Abstract
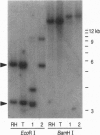
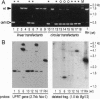
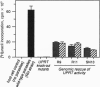
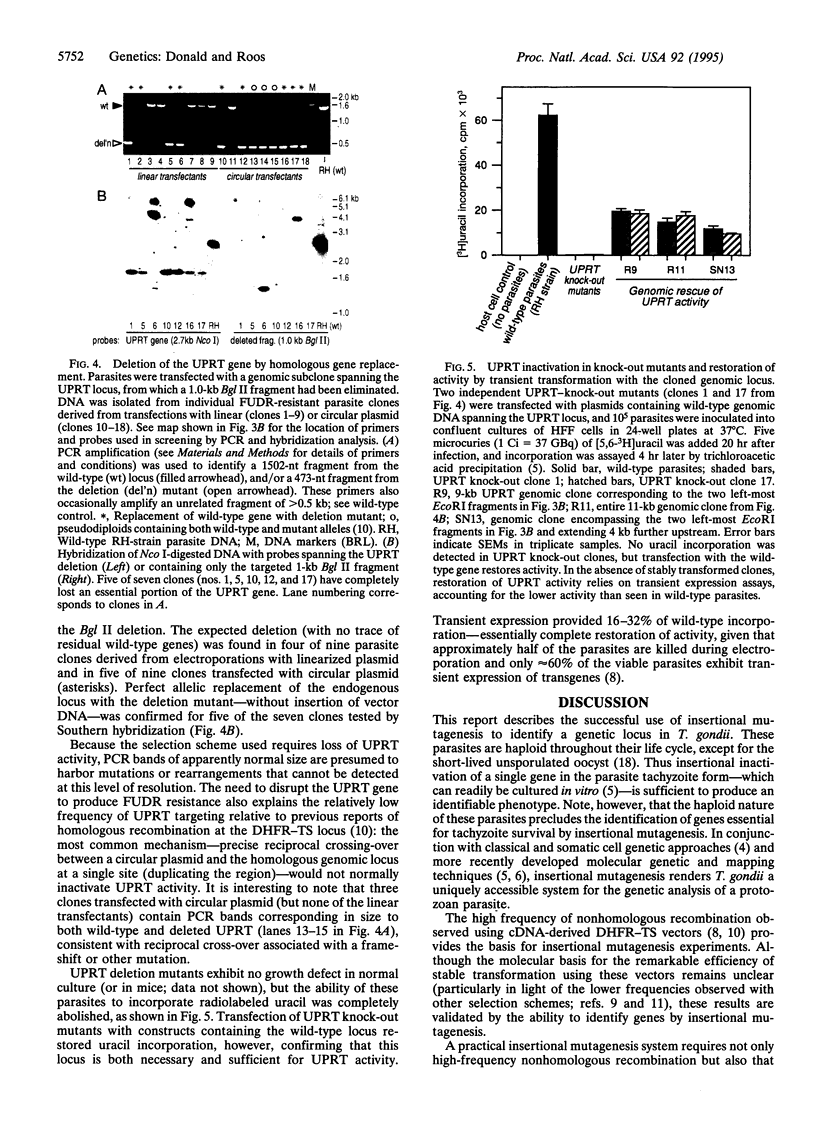
Nonhomologous integration vectors have been used to demonstrate the feasibility of insertional mutagenesis in haploid tachyzoites of the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Mutant clones resistant to 5-fluorouracil were identified at a frequency of approximately 10(-6) (approximately 2 x 10(-5) of the stable transformants). Four independent mutants were isolated, all of which were shown to lack uracil phosphoribosyl-transferase (UPRT) activity and harbor transgenes integrated at closely linked loci, suggesting inactivation of the UPRT-encoding gene. Genomic DNA flanking the insertion point (along with the integrated vector) was readily recovered by bacterial transformation with restriction-digested, self-ligated total genomic DNA. Screening of genomic libraries with the recovered fragment identified sequences exhibiting high homology to known UPRT-encoding genes from other species, and cDNA clones were isolated that contain a single open reading frame predicted to encode the 244-amino acid enzyme. Homologous recombination vectors were exploited to create genetic knock-outs at the UPRT locus, which are deficient in enzyme activity but can be complemented by transient transformation with wild-type sequences--formally confirming identification of the functional UPRT gene. Mapping of transgene insertion points indicates that multiple independent mutants arose from integration at distinct sites within the UPRT gene, suggesting that nonhomologous integration is sufficiently random to permit tagging of the entire parasite genome in a single transformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg C. A., Spradling A. C. Studies on the rate and site-specificity of P element transposition. Genetics. 1991 Mar;127(3):515–524. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen A. W., Overdulve J. P., van der Ploeg M. Determination of nuclear DNA of five eucoccidian parasites, Isospora (Toxoplasma) gondii, Sarcocystis cruzi, Eimeria tenella, E. acervulina and Plasmodium berghei, with special reference to gamontogenesis and meiosis in I. (T.) gondii. Parasitology. 1984 Jun;88(Pt 3):531–553. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Morry M. J., Biggs B. A., Cross G. A., Foote S. J. Amino acid changes linked to pyrimethamine resistance in the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9109–9113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Roos D. S. Homologous recombination and gene replacement at the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase locus in Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Feb;63(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Roos D. S. Stable molecular transformation of Toxoplasma gondii: a selectable dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase marker based on drug-resistance mutations in malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11703–11707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallerano R. H., Marr J. J., Sosa R. R. Therapeutic efficacy of allopurinol in patients with chronic Chagas' disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Aug;43(2):159–166. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iltzsch M. H. Pyrimidine salvage pathways in Toxoplasma gondii. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 Jan-Feb;40(1):24–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iltzsch M. H., Tankersley K. O. Structure-activity relationship of ligands of uracil phosphoribosyltransferase from Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 17;48(4):781–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern L., de Montigny J., Jund R., Lacroute F. The FUR1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning, structure and expression of wild-type and mutant alleles. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90026-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Soldati D., Boothroyd J. C. Gene replacement in Toxoplasma gondii with chloramphenicol acetyltransferase as selectable marker. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):911–914. doi: 10.1126/science.8235614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Allaudeen H. S., Becker J. M., Current W. L., Feinberg J., Frenkel J. K., Hafner R., Hughes W. T., Laughlin C. A., Meyers J. D. From the National Institutes of Health. Summary of the workshop on future directions in discovery and development of therapeutic agents for opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):244–251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;15(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez S., Marr J. J. Allopurinol in the treatment of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 12;326(11):741–744. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203123261105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. S., Walliker D., Wellems T. E. Evidence that a point mutation in dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase confers resistance to pyrimethamine in falciparum malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9114–9118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Borotz S. E. Toxoplasma gondii: characterization of a mutant resistant to 6-thioxanthine. Exp Parasitol. 1994 Nov;79(3):374–382. doi: 10.1006/expr.1994.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Toxoplasma gondii: characterization of a mutant resistant to 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Toxoplasma gondii: the enzymic defect of a mutant resistant to 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Feb;44(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn L. C., Pfefferkorn E. R. Toxoplasma gondii: genetic recombination between drug resistant mutants. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Dec;50(3):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D. S. Primary structure of the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene from Toxoplasma gondii. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6269–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman J. D., Pfefferkorn E. R. Pyrimidine synthesis by intracellular Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1981 Apr;67(2):150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., LeBlanc A. J., Pfefferkorn E. R., Boothroyd J. C. Generation of a restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map for Toxoplasma gondii. Genetics. 1992 Dec;132(4):1003–1015. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Messina M., Niesman I. R. Stable DNA transformation in the obligate intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii by complementation of tryptophan auxotrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5508–5512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati D., Boothroyd J. C. Transient transfection and expression in the obligate intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):349–352. doi: 10.1126/science.8469986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam L. W., Lefebvre P. A. Cloning of flagellar genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by DNA insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):375–384. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Gu H. M., Bzik D. J., Li W. B., Inselburg J. W. Dihydrofolate reductase mutations and chromosomal changes associated with pyrimethamine resistance of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Feb;39(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90015-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenant-Flowers M., Boyle M. J., Carey D., Marriott D. J., Harkness J. L., Penny R., Cooper D. A. Sulphadiazine desensitization in patients with AIDS and cerebral toxoplasmosis. AIDS. 1991 Mar;5(3):311–315. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199103000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoff M. J., Moorman A. F., Lamers W. H. Electroporation in 'intracellular' buffer increases cell survival. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2902–2902. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]