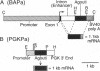
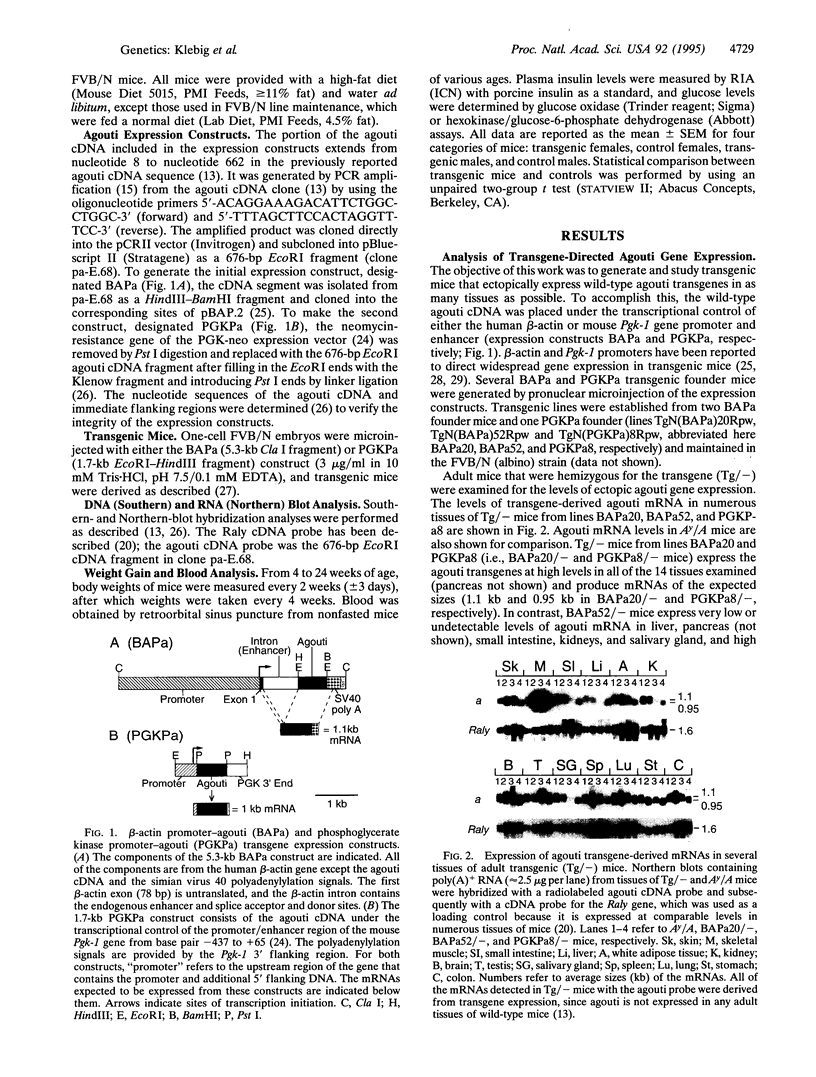
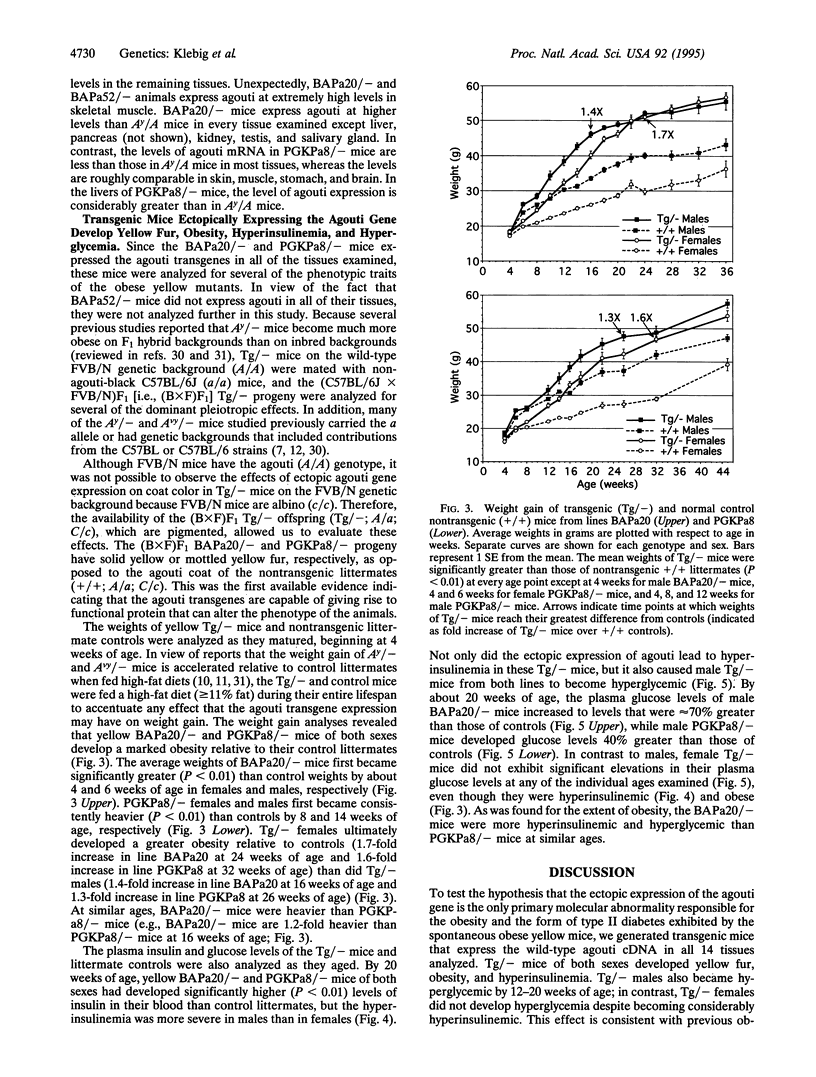
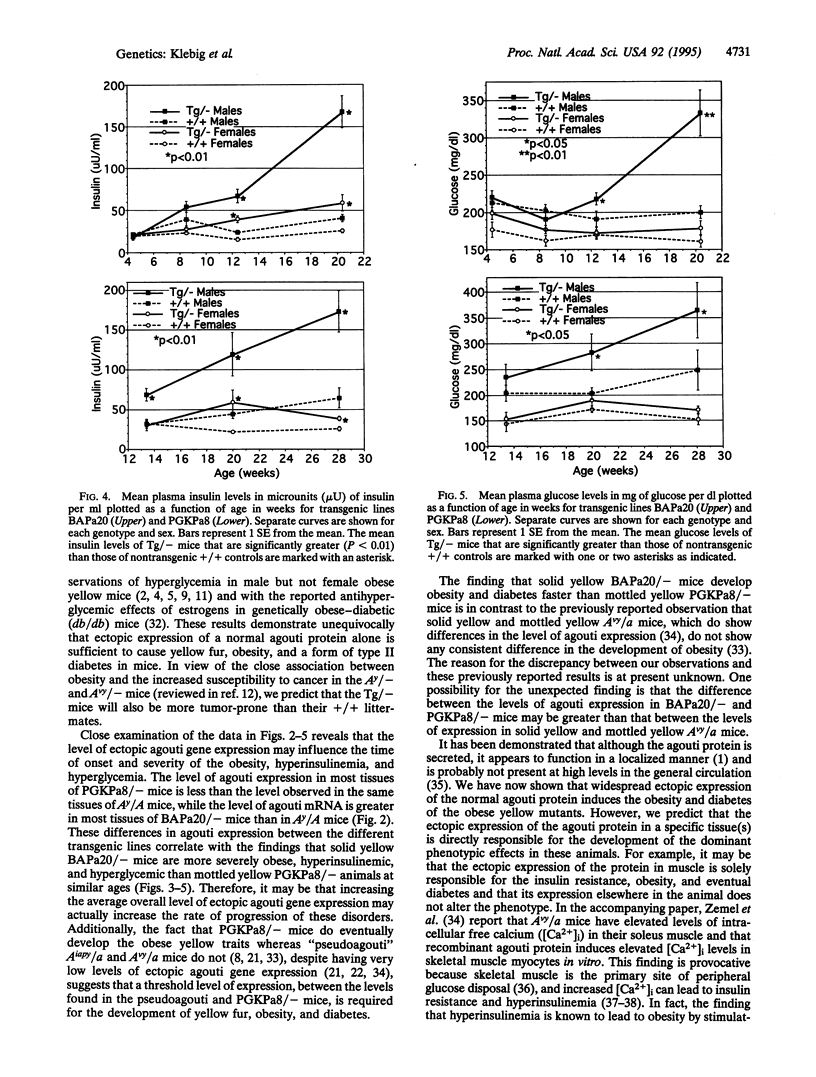
Abstract
Mice that carry the lethal yellow (Ay) or viable yellow (Avy) mutation, two dominant mutations of the agouti (a) gene in mouse chromosome 2, exhibit a phenotype that includes yellow fur, marked obesity, a form of type II diabetes associated with insulin resistance, and an increased susceptibility to tumor development. Molecular analyses of these and several other dominant "obese yellow" a-locus mutations suggested that ectopic expression of the normal agouti protein gives rise to this complex pleiotropic phenotype. We have now tested this hypothesis directly by generating transgenic mice that ectopically express an agouti cDNA clone encoding the normal agouti protein in all tissues examined. Transgenic mice of both sexes have yellow fur, become obese, and develop hyperinsulinemia. In addition, male transgenic mice develop hyperglycemia by 12-20 weeks of age. These results demonstrate conclusively that the ectopic agouti expression is responsible for most, if not all, of the phenotypic traits of the dominant, obese yellow mutants.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balling R., Mutter G., Gruss P., Kessel M. Craniofacial abnormalities induced by ectopic expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1.1 in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bultman S. J., Klebig M. L., Michaud E. J., Sweet H. O., Davisson M. T., Woychik R. P. Molecular analysis of reverse mutations from nonagouti (a) to black-and-tan (a(t)) and white-bellied agouti (Aw) reveals alternative forms of agouti transcripts. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):481–490. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bultman S. J., Michaud E. J., Woychik R. P. Molecular characterization of the mouse agouti locus. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER K. J., MAYER J. Physiologic observations on yellow obesity in the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jun;193(3):499–504. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson G. E., Gowen J. W. Hereditary Obesity and Efficient Food Utilization in Mice. Science. 1947 May 9;105(2732):496–498. doi: 10.1126/science.105.2732.496-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Sussman K., Kao M., Lewis D., Sherman N. The existence of an optimal range of cytosolic free calcium for insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14385–14388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhl D. M., Vrieling H., Miller K. A., Wolff G. L., Barsh G. S. Neomorphic agouti mutations in obese yellow mice. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):59–65. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENTON P. F., CHASE H. B. Effect of diet on obesity of yellow mice in inbred lines. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jul;77(3):420–422. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigeri L. G., Wolff G. L., Robel G. Impairment of glucose tolerance in yellow (Avy/A) (BALB/c X VY) F-1 hybrid mice by hyperglycemic peptide(s) from human pituitary glands. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2097–2105. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigeri L. G., Wolff G. L., Teguh C. Differential responses of yellow Avy/A and agouti A/a (BALB/c X VY) F1 hybrid mice to the same diets: glucose tolerance, weight gain, and adipocyte cellularity. Int J Obes. 1988;12(4):305–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz I., Miwa H., Konda Y., Shimoto Y., Tashiro T., Watson S. J., DelValle J., Yamada T. Molecular cloning, expression, and gene localization of a fourth melanocortin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15174–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill A. M., Yen T. T. Effects of ciglitazone on endogenous plasma islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin sensitivity in obese-diabetic viable yellow mice. Life Sci. 1991;48(7):703–710. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90546-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLERSTROM C., HELLMAN B. The Islets of Langerhans in yellow obese mice. Metabolism. 1963 Jun;12:527–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon H. Y., Bultman S. J., Löffler C., Chen W. J., Furdon P. J., Powell J. G., Usala A. L., Wilkison W., Hansmann I., Woychik R. P. Molecular structure and chromosomal mapping of the human homolog of the agouti gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9760–9764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Beamer W. G., Coleman D. L., Longcope C. Androgenic and estrogenic metabolites in serum of mice fed dehydroepiandrosterone: relationship to antihyperglycemic effects. Metabolism. 1987 Sep;36(9):863–869. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D., Willard D., Patel I. R., Kadwell S., Overton L., Kost T., Luther M., Chen W., Woychik R. P., Wilkison W. O. Agouti protein is an antagonist of the melanocyte-stimulating-hormone receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 27;371(6500):799–802. doi: 10.1038/371799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Sutherland L. C., Adra C. N., Leclair B., Rudnicki M. A., Jardine K. The mouse Pgk-1 gene promoter contains an upstream activator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5755–5761. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud E. J., Bultman S. J., Klebig M. L., van Vugt M. J., Stubbs L. J., Russell L. B., Woychik R. P. A molecular model for the genetic and phenotypic characteristics of the mouse lethal yellow (Ay) mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud E. J., Bultman S. J., Stubbs L. J., Woychik R. P. The embryonic lethality of homozygous lethal yellow mice (Ay/Ay) is associated with the disruption of a novel RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1203–1213. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud E. J., van Vugt M. J., Bultman S. J., Sweet H. O., Davisson M. T., Woychik R. P. Differential expression of a new dominant agouti allele (Aiapy) is correlated with methylation state and is influenced by parental lineage. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1463–1472. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. W., Duhl D. M., Vrieling H., Cordes S. P., Ollmann M. M., Winkes B. M., Barsh G. S. Cloning of the mouse agouti gene predicts a secreted protein ubiquitously expressed in mice carrying the lethal yellow mutation. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):454–467. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountjoy K. G., Robbins L. S., Mortrud M. T., Cone R. D. The cloning of a family of genes that encode the melanocortin receptors. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1248–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.1325670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pravtcheva D. D., Adra C. N., Ruddle F. H. Timing of paternal Pgk-1 expression in embryos of transgenic mice. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1109–1120. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistad G. B., Skinner W. S. Isolation and sequencing of insecticidal peptides from the primitive hunting spider, Plectreurys tristis (Simon). J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11098–11101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Higgins K. M., Tan J. C., Chu T. Y., Yee N. S., Nguyen H., Lacy E., Besmer P. Ectopic expression of a c-kitW42 minigene in transgenic mice: recapitulation of W phenotypes and evidence for c-kit function in melanoblast progenitors. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2265–2273. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M. A., Lewis U. J., Haro L. S., Kishi K., McAllister D. L., Seavey B. K., Bee G., Wolff G. L. Effects of hypophysectomy and the insulin-like and anti-insulin pituitary peptides on carbohydrate metabolism in yellow Avy/A (BALB/c x VY)F1 hybrid mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Sep;191(4):408–419. doi: 10.3181/00379727-191-42942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M. A., Wolff G. L. Potentiation of response to insulin and anti-insulin action by two human pituitary peptides in lean agouti A/a, obese yellow Avy/A, and C57BL/6J-ob/ob mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Jun;191(2):113–123. doi: 10.3181/00379727-191-42896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamate H. B., Takeuchi T. Action of the e locus of mice in the response of phaeomelanic hair follicles to alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in vitro. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1241–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.6328651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF G. L. BODY COMPOSITION AND COAT COLOR CORRELATION IN DIFFERENT PHENOTYPES OF "VIABLE YELLOW" MICE. Science. 1965 Mar 5;147(3662):1145–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3662.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF G. L. GROWTH OF INBRED YELLOW (AYA) AND NON-YELLOW (AA) MICE IN PARABIOSIS. Genetics. 1963 Aug;48:1041–1058. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.8.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warbritton A., Gill A. M., Yen T. T., Bucci T., Wolff G. L. Pancreatic islet cells in preobese yellow Avy/- mice: relation to adult hyperinsulinemia and obesity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1994 Jun;206(2):145–151. doi: 10.3181/00379727-206-43733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Greenman D. L., Frigeri L. G., Morrissey R. L., Suber R. L., Felton R. P. Diabetogenic response to streptozotocin varies among obese yellow and among lean agouti (BALB/c x VY)F1 hybrid mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1990 Feb;193(2):155–163. doi: 10.3181/00379727-193-43017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Pitot H. C. Influence of background genome on enzymatic characteristics of yellow (A v -, A vy -) mice. Genetics. 1973 Jan;73(1):109–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Roberts D. W., Galbraith D. B. Prenatal determination of obesity, tumor susceptibility, and coat color pattern in viable yellow (Avy/a) mice. The yellow mouse syndrome. J Hered. 1986 May-Jun;77(3):151–158. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. T., Gill A. M., Frigeri L. G., Barsh G. S., Wolff G. L. Obesity, diabetes, and neoplasia in yellow A(vy)/- mice: ectopic expression of the agouti gene. FASEB J. 1994 May;8(8):479–488. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.8.8181666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel M. B., Kim J. H., Woychik R. P., Michaud E. J., Kadwell S. H., Patel I. R., Wilkison W. O. Agouti regulation of intracellular calcium: role in the insulin resistance of viable yellow mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4733–4737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]