Abstract
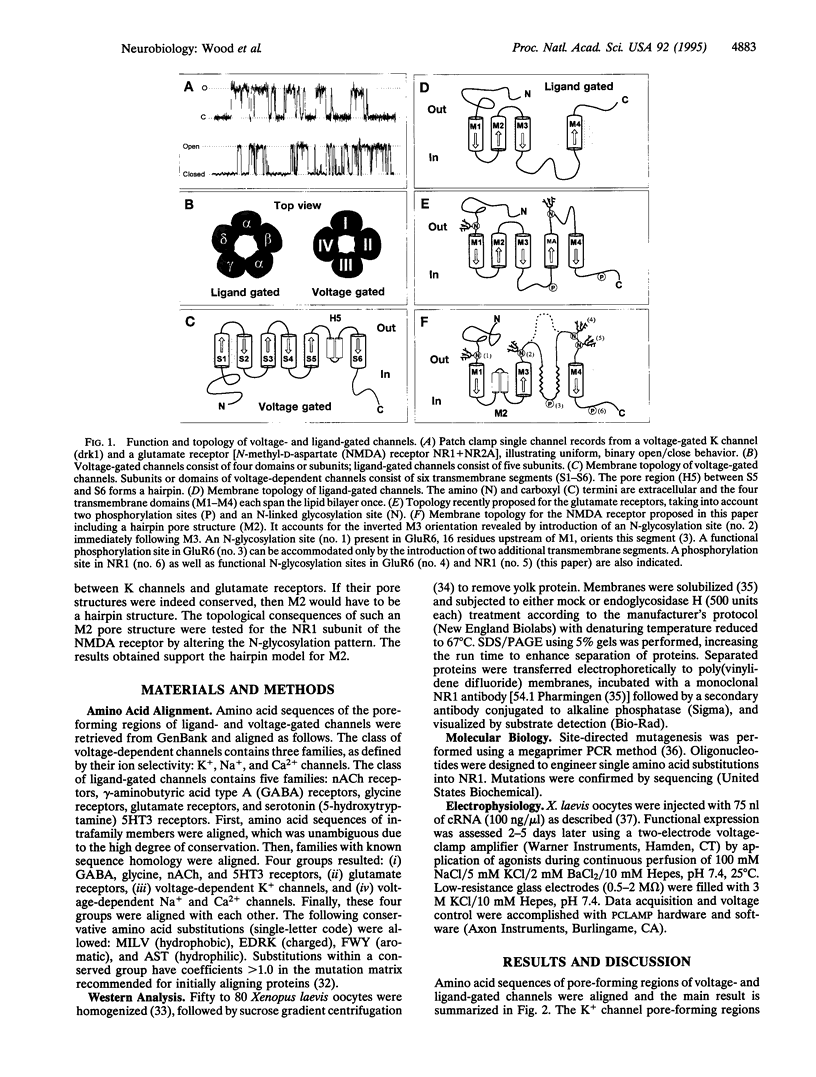
Single channel recordings demonstrate that ion channels switch stochastically between an open and a closed pore conformation. In search of a structural explanation for this universal open/close behavior, we have uncovered a striking degree of amino acid homology across the pore-forming regions of voltage-gated K channels and glutamate receptors. This suggested that the pores of these otherwise unrelated classes of channels could be structurally conserved. Strong experimental evidence supports a hairpin structure for the pore-forming region of K channels. Consequently, we hypothesized the existence of a similar structure for the pore of glutamate receptors. In ligand-gated channels, the pore is formed by M2, the second of four putative transmembrane segments. A hairpin structure for M2 would affect the subsequent membrane topology, inverting the proposed orientation of the next segments, M3. We have tested this idea for the NR1 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mutations that affected the glycosylation pattern of the NR1 subunit localize both extremes of the M3-M4 linker to the extracellular space. Whole cell currents and apparent agonist affinities were not affected by these mutations. Therefore it can be assumed that they represent the native transmembrane topology. The extracellular assignment of the M3-M4 linker challenged the current topology model by inverting M3. Taken together, the amino acid homology and the new topology suggest that the pore-forming M2 segment of glutamate receptors does not transverse the membrane but, rather, forms a hairpin structure, similar to that found in K channels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bormann J., Rundström N., Betz H., Langosch D. Residues within transmembrane segment M2 determine chloride conductance of glycine receptor homo- and hetero-oligomers. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3729–3737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Rundström N., Betz H., Langosch D. Residues within transmembrane segment M2 determine chloride conductance of glycine receptor homo- and hetero-oligomers. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3729–3737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brose N., Gasic G. P., Vetter D. E., Sullivan J. M., Heinemann S. F. Protein chemical characterization and immunocytochemical localization of the NMDA receptor subunit NMDA R1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22663–22671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez R. A., Hall Z. W. Expression of fusion proteins of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from mammalian muscle identifies the membrane-spanning regions in the alpha and delta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):385–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafvelin G., von Heijne G. Topological "frustration" in multispanning E. coli inner membrane proteins. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. A., Pheasant D. J., Miller C. The charybdotoxin receptor of a Shaker K+ channel: peptide and channel residues mediating molecular recognition. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1377–1388. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnet G. H., Cohen M. A., Benner S. A. Exhaustive matching of the entire protein sequence database. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1443–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.1604319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R. A structural model of the acetylcholine receptor channel based on partition energy and helix packing calculations. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84152-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Exchange of conduction pathways between two related K+ channels. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):942–944. doi: 10.1126/science.2000495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. A functional connection between the pores of distantly related ion channels as revealed by mutant K+ channels. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.1279807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Busch C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Konno T., Nakai J., Bujo H., Mori Y., Fukuda K., Numa S. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):645–648. doi: 10.1038/335645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuryatov A., Laube B., Betz H., Kuhse J. Mutational analysis of the glycine-binding site of the NMDA receptor: structural similarity with bacterial amino acid-binding proteins. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1291–1300. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Thomas L., Betz H. Conserved quaternary structure of ligand-gated ion channels: the postsynaptic glycine receptor is a pentamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7394–7398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Unwin N., Stauffer K. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Images of purified Shaker potassium channels. Curr Biol. 1994 Feb 1;4(2):110–115. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(94)00026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. Protein glycosylation. Structural and functional aspects. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Nov 15;218(1):1–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Heginbotham L., Abramson T. Mapping the receptor site for charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking potassium channel inhibitor. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):767–771. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90335-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguro H., Mori H., Araki K., Kushiya E., Kutsuwada T., Yamazaki M., Kumanishi T., Arakawa M., Sakimura K., Mishina M. Functional characterization of a heteromeric NMDA receptor channel expressed from cloned cDNAs. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):70–74. doi: 10.1038/357070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Translation of messenger RNA in injected frog oocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:288–296. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):31–37. doi: 10.1038/354031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem N., Green T. P., Martin I. L., Barnard E. A. Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis. J Neurochem. 1994 Feb;62(2):815–818. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara P. J., Sheppard P. O., Thøgersen H., Venezia D., Haldeman B. A., McGrane V., Houamed K. M., Thomsen C., Gilbert T. L., Mulvihill E. R. The ligand-binding domain in metabotropic glutamate receptors is related to bacterial periplasmic binding proteins. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90269-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond L. A., Blackstone C. D., Huganir R. L. Phosphorylation and modulation of recombinant GluR6 glutamate receptors by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):637–641. doi: 10.1038/361637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche K. W., Raymond L. A., Blackstone C., Huganir R. L. Transmembrane topology of the glutamate receptor subunit GluR6. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11679–11682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. The "megaprimer" method of site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):404–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The TiPS/TINS lecture: the molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Aug;14(8):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90047-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna F. A., Wang L. Y., MacDonald J. F., Hampson D. R. A transmembrane model for an ionotropic glutamate receptor predicted on the basis of the location of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14159–14164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingley W. G., Roche K. W., Thompson A. K., Huganir R. L. Regulation of NMDA receptor phosphorylation by alternative splicing of the C-terminal domain. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):70–73. doi: 10.1038/364070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N. Neurotransmitter action: opening of ligand-gated ion channels. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):31–41. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDongen A. M., Frech G. C., Drewe J. A., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Alteration and restoration of K+ channel function by deletions at the N- and C-termini. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90082-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1710829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wo Z. G., Oswald R. E. Transmembrane topology of two kainate receptor subunits revealed by N-glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley G. A., Wallace B. A. Model ion channels: gramicidin and alamethicin. J Membr Biol. 1992 Aug;129(2):109–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00219508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):939–942. doi: 10.1126/science.2000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yool A. J., Schwarz T. L. Alteration of ionic selectivity of a K+ channel by mutation of the H5 region. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):700–704. doi: 10.1038/349700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]