 pathway constituents are involved in defense against S. aureus and C. albicans in mice.
Murine skin/skin structure infection models
Recently, we evaluated the efficacy and immunological mechanisms of NDV-3 in mouse SSSI due to MRSA (141). Compared to adjuvant alone, NDV-3 immunization reduced abscess progression, severity, and MRSA density in skin following challenge by a variety of strains. Moreover, vaccination by NDV-3 mitigated hematogenous dissemination to kidneys. Corresponding to this, protective efficacy NDV-3 induced increases in CD3+ T-cell and neutrophil infiltration, and IL-17A, IL-22, and host-defense peptide expression in local settings of SSSI abscesses. These novel findings demonstrate that NDV-3 efficacy against MRSA in SSSI involves a robust and complementary response integrating innate and adaptive immune mechanisms.
Bovine mastitis models
Important insights regarding convergent antigen targeting S. aureus have also derived from recent efforts to control bovine mastitis. For example, Festa et al. used the domesticated tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum) to express the S. aureus virulence factor extracellular fibrinogen binding protein (Efb) as a vaccine immunogen (142). Expression of this bacterial antigen in the context of plant mechanisms of protein synthesis yields an immunogen that is homologous to the natural antigen. Mice orally immunized with this product have antigen-specific immune responses, which are likely discernable from those induced by the native bacterial antigen. The immune responses to native antigens, such as S. aureus whole cell and lysate preparations, have also been modified by novel means such as formulation with the ISCOM matrix adjuvant (143). This latter adjuvant has been reported to induce higher levels of specific antibody, as compared to aluminum hydroxide adjuvant (144). This suggests that an adjuvant can induce/enhance a non-natural response to a natural antigen. More detailed studies are needed to characterize the similarities and differences in immune response to this and other convergent antigens, as compared to those observed using the corresponding native antigens.
Human vaccination
Evidence for human immune responses to NDV-3 that parallel those in the above mouse models come from human clinical trials evaluating the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of NDV-3 versus saline placebo (81). NDV-3 formulations containing either 30 or 300 μg rAls3 were safe, well-tolerated, and achieved 100% seroconversion. Peak anti-rAls3 IgGtotal and IgA1 antibody levels were detected within 14 days of receiving a single dose of vaccine. Moreover, a single dose of NDV-3 resulted in IL-17A and IFN-γ production from Als3 peptide-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in the majority of vaccinated subjects within 7–28 days of vaccination. Seven days following a second dose of vaccine at 6 months post-initial vaccination, a modest increase was seen in anti-rAls3 IgGtotal and IgA1, essentially recapitulating the first dose antibody response. Importantly, after the second dose, rAls3-specific IFN-γ-producing PBMCs were found in 100% of subjects and Als3-specific IL-17A-producing PBMCs were seen in 50–80% of subjects. Such responses are consistent with the expectation that humans are naturally exposed only to the native Als3 antigen as a consequence of ubiquitous exposure to C. albicans. The robust and durable response to NDV-3 immunization indicates rapid T- and B-cell recognition and response to the NDV-3 immunogen, and an enduring anamnestic response in human subjects. Of special note, the immunological determinants corresponding to protective efficacy elicited by the convergent antigen in NDV-3 in murine models of invasive staphylococcal infection and SSSI (high anti-rAls3 antibody titers and Th17 responses) are also observed in the human immune response to NDV-3. Thus, the present findings support the potential for NDV-3 to prevent or mitigate severity of bacteremia and/or SSSI due to MRSA or MSSA strains in humans. Taken together, this body of evidence supports the continued clinical evaluation of NDV-3 as a vaccine candidate to protect against disease caused by S. aureus and Candida.
It should also be noted that much remains to be learned with respect to the critical difference between non-protective and protective immune responses relative to S. aureus. For example, among the interesting evidence emerging from the field is the finding that human antibody generated in response to the rAls3 antigen appears to enhance human neutrophil opsonophagocytosis of target pathogens (145). In contrast, initial findings from B-cell knock out mouse models of bacteremic S. aureus infection were interpreted to suggest that B cells, and therefore antibody, may have lesser roles in host defense against systemic S. aureus infection in mice (41). The limits of these prior studies should be recognized and not preclude the potential importance of human antibody in optimal host defense against SSSI or bacteremia caused by S. aureus in humans. For example, the importance of subclass switching, acute versus anamnestic responses, as well as anatomically targeted antibody (e.g., mucosal IgA versus circulating IgG) remain to be understood with respect to immunity to S. aureus, particularly as regards this convergent vaccine antigen.
Strategies for convergent vaccine antigens targeting S. aureus
The considerations detailed above provide an integrated framework for exploring novel convergent vaccine antigens targeting S. aureus. In effect, there may be other vaccine antigens that have one or more convergent features related to this target pathogen. These features may be due, if for no other reasons, to natural strain-to-strain variations of indigenous pathogens, and the collateral impacts of antigen production processes. However, potentially more transformative or paradigm-shifting approaches may be applied to develop convergent vaccine antigens that are specifically designed to induce protective immunity for S. aureus indications.
The remainder of this article focuses on strategies for designing and producing such antigens to induce convergent immunity for protection against disease due to S. aureus. The attractiveness of exploring convergent immunity in this respect is enhanced by a lack of success to date with conventional S. aureus-derived antigens. Collectively, these perspectives suggest that novel strategies will be required to address the challenge and increasing impact of multi-drug-resistant S. aureus infections with respect to public health. Although a multi-valent vaccine approach using native antigens may eventually prove successful, applying convergent immunity strategies is anticipated to accelerate or afford unique advantages in developing efficacious S. aureus vaccines or immunotherapies. This view is supported by the historical facts mentioned above and perspectives considered below.
Parallels in host-pathogen evolution
Divergent microorganisms, even across kingdoms, may develop identical or highly similar mechanisms to exploit shared targets or strategies in human hosts. This relationship is illustrated through the convergent structural, functional, and immunological determinants that transcend biological kingdoms in the fungus Candida albicans and the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus:
Candida and Staphylococcus occupy similar anatomical niches in humans (epidermal/mucosal barriers)
Both organisms have evolved similar pathogenesis strategies in humans (mucocutaneous colonization/opportunism/immune evasion/hematogenous dissemination)
These organisms appear to share evolutionary parallels in structural biology [e.g., Als/microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs) are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily]
Immunoglobulin superfamily proteins are functional homologs (e.g., Als3/ClfA and other homologous adhesins and invasins)
C. albicans and S. aureus interactions appear to synergize in pathogenesis [e.g., Ref. (85, 146)]
Immune defenses to both pathogens are alike, relying primarily upon host-defense peptides, induction of Th1 and Th17 pathways, and phagocyte-mediated responses that are likely potentiated by humoral and complement functions.
It follows that the human host almost certainly employs similar immune pathways and mechanisms to control these pathogens. Such relationships afford opportunities to develop innovative immunogenic agents and strategies including broad-spectrum vaccines and convergent immunogens that protect against diseases due to opportunistic pathogens such as S. aureus that are also normal flora.
Cross-kingdom convergent immunogens: Candida and Staphylococcus
We first identified the structural and functional homology among Als proteins of Candida albicans, and microbial surface components of Staphylococcus and other pathogens using computational bioinformatics and molecular modeling (139). Using 1° sequence homology threading and 3-D structural analysis, we found conservation of key sequence motifs and overall conformational homology among Als family proteins. Interestingly, hypervariable regions in sequences of these family members corresponded to diversity among extracellular loop regions. Next, we made the discovery that the N-terminal domains of Als1 and Als3 share unforeseen structural convergence with corresponding regions in S. aureus MSCRAMMS considered virulence factors, including clumping factor A (ClfA) (Figures 2 and 3; Table 4) (139). Similar to Als3 from Candida, such proteins mediate adhesion of S. aureus to host tissues or cells during pathogenesis. Notably, because Als3 and the S. aureus proteins have relatively low overall sequence identity (≤23%), their convergent structures would likely have been missed by sequence alignments alone. Based on this exciting discovery, we predicted that the rAls3 antigen derived from C. albicans could also induce protective immunity against S. aureus (41). We have since demonstrated the rAls3 vaccine to have efficacy in mouse models of hematogenous C. albicans infection (140, 147), vulvovaginal candidiasis (148), disseminated S. aureus infection (140), and in SSSI due to MRSA (141). Of importance, as predicted we found that vaccination with rAls3 induced robust humoral and cell-mediated immunity in these mouse models, paralleling responses observed in humans.
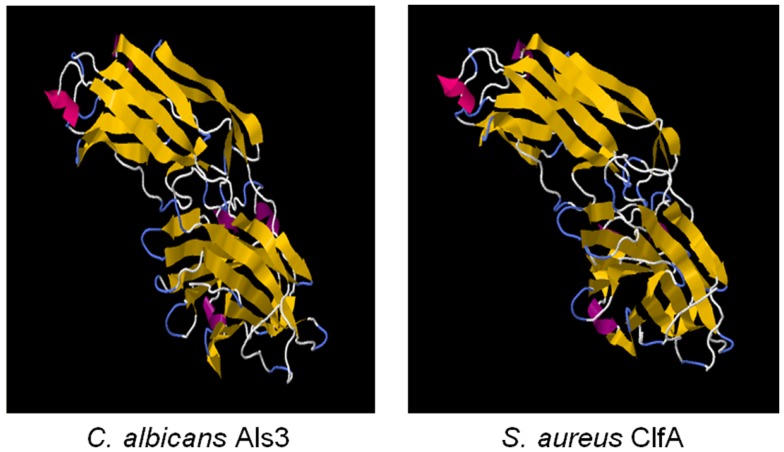
Figure 2.
The cross-kingdom immunogen rAls3 based on structure/function homology is shown. Illustrated here are structurally homologous regions in Als3 (C. albicans adhesin/invasin; model) and ClfA proteins (S. aureus adhesin; deterministic structure analysis). The structural model of the Als3 N-terminus was generated as previously described using sequence threading and molecular dynamics [left; (130, 131)]. The cognate region in a homolog from S. aureus (clumping factor A; ClfA; right) is shown for comparison. Both proteins are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and known virulence determinants. Note the overall highly similar three-dimensional β-barrel domains (gold arrows), interposed by hinge regions.
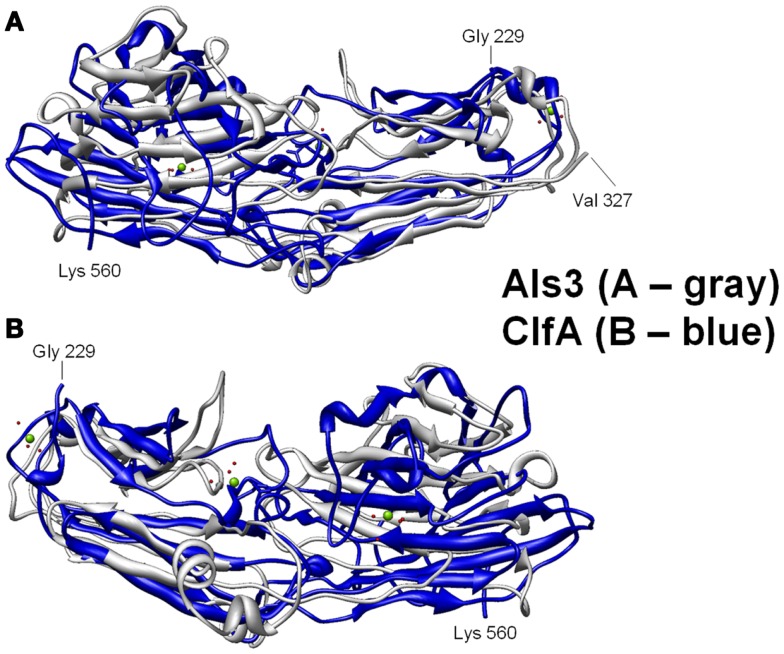
Figure 3.
Structural basis for B-cell epitopes shared in Als3 and ClfA is shown. Combinatorial extension analysis was used to compare the model of Als3 with that of the known structure of ClfA. (A) Front view of the 3-D structural superimposition of homologous structural domains of Als3 (Candida albicans; gray) and ClfA (Staphylococcus aureus; blue); (B) rear view of the same region in protein homologs. The discovery, prediction, and validation of T-cell epitopes in such homologs offers further promise in design of innovative convergent vaccine antigens that induce efficacious cell-mediated immunity. Such striking convergence of linear (T cell) and 3-D (B-cell) epitopes in proteins with analogous functional and immunoprotective properties is consistent with the observation that C. albicans and S. aureus occupy very similar anatomic niches. It follows that humans have likely evolved common pathways of host defense against both pathogens, which may be targeted in novel vaccines that leverage convergent immunity.
Table 4.
Quantitative sequence and three-dimensional structure homology analysis of C. albicans Als3 and selected homologs from S. aureus (139).
| Protein 1 | Protein 2 | SeqID (%) | SeqSIM (%) | RMSD | Z score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Als3 (model) | 1N67 (ClfA) | 9 | 19 | 4.82a | 5.19b |
| Als3 (model) | 1D2P (Cna) | 5 | 23 | 5.58 | 3.29 |
| 1N67 (ClfA) | 1D2P (Cna) | 9 | 20 | 5.44 | 3.50 |
aSignificance threshold <5.0.
bSignificance threshold <3.5.
ClfA, clumping factor A; Cna, collagen-binding protein.
Homology among B-cell epitopes
B-cell receptors identify three-dimensional epitopes, and the rAls3 antigen induces a strong antibody response in mice, primates, and humans. Moreover, antibodies from humans vaccinated with rAls3 promote opsonophagocytic activity in vitro against S. aureus (145). Therefore, the Als3 and homologous S. aureus antigens contain common immunogenic 3-D epitopes that are recognized by B cells. We have evaluated the structural features of such epitopes using complementary approaches. First, immune sera from mice and humans immunized with rAls3 antigen cross react with structural and functional homologs in C. albicans and S. aureus (Ibrahim and Yeaman, communication). Second, 3-D computational threading demonstrated robust conformational homology between Als3 from C. albicans and its functional homologs, for example, clumping factor A (ClfA) and collagen-binding protein A (Cna) of S. aureus (Table 4), as well as related homologs from other human pathogens (139). Third, our combinatorial extension analyses revealed specific conformational epitopes that are consistent with observed cross-reactivity of rAls3 immune sera to C. albicans and S. aureus (Figure 3). Taken together, these findings support the concept that these pathogens share common 3-D epitopes capable of inducing cross-reactive antibodies to both organisms.
Homology among T-cell epitopes
Our observations also pointed to common T-cell epitopes in C. albicans and S. aureus antigens, including: (1) protective efficacy of rAls3 in animal models of C. albicans and S. aureus infection; (2) T-cell response profiles indicating that rAls3 induced robust T-cell responses in both mice and humans; (3) sera predominantly include IgG subclasses that rely on T cells for B-cell activation and antibody production; and (4) overall low sequence identity between Als family proteins of Candida and MSCRAMM proteins of S. aureus suggested that regions where sequence homology did exist would hold insights into T-cell epitope sequences. Because vaccination of mice with rAsl3 induced protection by mechanisms including T-cell responses, we applied bioinformatic mining and computational modeling to predict T-cell epitopes in rAls3. In this process, we predicted an immunodominant epitope to have the sequence WNFPVSSDSFSYT (patent pending). As predicted, this epitope is very similar to the immunodominant human T-cell epitope of Als3 as experimentally validated by Bar et al. (149). Further, this epitope was reported to have 10-fold greater MHC-II peptide-binding groove affinity (264 nM) as compared with any other T-cell epitope, supporting robust predictive accuracy of our immunogen discovery and design approach.
Leveraging convergent immunity for innovative vaccines
As illustrated above, by discovering non-obvious parallels in host–pathogen relationships, and exploiting structurally and functionally convergent antigens, we have generated broad-spectrum vaccines, which induce protective immunity against multiple pathogens. Our work leverages three tenets: (1) host defenses protective against pathogens having antigenic or strategic parallels in pathogenesis may be elicited by convergent vaccine antigens; (2) bioinformatics integrated with computational systems modeling can reveal and optimize cryptic epitope and immunological homologies for use in designing convergent immunogens with efficacy against diverse pathogens; and (3) immune defenses may be optimized to afford protective efficacy in specific anatomic, physiological, immunological, and/or microbiological contexts. These concepts are consistent with innovative approaches, including convergent immunity, as illustrated below.
Designing convergent immunogens
Engineered changes are common in recombinant protein antigens. Small changes in the composition, sequence, and structure between a manufactured vaccine antigen and the native form of that antigen (e.g., amino acid substitution and/or truncations of proteins, modification of glycosylation, attenuation of pathogenic capacity, or replication), have the potential to alter protective immune responses. If such modifications are too moderate, these strategies are likely to be silent or undecipherable to the functional immune response. For purposes of this discussion, we are more concerned with larger changes that are expected to impose distinct differences from the native antigen. Fundamental to the design of antigens is the consideration of primary sequence, post-translational or production process-induced modifications, higher-order structure, and molecular size and/or aggregation state.
Linear sequence epitopes
T lymphocytes detect linear peptide sequence epitopes presented by APC in the context of MHC class I (e.g., HLA A, B, or C; CD8+ T cells) or MHC class II (e.g., HLA DP, DQ, DR; CD4+ T cells). Thus, vaccines that induce efficacious T-cell responses rely upon the appropriate presentation of primary sequence epitopes and ensuing polarization to govern appropriate and protective immune response paradigms (e.g., Th1, Th2, Th17). As detailed above, vaccines that appear to induce efficacious responses in experimental models, and those which are immunogenic in humans, induce robust biomarkers of T-cell response. For example, IFN-γ and IL-17A are involved in efficacious vaccine responses in mouse models of MRSA bacteremia (41, 140) and SSSI (141) due to S. aureus, and these same immune response profiles are observed in humans immunized with this vaccine candidate (81). A key to design of efficacious vaccines targeting S. aureus is the understanding of biomarkers that offer the greatest insight into protective efficacy. For example, because IFN-γ and IL-17A counter-modulate one another, vaccines that promote maximal T- cell induction of such cytokines may not confer maximal protection. Thus, the identification of optimal T cell-mediated immune signatures, rather than maximal responses, may provide new opportunities to develop vaccines targeting S. aureus. Moreover, it remains to be determined whether such biomarkers may be best sought from bloodstream or tissue-specific biological specimens (e.g., mucosa, lymph node, other). In addition to design of cognate T-cell epitopes from pathogens themselves, engineering flanking or other common sequence motifs known to stimulate T cells and perhaps polarize to a given paradigm (e.g., Th17 versus Th1) is emerging in the design of vaccines that induce cell-mediated immunity (150).
Higher-order structures
The importance of T-cell responses in designing efficacious vaccines has received increased attention with respect to linear immune epitopes. However, large, conformational antigens designed to induce convergent immune responses also have emerging promise in the generation of novel efficacious vaccines. In this respect, a non-exhaustive list of examples might include the following.
3-D structural homologs
As mentioned above, antibody induction has been a mainstay of immunization strategies classically. However, exemplified in the HIV experience and more recently with S. aureus, antibody alone may not prove to be the optimally protective immune response. However, there is important crosstalk that occurs between antibody and other immune effector systems (e.g., phagocytes, complement, etc.). Thus, vaccines that evoke convergent humoral immunity could be designed to optimize the most efficacious functional type of antibodies. For example, human IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses typically interact with Fcγ receptors on professional phagocytes most efficiently. Therefore, enhancing protective phagocytic defenses against S. aureus could involve design of convergent immunogens having 3-D structures that evoke high target-affinity Fab domains, and also promote subclass switching as above to optimize Fc-mediated opsonic functions. By comparison, protective immunity requiring complement fixation may best promote induction of antigen-restricted IgM and IgG2 antibody subclasses, for example. Likewise, vaccines intended to protect against colonization or infection of mucosal surfaces may be optimized to induce secretory IgA subclasses. Through each of these examples, convergent 3-D or conformational immunogens provide opportunities to induce antibody profiles distinct from those induced by B-cell epitopes inherent to the native antigens themselves. Also important in this regard is a need for cytokine conditioning and T-cell signaling for B-cell activation and antibody generation in response to an antigen. Obviously, recent discoveries point to the importance of B cells as APC for T-cell activation. Such considerations further suggest critical immunogenic relationships between T- and B-cell epitopes needed in an optimally efficacious vaccine.
Fusion constructs
Fusion protein constructs have also been explored as a means of creating efficient “designer” antigens. This approach has the advantage that multiple epitopes can be combined into a smaller number of recombinant proteins, assuming that the essential features of the epitopes can be conserved in the resulting protein product (Figure 4). A particularly extreme example of a fusion protein antigen appears to be the Group A Streptococcus (GAS) vaccine originally developed by ID Biomedical, which consisted of multiple recombinant proteins, each of which was a fusion of immunogenic regions from a given surface protein from a total of 26 serotypes of GAS (151).
Figure 4.
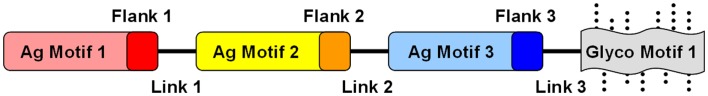
Conceptual design of modular and combinatorial convergent vaccine immunogens. Illustrated here is an example of a convergent vaccine immunogen that integrates multiple antigen motifs (Ag motif) containing flanking sequences (Flank) optimized as T-cell epitopes, interposed by strategic linker domains (Link) in a fusion construct. By virtue of its expression in a strategic heterologous system, glycosylation motifs (Glyco motif) or lack thereof would be favored to stimulate or target immune pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to evoke optimal responses for protective efficacy.
Fusion constructs may contain structural elements already demonstrated to be determinants of protective efficacy. In addition to the known virulence antigens (or immunogenic domains thereof) that contain fundamental B- and T-cell motifs, fusion proteins can be further designed to encompass antigens to enhance mechanisms of efficacy against the target organism(s) (Figure 4). Immunogenic modules can be interposed by linker domains that enable high-fidelity presentation of the 3-D structure of each antigen to be maintained (152). Such strategies can also facilitate appropriate processing of the fusion protein (e.g., proteolysis and presentation of linear epitopes) by APC for T-cell receptors. Such modular components will likely impose conformational influences on one another, and can be rearranged to optimize protective effects based on in vivo efficacy and immune response. Furthermore, such constructs can be engineered to contain sequences that enhance antigen-presenting and intrinsic adjuvant effects that promote ideal polarization of the immune system to the target pathogen.
Antigen context
Traditionally, many vaccines have been viewed as protein-based immunogens in solution, functioning individually to prompt specific responses targeting the cognate antigen(s). Beyond this view, interactions of antigens, or antigens organized in macromolecular systems or nanoparticles, afford additional strategies for beneficial impacts of convergent immunity (153, 154). For example, a protein in solution may have very different conformational epitopes as compared to the identical protein in context of a lipid bilayer. As many vaccine antigens derive from membrane-associated virulence factors, solution-based immunogens may miss important opportunities to induce protective immunity. Likewise, distinct antigens may interact with one another in a vaccine suspension, creating second or greater order epitopes for immune exposure. From these examples, it is reasonable to anticipate that novel vaccines targeting S. aureus may contain one or more antigens in conditional states. Development of liposomal or nanoparticle vaccines allow some immunogens to be presented in context of biological membrane systems (Figure 5). Such strategies offer advantages in presenting epitopes so as to engender optimally protective, rather than maximally quantitative, B-cell responses.
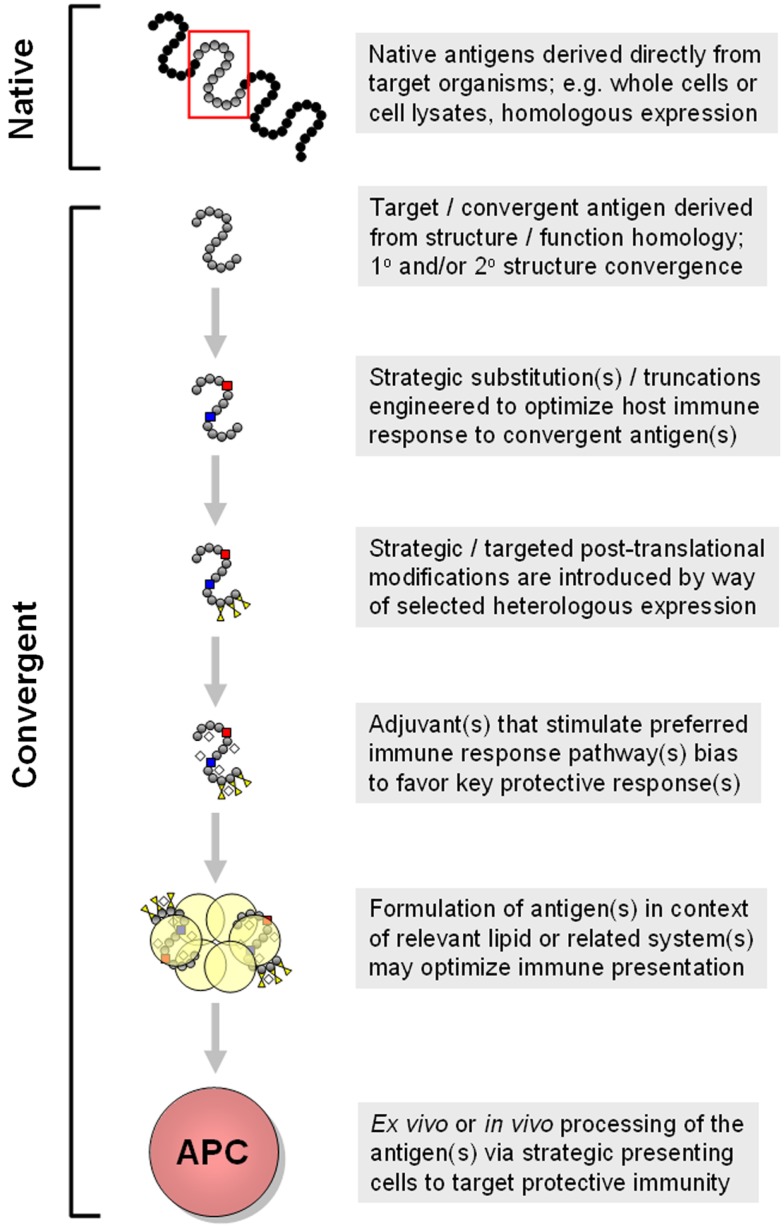
Figure 5.
Progressive modes for generation of convergent immunogens are shown. In this example, multiple concepts detailed in the text are shown in a sequential manner that yields increasingly strategic convergent immunogens. Approaches such as these are being employed in design of vaccines to elicit optimally protective immune responses that include tissue-targeted and cross-kingdom mechanisms of action. These and related aspects of convergent immunity may be necessary for efficacious vaccines targeting opportunistic pathogens such as S. aureus.
Targeted antigen presentation
It is increasingly apparent that the human immune system detects immunogenic determinants in specific contexts that bias specific immune responses. For example, in mammalian lung mucosa, resident dendritic cells (e.g., class I; MHCIIhi/CD11b+/CD11c+) appear to detect, process, and traffic antigens in a manner optimized for MHC class II presentation and ensuing activation of proximate stromal CD4+ T cells (155, 156). These functions are not identical in class II monocytic dendritic cells (e.g., IL-12 secreting), or class V dermal dendritic cells. As a result, immune responses from such distinct contexts of antigen processing, presentation, and trafficking can be very different. It follows that convergent immunity best suited to protect against S. aureus infections of specific tissue sites or anatomic contexts may necessarily need to be designed to engage APC most relevant to a given site. Further, specific vaccines designed to target antigen presentation to specific T and/or B-cell subsets is a logical extension of this strategy of convergent immunity (157). These examples illustrate the larger concepts that convergent vaccine antigens might be designed to comprise multi-component sets of core epitopes engineered to stimulate specific subsets of APC to evoke optimal host defenses for specific anatomic niche(s).
Post-translational or production process-induced modifications
Beyond the design of non-natural antigenic sequences or constructs themselves, the use of non-native hosts for their expression affords further dimensions in the generation of antigens for stimulation of convergent immunity. For example, purposeful substitutions, additions (e.g., six-His tags) and/or truncations are commonly employed to improve the productivity of expression cell lines or to minimize or eliminate aggregation of recombinant proteins. Such specifications may be integrated into various approaches for strategic heterologous expression of a given antigen for optimal induction of protective immunity. These strategies might also incorporate the choice of a heterologous host organism, as well as conditions under which an organism is induced to express an antigen. A non-exhaustive illustration of the spectrum of potential considerations in this regard might include strategic uses of Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris non-human mammalian cell lines (e.g., Chinese hamster ovary cells), or human cell lines. Each has its advantages and drawbacks, including a greater theoretical potential to generate “humanized” antigens that, in concept, may have heightened risk of inducing autoimmune disease.
Combination vaccine products
Identification and development of convergent immunogens such as rAls3 for an S. aureus vaccine may also complement the use of native antigens and provide surrogate antigens to induce extended immunological response. Moreover, this approach represents a new category of antigen that may be considered in the context of a combination vaccine product. The choice of antigens to use in such a combination product is driven by considering multiple factors, including the role of the antigen in the biology of the organism (e.g., function; accessibility), the uniqueness of the immunogen with respect to human proteins or other microbial targets, the type of immune response induced by the antigen, or a combination of the above. To date, most multi-component vaccines used in clinical evaluations (see Table 2) have been driven more so by consideration of the roles of the antigens in the biology of the organism. In some cases, adjuvants are used to influence the type of immune response being brought to bear (see below). However, more recently, consideration is being directed to a mixed approach that also considers the relationship among antigens, and types of immune responses they induce with respect to S. aureus (118, 158, 159).
Adjuvants
The role of adjuvants in vaccines can be considered either as a way to direct the immune response to the vaccine antigens (e.g., use of aluminum hydroxide suspension to bias toward a Th2 response) or as a way to enhance immune responses to the immune stimuli inherent to a given antigen (e.g., inclusion of aluminum hydroxide does not appear to influence the T-cell response to rAls3). As such, the inclusion of an adjuvant in a formulation with a convergent antigen provides yet another opportunity to influence the immune responses to a vaccine. The real value of the adjuvant can only be determined by comparative studies in the target human population to: (1) establish an increase in efficacy with use of the adjuvant (versus without the adjuvant); or (2) by first establishing surrogate markers of protection and then observing the increase in those markers in the presence versus the absence of the adjuvant. While animal models may be useful in these respects, final evaluation in humans remains the only convincing way to establish the value of adding a given adjuvant to a vaccine formulation.
Strategic immunization regimens
Convergent immunity may also benefit from thoughtful timing and modes of vaccine administration. With S. aureus being a commensal pathogen, it stands to reason that most if not all humans have been primed for S. aureus natural antigens by exposure to the bacterium. In this case, strategic vaccination regimens that may bias acute or more durable responses might be favored, depending on whether long-term or short-term immunization is the objective of vaccination. Long-term efficacy is necessary in protection against chronic threat of infection, whereas short-term protection may be sufficient when risk of infection can be anticipated (e.g., transplantation, chemotherapy, surgery, etc.). Short-term immunization may only require a single dose of vaccine, which in the presence of pre-existing immune response to the immunogen homolog, can be used to extend the scope of natural anamnestic response that enhance convergent immunity. As has been shown with the rAls3 antigen, the magnitude of this boost in both B- and T-cell responses may be moderated by the dose level of antigen administered (81). For vaccines containing a combination of antigens, the option for a single dose to induce a natural anamnestic response relies on each antigen having been primed by natural exposure to the pathogen. Longer-term immunity may require additional doses of vaccine, particularly if a strong T-cell response is needed. In this situation, doses may be given as a series of vaccinations over a short period of time to prompt a robust initial immune response, or given over longer time intervals (e.g., annually) to maintain an elevated state of immune readiness. However, it should be kept in mind that a maximal immune response may not be an optimal immune response, as the ultimate goal is not to induce immune response but to prevent or treat disease.
Beyond timing, it is increasingly evident that mode of vaccine administration can have significant impact on immune response. For example, as above, an identical immunogen that is administered via intra-muscular, subcutaneous, or even intra-dermal routes often induce distinctive immune response profiles. These considerations illustrate the larger concepts that convergent vaccine antigens might be designed to comprise multi-component sets of core antigens that have been engineered to stimulate specific subsets of dendritic or other APC in such a manner as to evoke collectively optimal host defenses for specific anatomic niche(s).
Coordinate induction
Protective host defense versus S. aureus requires a highly coordinated and multi-focused immune response. An overarching strategy in convergent immunity is to develop vaccines or immunotherapeutics that bring complementary host defenses together to achieve protection against infection that could not be achieved by any single immune mechanism alone. This strategy addresses the reality that an infection caused by S. aureus contains organisms in different growth phases, that occupy different anatomic niches, and that may be refractory to one or more immune effectors alone. A conceptual example would be a multi-component vaccine, in which distinct immunogens are optimized to induce a Th17 response for neutrophil enhancement, Th2 response for induction of IgG1/IgG3 opsonophagocytic antibodies, and Th22 response to promote the induction of host-defense peptides most appropriate to act on the target pathogen in relevant tissues. Such strategies for coordinate induction may afford advantages in optimizing efficacy via inclusion of both natural and convergent immunity. It is possible if not likely that combinations of such strategies will be leveraged in design and evaluation of multi-valent vaccines targeting S. aureus. It may also be more realistic than not that distinct vaccines or immunotherapeutic modalities may be needed to protect against S. aureus infections of specific anatomic niches or compartments. Such vaccines would be optimized to marshal the optimally protective host defenses for a given niche. For example, vaccines designed to protect mucocutaneous tissues may induce distinct adaptive and effector mechanisms than those most efficacious in defending against S. aureus bacteremia. These concepts integrate the realties that the repertoire of immune targets and virulence strategies of this organism in distinct compartments are very different, as are immune responses best to defend against them.
Prospectus
The application and optimization of convergent immunity derives from historical success in vaccine discovery and development. In this sense, vaccines that induce protective immunity in response to antigens, which are non-identical to those found in nature has many potential advantages in development of improved vaccines targeting S. aureus or other pathogens. Yet, much remains to be learned regarding the secrets by which the human immune system largely outwits S. aureus on a day-to-day basis. By unlocking these mechanisms, vaccines comprising convergent as well as natural antigens have the potential to address the public health concerns imposed by S. aureus and likely other pathogens as well.
As proposed herein, optimally efficacious vaccines and immunotherapeutics protective against S. aureus disease will likely rely upon:
A more comprehensive understanding of the critical immunoprotective mechanisms targeting this organism, including those that may not be known or fully appreciated at present. A key to this concept is differentiating non-protective versus protective immune responses. It follows that specific biomarkers that prioritize protective immune responses over those, which are not protective are much needed. Included in these concepts are molecular and cellular effectors of immunity not traditionally considered to be active in defense against S. aureus (e.g., cell-mediated immunity; interactions between innate host-defense peptides and professional phagocytes, etc.). These effector mechanisms may be additive or synergistic interactions of immune responses, and/or not currently detected or prioritized in the evaluation of vaccines.
Leveraging of convergent immunity in targeting normal flora organisms for which there may be pre-existing baseline immune responses.
Innovative design and deployment of convergent antigens as surrogates of natural antigens that trigger protective immune responses, which optimize efficacy or promote immunity that would not otherwise be induced by recapitulation of native antigens.
Immunization regimens and strategies that induce dynamic and coordinated immune responses that are optimized to anatomic, physiological, or microbiological contexts best suited to address S. aureus pathogenesis or immune subversion strategies.
Use of strategic adjuvants to promote antigen-restricted immune responses that afford protection against the ultimate target pathogen(s), even if the antigen(s) themselves may not be native to these pathogens.
Combinations of the above that employ strategic use of heterologous expression, modular antigen design, and emerging technologies to evoke optimally protective rather than maximally detectable immune responses, and advances in biomarker signatures to discern the difference; and
Avoidance of untoward effects in dysregulated or dysfunctional immune responses to vaccine antigens, including autoimmune disease.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors are founders, consultants, or employees of NovaDigm Therapeutics, Inc., which is developing novel vaccines targeting Staphylococcus aureus and other pathogens. Some of the authors are inventors on patent applications related to the use of Candida albicans Als3 as a vaccine antigen targeting Candida spp. and the cross-kingdom protection targeting S. aureus. NovaDigm has licensed the world-wide rights to this intellectual property.
Acknowledgments
The authors recognize the many excellent contributions made to the field of vaccinology in general, and vaccines and immunotherapeutics targeting Staphylococcus aureus more specifically. We appreciate the efforts of Dr. Dennis Dixon, Dr. Rory Duncan, and other members of the National Institutes of Health, and U.S. Department of Defense for prior support of programs aimed to develop innovative anti-infectives targeting high-priority pathogens. The present manuscript was supported in-part by grants from the National Institutes of Health [AI111661 (Michael R. Yeaman), AI19990 (John E. Edwards Jr.), AI063382 (John E. Edwards Jr.)], and U.S. Department of Defense [W81XWH-12-2-0101 (Michael R. Yeaman), W81XWH-11-1-0686 (John P. Hennessey Jr.)].
References
- 1.David MZ, Daum RS. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin Microbiol Rev (2010) 23(3):616–87 10.1128/CMR.00081-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gunderson CG, Martinello RA. A systematic review of bacteremias in cellulitis and erysipelas. J Infect (2012) 64(2):148–55 10.1016/j.jinf.2011.11.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.DeLeo FR, Otto M, Kreiswirth BN, Chambers HF. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet (2010) 375(9725):1557–68 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61999-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Geria AN, Schwartz RA. Impetigo update: new challenges in the era of methicillin resistance. Cutis (2010) 85(2):65–70 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Karamatsu ML, Thorp AW, Brown L. Changes in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue infections presenting to the pediatric emergency department: comparing 2003 to 2008. Pediatr Emerg Care (2012) 28(2):131–5 10.1097/PEC.0b013e318243fa36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hersh AL, Chambers HF, Maselli JH, Gonzales R. National trends in ambulatory visits and antibiotic prescribing for skin and soft-tissue infections. Arch Intern Med (2008) 168(14):1585–91 10.1001/archinte.168.14.1585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chambers HF. Community-associated MRSA – resistance and virulence converge. N Engl J Med (2005) 352(14):1485–7 10.1056/NEJMe058023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dantes R, Mu Y, Belflower R, Aragon D, Dumyati G, Harrison LH, et al. National burden of invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, United States, 2011. JAMA Intern Med (2013) 173(21):1970–8 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tattevin P, Schwartz BS, Graber CJ, Volinski J, Bhukhen A, Bhukhen A, et al. Concurrent epidemics of skin and soft tissue infection and bloodstream infection due to community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis (2012) 55(6):781–8 10.1093/cid/cis527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA (2007) 298(15):1763–71 10.1001/jama.298.15.1763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Song X, Cogen J, Singh N. Incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in a children’s hospital in the Washington metropolitan area of the United States, 2003-2010. Emerg Microbes Infect (2013) 2(10):e69. 10.1038/emi.2013.69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chambers HF, DeLeo FR. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat Rev Microbiol (2009) 7:629–41 10.1038/nrmicro2200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dryden MS. Complicated skin and soft tissue infection. J Antimicrob Chemother (2010) 65(Suppl 3):iii35–44 10.1093/jac/dkq302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Iwamoto M, Mu Y, Lynfield R, Bulens SN, Nadle J, Aragon D, et al. Trends in invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Pediatrics (2013) 132(4):e817–24 10.1542/peds.2013-1112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Catry B, Latour K, Jans B, Vandendriessche S, Preal R, Mertens K, et al. Risk factors for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a multi-laboratory study. PLoS One (2014) 9(2):e89579. 10.1371/journal.pone.0089579 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jiménez JN, Ocampo AM, Vanegas JM, Rodriguez EA, Mediavilla JR, Chen L, et al. A comparison of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus reveals no clinical and epidemiological but molecular differences. Int J Med Microbiol (2013) 303(2):76–83 10.1016/j.ijmm.2012.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stenehjem E, Rimland D. MRSA nasal colonization burden and risk of MRSA infection. Am J Infect Control (2013) 41(5):405–10 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.07.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Quezada SM, Steinberger EK, Cross RK. Association of age at diagnosis and Crohn’s disease phenotype. Age Ageing (2013) 42(1):102–6 10.1093/ageing/afs107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Duffy J, Dumyati G, Bulens S, Namburi S, Gellert A, Fridkin SK, et al. Community-onset invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections following hospital discharge. Am J Infect Control (2013) 41(9):782–6 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.10.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Datta R, Shah A, Huang SS, Cui E, Nguyen V, Welbourne SJ, et al. High nasal burden of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus increases risk of invasive disease. J Clin Microbiol (2014) 52(1):312–4 10.1128/JCM.01606-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Suresh R, Mosser DM. Pattern recognition receptors in innate immunity, host defense, and immunopathology. Adv Physiol Educ (2013) 37(4):284–91 10.1152/advan.00058.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhong Y, Kinio A, Saleh M. Functions of NOD-like receptors in human diseases. Front Immunol (2013) 4:333. 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bauer S, Muller T, Hamm S. Pattern recognition by toll-like receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol (2009) 653:15–34 10.1007/978-1-4419-0901-5_2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yeaman MR. Platelets: at the nexus of antimicrobial defence. Nat Rev Microbiol (2014) 12(6):426–37 10.1038/nrmicro3269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nestle FO, Di Meglio P, Qin JZ, Nickoloff BJ. Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol (2009) 9(10):679–91 10.1038/nri2622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kupper TS, Fuhlbrigge RC. Immune surveillance in the skin: mechanisms and clinical consequences. Nat Rev Immunol (2004) 4(3):211–22 10.1038/nri1310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Renner ED, Rylaarsdam S, Anover-Sombke S, Rack AL, Reichenbach J, Carey JC, et al. Novel signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) mutations, reduced T(H)17 cell numbers, and variably defective STAT3 phosphorylation in hyper-IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2008) 122(1):181–7 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.04.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Horváth R, Rožková D, Laštovička J, Poločcková A, Sedláček P, Sedivá A, et al. Expansion of T helper type 17 lymphocytes in patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Exp Immunol (2011) 166(1):26–33 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04449.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.de Luca A, Smeekens SP, Casagrande A, Iannitti R, Conway KL, Gresnigt MS, et al. IL-1 receptor blockade restores autophagy and reduces inflammation in chronic granulomatous disease in mice and in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2014) 111(9):3526–31 10.1073/pnas.1322831111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miller LS, Pietras EM, Uricchio LH, Hirano K, Rao S, Lin H, et al. Inflammasome-mediated production of IL-1beta is required for neutrophil recruitment against Staphylococcus aureus in vivo. J Immunol (2007) 179(10):6933–42 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Miller LS, Cho JS. Immunity against Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infections. Nat Rev Immunol (2011) 11(8):505–18 10.1038/nri3010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Greenberg JA, David MZ, Hall JB, Kress JP. Immune dysfunction prior to Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia is a determinant of long-term mortality. PLoS One (2014) 9(2):e88197. 10.1371/journal.pone.0088197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Metzger DW, Sun K. Immune dysfunction and bacterial coinfections following influenza. J Immunol (2013) 191(5):2047–52 10.4049/jimmunol.1301152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cho JS, Pietras EM, Garcia NC, Ramos RI, Farzam DM, Monroe HR, et al. IL-17 is essential for host defense against cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. J Clin Invest (2010) 120(5):1762–73 10.1172/JCI40891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Murphy AG, O’Keeffe KM, Lalor SJ, Maher BM, Mills KH, McLoughlin RM. Staphylococcus aureus infection of mice expands a population of memory gammadelta T cells that are protective against subsequent infection. J Immunol (2014) 192(8):3697–708 10.4049/jimmunol.1303420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Krishna S, Miller LS. Host-pathogen interactions between the skin and Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Opin Microbiol (2012) 15(1):28–35 10.1016/j.mib.2011.11.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bergstresser PR, Tigelaar RE, Dees JH, Streilein JW. Thy-1 antigen-bearing dendritic cells populate murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol (1983) 81(3):286–8 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12518332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McLoughlin RM, Solinga RM, Rich J, Zaleski KJ, Cocchiaro JL, Risley A, et al. CD4+ T cells and CXC chemokines modulate the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus wound infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2006) 103(27):10408–13 10.1073/pnas.0508961103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mölne L, Corthay A, Holmdahl R, Tarkowski A. Role of gamma/delta T cell receptor-expressing lymphocytes in cutaneous infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Exp Immunol (2003) 132(2):209–15 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02151.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Nagai T, Kadoki M, Nambu A, Komiyama Y, et al. Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity (2009) 30(1):108–19 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Spellberg B, Ibrahim AS, Yeaman MR, Lin L, Fu Y, Avanesian V, et al. The antifungal vaccine derived from the recombinant N terminus of Als3p protects mice against the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun (2008) 76(10):4574–80 10.1128/IAI.00700-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cho JS, Zussman J, Donegan NP, Ramos RI, Garcia NC, Uslan DZ, et al. Noninvasive in vivo imaging to evaluate immune responses and antimicrobial therapy against Staphylococcus aureus and USA300 MRSA skin infections. J Invest Dermatol (2011) 131(4):907–15 10.1038/jid.2010.417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Montgomery CP, Daniels M, Zhao F, Alegre ML, Chong AS, Daum RS. Protective immunity against recurrent Staphylococcus aureus skin infection requires antibody and interleukin-17A. Infect Immun (2014) 82(5):2125–34 10.1128/IAI.01491-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zeng WP. “All things considered”: transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 cell differentiation from precursor to effector activation. Immunology (2013) 140(1):31–8 10.1111/imm.12121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Conlan S, Kong HH, Segre JA. Species-level analysis of DNA sequence data from the NIH Human Microbiome Project. PLoS One (2012) 7(10):e47075. 10.1371/journal.pone.0047075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fischer CL, Drake DR, Dawson DV, Blanchette DR, Brogden KA, Wertz PW. Antibacterial activity of sphingoid bases and fatty acids against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (2012) 56(3):1157–61 10.1128/AAC.05151-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wille JJ, Kydonieus A. Palmitoleic acid isomer (C16:1delta6) in human skin sebum is effective against gram-positive bacteria. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol (2003) 16(3):176–87 10.1159/000069757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yount NY, Yeaman MR. Emerging themes and therapeutic prospects for anti-infective peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol (2012) 52:337–60 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yeaman MR, Yount NY. Unifying themes in host defence effector polypeptides. Nat Rev Microbiol (2007) 5(9):727–40 10.1038/nrmicro1744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yeaman MR, Yount NY. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev (2003) 55(1):27–55 10.1124/pr.55.1.2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Korting HC, Schöllmann C, Stauss-Grabo M, Schäfer-Korting M. Antimicrobial peptides and skin: a paradigm of translational medicine. Skin Pharmacol Physiol (2012) 25(6):323–34 10.1159/000341990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dawson MJ, Scott RW. New horizons for host defense peptides and lantibiotics. Curr Opin Pharmacol (2012) 12(5):545–50 10.1016/j.coph.2012.06.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Thomsen IP, Dumont AL, James DB, Yoong P, Saville BR, Soper N, et al. Children with invasive Staphylococcus aureus disease exhibit a potently neutralizing antibody response to the cytotoxin LukAB. Infect Immun (2014) 82(3):1234–42 10.1128/IAI.01558-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Barnett LG, Simkins HM, Barnett BE, Korn LL, Johnson AL, Wherry EJ, et al. B cell antigen presentation in the initiation of follicular helper T cell and germinal center differentiation. J Immunol (2014) 192(8):3607–17 10.4049/jimmunol.1301284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Harvey BP, Raycroft MT, Quan TE, Rudenga BJ, Roman RM, Craft J, et al. Transfer of antigen from human B cells to dendritic cells. Mol Immunol (2014) 58(1):56–65 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.10.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rodriguez-Pinto D, Saravia NG, McMahon-Pratt D. CD4 T cell activation by B cells in human Leishmania (Viannia) infection. BMC Infect Dis (2014) 14:108. 10.1186/1471-2334-14-108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pancari G, Fan H, Smith S, Joshi A, Haimbach R, Clark D, et al. Characterization of the mechanism of protection mediated by CS-D7, a monoclonal antibody to Staphylococcus aureus iron regulated surface determinant B (IsdB). Front Cell Infect Microbiol (2012) 2:36. 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lambris JD, Ricklin D, Geisbrecht BV. Complement evasion by human pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol (2008) 6(2):132–42 10.1038/nrmicro1824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gasque P. Complement: a unique innate immune sensor for danger signals. Mol Immunol (2004) 41(11):1089–98 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Quilty S, Kwok G, Hajkowicz K, Currie B. High incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sepsis and death in patients with febrile neutropenia at Royal Darwin Hospital. Intern Med J (2009) 39(8):557–9 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.02003.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Swati M, Gita N, Sujata B, Farah J, Preeti M. Microbial etiology of febrile neutropenia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus (2010) 26(2):49–55 10.1007/s12288-010-0029-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Morris PG, Hassan T, McNamara M, Hassan A, Wiig R, Grogan L, et al. Emergence of MRSA in positive blood cultures from patients with febrile neutropenia – a cause for concern. Support Care Cancer (2008) 16(9):1085–8 10.1007/s00520-007-0398-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shaw BE, Boswell T, Byrne JL, Yates C, Russell NH. Clinical impact of MRSA in a stem cell transplant unit: analysis before, during and after an MRSA outbreak. Bone Marrow Transplant (2007) 39(10):623–9 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Roos D, de Boer M. Molecular diagnosis of chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Exp Immunol (2014) 175(2):139–49 10.1111/cei.12202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Song E, Jaishankar GB, Saleh H, Jithpratuck W, Sahni R, Krishnaswamy G. Chronic granulomatous disease: a review of the infectious and inflammatory complications. Clin Mol Allergy (2011) 9(1):10. 10.1186/1476-7961-9-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Holland SM, DeLeo FR, Elloumi HZ, Hsu AP, Uzel G, Brodsky N, et al. STAT3 mutations in the hyper-IgE syndrome. N Engl J Med (2007) 357(16):1608–19 10.1056/NEJMoa073687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.White CJ, Gallin JI. Phagocyte defects. Clin Immunol Immunopathol (1986) 40(1):50–61 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90068-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Badolato R. Defects of leukocyte migration in primary immunodeficiencies. Eur J Immunol (2013) 43(6):1436–40 10.1002/eji.201243155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Schmidt S, Moser M, Sperandio M. The molecular basis of leukocyte recruitment and its deficiencies. Mol Immunol (2013) 55(1):49–58 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Greenlee-Wacker MC, Rigby KM, Kobayashi SD, Porter AR, DeLeo FR, Nauseef WM. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by human neutrophils prevents macrophage efferocytosis and induces programmed necrosis. J Immunol (2014) 192(10):4709–17 10.4049/jimmunol.1302692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schindler D, Gutierrez MG, Beineke A, Rauter Y, Rohde M, Foster S, et al. Dendritic cells are central coordinators of the host immune response to Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Am J Pathol (2012) 181(4):1327–37 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sun K, Metzger DW. Influenza infection suppresses NADPH oxidase-dependent phagocytic bacterial clearance and enhances susceptibility to secondary methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol (2014) 192(7):3301–7 10.4049/jimmunol.1303049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Doisne JM, Tan TC, Colucci F. Guardian of the genome turns on genes that alert natural killer cells. Cell Cycle (2011) 10(22):3822–3 10.4161/cc.10.22.18196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wallemacq H, Bedoret D, Pujol J, Desmet C, Drion PV, Farnir F, et al. CD40 triggering induces strong cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus immunization in mice: a new vaccine strategy for staphylococcal mastitis. Vaccine (2012) 30(12):2116–24 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.01.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.van Belkum A, Melles DC, Nouwen J, van Leeuwen WB, van Wamel W, Vos MC, et al. Co-evolutionary aspects of human colonisation and infection by Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Genet Evol (2009) 9(1):32–47 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.van Gils EJ, Hak E, Veenhoven RH, Rodenburg GD, Bogaert D, Bruin JP, et al. Effect of seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on Staphylococcus aureus colonisation in a randomised controlled trial. PLoS One (2011) 6(6):e20229. 10.1371/journal.pone.0020229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mina MJ, McCullers JA, Klugman KP. Live attenuated influenza vaccine enhances colonization of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in mice. MBio (2014) 5(1):e1040–1013 10.1128/mBio.01040-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Eloe-Fadrosh EA, McArthur MA, Seekatz AM, Drabek EF, Rasko DA, Sztein MB, et al. Impact of oral typhoid vaccination on the human gut microbiota and correlations with S. typhi-specific immunological responses. PLoS One (2013) 8(4):e62026. 10.1371/journal.pone.0062026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ferreira RB, Antunes LC, Finlay BB. Should the human microbiome be considered when developing vaccines? PLoS Pathog (2010) 6(11):e1001190. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Baquir B, Lin L, Ibrahim AS, Fu Y, Avanesian V, Tu A, et al. Immunological reactivity of blood from healthy humans to the rAls3p-N vaccine protein. J Infect Dis (2010) 201(3):473–7 10.1086/649901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Schmidt CS, White CJ, Ibrahim AS, Filler SG, Fu Y, Yeaman MR, et al. NDV-3, a recombinant alum-adjuvanted vaccine for Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, is safe and immunogenic in healthy adults. Vaccine (2012) 30(52):7594–600 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.10.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Harro CD, Betts RF, Hartzel JS, Onorato MT, Lipka J, Smugar SS, et al. The immunogenicity and safety of different formulations of a novel Staphylococcus aureus vaccine (V710): results of two phase I studies. Vaccine (2012) 30(9):1729–36 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ibarz-Pavón AB, Maclennan J, Andrews NJ, Gray SJ, Urwin R, Clarke SC, et al. Changes in serogroup and genotype prevalence among carried meningococci in the United Kingdom during vaccine implementation. J Infect Dis (2011) 204(7):1046–53 10.1093/infdis/jir466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Feikin DR, Kagucia EW, Loo JD, Link-Gelles R, Puhan MA, Cherian T, et al. Serotype-specific changes in invasive pneumococcal disease after pneumococcal conjugate vaccine introduction: a pooled analysis of multiple surveillance sites. PLoS Med (2013) 10(9):e1001517. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Shirtliff ME, Peters BM, Jabra-Rizk MA. Cross-kingdom interactions: Candida albicans and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett (2009) 299(1):1–8 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01668.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chotirmall SH, O’Donoghue E, Bennett K, Gunaratnam C, O’Neill SJ, McElvaney NG. Sputum Candida albicans presages FEV(1) decline and hospital-treated exacerbations in cystic fibrosis. Chest (2010) 138(5):1186–95 10.1378/chest.09-2996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Baldan R, Cigana C, Testa F, Bianconi I, De Simone M, Pellin D, et al. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis airways influences virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and murine models of co-infection. PLoS One (2014) 9(3):e89614. 10.1371/journal.pone.0089614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Shinefield H, Black S, Fattom A, Horwith G, Rasgon S, Ordonez J, et al. Use of a Staphylococcus aureus conjugate vaccine in patients receiving hemodialysis. N Engl J Med (2002) 346(7):491–6 10.1056/NEJMoa011297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Fowler VG, Allen KB, Moreira ED, Moustafa M, Isgro F, Boucher HW, et al. Effect of an investigational vaccine for preventing Staphylococcus aureus infections after cardiothoracic surgery: a randomized trial. JAMA (2013) 309(13):1368–78 10.1001/jama.2013.3010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Boles JW, Pitt ML, LeClaire RD, Gibbs PH, Torres E, Dyas B, et al. Generation of protective immunity by inactivated recombinant staphylococcal enterotoxin B vaccine in nonhuman primates and identification of correlates of immunity. Clin Immunol (2003) 108(1):51–9 10.1016/S1521-6616(03)00066-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Stiles BG, Garza AR, Ulrich RG, Boles JW. Mucosal vaccination with recombinantly attenuated staphylococcal enterotoxin B and protection in a murine model. Infect Immun (2001) 69(4):2031–6 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2031-2036.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Anderson AS, Miller AA, Donald RG, Scully IL, Nanra JS, Cooper D, et al. Development of a multicomponent Staphylococcus aureus vaccine designed to counter multiple bacterial virulence factors. Hum Vaccin Immunother (2012) 8(11):1585–94 10.4161/hv.21872 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fattom AI, Horwith G, Fuller S, Propst M, Naso R. Development of StaphVAX, a polysaccharide conjugate vaccine against S. aureus infection: from the lab bench to phase III clinical trials. Vaccine (2004) 22(7):880–7 10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.11.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.O’Brien CN, Guidry AJ, Fattom A, Shepherd S, Douglass LW, Westhoff DC. Production of antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus serotypes 5, 8, and 336 using poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J Dairy Sci (2000) 83(8):1758–66 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)75046-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zecconi A, Scali F. Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors in evasion from innate immune defenses in human and animal diseases. Immunol Lett (2013) 150(1–2):12–22 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kraus D, Peschel A. Staphylococcus aureus evasion of innate antimicrobial defense. Future Microbiol (2008) 3(4):437–51 10.2217/17460913.3.4.437 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Rigby KM, DeLeo FR. Neutrophils in innate host defense against Staphylococcus aureus infections. Semin Immunopathol (2012) 34(2):237–59 10.1007/s00281-011-0295-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Skurnik D, Kropec A, Roux D, Theilacker C, Huebner J, Pier GB. Natural antibodies in normal human serum inhibit Staphylococcus aureus capsular polysaccharide vaccine efficacy. Clin Infect Dis (2012) 55(9):1188–97 10.1093/cid/cis624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ehrhardt GR, Hijikata A, Kitamura H, Ohara O, Wang JY, Cooper MD. Discriminating gene expression profiles of memory B cell subpopulations. J Exp Med (2008) 205(8):1807–17 10.1084/jem.20072682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kobrynski LJ, Tanimune L, Kilpatrick L, Campbell DE, Douglas SD. Production of T-helper cell subsets and cytokines by lymphocytes from patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol (1996) 3(6):740–5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Turner DL, Gordon CL, Farber DL. Tissue-resident T cells, in situ immunity and transplantation. Immunol Rev (2014) 258(1):150–66 10.1111/imr.12149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Fowler VG, Jr, Proctor RA. Where does a Staphylococcus aureus vaccine stand? Clin Microbiol Infect (2014) 20(Suppl 5):66–75 10.1111/1469-0691.12570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Schreiner J, Kretschmer D, Klenk J, Otto M, Bühring HJ, Stevanovic S, et al. Staphylococcus aureus phenol-soluble modulin peptides modulate dendritic cell functions and increase in vitro priming of regulatory T cells. J Immunol (2013) 190(7):3417–26 10.4049/jimmunol.1202563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Ardura MI, Banchereau R, Mejias A, Di Pucchio T, Glaser C, Allantaz F, et al. Enhanced monocyte response and decreased central memory T cells in children with invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections. PLoS One (2009) 4(5):e5446. 10.1371/journal.pone.0005446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Rabe H, Nordström I, Andersson K, Lundell AC, Rudin A. Staphylococcus aureus convert neonatal conventional CD4(+) T cells into FOXP3(+) CD25(+) CD127(low) T cells via the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. Immunology (2014) 141(3):467–81 10.1111/imm.12209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Chen Z, Han Y, Gu Y, Liu Y, Jiang Z, Zhang M, et al. CD11c(high)CD8+ regulatory T cell feedback inhibits CD4 T cell immune response via Fas ligand-Fas pathway. J Immunol (2013) 190(12):6145–54 10.4049/jimmunol.1300060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Farkas T, Thornton SA, Wilton N, Zhong W, Altaye M, Jiang X. Homologous versus heterologous immune responses to Norwalk-like viruses among crew members after acute gastroenteritis outbreaks on 2 US Navy vessels. J Infect Dis (2003) 187(2):187–93 10.1086/367809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Díaz I, Gimeno M, Darwich L, Navarro N, Kuzemtseva L, López S, et al. Characterization of homologous and heterologous adaptive immune responses in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Vet Res (2012) 43:30. 10.1186/1297-9716-43-30 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Nabel GJ, Fauci AS. Induction of unnatural immunity: prospects for a broadly protective universal influenza vaccine. Nat Med (2010) 16(12):1389–91 10.1038/nm1210-1389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Casadevall A, Pirofski LA. Antibody-mediated regulation of cellular immunity and the inflammatory response. Trends Immunol (2003) 24(9):474–8 10.1016/S1471-4906(03)00228-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.DeJonge M, Burchfield D, Bloom B, Duenas M, Walker W, Polak M, et al. Clinical trial of safety and efficacy of INH-A21 for the prevention of nosocomial staphylococcal bloodstream infection in premature infants. J Pediatr (2007) 151(3):260–5, 265.e1. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.04.060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Burnside K, Lembo A, Harrell MI, Klein JA, Lopez-Guisa J, Siegesmund AM, et al. Vaccination with a UV-irradiated genetically attenuated mutant of Staphylococcus aureus provides protection against subsequent systemic infection. J Infect Dis (2012) 206(11):1734–44 10.1093/infdis/jis579 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Hua L, Hilliard JJ, Shi Y, Tkaczyk C, Cheng LI, Yu X, et al. Assessment of an anti-alpha-toxin monoclonal antibody for prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (2014) 58(2):1108–17 10.1128/AAC.02190-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Ragle BE, Bubeck Wardenburg J. Anti-alpha-hemolysin monoclonal antibodies mediate protection against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Infect Immun (2009) 77(7):2712–8 10.1128/IAI.00115-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Mocca CP, Brady RA, Burns DL. Role of antibodies in protection elicited by active vaccination with genetically inactivated alpha hemolysin in a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue infections. Clin Vaccine Immunol (2014) 21(5):622–7 10.1128/CVI.00051-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Yoong P, Pier GB. Antibody-mediated enhancement of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010) 107(5):2241–6 10.1073/pnas.0910344107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Weems JJ, Jr, Steinberg JP, Filler S, Baddley JW, Corey GR, Sampathkumar P, et al. Phase II, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study comparing the safety and pharmacokinetics of tefibazumab to placebo for treatment of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (2006) 50(8):2751–5 10.1128/AAC.00096-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Proctor RA. Challenges for a universal Staphylococcus aureus vaccine. Clin Infect Dis (2012) 54(8):1179–86 10.1093/cid/cis033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG, Mindrinos MN, Baker HV, Xu W, et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2013) 110(9):3507–12 10.1073/pnas.1222878110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kim HK, Missiakas D, Schneewind O. Mouse models for infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol Methods (2014) 410:88–99 10.1016/j.jim.2014.04.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Sung JM, Lloyd DH, Lindsay JA. Staphylococcus aureus host specificity: comparative genomics of human versus animal isolates by multi-strain microarray. Microbiology (2008) 154(Pt 7):1949–59 10.1099/mic.0.2007/015289-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Jansen KU, Girgenti DQ, Scully IL, Anderson AS. Vaccine review: “Staphylococcus aureus vaccines: problems and prospects”. Vaccine (2013) 31(25):2723–30 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ahn SH, Tsalik EL, Cyr DD, Zhang Y, van Velkinburgh JC, Langley RJ, et al. Gene expression-based classifiers identify Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice and humans. PLoS One (2013) 8(1):e48979. 10.1371/journal.pone.0048979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Date SV, Modrusan Z, Lawrence M, Morisaki JH, Toy K, Shah IM, et al. Global gene expression of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 during human and mouse infection. J Infect Dis (2014) 209(10):1542–50 10.1093/infdis/jit668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Casadevall A, Pirofski LA. Exploiting the redundancy in the immune system: vaccines can mediate protection by eliciting “unnatural” immunity. J Exp Med (2003) 197(11):1401–4 10.1084/jem.20030637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Jenner E. On Vaccination Against Smallpox: An Inquiry into the Causes and Effects of the Variole Vaccine, or Cow Pox. London: Sampson Low; (1798). [Google Scholar]
- 127.Murphy SG. Tetanus toxin and antigenic derivatives. II. Effect of protein and formaldehyde concentration on toxoid formation. J Bacteriol (1967) 94(3):586–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Novitsky V, Smith UR, Gilbert P, McLane MF, Chigwedere P, Williamson C, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C molecular phylogeny: consensus sequence for an AIDS vaccine design? J Virol (2002) 76(11):5435–51 10.1128/JVI.76.11.5435-5451.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Koita OA, Dabitao D, Mahamadou I, Tall M, Dao S, Tounkara A, et al. Confirmation of immunogenic consensus sequence HIV-1 T-cell epitopes in Bamako, Mali and Providence, Rhode Island. Hum Vaccin (2006) 2(3):119–28 10.4161/hv.2869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Giles BM, Ross TM. A computationally optimized broadly reactive antigen (COBRA) based H5N1 VLP vaccine elicits broadly reactive antibodies in mice and ferrets. Vaccine (2011) 29(16):3043–54 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.01.100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Hausdorff WP, Hoet B, Schuerman L. Do pneumococcal conjugate vaccines provide any cross-protection against serotype 19A? BMC Pediatr (2010) 10:4. 10.1186/1471-2431-10-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.McNeely TB, Staub JM, Rusk CM, Blum MJ, Donnelly JJ. Antibody responses to capsular polysaccharide backbone and O-acetate side groups of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 9V in humans and rhesus macaques. Infect Immun (1998) 66(8):3705–10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Jakobsen H, Sigurdsson VD, Sigurdardottir S, Schulz D, Jonsdottir I. Pneumococcal serotype 19F conjugate vaccine induces cross-protective immunity to serotype 19A in a murine pneumococcal pneumonia model. Infect Immun (2003) 71(5):2956–9 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2956-2959.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Richter SS, Heilmann KP, Dohrn CL, Riahi F, Diekema DJ, Doern GV. Pneumococcal serotypes before and after introduction of conjugate vaccines, United States, 1999-2011(1.). Emerg Infect Dis (2013) 19(7):1074–83 10.3201/eid1907.121830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Hulten KG, Kaplan SL, Lamberth LB, Barson WJ, Romero JR, Lin PL, et al. Changes in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A invasive infections in children from 1993 to 2011. J Clin Microbiol (2013) 51(4):1294–7 10.1128/JCM.00058-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Dudas RA, Karron RA. Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines. Clin Microbiol Rev (1998) 11(3):430–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Fu Y, Ibrahim AS, Sheppard DC, Chen YC, French SW, Cutler JE, et al. Candida albicans Als1p: an adhesin that is a downstream effector of the EFG1 filamentation pathway. Mol Microbiol (2002) 44:61–72 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02873.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Phan QT, Myers CL, Fu Y, Sheppard DC, Yeaman MR, Welch WH, et al. Als3 is a Candida albicans invasin that binds to cadherins and induces endocytosis by host cells. PLoS Biol (2007) 5(3):e64. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Sheppard DC, Yeaman MR, Welch WH, Phan QT, Fu Y, Ibrahim AS, et al. Functional and structural diversity in the Als protein family of Candida albicans. J Biol Chem (2004) 279:30480–9 10.1074/jbc.M401929200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Lin L, Ibrahim AS, Xu X, Farber JM, Avanesian V, Baquir B, et al. Th1-Th17 cells mediate protective adaptive immunity against Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans infection in mice. PLoS Pathog (2009) 5(12):e1000703. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Yeaman MR, Filler SG, Schmidt CS, Chaili S, Barr K, Wang H, et al. Efficacy and immunologic mechanisms of NDV-3 vaccine in a murine model of MRSA skin/skin structure infection. 52nd ICAAC. San Francisco, CA: (2012). Abstract No. G-868. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Festa M, Brun P, Piccinini R, Castagliuolo I, Basso B, Zecconi A. Staphylococcus aureus Efb protein expression in Nicotiana tabacum and immune response to oral administration. Res Vet Sci (2013) 94(3):484–9 10.1016/j.rvsc.2012.10.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Camussone CM, Veaute CM, Pujato N, Morein B, Marcipar IS, Calvinho LF. Immune response of heifers against a Staphylococcus aureus CP5 whole cell and lysate vaccine formulated with ISCOM matrix adjuvant. Res Vet Sci (2014) 96(1):86–94 10.1016/j.rvsc.2013.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Camussone CM, Veaute CM, Porporatto C, Morein B, Marcipar IS, Calvinho LF. Immune response of heifers against a Staphylococcus aureus CP5 whole cell vaccine formulated with ISCOMATRIX adjuvant. J Dairy Res (2013) 80(1):72–80 10.1017/S0022029912000593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Luo G, Hennessey JP, Jr, Schmidt CS, Fu Y, Yeaman MR, Filler SG, et al. Human vaccination with rAls3p-N produces antibodies that enhance phagocyte-mediated killing of C. albicans and S. aureus and mitigate Als3p functions. 18th Congress of the International Society for Human and Animal Mycology. Berlin: (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 146.Klotz SA, Chasin BS, Powell B, Gaur NK, Lipke PN. Polymicrobial bloodstream infections involving Candida species: analysis of patients and review of the literature. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis (2007) 59(4):401–6 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Spellberg BJ, Ibrahim AS, Avanesian V, Fu Y, Myers C, Phan QT, et al. Efficacy of the anti-Candida rAls3p-N or rAls1p-N vaccines against disseminated and mucosal candidiasis. J Infect Dis (2006) 194(2):256–60 10.1086/504691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ibrahim AS, Luo G, Gebremariam T, Lee H, Schmidt CS, Hennessey JP, Jr, et al. NDV-3 protects mice from vulvovaginal candidiasis through T- and B-cell immune response. Vaccine (2013) 31(47):5549–56 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.09.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Bär E, Gladiator A, Bastidas S, Roschitzki B, Acha-Orbea H, Oxenius A, et al. A novel Th cell epitope of Candida albicans mediates protection from fungal infection. J Immunol (2012) 188(11):5636–43 10.4049/jimmunol.1200594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Pentier JM, Sewell AK, Miles JJ. Advances in T-cell epitope engineering. Front Immunol (2013) 4:133. 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.McNeil SA, Halperin SA, Langley JM, Smith B, Warren A, Sharratt GP, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of 26-valent group a Streptococcus vaccine in healthy adult volunteers. Clin Infect Dis (2005) 41(8):1114–22 10.1086/444458 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Zeng W, Horrocks KJ, Robevska G, Wong CY, Azzopardi K, Tauschek M, et al. A modular approach to assembly of totally synthetic self-adjuvanting lipopeptide-based vaccines allows conformational epitope building. J Biol Chem (2011) 286(15):12944–51 10.1074/jbc.M111.227744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sahdev P, Ochyl LJ, Moon JJ. Biomaterials for nanoparticle vaccine delivery systems. Pharm Res (2014). 10.1007/s11095-014-1419-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Gregory AE, Titball R, Williamson D. Vaccine delivery using nanoparticles. Front Cell Infect Microbiol (2013) 3:13. 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. Biology of lung dendritic cells at the origin of asthma. Immunity (2009) 31(3):412–24 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Vander Lugt B, Khan AA, Hackney JA, Agrawal S, Lesch J, Zhou M, et al. Transcriptional programming of dendritic cells for enhanced MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat Immunol (2014) 15(2):161–7 10.1038/ni.2795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Cruz LJ, Rueda F, Simón L, Cordobilla B, Albericio F, Domingo JC. Liposomes containing NYESO1/tetanus toxoid and adjuvant peptides targeted to human dendritic cells via the Fc receptor for cancer vaccines. Nanomedicine (Lond) (2014) 9(4):435–49 10.2217/NNM.13.66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kaslow DC, Shiver JW. Clostridium difficile and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: emerging concepts in vaccine development. Annu Rev Med (2011) 62:201–15 10.1146/annurev-med-051109-101544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Proctor RA. Is there a future for a Staphylococcus aureus vaccine? Vaccine (2012) 30(19):2921–7 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]