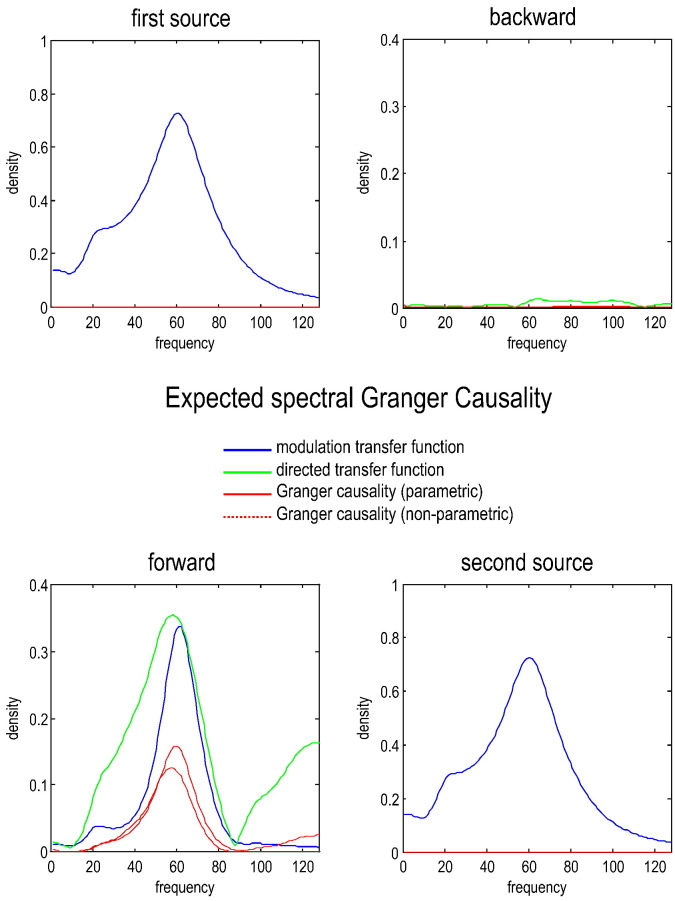
Fig. 4.
This figure reports the expected modulation transfer functions (blue lines), normalised directed transfer functions (green lines) and the associated spectral Granger causality (red lines: parametric — solid and nonparametric — dotted) under the dynamic causal model shown in Fig. 1. In this example, measurement noise was suppressed (with log-amplitude of − 8). The log-amplitude of the neuronal fluctuations was set at a fairly low level of − 2. These fluctuations had a power law form with an exponent of one. The spectral measures are the expected values, given the model parameters, and correspond to what would be seen with a very large amount of data. Under these conditions, the (expected) directed transfer functions and Granger causality identify the predominance of gamma in the forward connections — and correctly detect that there is no reciprocal or backward connection.