Abstract
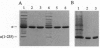
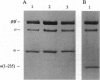
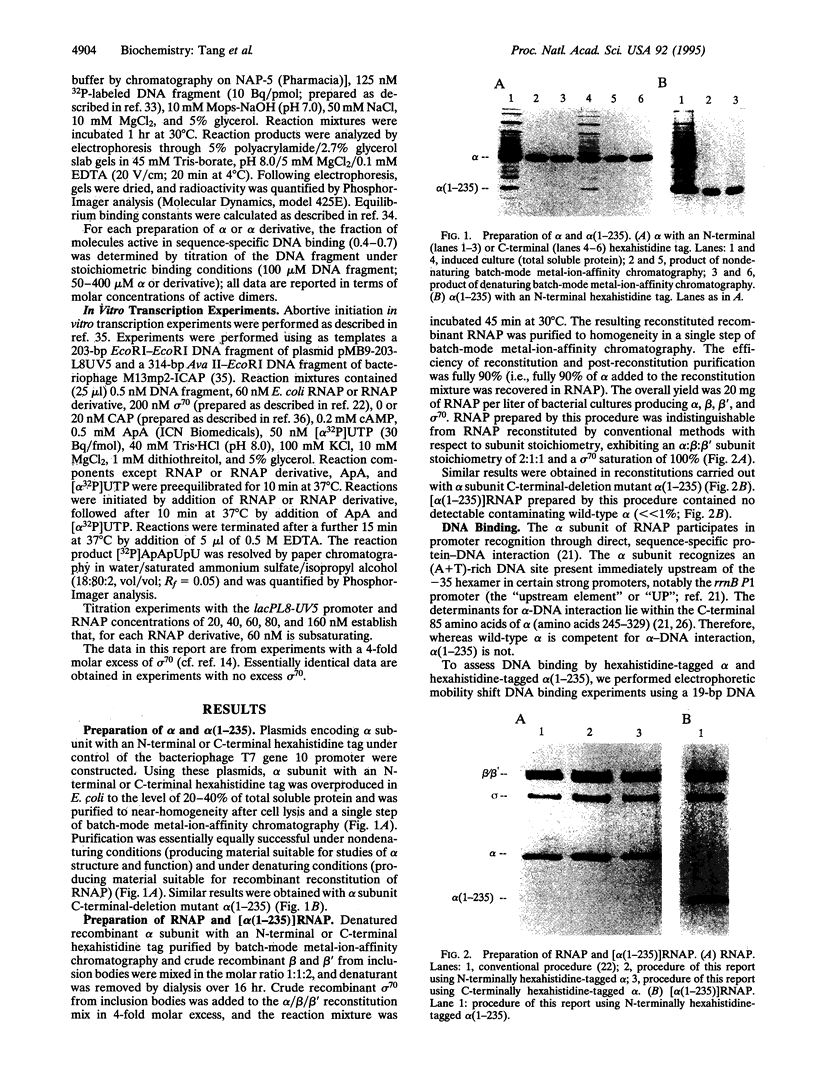
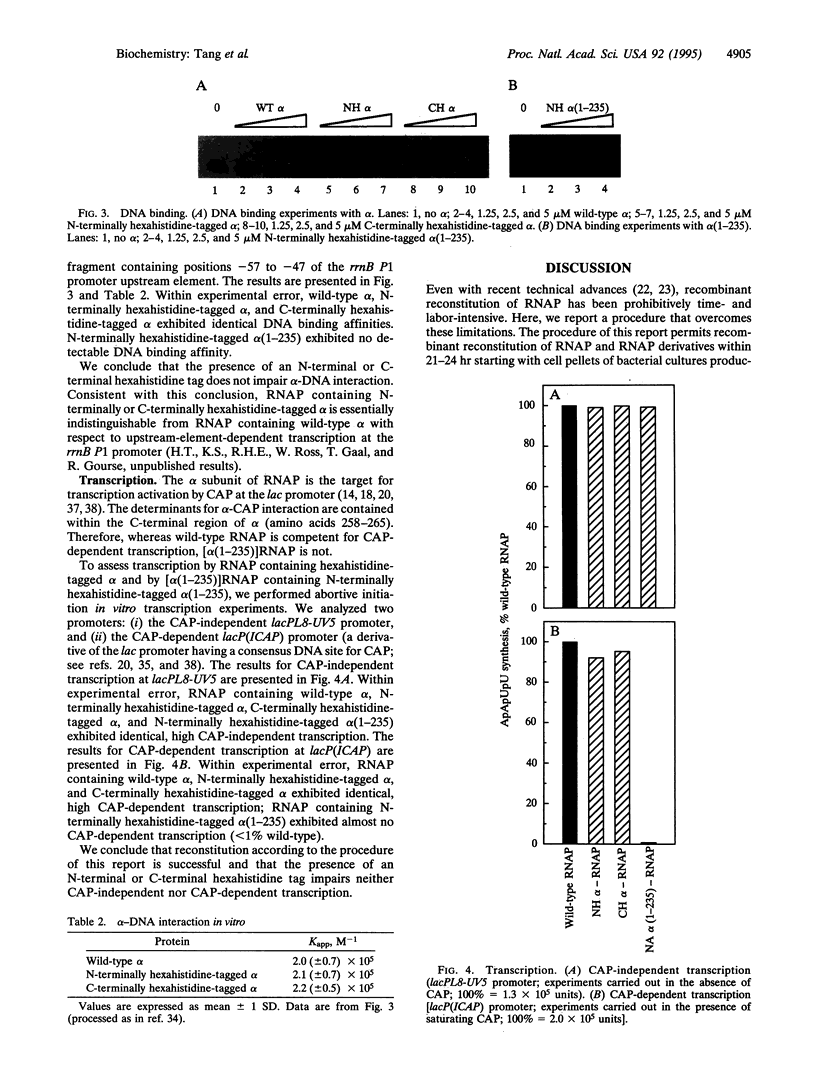
We present a simple, rapid procedure for reconstitution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme (RNAP) from individual recombinant alpha, beta, beta', and sigma 70 subunits. Hexahistidine-tagged recombinant alpha subunit purified by batch-mode metal-ion-affinity chromatography is incubated with crude recombinant beta, beta', and sigma 70 subunits from inclusion bodies, and the resulting reconstituted recombinant RNAP is purified by batch-mode metal-ion-affinity chromatography. RNAP prepared by this procedure is indistinguishable from RNAP prepared by conventional methods with respect to subunit stoichiometry, alpha-DNA interaction, catabolite gene activator protein (CAP)-independent transcription, and CAP-dependent transcription. Experiments with alpha (1-235), an alpha subunit C-terminal deletion mutant, establish that the procedure is suitable for biochemical screening of subunit lethal mutants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archambault J., Friesen J. D. Genetics of eukaryotic RNA polymerases I, II, and III. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):703–724. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.703-724.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ross W., Tang H., Gourse R. L., Ebright R. H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase alpha subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Goldfarb A. Recombinant Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: purification of individually overexpressed subunits and in vitro assembly. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Dec;4(6):503–511. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Ebright R. H. Promoter structure, promoter recognition, and transcription activation in prokaryotes. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):743–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Identification of the target of a transcription activator protein by protein-protein photocrosslinking. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):90–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8016656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Gunasekera A. Consensus DNA site for the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): CAP exhibits a 450-fold higher affinity for the consensus DNA site than for the E. coli lac DNA site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10295–10305. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Ishihama A. Subunits of RNA polymerase in function and structure; Maturation in vitro of core enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):523–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Overexpression and purification of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekera A., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. DNA sequence determinants for binding of the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14713–14720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A., Fukuda R., Ito K. Subunits of RNA polymerase in function and structure. IV. Enhancing role of sigma in the subunit assembly of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 5;79(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90274-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashlev M., Lee J., Zalenskaya K., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Blocking of the initiation-to-elongation transition by a transdominant RNA polymerase mutation. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1006–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.1693014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashlev M., Martin E., Polyakov A., Severinov K., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Histidine-tagged RNA polymerase: dissection of the transcription cycle using immobilized enzyme. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Kashlev M., Borukhov S., Goldfarb A. A beta subunit mutation disrupting the catalytic function of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6018–6022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Sagitov V., Burova E., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Genetic dissection of the transcription cycle. A mutant RNA polymerase that cannot hold onto a promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20175–20180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustaev A., Kashlev M., Lee J. Y., Polyakov A., Lebedev A., Zalenskaya K., Grachev M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. Mapping of the priming substrate contacts in the active center of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23927–23931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Ishihama A. Subunits of RNA polymerase in function and structure. VI. Sequence of the assembly in vitro of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):621–635. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Soushko M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. Rifampicin region revisited. New rifampicin-resistant and streptolydigin-resistant mutants in the beta subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14820–14825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Fenyo D., Chait B., Ebright R. H. Location, structure, and function of the target of a transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3058–3067. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II: subunit structure and function. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90074-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalenskaya K., Lee J., Gujuluva C. N., Shin Y. K., Slutsky M., Goldfarb A. Recombinant RNA polymerase: inducible overexpression, purification and assembly of Escherichia coli rpo gene products. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. P., Gunasekera A., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Derivatives of CAP having no solvent-accessible cysteine residues, or having a unique solvent-accessible cysteine residue at amino acid 2 of the helix-turn-helix motif. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Dec;9(3):463–473. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Zhou Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) is not an "acidic activating region" transcription activator protein. Negatively charged amino acids of CAP that are solvent-accessible in the CAP-DNA complex play no role in transcription activation at the lac promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8136–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou C., Fujita N., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Mapping the cAMP receptor protein contact site on the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2599–2605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]