Abstract
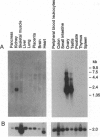
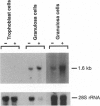
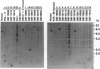
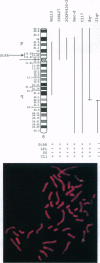
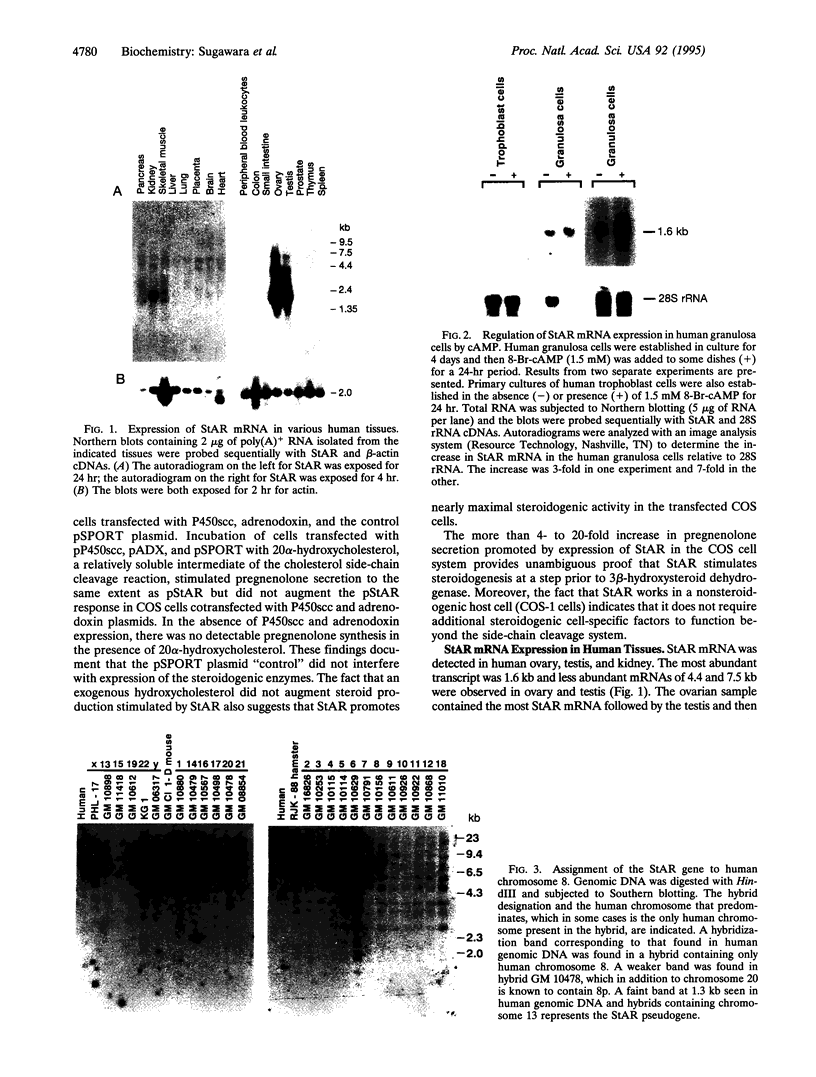
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) appears to mediate the rapid increase in pregnenolone synthesis stimulated by tropic hormones. cDNAs encoding StAR were isolated from a human adrenal cortex library. Human StAR, coexpressed in COS-1 cells with cytochrome P450scc and adrenodoxin, increased pregnenolone synthesis > 4-fold. A major StAR transcript of 1.6 kb and less abundant transcripts of 4.4 and 7.5 kb were detected in ovary and testis. Kidney had a lower amount of the 1.6-kb message. StAR mRNA was not detected in other tissues including placenta. Treatment of granulosa cells with 8-bromo-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate for 24 hr increased StAR mRNA 3-fold or more. The structural gene encoding StAR was mapped using somatic cell hybrid mapping panels to chromosome 8p. Fluorescence in situ hybridization placed the StAR locus in the region 8p11.2. A StAR pseudogene was mapped to chromosome 13. We conclude that StAR expression is restricted to tissues that carry out mitochondrial sterol oxidations subject to acute regulation by cAMP and that StAR mRNA levels are regulated by cAMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang Y. J., McCabe R. T., Rennert H., Budarf M. L., Sayegh R., Emanuel B. S., Skolnick P., Strauss J. F., 3rd The human "peripheral-type" benzodiazepine receptor: regional mapping of the gene and characterization of the receptor expressed from cDNA. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jul-Aug;11(6):471–480. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. J., Wells J., King S. R., Stocco D. M. The purification, cloning, and expression of a novel luteinizing hormone-induced mitochondrial protein in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Characterization of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR). J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28314–28322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. F., Orme-Johnson N. R. Regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Identification of precursors of a phosphoprotein targeted to the mitochondrion in stimulated rat adrenal cortex cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19739–19745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON J. J., Jr PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND ADRENOCORTICOTROPIN RESPONSIVENESS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2754–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink T. M., Zimmer M., Tschopp J., Etienne J., Jenne D. E., Lichter P. Human clusterin (CLI) maps to 8p21 in proximity to the lipoprotein lipase (LPL) gene. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):526–528. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Digitized and differentially shaded human chromosome ideograms for genomic applications. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;65(3):206–218. doi: 10.1159/000133633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garren L. D., Ney R. L., Davis W. W. Studies on the role of protein synthesis in the regulation of corticosterone production by adrenocorticotropic hormone in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1443–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golos T. G., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Human chorionic gonadotropin and 8-bromo cyclic adenosine monophosphate promote an acute increase in cytochrome P450scc and adrenodoxin messenger RNAs in cultured human granulosa cells by a cycloheximide-insensitive mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):896–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI113149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. F. Trophic stimulation of steroidogenesis: in search of the elusive trigger. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:1–39. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571141-8.50005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Molecular structure and functional characterization of a human complement cytolysis inhibitor found in blood and seminal plasma: identity to sulfated glycoprotein 2, a constituent of rat testis fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7123–7127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang G., McKenzie T. L., Conrad D. G., Shechter I. Transcriptional regulation by lovastatin and 25-hydroxycholesterol in HepG2 cells and molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the human hepatic squalene synthase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12818–12824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman S., Prasad V. V. Heterodox notions on pathways of steroidogenesis. Endocr Rev. 1990 Nov;11(4):469–493. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-4-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H. Neurosteroids: biochemistry, modes of action, and clinical relevance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 May;78(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.5.8175951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Jones C., Hart I., Bleskan J., Berger R., Geyer D., Eisenberg S. P., Smith M. F., Jr, Arend W. P. The human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) gene is located in the chromosome 2q14 region. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):173–176. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Voutilainen R., Kao L. C., Chung B. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin: cloning of three cDNAs and cycloheximide enhancement in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon L. A., Orme-Johnson N. R. Acute stimulation of steroidogenesis in corpus luteum and adrenal cortex by peptide hormones. Rapid induction of a similar protein in both tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6594–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler G. E., Kao L. C., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Effects of 8-bromo-cAMP on expression of endocrine functions by cultured human trophoblast cells. Regulation of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;61(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Cheng S. V., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Drabkin H. A., Patterson D., Haines J. H., Papas T. S. The ETS genes on chromosome 21 are distal to the breakpoint of the acute myelogenous leukemia translocation (8;21). Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Conrad D. G., Hart I., Berger R. C., McKenzie T. L., Bleskan J., Patterson D. Localization of the squalene synthase gene (FDFT1) to human chromosome 8p22-p23.1. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):116–118. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., McCarthy J. L., Peterson J. A. Evidence that the cycloheximide-sensitive site of adrenocorticotropic hormone action is in the mitochondrion. Changes in pregnenolone formation, cholesterol content, and the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocco D. M., Ascoli M. The use of genetic manipulation of MA-10 Leydig tumor cells to demonstrate the role of mitochondrial proteins in the acute regulation of steroidogenesis. Endocrinology. 1993 Mar;132(3):959–967. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.3.8382603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocco D. M., Chen W. Presence of identical mitochondrial proteins in unstimulated constitutive steroid-producing R2C rat Leydig tumor and stimulated nonconstitutive steroid-producing MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Apr;128(4):1918–1926. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-4-1918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocco D. M., Sodeman T. C. The 30-kDa mitochondrial proteins induced by hormone stimulation in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells are processed from larger precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19731–19738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toaff M. E., Schleyer H., Strauss J. F., 3rd Metabolism of 25-hydroxycholesterol by rat luteal mitochondria and dispersed cells. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1785–1790. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Ge Y., Siciliano M., Wells D. E. A hybrid cell mapping panel for regional localization of probes to human chromosome 8. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):114–125. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90491-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wion K. L., Kirchgessner T. G., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C., Lawn R. M. Human lipoprotein lipase complementary DNA sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1638–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.3823907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R., Kallen C. B., Babalola G. O., Rennert H., Billheimer J. T., Strauss J. F., 3rd Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding human sterol carrier protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):463–467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Harmony J. A., Stuart W. D., Gil C. M., Robbins J. Apolipoprotein J: structure and tissue distribution. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5380–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]