Abstract
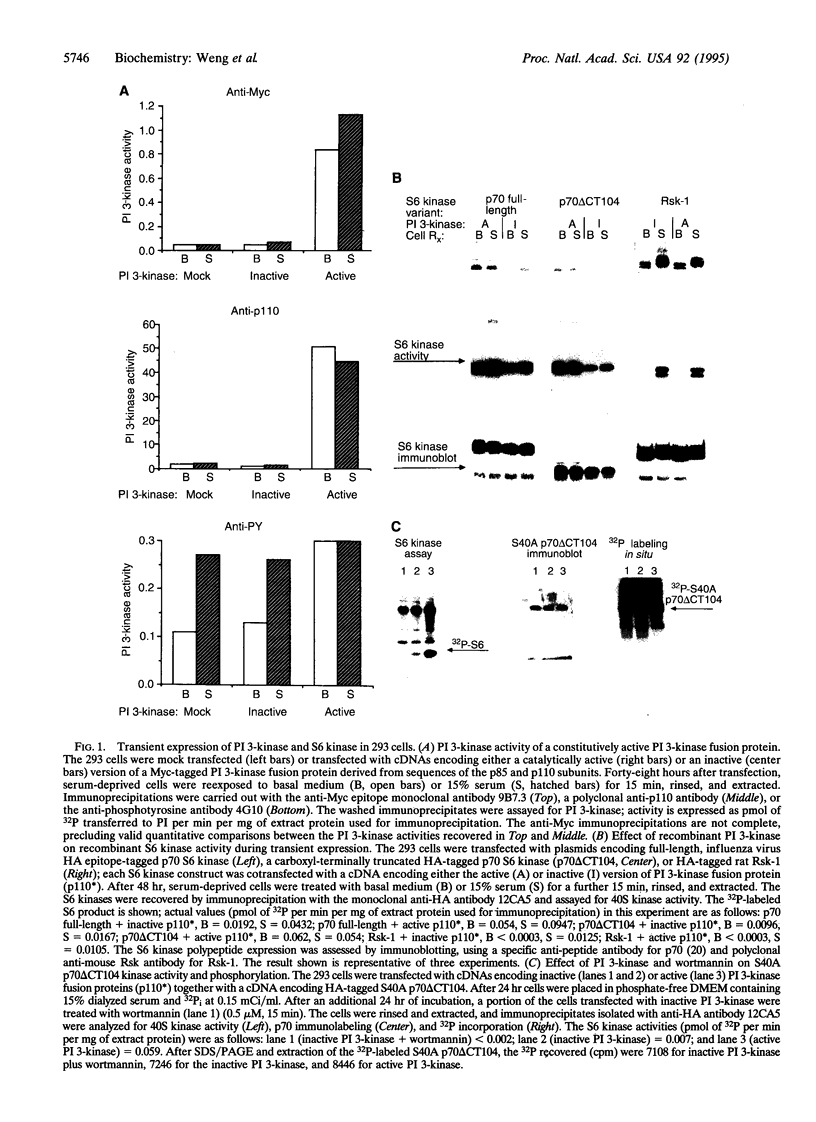
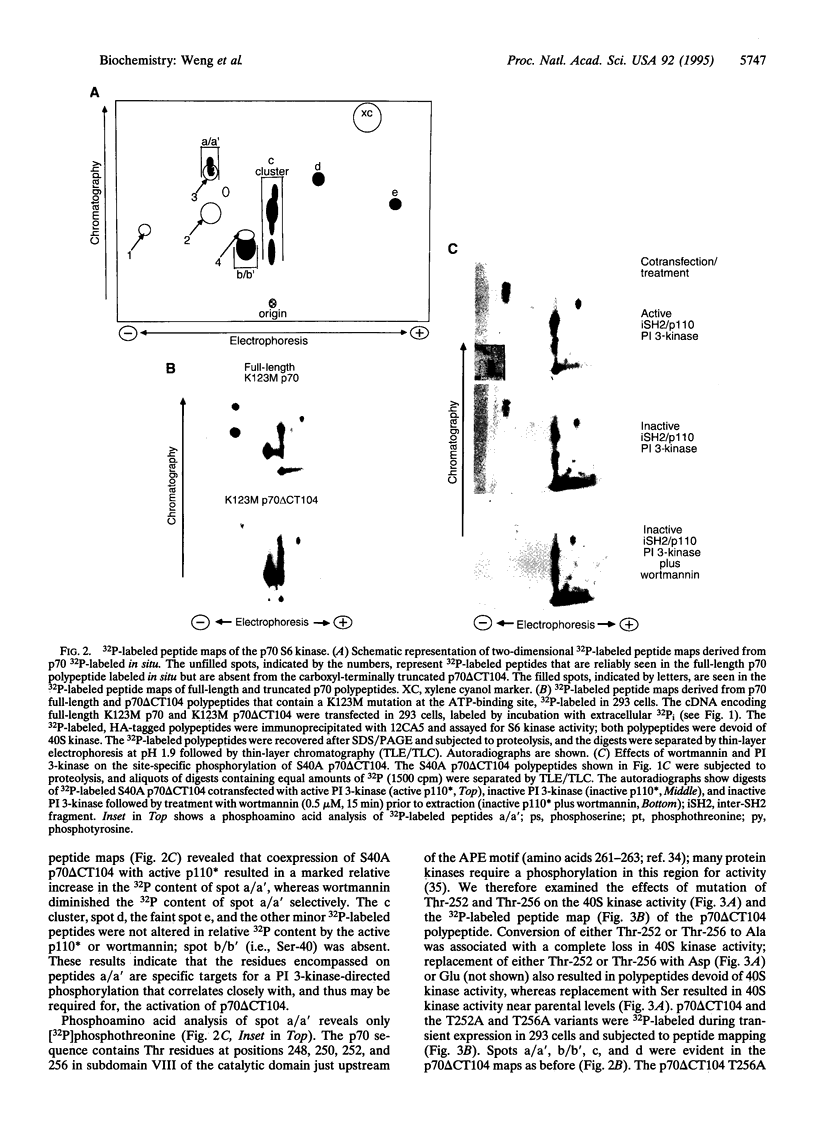
The p70 S6 kinase is activated by insulin and mitogens through multisite phosphorylation of the enzyme. One set of activating phosphorylations occurs in a putative autoinhibitory domain in the noncatalytic carboxyl-terminal tail. Deletion of this tail yields a variant (p70 delta CT104) that nevertheless continues to be mitogen regulated. Coexpression with a recombinant constitutively active phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase (EC 2.7.1.137) gives substantial activation of both full-length p70 and p70 delta CT104 but not Rsk. Activation of p70 delta CT104 by PI 3-kinase and inhibition by wortmannin are each accompanied by parallel and selective changes in the phosphorylation of p70 Thr-252. A Thr or Ser at this site, in subdomain VIII of the catalytic domain just amino-terminal to the APE motif, is necessary for p70 40S kinase activity. The inactive ATP-binding site mutant K123M p70 delta CT104 undergoes phosphorylation of Thr-252 in situ but does not undergo direct phosphorylation by the active PI 3-kinase in vitro. PI 3-kinase provides a signal necessary for the mitogen activation of the p70 S6 kinase, which directs the site-specific phosphorylation of Thr-252 in the p70 catalytic domain, through a distinctive signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee P., Ahmad M. F., Grove J. R., Kozlosky C., Price D. J., Avruch J. Molecular structure of a major insulin/mitogen-activated 70-kDa S6 protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Duckworth B. C., Hou W. M., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L. C. A tightly associated serine/threonine protein kinase regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1657–1665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhand R., Hara K., Hiles I., Bax B., Gout I., Panayotou G., Fry M. J., Yonezawa K., Kasuga M., Waterfield M. D. PI 3-kinase: structural and functional analysis of intersubunit interactions. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):511–521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06289.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhand R., Hiles I., Panayotou G., Roche S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Vicendo P., Yonezawa K. PI 3-kinase is a dual specificity enzyme: autoregulation by an intrinsic protein-serine kinase activity. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):522–533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Bannwarth W., Morley S. J., Totty N. F., Thomas G. Activation of p70s6k is associated with phosphorylation of four clustered sites displaying Ser/Thr-Pro motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7282–7286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Banerjee P., Balasubramanyam A., Coffer P. J., Price D. J., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. Cloning and expression of two human p70 S6 kinase polypeptides differing only at their amino termini. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5541–5550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Price D. J., Banerjee P., Balasubramanyam A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J. Regulation of an epitope-tagged recombinant Rsk-1 S6 kinase by phorbol ester and erk/MAP kinase. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 3;32(30):7727–7738. doi: 10.1021/bi00081a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Schlessinger J. Direct association of p110 beta phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with p85 is mediated by an N-terminal fragment of p110 beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2577–2583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q., Klippel A., Muslin A. J., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. Ras-dependent induction of cellular responses by constitutively active phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Apr 7;268(5207):100–102. doi: 10.1126/science.7701328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Hirano M., Williams L. T. The interaction of small domains between the subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase determines enzyme activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2675–2685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Hu Q., Williams L. T. A region of the 85-kilodalton (kDa) subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binds the 110-kDa catalytic subunit in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5560–5566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. A., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J., Thomas G. p70s6k function is essential for G1 progression. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):170–172. doi: 10.1038/363170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoinne A., Erikson E., Maller J. L., Price D. J., Avruch J., Cohen P. Purification and characterisation of the insulin-stimulated protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle; close similarity to S6 kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):723–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Signal transduction. Hot lips and phosphorylation of protein kinases. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):686–686. doi: 10.1038/367686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay N. K., Price D. J., Kyriakis J. M., Pelech S., Sanghera J., Avruch J. An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3325–3335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T., Kawano Y., Sakakibara T., Hazeki O., Ui M. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced glucose transport and antilipolysis in rat adipocytes. Studies with a selective inhibitor wortmannin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3568–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Gunsalus J. R., Avruch J. Insulin activates a 70-kDa S6 kinase through serine/threonine-specific phosphorylation of the enzyme polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7944–7948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Mukhopadhyay N. K., Avruch J. Insulin-activated protein kinases phosphorylate a pseudosubstrate synthetic peptide inhibitor of the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16281–16284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J., Thomas G. Nuclear localization of p85s6k: functional requirement for entry into S phase. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1557–1565. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schu P. V., Takegawa K., Fry M. J., Stack J. H., Waterfield M. D., Emr S. D. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.8385367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos C. J., Matter W. F., Hui K. Y., Brown R. F. A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5241–5248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Q. P., Andrabi K., Kozlowski M. T., Grove J. R., Avruch J. Multiple independent inputs are required for activation of the p70 S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2333–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano H., Nakanishi S., Kimura K., Hanai N., Saitoh Y., Fukui Y., Nonomura Y., Matsuda Y. Inhibition of histamine secretion by wortmannin through the blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25846–25856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]