Abstract
Alterations in brain glutamate levels may be associated with psychosis risk, but the relationship to clinical outcome in at-risk individuals is unknown. Glutamate concentration was measured in the left thalamus and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) using 3-Tesla proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in 75 participants at ultra high risk (UHR) of psychosis and 56 healthy controls. The severity of attenuated positive symptoms and overall functioning were assessed. Measures were repeated in 51 UHR and 33 Control subjects after a mean of 18 months. UHR subjects were allocated to either remission (no longer meeting UHR criteria) or non-remission (meeting UHR or psychosis criteria) status on follow-up assessment. Thalamic glutamate levels at presentation were lower in the UHR non-remission (N=29) compared with the remission group (N=22) (t(49)=3.03; P=0.004), and were associated with an increase in the severity of total positive symptoms over time (r=−0.33; df=47; P=0.02), most notably abnormal thought content (r=−0.442; df=47; P=0.003). In the UHR group, ACC glutamate levels were lower at follow-up compared with baseline (F(80)=4.28; P=0.04). These findings suggest that measures of brain glutamate function may be useful as predictors of clinical outcome in individuals at high risk of psychosis.
INTRODUCTION
Abnormalities in glutamatergic neurotransmission are thought to have a key role in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia (Goff and Coyle, 2001; Javitt and Zukin, 1991; Olney and Farber, 1995), and this is supported by evidence from postmortem, neuroimaging, and genetic studies (Harrison and Weinberger, 2005; Konradi and Heckers, 2003; Pilowsky et al, 2006). In experimental animals, administration of antagonists at the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor complex leads to injury to cortical neurons (Sharp et al, 2001) and overactivity of medial temporal glutamatergic projections induces striatal hyperdopaminergia (Lodge and Grace, 2007). Glutamatergic dysfunction could thus contribute to the loss of gray matter and dopamine dysfunction that are robust features of schizophrenia (Carlsson et al, 2001; Javitt, 2007; Olney et al, 1999).
The thalamus is a central component of the cortical–subcortical circuits through which psychotic symptoms are thought to be generated (Jones, 1997). Postmortem in schizophrenia, reduced expression of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits specifically occurs in thalamic relay neurons that send projections to the cortex (Sodhi et al, 2011). Thalamic nuclei are especially sensitive to the effects of NMDA antagonist administration, leading to disruptions in cortical activity (Kargieman et al, 2008) and cortical damage (Tomitaka et al, 2000), probably via increased cortical glutamate release from thalamocortical projections (Tomitaka et al, 2000).
The first episode of psychosis is often preceded by a clinical syndrome, termed an ‘at-risk mental state', characterized by attenuated psychotic symptoms and a marked decline in functioning, which can be identified using the ultra high risk (UHR) criteria (Yung et al, 2004). The UHR state is associated with a 20% risk for developing psychosis within 1 year (Fusar-Poli et al, 2012), and risk of transition is greatest in UHR individuals who have low levels of functioning, marked negative symptoms, and disorders of thought content (Nelson et al, 2013). Recent work has questioned the meaningfulness of no-transition/transition outcomes in UHR research (Yung et al, 2010), as the threshold for transition is solely based on the intensity of positive symptoms, and as functional outcomes may be persistently poor in the absence of transition. It is difficult to predict outcome at an individual level on the basis of presenting clinical features (Nelson and Yung, 2010), and neuroimaging measures may be able to help improve prediction (Fusar-Poli et al, 2013a).
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) studies at high field strengths in never or minimally medicated early psychosis have reported elevated levels of the glutamate metabolite glutamine in the thalamus and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) (Theberge et al, 2002; Theberge et al, 2007), elevated ACC glutamine/glutamate ratio (Bustillo et al, 2010), elevated striatal glutamate (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2013b; de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2011), and elevated glutamate plus glutamine in the hippocampus (Kraguljac et al, 2013). In an UHR cohort, we reported lower levels of glutamate in the thalamus, but not ACC, compared with healthy individuals (Stone et al, 2009a). This reduction in thalamic glutamate is associated with lower gray matter volume (Stone et al, 2009a), and abnormal cortical responses during executive functioning (Fusar-Poli et al, 2011), and to auditory stimuli (Stone et al, 2010). Another study in UHR subjects suggests that glutamate levels may be elevated in the striatum (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2011). These findings are consistent with the proposal that glutamatergic abnormalities predate the onset of psychosis (Stone et al, 2009a; Stone and Fusar-Poli, 2009b) leading to the hypothesis that the extent of glutamate dysfunction may contribute to clinical outcome. This issue can best be addressed through longitudinal studies of glutamatergic abnormalities in this group. Preliminary data from a study in a small UHR cohort have recently indicated that greater risk of transition and longer duration of illness were associated with higher glutamate levels in the striatum at baseline (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2013a).
The primary aim of this study was to determine whether regional glutamate levels in UHR subjects at first presentation are predictive of subsequent clinical outcome. The secondary aim was to determine relationships between longitudinal changes in glutamate and mental state. In extension of our previous work that identified reduced glutamate in the left thalamus in UHR individuals (Stone et al, 2009a), we hypothesized that lower thalamic glutamate levels at presentation would be associated with worse clinical outcome, and that longitudinal decreases in thalamic glutamate may be associated with declining mental state. As studies in early psychosis report elevated glutamine or glutamine/glutamate ratio in the ACC (Theberge et al, 2002; Theberge et al, 2007), and meta-analysis suggests that decreases in frontal glutamate in schizophrenia may progress over time (Marsman et al, 2011), we hypothesized ACC glutamate may decline over the study period and associate with increasing symptom severity.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Participants
This study was approved by the Joint South London and Maudsley NHS Trust Research Ethics Committee. All participants gave their written consent to participate. The sample consisted of the 27 healthy control and 27 UHR subjects who had participated in our cross-sectional study (Stone et al, 2009a), plus an additional recruitment of 29 Control and 48 UHR subjects, giving total samples of 56 Control and 75 UHR subjects.
UHR subjects were recruited from OASIS (Outreach and Support in South London) (Fusar-Poli et al, 2013b), and met at-risk mental state criteria (Yung et al, 2005) at the time of baseline imaging. The Control group was recruited from the same geographic area, and had no personal history of psychiatric symptoms, psychotropic medication, or medical illness, and no family history of psychiatric illness. Exclusion criteria included history of head injury, drug or alcohol dependence, metallic implants, or other contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptomatology was assessed using the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental State (CAARMS, severity of abnormal thought content, abnormal speech, and perceptual abnormalities, which were also summed to provide a total severity score for attenuated psychotic symptoms) (Yung et al, 2005) and the positive and negative syndrome scale for schizophrenia. Social and occupational functioning was assessed using the global assessment of functioning scale (GAF), which provides a single score out of a maximum of 100 for social and occupational functioning as well as symptoms. OASIS uses the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental State and GAF to determine UHR inclusion criteria (Fusar-Poli et al, 2013b).
1H-MRS
Scans were acquired at 3-Tesla, as described previously (Egerton et al, 2012a; Stone et al, 2009a) in Control and UHR subjects in parallel. 1H-MRS spectra were acquired using Point RESolved Spectroscopy) (TE=30 msec; TR=3000 msec; 96 averages), further details of 1H-MRS data acquisition and analysis are provided in Supplementary Material. Spectra were analyzed using LC Model version 6.1-4 F (Provencher, 1993), and water-scaled metabolite values were corrected for voxel cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) content. Our approach using PRESS with a TE=30 ms at 3-Tesla is documented to reliably detect glutamate concentrations (Mullins et al, 2008), with contamination by glutamine estimated as <10% (Snyder and Wilman, 2010). Regarding spectral quality, the mean±SD signal to noise ratio and line width as reported by LC Model were: left thalamus; 20±3 and 0.05±0.01 Hz respectively and ACC: 21±6 and 0.04±0.06 Hz respectively. There were no significant group differences in spectral quality. Data relating to the voxel tissue content and the Cramer–Rao minimum variance bounds (CRLB) estimates of fit of the metabolite peaks are presented in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. The primary 1H-MRS glutamate measure was glutamate corrected for voxel CSF content (GLUCSF). For completeness, and to allow comparison with previous literature, where significant results for CSF-corrected glutamate data were detected, CSF-corrected glutamate plus glutamine (GLXCSF) and creatine-scaled glutamate (GLUCR) and glutamate plus glutamine (GLXCR) are also reported.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed in SPSS version 15.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Group differences in demographic or clinical variables were assessed using two-tailed independent samples t-tests or Pearson χ2 as appropriate. For primary analyses relating to GLUCSF, statistical significance was defined as P<0.05 uncorrected. Exploratory analyses of the other metabolites present in the spectra were corrected for multiple comparisons (threshold for 4 metabolites, 2 voxels; P=0.05÷8=0.006).
Group differences in thalamic glutamate levels in the extended cohort of UHR and Control subjects, were initially examined using independent samples t-tests, followed up by ANOVA to control for significant or near-significant group differences in drug use. Potential differences between UHR and Control subjects in glutamate levels at follow-up and in change in glutamate levels over time were determined using linear mixed models with group as the fixed variable and time (baseline and follow-up) as the repeated measure.
In testing the primary hypothesis, that lower thalamic glutamate levels at presentation would be associated with worse clinical outcome, UHR subjects were subdivided into remission (UHR-R) and non-remission (UHR-NR) groups on the basis of the follow-up clinical assessment. The UHR-NR group included UHR patients who still met criteria for attenuated psychosis or who had transitioned to overt psychosis (Phillips et al, 2000). The UHR-R group included patients who no longer fulfilled criteria for UHR status and had not converted to psychosis. The number of participants who transitioned to psychosis was too small to permit meaningful statistical analysis of data in this group alone, but transition cases are indicated in the figures. The predictive value of thalamic glutamate in determining clinical outcome (UHR-R vs UHR-NR) was assessed using binary logistic regression. Potentially confounding baseline variables, such as drug use, were added to the regression model in secondary analyses. Pearson's correlation was used to determine relationships between glutamate levels at baseline and GAF score or total attenuated psychotic symptoms at follow-up. Where a significant relationship with total attenuated psychotic symptoms was detected, secondary analysis tested the strength of correlation (uncorrected) with the individual attenuated psychotic symptom scales (abnormalities of thought content, speech, and perception). Relationships between baseline glutamate concentrations and absolute change in attenuated psychotic symptoms or GAF score over time were calculated using partial correlation coefficients, co-varying for baseline scores to control for regression to the mean. The secondary hypothesis, that longitudinal changes in glutamate may relate to change in mental state, was examined using linear mixed models with group (UHR-R vs UHR-NR) as the fixed variable and time (baseline and follow-up) as the repeated measure.
RESULTS
Demographic and Clinical Variables
Demographic and clinical variables at baseline are presented in Table 1. Three of the 75 UHR subjects (9%) were taking an antipsychotic medication at the time of baseline imaging (quetiapine, olanzapine and risperidone) and six were taking antidepressant medication (all citalopram). The newly recruited cohort were on average younger than the previous cohort (mean±SD age, cohort 1: 25.1±5.3; cohort 2: 22.2±4.2 years; t(78)=2.6; P=0.012), and had marginally lower GAF scores (mean±SD cohort 1: 63.0±14.9; cohort 2: 57.0±8.4; t(78)=2.0; P=0.05) but did not differ in severity of total attenuated positive symptoms (mean±SD cohort 1: 6.7±3.5; cohort 2: 7.7±3.7; t(78)=0.6; P=0.57).
Table 1. Baseline Demographic and Clinical Variables.
| Control N=56 | UHR N=75 | P | UHR-R N=22 | UHR-NR N=29 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years; mean (SD) | 24.6 (4.2) | 23.3 (4.8) | 0.10 | 23.8 (5.6) | 22.7 (4.7) | 0.44 |
| Gender, male/female | 32/24 | 41/34 | 0.79 | 11/11 | 16/13 | 0.78 |
| Handedness, right/left | 49/7 | 67/8 | 0.74 | 22/0 | 26/3 | 0.25 |
| Education, years; mean (SD) | 14.9 (2.3) | 12.6 (2.0) | <0.001 | 12.3 (2.0) | 13.0 (2.0) | 0.24 |
| IQ: NART errors; mean (SD) | 17.1 (8.2) | 22.6 (10.8) | 0.003 | 20.3 (8.90) | 23.4 (12.1) | 0.32 |
| Baseline antipsychotic medication: no/yes | 56/0 | 72/3 | — | 20/2 | 29/1 | 0.57 |
| Baseline antidepressant medication: no/yes | 50/0 | 69/6 | — | 21/1 | 24/5 | 0.22 |
| Current smoker: no/yes | 42/14 | 29/46 | <0.001 | 11/11 | 8/21 | 0.15 |
| Cigarettes/day, mean (SD) | 1.7 (3.6) | 5.4 (6.4) | <0.001 | 4.9 (5.9) | 6.8 (7.1) | 0.30 |
| Current alcohol drinker: no/yes | 9/47 | 18/57 | 0.27 | 6/16 | 6/23 | 0.74 |
| Alcohol units/week, mean (SD) | 8.4 (8.7) | 7.8 (11.5) | 0.75 | 4.0 (5.7) | 9.2 (11.7) | 0.06 |
| Cannabis, ever used: no/yes | 22/34 | 24/51 | 0.39 | 7/15 | 11/18 | 0.77 |
| Amphetamine, ever used: no/yes | 48/8 | 55/20 | 0.09 | 16/6 | 23/6 | 0.74 |
| Cocaine, ever used: no/yes | 45/11 | 50/25 | 0.08 | 14/8 | 19/10 | >0.99 |
| Ecstasy/MDMA, ever used: no/yes | 42/14 | 58/17 | 0.06 | 16/6 | 23/6 | 0.74 |
| Ketamine, ever used: no/yes | 54/2 | 65/10 | 0.06 | 19/3 | 25/5 | >0.99 |
| Thought content abnormalities | 0.1 (0.4) | 3.0 (1.7) | <0.001 | 2.8 (1.6) | 3.2 (1.7) | 0.35 |
| Perception abnormalities | 0.2 (0.7) | 2.7 (2.0) | <0.001 | 1.7 (1.9) | 3.0 (2.0) | 0.02 |
| Speech abnormalities | 0.1 (0.5) | 1.6 (1.6) | <0.001 | 1.0 (1.2) | 1.9 (1.9) | 0.05 |
| Total attenuated positive symptoms | 0.4 (1.2) | 7.3 (3.6) | <0.001 | 5.5 (3.0) | 8.1 (4.1) | 0.01 |
| GAF score | 85.9 (6.7) | 59.2 (11.5) | <0.001 | 62.4 (12.0) | 57.7 (11.3) | 0.16 |
| PANSS-P | 7.1 (0.6) | 12.9 (4.7) | <0.001 | 10.8 (3.6) | 13.4 (4.6) | 0.04 |
| PANSS-N | 7.1 (0.5) | 11.4 (4.3) | <0.001 | 10.5 (3.7) | 11.6 (4.2) | 0.33 |
| PANSS-G | 16.5 (1.0) | 26.2 (6.6) | <0.001 | 25.3 (7.0) | 26.2 (5.9) | 0.60 |
| PANSS-T | 30.7 (1.5) | 50.8 (13.1) | <0.001 | 46.5 (11.8) | 51.6 (12.0) | 0.14 |
Abbreviations: G, general; GAF, global assessment of functioning scale; MDMA, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine; N, negative; NART, National Adult Reading Test; NR, no remission; P, positive; PANSS, positive and negative syndrome scale, T, total symptom scores; UHR-R, ultra high risk - remission; UHR-NR, ultra high risk - non remission.
Follow-up clinical measures were available in 51 UHR subjects (68% of the original sample) (Table 2). There was no difference in baseline demographic or clinical measures between UHR subjects in whom follow-up assessment was or was not available (data not shown). The mean±SD time between clinical assessments was 18.1±8.5 months (min: 2.9; max: 58.7 months). With the exception of cases where subjects made transition to psychosis, follow-up occurred at least 12 months after baseline imaging. In 18 of the 24 UHR subjects who could not be reassessed in person, follow-up information was available from their clinical records. There was no recorded evidence that any of these subjects had developed psychosis over at least a 12-month period following baseline assessment, but records did not provide sufficient information to assess remission status. At follow-up, 23 UHR participants (45%) still met criteria for attenuated psychosis and 6 met criteria for first episode psychosis (4 from cohort 1 and 2 from cohort 2). The mean±SD time to transition after baseline assessment was 473±326 days, range 78–898 days. These subjects together formed the UHR-NR group (N=29). In contrast, 22 UHR subjects (43%) no longer met UHR criteria (UHR-R). At follow-up two UHR subjects (both in the UHR-R group) were taking quetiapine. Baseline demographic variables did not differ between the UHR-R and UHR-NR groups (Table 1). The UHR-NR group presented with higher levels of attenuated positive symptoms (Table 1). Thirty-three subjects in the Control group completed follow-up assessments, with a mean±SD length of time to follow-up of 16.9±6.7 months (min: 9.5, max: 35.1 months).
Table 2. Follow-up Clinical Measures in UHR Participants.
| UHR-R N=22 | UHR-NR N=29 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thought content abnormalities | 0.2 (0.5) | 3.6 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| Perception abnormalities | 0.2 (0.5) | 3.6 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| Speech abnormalities | 0.7 (0.9) | 2.1 (1.8) | 0.001 |
| Total attenuated positive symptoms | 1.1 (1.3) | 9.3 (3.9) | <0.001 |
| GAF score | 72.5 (11.2) | 54.6 (15.8) | <0.001 |
| PANSS-P | 8.2 (1.7) | 14.9 (4.9) | <0.001 |
| PANSS-N | 8.3 (2.5) | 11.2 (5.0) | 0.02 |
| PANSS-G | 18.7 (3.7) | 25.5 (7.5) | 0.001 |
| PANSS-T | 35.2 (7.0) | 51.6 (15.8) | <0.001 |
Abbreviations: G, general; GAF, global assessment of functioning scale; N, negative; P, positive; PANSS, positive and negative syndrome scale, T, total symptom scores; UHR-R, ultra high risk - remission; UHR-NR, ultra high risk - non remission.
Glutamate Levels in the UHR Compared with Control Group
At baseline, compared with Control, UHR subjects had lower levels of GLUCSF in the thalamus (t(127)=2.15; P=0.03; d=0.41, Table 3), but not the ACC (t(124)=0.04; P=0.97, Table 3). This group difference remained significant after co-varying for smoking status (F(1, 128)=3.75; P=0.03), ketamine use (F(1,128)=5.51; P=0.02), ecstasy use (F(2,128)=4.43; P=0.04) and voxel gray matter proportion (%GM=GM/(GM+WM)*100, where GM=gray matter; WM=white matter) (F(1,128)=5.83; P=0.02). However, thalamic GLXCSF, GLUCR, and GLXCR did not differ between UHR and Control (P=0.20–0.43), and differences in glutamate metabolites between UHR and Control groups were not apparent when analysis was restricted to only the newly recruited subjects (P=0.56).
Table 3. Metabolite Levels.
|
Left thalamus |
ACC |
Left thalamus |
ACC |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control N=55 | UHR N=75 | P* | Control N=55 | UHR N=75 | P* | UHR-R N=22 | UHR-NR N=29 | P** | UHR-R N=22 | UHR-NR N=29 | P** | |
| Baseline | ||||||||||||
| Glutamate | 7.6±1.5 | 7.0±1.4 | 0.03 | 13.2±2.3 | 13.1±2.8 | 0.97 | 7.7±1.3 | 6.6±1.3 | 0.003 | 13.0±2.8 | 13.4±3.1 | 0.36 |
| Glx | 9.3±2.4 | 8.8±2.0 | 0.20 | 18.0±4.1 | 18.1±5.6 | 0.98 | 9.7+2.1 | 8.1±1.9 | 0.01 | 17.6±5.9 | 18.8±6.1 | 0.27 |
| NAA | 12.4±0.9 | 12.1±1.2 | 0.10 | 13.0±2.1 | 12.9±2.0 | 0.80 | 12.2±1.8 | 12.1±0.8 | 0.65 | 12.6±2.2 | 13.2±2.0 | 0.14 |
| Cr | 7.2±0.8 | 6.9±0.8 | 0.11 | 10.1±1.7 | 10.0±1.7 | 0.91 | 7.2±1.1 | 6.9±0.7 | 0.33 | 9.8±2.2 | 10.2±1.6 | 0.23 |
| mI | 4.9±2.1 | 4.6±1.5 | 0.28 | 8.4±1.4 | 8.2±1.7 | 0.45 | 4.3±1.1 | 4.4±1.3 | 0.88 | 7.9±2.0 | 8.5±1.7 | 0.13 |
| TCho | 2.1±0.2 | 1.9±0.3 | 0.01 | 2.8±0.7 | 2.6±0.5 | 0.24 | 2.0±0.3 | 1.9±0.2 | 0.03 | 2.6±0.7 | 2.7±0.5 | 0.29 |
|
Left thalamus |
ACC |
Left thalamus |
ACC |
|||||||||
| |
Control
N=33 |
UHR
N=47 |
P*** |
Control
N=33 |
UHR
N=47 |
P*** |
UHR-R
N=22 |
UHR-NR
N=26 |
P*** |
UHR-R
N=21 |
UHR-NR
N=26 |
P*** |
| Follow-up | ||||||||||||
| Glutamate | 7.1±1.7 | 6.9±1.4 | 0.49 | 13.2±2.4 | 12.0±2.3 | 0.13 | 6.8±1.4 | 7.1±1.4 | 0.07 | 11.8±2.4 | 12.1±2.4 | 0.52 |
| Glx | 8.7±2.3 | 8.5±2.1 | 0.26 | 17.8±3.7 | 16.4±3.5 | 0.56 | 8.8±2.6 | 8.2±1.5 | 0.02 | 16.5±3.7 | 16.4±3.4 | 0.56 |
| NAA | 11.6±1.6 | 11.8±1.1 | 0.09 | 13.0±1.5 | 12.4±1.5 | 0.14 | 11.6±1.3 | 12.0±0.9 | 0.48 | 12.2±1.3 | 12.6±1.6 | 0.21 |
| Cr | 6.9±0.6 | 6.9±6.2 | 0.99 | 9.6±1.4 | 9.7±1.4 | 0.38 | 6.9±0.6 | 6.9±0.6 | 0.58 | 9.3±1.5 | 10.0±1.3 | 0.13 |
| mI | 4.2±0.9 | 4.2±0.8 | 0.07 | 8.7±2.2 | 8.0±1.6 | 0.27 | 4.1±0.8 | 4.2±0.9 | 0.67 | 7.7±1.6 | 8.3±1.6 | 0.10 |
| TCho | 1.9±0.2 | 1.9±0.2 | 0.17 | 2.6±0.6 | 2.5±0.5 | 0.09 | 1.9±0.2 | 1.9±0.2 | 0.11 | 2.5±0.5 | 2.6±0.5 | 0.63 |
Abbreviations: ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; Cr, creatine; mI, myo-Inositol; NAA, N-acetyl aspartate; TCho, total choline; UHR-R, ultra high risk - remission; UHR-NR, ultra high risk - non remission. P*, P-value determined by independent samples t-test; P**, P-value determined by binary logistic regression; P***, P-value relating to main effect of group on follow-up metabolite level determined using linear mixed models.
Longitudinal Glutamate Levels in Control vs UHR Groups
Follow-up scans were completed in 33 Control subjects and 47 UHR subjects, including 5 UHR subjects who had developed a psychotic disorder (Table 3). In the linear mixed effect models, there were no significant main effects of group (UHR vs Control), time or group by time interactions on GLUCSF. The P-values associated with the lack of main effect of group, time or time × group interactions for GLUCSF values were thalamus: group P=0.49; time P=0.32; interaction P=0.53 and ACC: group P=0.13; time P=0.11; interaction P=0.24. For the other metabolites present in the spectra, there were no significant main effects of group (Table 3), time or group × time interactions (all P>0.05).
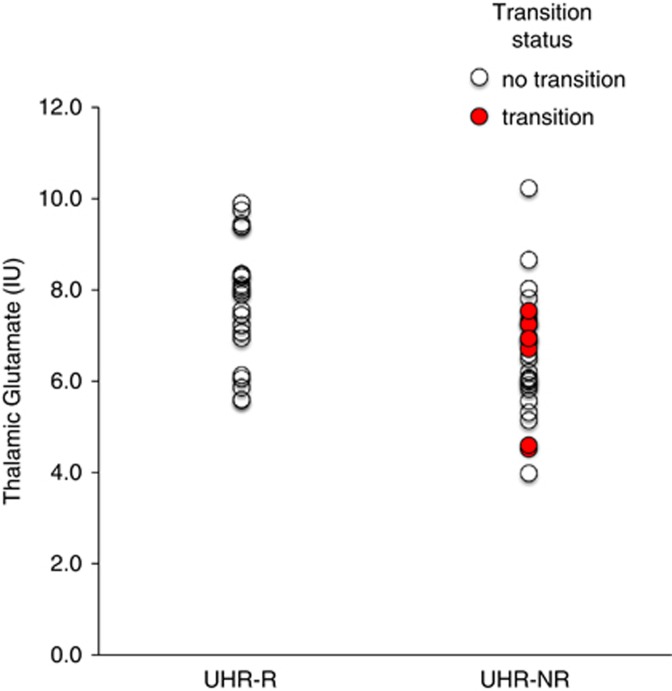
Thalamic Glutamate Levels at Intake and Prediction of Clinical Outcome
The predictive value of baseline thalamic GLUCSF on clinical outcome (UHR-R vs UHR-NR) was statistically significant (χ2 (1, N=51)=8.63; P=0.003; B=−0.66; SE=0.25; df=1; Wald=6.49; OR=0.52 (0.31–0.85); P=0.009), indicating that baseline thalamic GLUCSF reliably distinguished UHR-R from UHR-NR (Figure 1). This effect remained significant when controlling for baseline severity of attenuated positive symptoms (χ2 (2, N=51)=14.61; P=0.001), weekly alcohol units (χ2 (2, N=51)=16.19; P<0.001), or %GM (χ2 (2, N=51)=8.67; P=0.01), and was also significant for glutamate assessed as GLXCSF, GLUCR, and GLXCR (P=0.005–0.008). Baseline levels of other metabolites visible in the spectra did not associate with outcome (Table 3).
Figure 1.
Left thalamic glutamate at presentation in ultra high risk (UHR) subjects grouped by clinical outcome; UHR-R: remission, N=22; UHR-NR: non remission, N=29. Glutamate is presented as data corrected for voxel cerebrospinal fluid content, in institutional units (IU). Glutamate significantly predicted UHR remission status P=0.003. UHR subjects who made transition to psychosis are indicated in red/filled circles. The color reproduction of this figure is available on the html full text version of the manuscript.
Thalamic Glutamate Levels at Intake and Symptom Severity at Follow-up
Baseline thalamic GLUCSF was negatively associated with the severity of positive symptoms at follow-up (r=−0.39; df=51; P=0.004). This relationship was strongest for the severity of abnormal thought content (r=−0.42; df=51; P=0.002), and significant for the severity of perceptual abnormalities (r=−0.317; df=51; P=0.02), but not for the severity of speech abnormalities (r=−0.22; df=51; P=0.12). The negative relationships between baseline thalamic glutamate and follow-up total positive symptoms or abnormal thought content were also significant for GLXCSF, GLUCR and GLXCR (P=0.037 to 0.004), or co-varying for %GM (P=0.02). The positive correlation between baseline thalamic GLUCSF and follow-up GAF score was below the threshold for significance (r=0.27; df=51; P=0.06).
Thalamic Glutamate Levels at Intake and Longitudinal Change in Symptom Severity
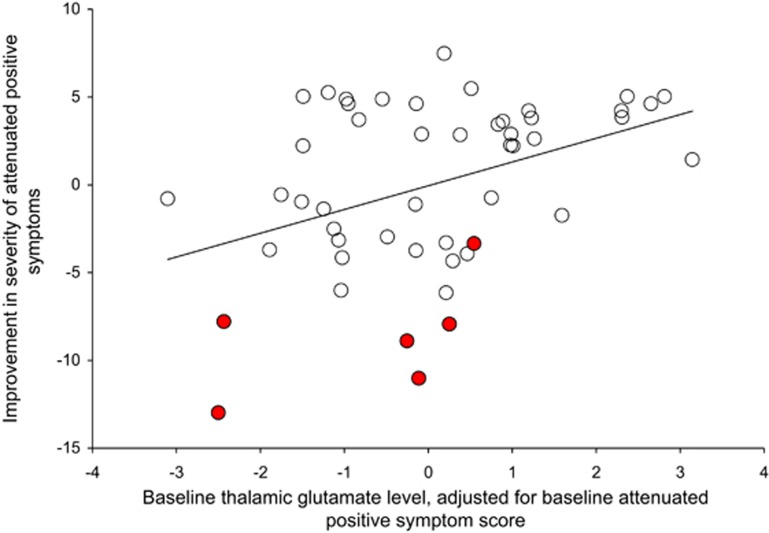
Thalamic GLUCSF was negatively associated with the longitudinal change in attenuated positive symptoms over time, such that an increase in severity of symptoms occurred in those with lower thalamic GLUCSF at presentation (r=−0.40; df=47; P=0.005, Figure 2, and where for GLXCSF, GLUCR and GLXCR P=0.06–0.009). This relationship was strongest for the severity of abnormal thought content (r=−0.42; df=47; P=0.003; GLXCSF, GLUCR, and GLXCR P=0.005–0.04, co-varying for %GM: P=0.02), significant for the severity of perceptual abnormalities (r=−0.33; df=47; P=0.02; GLXCSF, GLUCR, and GLXCR P=0.05–0.16) but not speech abnormalities (r=−0.21; df=47; P=0.14). Baseline thalamic GLUCSF also correlated with change in GAF score over time, such that lower glutamate levels were associated with declining functioning (r=0.31; df=47; P=0.03), but this relationship did not reach significance for GLXCSF, GLUCR, or GLXCR (P=0.12–0.44).
Figure 2.
Partial correlation between the baseline thalamic glutamate level and the change in the severity of attenuated positive symptoms (r=−0.40; df=47; P=0.005). UHR subjects who made transition to psychosis are indicated in red/filled circles. The color reproduction of this figure is available on the html full text version of the manuscript.
Longitudinal Glutamate Levels in UHR-R vs UHR-NR Groups
Metabolite levels at follow-up are presented in Table 3. The main effect of group (UHR-R vs UHR-NR) on thalamic GLUCSF concentrations over time was slightly above the threshold for statistical significance (F(79)=3.39; P=0.07), and reached significance for GLXCSF (P=0.02, Table 3). There was no significant main effect of time (P=0.10) or group by time interaction (P=0.58). For ACC GLUCSF concentrations, there was no significant effect of group (P=0.52) or time × group interaction (P=0.99) but ACC GLUCSF was lower overall in UHR participants at follow-up (main effect of time F(80)=4.28; P=0.04). The P-values associated with main effects of time for ACC GLXCSF, GLUCR, and GLXCR were P=0.09, 0.43, and 0.04, respectively. No significant main effects or interactions were apparent for the other metabolites present in the spectra (all P>0.05 and see Table 3).
DISCUSSION
The main finding of this study was that low levels of thalamic glutamate at presentation are associated with poor clinical outcomes in UHR individuals. Low thalamic glutamate was associated with the persistence or worsening of positive symptoms, and particularly abnormal thought content. This extends previous cross-sectional studies suggesting that brain glutamatergic abnormalities are present in individuals at high risk of developing psychosis (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2011; Lutkenhoff et al, 2010; Stone et al, 2009a; Tibbo et al, 2004), in that it suggests that the magnitude of these abnormalities is related to subsequent clinical outcome. In the UHR group, longitudinal data found no evidence that changes in glutamate levels over time were related to change in mental state.
Consistent with our previous report (Stone et al, 2009a) in what was a subsample of the UHR group in the present study, we found that the levels of thalamic GLUCSF in the UHR subjects at baseline was significantly lower than that in controls. However, this difference does not appear robust, as it did not reach significance when glutamate was analyzed in combination with glutamine (Glx) or using scaling to creatine, was less marked following the additional recruitment to the present study (and not significant in only the newly recruited sample), and was not apparent in the smaller sample at the follow-up time point. Consistent with a lack of difference in thalamic glutamate in UHR compared with control subjects, previous studies have reported a lack a difference in thalamic glutamate levels in never or minimally medicated early psychosis (Aoyama et al, 2011; Theberge et al, 2002; Theberge et al, 2007), although thalamic glutamine may be elevated (Aoyama et al, 2011; Theberge et al, 2002; Theberge et al, 2007). Our finding that thalamic glutamate levels may be lower, specifically in those UHR subjects who show poor outcomes may contribute to the overlap between the overall UHR group and control sample.
In addition to the present finding that low thalamic glutamate levels are associated with poor outcomes in UHR individuals, there is also evidence in a small cohort that striatal glutamate levels may be specifically elevated in UHR individuals who transition to psychosis (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2013a). In contrast, the hippocampal Glx levels do not differ between subsequent transition and non-transition cases (Wood et al, 2010), and our present data additionally did not find any association between ACC glutamate and outcome. This may highlight the importance of prospective, rather than simply cross-sectional studies of glutamate in UHR cohorts, and also suggest regionally and perhaps temporarily distinct glutamatergic dysfunctions.
Over the course of this longitudinal study, of the 69 UHR individuals in whom the clinical outcome was known, 6 (8.7%) developed a psychotic disorder. This is lower than the transition rate that has been observed in previous follow-up studies of UHR samples (Fusar-Poli et al, 2012), although more transitions may occur as the follow-up period is extended. Nevertheless, relatively low transition rates have been reported in some recent studies with long follow-up periods (Yung et al, 2007). Further, two individuals made transition within 6 months of baseline assessment, indicating they may have been close to conversion at baseline. As only a small number of subjects in our study developed psychosis, there was inadequate statistical power to test whether regional glutamate levels were significantly related to later transition, and this limits the clinical relevance of our findings. Instead, we classified clinical outcome according to whether or not UHR symptoms had remitted at follow-up, with transition cases forming a subset of the broader ‘non-remission' group. In our sample, presenting UHR symptoms subsequently remitted in 43% of subjects, which is similar to the rate reported in other cohorts (Simon et al, 2013). We found that low thalamic glutamate levels at baseline were related to the non-remission of symptoms, and a progressive worsening of symptoms over time. These findings were also apparent when glutamate was analyzed in combination with glutamine, or when using creatine-scaled rather than CSF-corrected data. In the subsample of UHR participants who completed follow-up scans, there was some indication that the lower thalamic glutamate levels in non-remission compared with remission cases were stable over time, as analysis of longitudinal data showed a near-significant main effect of remission status on glutamate level (P=0.07), which reached significance for Glx. Thus, these results suggest that in UHR subjects, low thalamic glutamate levels are linked to poor clinical outcomes. In line with this, loss of thalamic glutamate plus glutamine has been associated with deteriorations in social functioning in schizophrenia (Aoyama et al, 2011).
In the UHR group as a whole, ACC glutamate levels were lower at follow-up than at baseline. However, this could not be specifically attributed to declining ACC glutamate levels in the UHR compared with Control group, as the time by group interaction was above the threshold for statistical significance, and there was no evidence in UHR individuals that change in ACC glutamate levels were related to change in mental state. Nonetheless, lower levels of ACC glutamate in UHR subjects would consistent with the lower levels of frontal glutamate in schizophrenia reported by meta-analysis (Marsman et al, 2011), and in unaffected twins of patients with schizophrenia (Lutkenhoff et al, 2010), and partially consistent with studies in early psychosis that have reported elevated ACC glutamine (Theberge et al, 2002; Theberge et al, 2007), or elevated glutamine/glutamate ratio (Bustillo et al, 2010) as elevated glutamine may correspond to glutamate reduction.
Both the UHR and Control group included participants who currently or previously used recreational drugs. While their inclusion maintains generalizability to the UHR population at our clinical service, drug use may potentially impact on both brain glutamate levels and clinical symptoms or outcomes. Secondary analysis found no evidence for influences of substance abuse, although we did not include analyses of current use of substances (apart from nicotine or alcohol) due to relatively low frequencies. The present study employed a region of interest approach, and thus it was not possible to assess the role of brain areas other than the thalamus and ACC. However, it is likely that glutamatergic transmission in other regions, such as the hippocampus (Kraguljac et al, 2013; Lisman et al, 2008), and striatum (de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2013a; de la Fuente-Sandoval et al, 2011) is also important. Abnormalities in regional gray matter volume (Mechelli et al, 2011) and striatal dopamine synthesis capacity (Howes et al, 2011) are also associated with the later transition to psychosis, while functional imaging studies have implicated changes in prefrontal, hippocampal, and midbrain regions (Allen et al, 2012). At the behavioral level, poor overall functioning, negative symptoms, and disorders of thought content at presentation have also been linked to poor subsequent outcomes (Nelson et al, 2013). Studies that combine measurements from different imaging modalities along with behavioral measures may be more predictive of outcomes than measures in a single modality, although this has yet to be demonstrated in UHR subjects.
In conclusion, this study found evidence that glutamatergic abnormalities are associated with poor clinical outcomes in subjects at high risk of psychosis. This suggests that altered glutamatergic function may be an early component of a neuropathological process that leads to clinical and functional decline, and may result in a psychotic disorder, and that glutamatergic compounds may have therapeutic potential in the early phases of psychosis, as well as in established schizophrenia (Egerton et al, 2012b). Further studies should address the value of brain glutamate measures in predicting transition to psychosis and outcome in psychotic disorders.
FUNDING AND DISCLOSURE
This study was funded by a Medical Research Council (MRC) Clinical Training Fellowship awarded to JS and MRC grant number G0700995. GJB receives honoraria for teaching from General Electric and acts as a consultant for IXICO. ODH has received unrestricted investigator-led charitable funding from or spoken at meetings organized by Astra-Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Jansse, Hoffman la Roche, Leyden-Delta and Eli Lilly. AE has received consultant fees from Heptares Therapeutics Ltd. RM has received honoraria from Janssen, Lilly, Astra-Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche. JMS has received honoraria from Janssen, Hoffman la Roche, and Sunovion. PM has received consultancy fees from Hoffman la Roche and Sunovion.
Acknowledgments
This study presents independent research supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King's College London. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. We thank members of the OASIS team who were involved in the recruitment, management, and clinical follow-up of the at-risk mental state subjects in this study.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website (http://www.nature.com/npp)
Supplementary Material
References
- Allen P, Luigjes J, Howes OD, Egerton A, Hirao K, Valli I, et al. Transition to psychosis associated with prefrontal and subcortical dysfunction in ultra high-risk individuals. Schizophr Bull. 2012;38:1268–1276. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama N, Theberge J, Drost DJ, Manchanda R, Northcott S, Neufeld RW, et al. Grey matter and social functioning correlates of glutamatergic metabolite loss in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 2011;198:448–456. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.110.079608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustillo JR, Rowland LM, Mullins P, Jung R, Chen H, Qualls C, et al. 1H-MRS at 4 tesla in minimally treated early schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:629–636. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A, Waters N, Holm-Waters S, Tedroff J, Nilsson M, Carlsson ML. Interactions between monoamines, glutamate, and GABA in schizophrenia: new evidence. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:237–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Leon-Ortiz P, Azcarraga M, Favila R, Stephano S, Graff-Guerrero A. Striatal glutamate and the conversion to psychosis: a prospective 1H-MRS imaging study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013a;16:471–475. doi: 10.1017/S1461145712000314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Leon-Ortiz P, Azcarraga M, Stephano S, Favila R, Diaz-Galvis L, et al. Glutamate levels in the associative striatum before and after 4 weeks of antipsychotic treatment in first-episode psychosis: a longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013b;70:1057–1066. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Leon-Ortiz P, Favila R, Stephano S, Mamo D, Ramirez-Bermudez J, et al. Higher levels of glutamate in the associative-striatum of subjects with prodromal symptoms of schizophrenia and patients with first-episode psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:1781–1791. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton A, Brugger S, Raffin M, Barker GJ, Lythgoe DJ, McGuire PK, et al. Anterior cingulate glutamate levels related to clinical status following treatment in first-episode schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012a;37:2515–2521. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton A, Fusar-Poli P, Stone JM. Glutamate and psychosis risk. Curr Pharm Des. 2012b;18:466–478. doi: 10.2174/138161212799316244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusar-Poli P, Bonoldi I, Yung AR, Borgwardt S, Kempton MJ, Valmaggia L, et al. Predicting psychosis: meta-analysis of transition outcomes in individuals at high clinical risk. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:220–229. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusar-Poli P, Borgwardt S, Bechdolf A, Addington J, Riecher-Rossler A, Schultze-Lutter F, et al. The psychosis high-risk state: a comprehensive state-of-the-art review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013a;70:107–120. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusar-Poli P, Byrne M, Badger S, Valmaggia LR, McGuire PK. Outreach and support in south London (OASIS), 2001–2011: ten years of early diagnosis and treatment for young individuals at high clinical risk for psychosis. Eur Psychiatry. 2013b;28:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2012.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusar-Poli P, Stone JM, Broome MR, Valli I, Mechelli A, McLean MA, et al. Thalamic glutamate levels as a predictor of cortical response during executive functioning in subjects at high risk for psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:881–890. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff DC, Coyle JT. The emerging role of glutamate in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1367–1377. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.9.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR. Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neuropathology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:40–68. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes OD, Bose SK, Turkheimer F, Valli I, Egerton A, Valmaggia LR, et al. Dopamine synthesis capacity before onset of psychosis: a prospective [18F]-DOPA PET imaging study. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168:1311–1317. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11010160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt DC. Glutamate and schizophrenia: phencyclidine, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, and dopamine-glutamate interactions. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;78:69–108. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(06)78003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt DC, Zukin SR. Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148:10. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.10.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones EG. Cortical development and thalamic pathology in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1997;23:483–501. doi: 10.1093/schbul/23.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kargieman L, Santana N, Mengod G, Celada P, Artigas F. NMDA antagonist and antipsychotic actions in cortico-subcortical circuits. Neurotox Res. 2008;14:129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF03033805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konradi C, Heckers S. Molecular aspects of glutamate dysregulation: implications for schizophrenia and its treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2003;97:153–179. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00328-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraguljac NV, White DM, Reid MA, Lahti AC. Increased hippocampal glutamate and volumetric deficits in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:1294–1302. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman JE, Coyle JT, Green RW, Javitt DC, Benes FM, Heckers S, et al. Circuit-based framework for understanding neurotransmitter and risk gene interactions in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:234–242. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge DJ, Grace AA. Aberrant hippocampal activity underlies the dopamine dysregulation in an animal model of schizophrenia. J Neurosci. 2007;27:11424–11430. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2847-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhoff ES, van Erp TG, Thomas MA, Therman S, Manninen M, Huttunen MO, et al. Proton MRS in twin pairs discordant for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:308–318. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsman A, van den Heuvel MP, Klomp DW, Kahn RS, Luijten PR, Hulshoff Pol HE. Glutamate in schizophrenia: a focused review and meta-analysis of 1H-MRS studies. Schizophr Bull. 2011;39:120–129. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechelli A, Riecher-Rossler A, Meisenzahl EM, Tognin S, Wood SJ, Borgwardt SJ, et al. Neuroanatomical abnormalities that predate the onset of psychosis: a multicenter study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:5. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins PG, Chen H, Xu J, Caprihan A, Gasparovic C. Comparative reliability of proton spectroscopy techniques designed to improve detection of J-coupled metabolites. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:964–969. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B, Yuen HP, Wood SJ, Lin A, Spiliotacopoulos D, Bruxner A, et al. Long-term follow-up of a group at ultra high risk (‘Prodromal') for psychosis: the PACE 400 study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:793–802. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B, Yung AR. Can clinicians predict psychosis in an ultra high risk group. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2010;44:625–630. doi: 10.3109/00048671003620210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney JW, Farber NB. Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52:998–1007. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950240016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney JW, Newcomer JW, Farber NB. NMDA receptor hypofunction model of schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 1999;33:523–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(99)00029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips LJ, Yung AR, McGorry PD. Identification of young people at risk of psychosis: validation of Personal Assessment and Crisis Evaluation Clinic intake criteria. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2000;34 (Suppl:S164–S169. doi: 10.1080/000486700239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilowsky LS, Bressan RA, Stone JM, Erlandsson K, Mulligan RS, Krystal JH, et al. First in vivo evidence of an NMDA receptor deficit in medication-free schizophrenic patients. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:118–119. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher SW. Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med. 1993;30:672–679. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp FR, Tomitaka M, Bernaudin M, Tomitaka S. Psychosis: pathological activation of limbic thalamocortical circuits by psychomimetics and schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:330–334. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01817-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon AE, Borgwardt S, Riecher-Rossler A, Velthorst E, de Haan L, Fusar-Poli P. Moving beyond transition outcomes: meta-analysis of remission rates in individuals at high clinical risk for psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2013;209:266–272. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2013.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J, Wilman A. Field strength dependence of PRESS timings for simultaneous detection of glutamate and glutamine from 1.5 to 7T. J Magn Reson. 2010;203:66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2009.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi MS, Simmons M, McCullumsmith R, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH. Glutamatergic gene expression is specifically reduced in thalamocortical projecting relay neurons in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70:646–654. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone JM, Bramon E, Pauls A, Sumich A, McGuire PK. Thalamic neurochemical abnormalities in individuals with prodromal symptoms of schizophrenia - relationship to auditory event-related potentials. Psychiatry Res. 2010;183:174–176. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone JM, Day F, Tsagaraki H, Valli I, McLean MA, Lythgoe DJ, et al. Glutamate dysfunction in people with prodromal symptoms of psychosis: relationship to gray matter volume. Biol Psychiatry. 2009a;66:533–539. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone JM, Fusar-Poli P. Abnormal thalamic glutamate and liability to psychosis: state or trait marker. Schizophr Res. 2009b;115:94–95. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theberge J, Bartha R, Drost DJ, Menon RS, Malla A, Takhar J, et al. Glutamate and glutamine measured with 4.0T proton MRS in never-treated patients with schizophrenia and healthy volunteers. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:1944–1946. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.11.1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theberge J, Williamson KE, Aoyama N, Drost DJ, Manchanda R, Malla AK, et al. Longitudinal grey-matter and glutamatergic losses in first-episode schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 2007;191:325–334. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.106.033670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbo P, Hanstock C, Valiakalayil A, Allen P. 3-T proton MRS investigation of glutamate and glutamine in adolescents at high genetic risk for schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1116–1118. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.6.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomitaka S, Tomitaka M, Tolliver BK, Sharp FR. Bilateral blockade of NMDA receptors in anterior thalamus by dizocilpine (MK-801) injures pyramidal neurons in rat retrosplenial cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:1420–1430. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood SJ, Kennedy D, Phillips LJ, Seal ML, Yucel M, Nelson B, et al. Hippocampal pathology in individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis: a multi-modal magnetic resonance study. Neuroimage. 2010;52:62–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung AR, Nelson B, Thompson A, Wood SJ. The psychosis threshold in Ultra High Risk (prodromal) research: is it valid. Schizophr Res. 2010;120:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung AR, Phillips LJ, Yuen HP, McGorry PD. Risk factors for psychosis in an ultra high-risk group: psychopathology and clinical features. Schizophr Res. 2004;67:131–142. doi: 10.1016/S0920-9964(03)00192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung AR, Yuen HP, Berger G, Francey S, Hung TC, Nelson B, et al. Declining transition rate in ultra high risk (prodromal) services: dilution or reduction of risk. Schizophr Bull. 2007;33:673–681. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbm015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung AR, Yuen HP, McGorry PD, Phillips LJ, Kelly D, Dell'Olio M, et al. Mapping the onset of psychosis: the comprehensive assessment of at-risk mental states. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2005;39:964–971. doi: 10.1080/j.1440-1614.2005.01714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.