Abstract
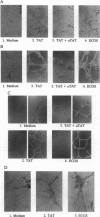
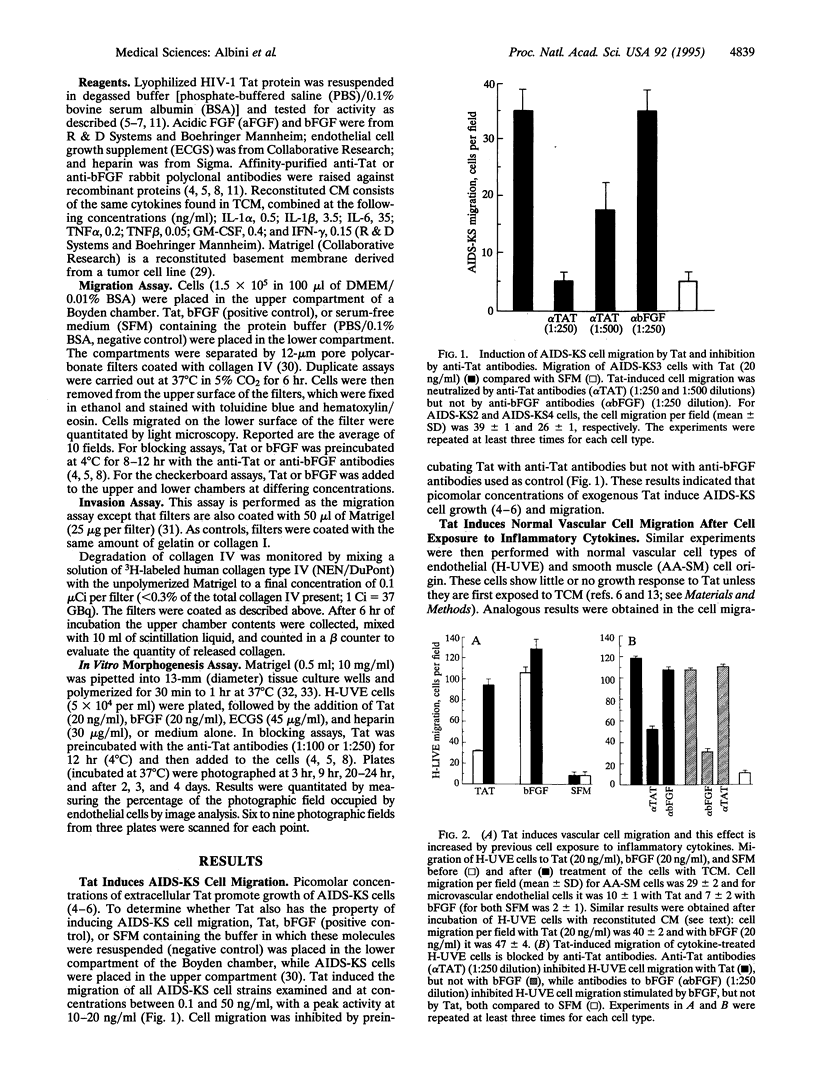
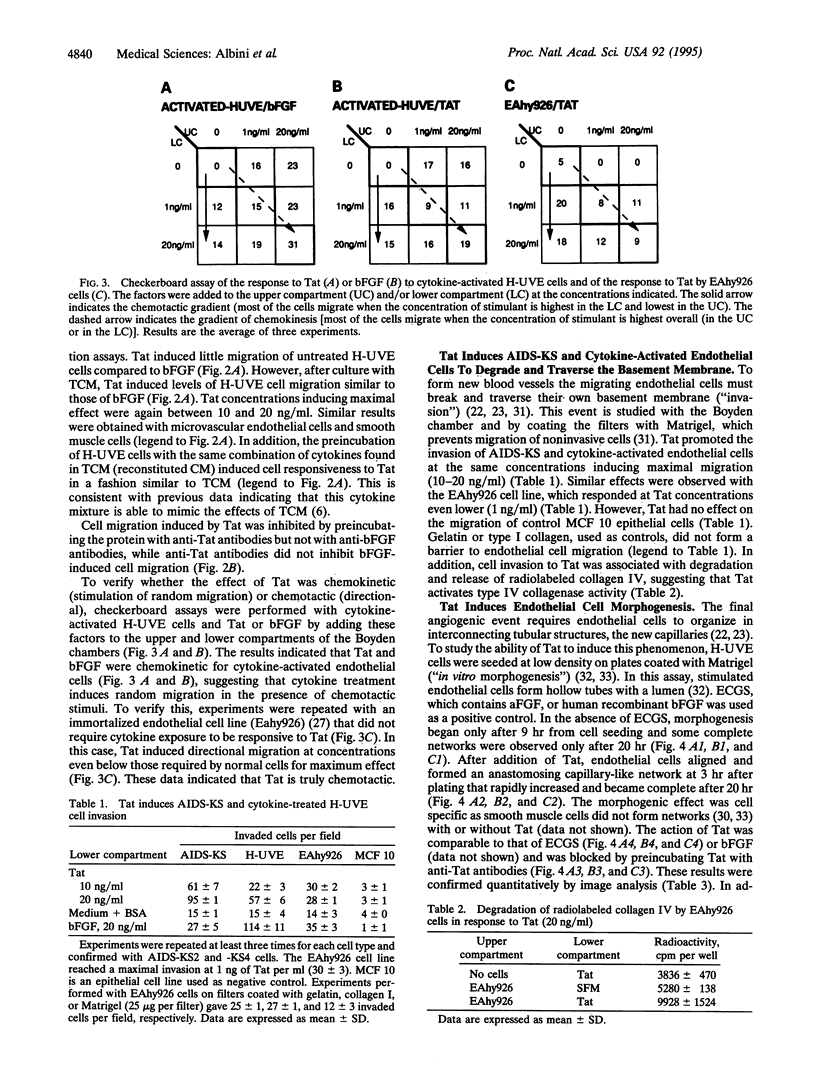
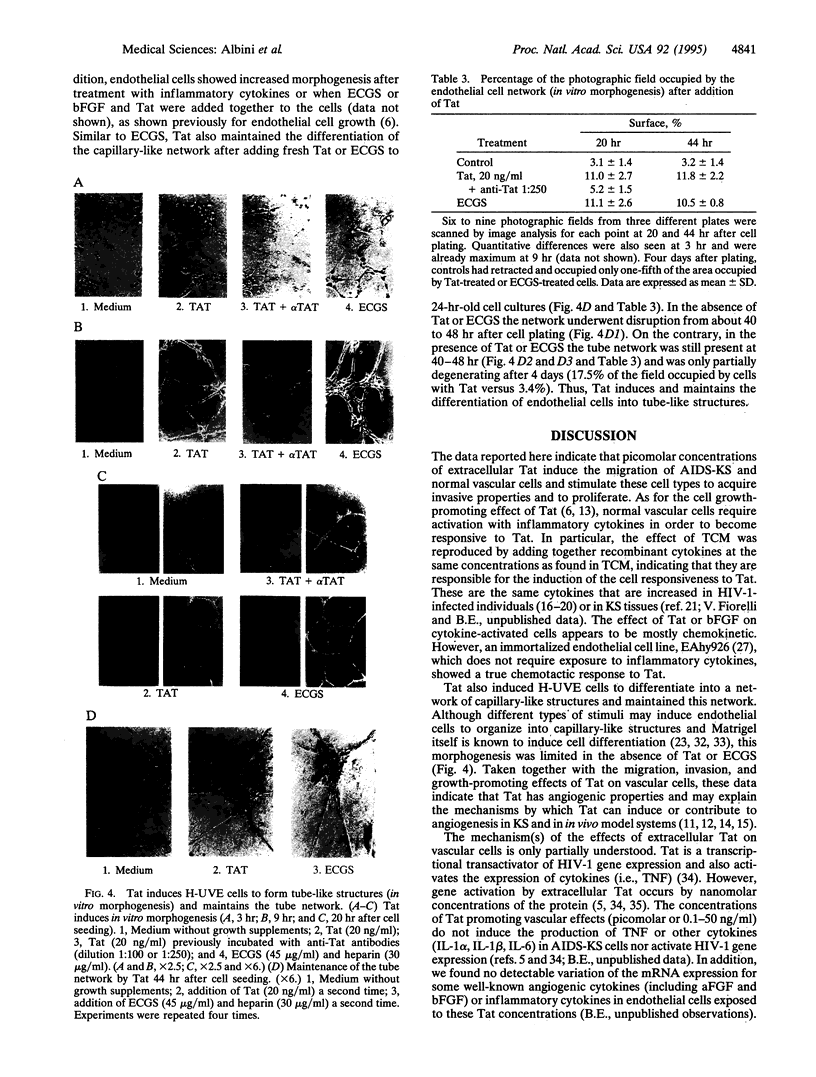
Extracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Tat protein promotes growth of spindle cells derived from AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma (AIDS-KS), an angioproliferative disease very frequent in HIV-1-infected individuals. Normal vascular cells, progenitors of AIDS-KS cells, proliferate in response to Tat after exposure to inflammatory cytokines, whose levels are augmented in HIV-1-infected individuals and in KS lesions. Here we show that Tat also promotes AIDS-KS and normal vascular cells to migrate and to degrade the basement membrane and stimulates endothelial cell morphogenesis on a matrix substrate. These effects are obtained at picomolar concentrations of exogenous Tat and are promoted by the treatment of the cells with the same inflammatory cytokines stimulating expression of the receptors for Tat, the integrins alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3. Thus, under specific circumstances, Tat has angiogenic properties. As Tat and its receptors are present in AIDS-KS lesions, these data may explain some of the mechanisms by which Tat can induce angiogenesis and cooperate in the development of AIDS-KS.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Allavena G., Melchiori A., Giancotti F., Richter H., Comoglio P. M., Parodi S., Martin G. R., Tarone G. Chemotaxis of 3T3 and SV3T3 cells to fibronectin is mediated through the cell-attachment site in fibronectin and a fibronectin cell surface receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1867–1872. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albini A., Fontanini G., Masiello L., Tacchetti C., Bigini D., Luzzi P., Noonan D. M., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Angiogenic potential in vivo by Kaposi's sarcoma cell-free supernatants and HIV-1 tat product: inhibition of KS-like lesions by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2. AIDS. 1994 Sep;8(9):1237–1244. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199409000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albini A., Iwamoto Y., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Aaronson S. A., Kozlowski J. M., McEwan R. N. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barillari G., Buonaguro L., Fiorelli V., Hoffman J., Michaels F., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. Effects of cytokines from activated immune cells on vascular cell growth and HIV-1 gene expression. Implications for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3727–3734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barillari G., Gendelman R., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. The Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, a growth factor for AIDS Kaposi sarcoma and cytokine-activated vascular cells, induces adhesion of the same cell types by using integrin receptors recognizing the RGD amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Clark R. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.7512751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonaguro L., Barillari G., Chang H. K., Bohan C. A., Kao V., Morgan R., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7159–7167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7159-7167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corallini A., Altavilla G., Pozzi L., Bignozzi F., Negrini M., Rimessi P., Gualandi F., Barbanti-Brodano G. Systemic expression of HIV-1 tat gene in transgenic mice induces endothelial proliferation and tumors of different histotypes. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5569–5575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W., Lipsky P. E. Fibronectin promotes proliferation of naive and memory T cells by signaling through both the VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrin molecules. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell C. J., McDonald C. C., Graham J. B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Buonaguro L., Barillari G., Fiorelli V., Gendelman R., Morgan R. A., Wingfield P., Gallo R. C. Release, uptake, and effects of extracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on cell growth and viral transactivation. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):277–287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.277-287.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Gendelman R., Markham P., Fiorelli V., Colombini S., Raffeld M., Cafaro A., Chang H. K., Brady J. N., Gallo R. C. Synergy between basic fibroblast growth factor and HIV-1 Tat protein in induction of Kaposi's sarcoma. Nature. 1994 Oct 20;371(6499):674–680. doi: 10.1038/371674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Markham P., Kao V., Barillari G., Fiorelli V., Gendelman R., Raffeld M., Zon G., Gallo R. C. Block of AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cell growth, angiogenesis, and lesion formation in nude mice by antisense oligonucleotide targeting basic fibroblast growth factor. A novel strategy for the therapy of KS. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):1736–1746. doi: 10.1172/JCI117521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Larsson L., Beaver B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells express cytokines with autocrine and paracrine growth effects. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2643161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J., Bass H. Z., Fahey J. L. Elevated IFN-gamma and decreased IL-2 gene expression are associated with HIV infection. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):5031–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E. Disseminated Kaposi's sarcoma syndrome in young homosexual men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Oct;5(4):468–471. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D., Zangerle R., Artner-Dworzak E., Weiss G., Werner-Felmayer G., Wachter H. Increased interferon-gamma and reduced hemoglobin in patients with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(4):424–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. S., Tashiro K., Segui-Real B., Yamada Y., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. Two different laminin domains mediate the differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures in vitro. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumkowski F., Kaminska G., Kaminski M., Morrissey L. W., Auerbach R. Heterogeneity of mouse vascular endothelium. In vitro studies of lymphatic, large blood vessel and microvascular endothelial cells. Blood Vessels. 1987;24(1-2):11–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hober D., Haque A., Wattre P., Beaucaire G., Mouton Y., Capron A. Production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) in patients with AIDS. Enhanced level of TNF-alpha is related to a higher cytotoxic activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):329–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Prusty D., Frangioni J. V., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C., Schwartz M. A. Control of intracellular pH and growth by fibronectin in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1803–1811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Hassell J. R., Star V. L., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Martin G. R. Basement membrane complexes with biological activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):312–318. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Lawley T. J. Role of laminin and basement membrane in the morphological differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1589–1598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., von Asmuth E. J., Jeunhomme T. M., Buurman W. A. IFN-gamma regulates the expression of the adhesion molecule ELAM-1 and IL-6 production by human endothelial cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2110–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepe-Zuniga J. L., Mansell P. W., Hersh E. M. Idiopathic production of interleukin-1 in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1695–1700. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1695-1700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Ensoli B., Markham P. D., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Kaposi's sarcoma cells: long-term culture with growth factor from retrovirus-infected CD4+ T cells. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.3262925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochieng J., Basolo F., Albini A., Melchiori A., Watanabe H., Elliott J., Raz A., Parodi S., Russo J. Increased invasive, chemotactic and locomotive abilities of c-Ha-ras-transformed human breast epithelial cells. Invasion Metastasis. 1991;11(1):38–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxholm A., Oxholm P., Permin H., Bendtzen K. Epidermal tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6-like activities in AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. An immunohistological study. APMIS. 1989 Jun;97(6):533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regezi J. A., MacPhail L. A., Daniels T. E., DeSouza Y. G., Greenspan J. S., Greenspan D. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated oral Kaposi's sarcoma. A heterogeneous cell population dominated by spindle-shaped endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):240–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safai B., Johnson K. G., Myskowski P. L., Koziner B., Yang S. Y., Cunningham-Rundles S., Godbold J. H., Dupont B. The natural history of Kaposi's sarcoma in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):744–750. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Nakamura S., Biberfeld P., Kaplan M. H., Markham P. D., Larsson L., Gallo R. C. Angiogenic properties of Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells after long-term culture in vitro. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):430–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2459779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Wacher M. P., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. The activation of human type IV collagenase proenzyme. Sequence identification of the major conversion product following organomercurial activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1353–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. W., Nakamura S., Shima T. B., Melchiori A., Martin G. R., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Albini A. Supernatants of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related Kaposi's sarcoma cells induce endothelial cell chemotaxis and invasiveness. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2670–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Thorgeirsson U. P., Rao C. N., Liotta L. A. Laminin increases the release of type IV collagenase from malignant cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Luciw P. A., Jay G. The HIV tat gene induces dermal lesions resembling Kaposi's sarcoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):606–611. doi: 10.1038/335606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xerri L., Hassoun J., Planche J., Guigou V., Grob J. J., Parc P., Birnbaum D., deLapeyriere O. Fibroblast growth factor gene expression in AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma detected by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):9–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]