Abstract
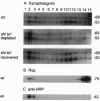
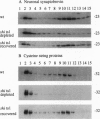
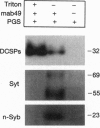
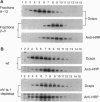
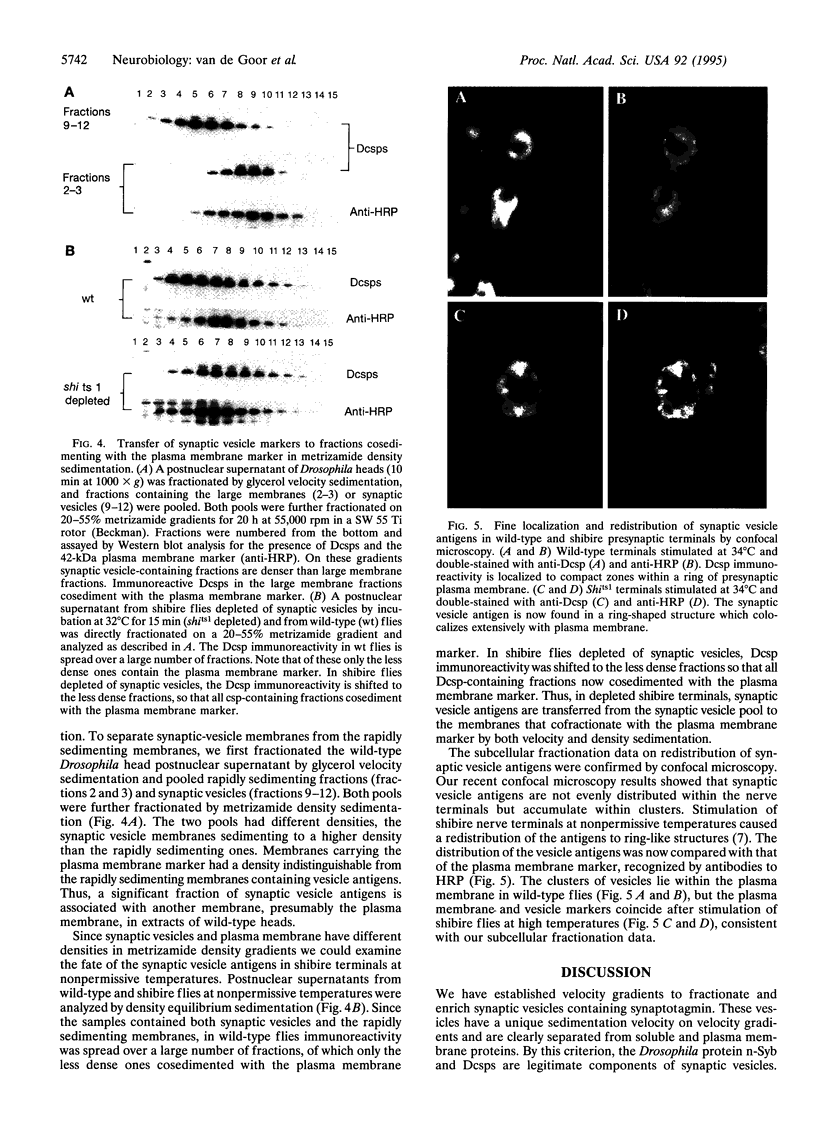
From an extract of Drosophila melanogaster head homogenates, a membrane fraction can be isolated that has the same sedimentation properties as vertebrate synaptic vesicles and contains Drosophila synaptotagmin. The fraction disappears from homogenates of temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant shibire(ts1) (shi(ts1)) flies paralyzed by exposure to non-permissive temperatures, and reappears on return to permissive temperatures. Since reversible, temperature-dependent depletion of synaptic vesicles is known to occur in shibire(ts1) flies, we conclude that the fraction we have identified contains synaptic vesicles. We have examined the fate of synaptic vesicle membrane proteins in shibire flies at nonpermissive temperatures and found that all of these vesicle antigens are transferred to rapidly sedimenting membranes and codistribute with a plasma membrane marker by both glycerol velocity and metrizamide density sedimentation and by confocal microscopy. Three criteria were used to establish that other neuron-specific antigens--neuronal synaptobrevin and cysteine-string proteins--are legitimate components of synaptic vesicles: cosedimentation with Drosophila synaptotagmin, immunoadsorption, and disappearance of these antigens from the vesicle fractions in paralyzed shibire flies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin A. C., Burgess R. W., Wong B. R., Schwarz T. L., Scheller R. H. Differential expression of transcripts from syb, a Drosophila melanogaster gene encoding VAMP (synaptobrevin) that is abundant in non-neuronal cells. Gene. 1993 Sep 15;131(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90291-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clift-O'Grady L., Linstedt A. D., Lowe A. W., Grote E., Kelly R. B. Biogenesis of synaptic vesicle-like structures in a pheochromocytoma cell line PC-12. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1693–1703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiAntonio A., Burgess R. W., Chin A. C., Deitcher D. L., Scheller R. H., Schwarz T. L. Identification and characterization of Drosophila genes for synaptic vesicle proteins. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4924–4935. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04924.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. D., Broadie K., van de Goor J., Rubin G. M. Mutations in the Drosophila Rop gene suggest a function in general secretion and synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1994 Sep;13(3):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman G. A., Bonzelius F., Cieutat A. M., Kelly R. B. A distinct class of intracellular storage vesicles, identified by expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12750–12754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Antibodies to horseradish peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and in grasshopper embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F., Moats W., Jan Y. N. A carbohydrate epitope expressed uniquely on the cell surface of Drosophila neurons is altered in the mutant nac (neurally altered carbohydrate). EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3471–3477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. H., Ikeda K. Disappearance and reformation of synaptic vesicle membrane upon transmitter release observed under reversible blockage of membrane retrieval. J Neurosci. 1989 Nov;9(11):3844–3860. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-11-03844.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Ikeda K. Possible temperature-dependent blockage of synaptic vesicle recycling induced by a single gene mutation in Drosophila. J Neurobiol. 1983 May;14(3):207–225. doi: 10.1002/neu.480140305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Bellen H. J., Perin M. S. Expression of synaptotagmin in Drosophila reveals transport and localization of synaptic vesicles to the synapse. Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1077–1088. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Stern M., Schulze K., Perin M., Bellen H. J. Mutational analysis of Drosophila synaptotagmin demonstrates its essential role in Ca(2+)-activated neurotransmitter release. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1125–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. P., Sim A. T., Robinson P. J. Calcineurin inhibition of dynamin I GTPase activity coupled to nerve terminal depolarization. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):970–973. doi: 10.1126/science.8052858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrogiacomo A., Parsons S. M., Zampighi G. A., Jenden D. J., Umbach J. A., Gundersen C. B. Cysteine string proteins: a potential link between synaptic vesicles and presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Science. 1994 Feb 18;263(5149):981–982. doi: 10.1126/science.7906056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poodry C. A., Edgar L. Reversible alteration in the neuromuscular junctions of Drosophila melanogaster bearing a temperature-sensitive mutation, shibire. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):520–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswami M., Krishnan K. S., Kelly R. B. Intermediates in synaptic vesicle recycling revealed by optical imaging of Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Sontag J. M., Liu J. P., Fykse E. M., Slaughter C., McMahon H., Südhof T. C. Dynamin GTPase regulated by protein kinase C phosphorylation in nerve terminals. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):163–166. doi: 10.1038/365163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L., Kelly L. Temperature-induced seizure and frequency-dependent neuromuscular block in a ts mutant of Drosophila. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):156–158. doi: 10.1038/273156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Sun B., Yasuyama K., Salvaterra P. M. Biochemical analysis of proteins recognized by anti-HRP antibodies in Drosophila melanogaster: identification and characterization of neuron specific and male specific glycoproteins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1994 Mar;24(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinsmaier K. E., Eberle K. K., Buchner E., Walter N., Benzer S. Paralysis and early death in cysteine string protein mutants of Drosophila. Science. 1994 Feb 18;263(5149):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.8310297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinsmaier K. E., Hofbauer A., Heimbeck G., Pflugfelder G. O., Buchner S., Buchner E. A cysteine-string protein is expressed in retina and brain of Drosophila. J Neurogenet. 1990 Nov;7(1):15–29. doi: 10.3109/01677069009084150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]