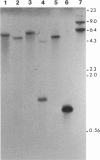
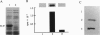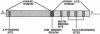Abstract
Calcium, a universal second messenger, regulates diverse cellular processes in eukaryotes. Ca2+ and Ca2+/calmodulin-regulated protein phosphorylation play a pivotal role in amplifying and diversifying the action of Ca(2+)-binding domain was cloned and characterized from lily. The cDNA clone contains an open reading frame coding for a protein of 520 amino acids. The predicted structure of CCaMK contains a catalytic domain followed by two regulatory domains, a calmodulin-binding domain and a visinin-like Ca(2+)-binding domain. The amino-terminal region of CCaMK contains all 11 conserved subdomains characteristic of serine/threonine protein kinases. The calmodulin-binding region of CCaMK has high homology (79%) to alpha subunit of mammalian Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. The calmodulin-binding region is fused to a neural visinin-like domain that contains three Ca(2+)-binding EF-hand motifs and a biotin-binding site. The Escherichia coli-expressed protein (approximately 56 kDa) binds calmodulin in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. Furthermore, 45Ca-binding assays revealed that CCaMK directly binds Ca2+. The CCaMK gene is preferentially expressed in developing anthers. Southern blot analysis revealed that CCaMK is encoded by a single gene. The structural features of the gene suggest that it has multiple regulatory controls and could play a unique role in Ca2+ signaling in plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buoncristiani M. R., Otsuka A. J. Overproduction and rapid purification of the biotin operon repressor from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1013–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Signal integration at the level of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and their substrates. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Schworer C. M., Hashimoto Y., Fong Y. L., Rich D. P., Smith M. K., Soderling T. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2580313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Soderling T. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1990;31:181–221. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152831-7.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara T., Ohsako S., Yamauchi T. Studies on the regulatory domain of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by expression of mutated cDNAs in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16401–16408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Sussman M. R., Schaller G. E., Putnam-Evans C., Charbonneau H., Harmon A. C. A calcium-dependent protein kinase with a regulatory domain similar to calmodulin. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):951–954. doi: 10.1126/science.1852075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jena P. K., Reddy A. S., Poovaiah B. W. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for plant calmodulin: signal-induced changes in the expression of calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3644–3648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. R., Kim Y., An G. Molecular cloning and characterization of anther-preferential cDNA encoding a putative actin-depolymerizing factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;21(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00039616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Takamatsu K., Saitoh S., Miura M., Noguchi T. Molecular cloning of hippocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein of the recoverin family exclusively expressed in hippocampus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91587-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornstein L. B., Gaiso M. L., Hammell R. L., Bartelt D. C. Cloning and sequence determination of a cDNA encoding Aspergillus nidulans calmodulin-dependent multifunctional protein kinase. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90671-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Kajimoto Y., Hashimoto T., Mukai H., Shirai Y., Saheki S., Tanaka C. cDNA cloning of a neural visinin-like Ca(2+)-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1219–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz S. E., Henschel Y., Zopf D., Voss B., Gundelfinger E. D. VILIP, a cognate protein of the retinal calcium binding proteins visinin and recoverin, is expressed in the developing chicken brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Sep;15(1-2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90160-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H., Goodman M. Evolution of EF-hand calcium-modulated proteins. I. Relationships based on amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jun;30(6):522–562. doi: 10.1007/BF02101108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Picciotto M. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Aug;5(4):295–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., DeGrado W. F. How calmodulin binds its targets: sequence independent recognition of amphiphilic alpha-helices. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Feb;15(2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90177-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Watanabe M., Ando Y., Hagiwara M., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. Full sequence of neurocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein abundant in central nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80968-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pausch M. H., Kaim D., Kunisawa R., Admon A., Thorner J. Multiple Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase genes in a unicellular eukaryote. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1511–1522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Lindemeier J., Zhu X. R., Theil T., Engelkamp D., Krah-Jentgens I., Lambrecht H. G., Koch K. W., Schwemer J., Rivosecchi R. Frequenin--a novel calcium-binding protein that modulates synaptic efficacy in the Drosophila nervous system. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90267-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium and signal transduction in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1993;12(3):185–211. doi: 10.1080/07352689309701901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikela J. M., Hahn W. E. Screening an expression library with a ligand probe: isolation and sequence of a cDNA corresponding to a brain calmodulin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3038–3042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A., Gilroy S. Signal transduction in plant cells. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90255-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Wolchok S. R. Conditions for reproducible detection of calmodulin and S100 beta in immunoblots. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):752–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Calcium-promoted protein phosphorylation in plants. Science. 1984 Jan 13;223(4632):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4632.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwoerd T. C., Dekker B. M., Hoekema A. A small-scale procedure for the rapid isolation of plant RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2362–2362. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watillon B., Kettmann R., Boxus P., Burny A. A calcium/calmodulin-binding serine/threonine protein kinase homologous to the mammalian type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase is expressed in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1993 Apr;101(4):1381–1384. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]