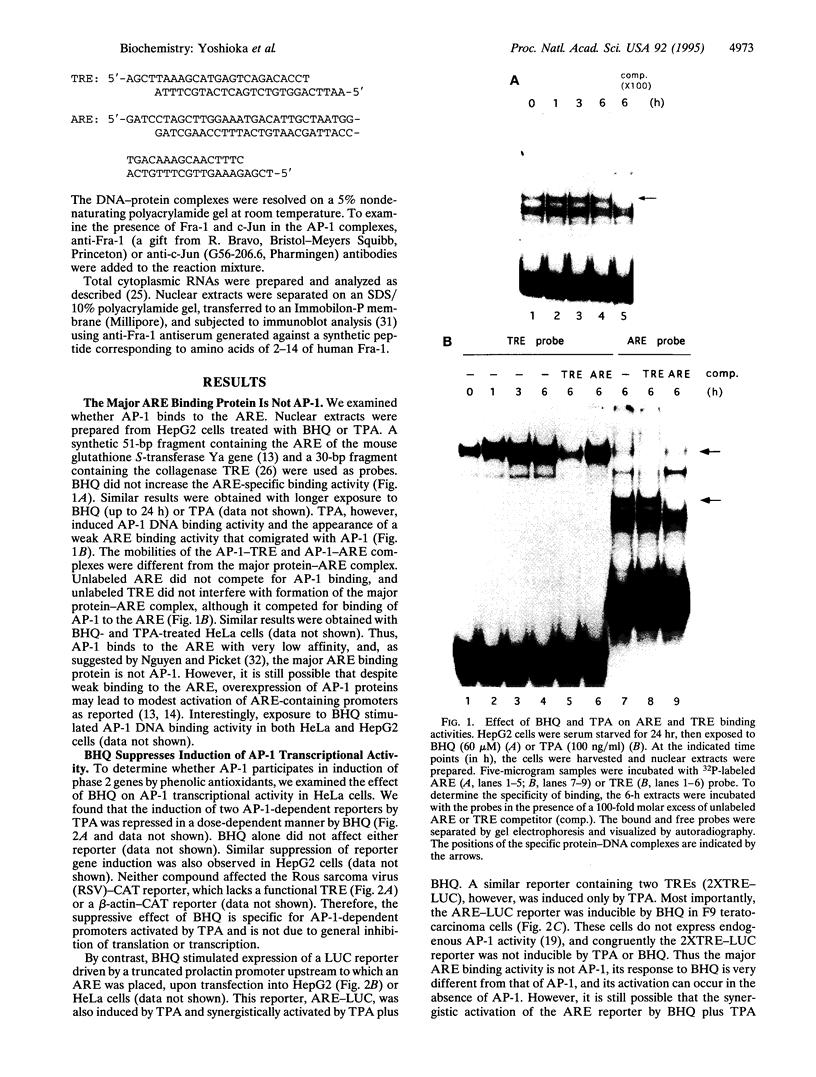
Abstract
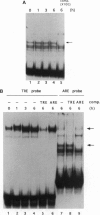
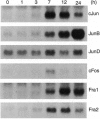
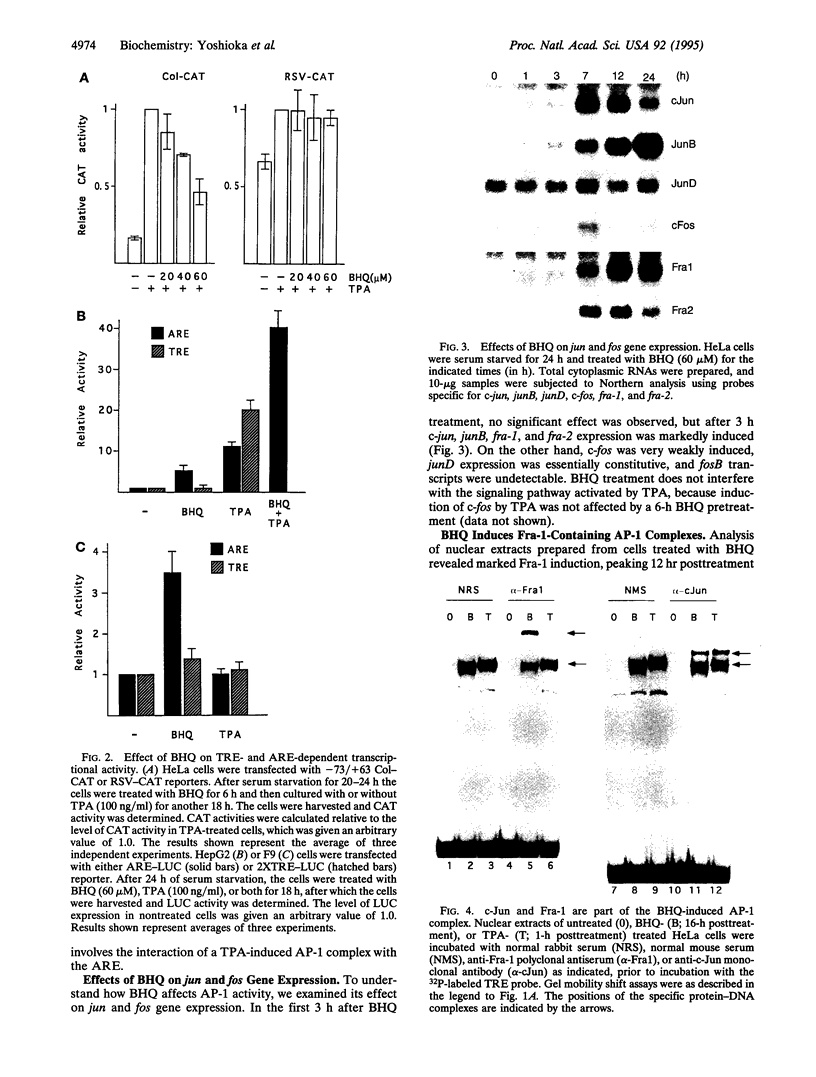
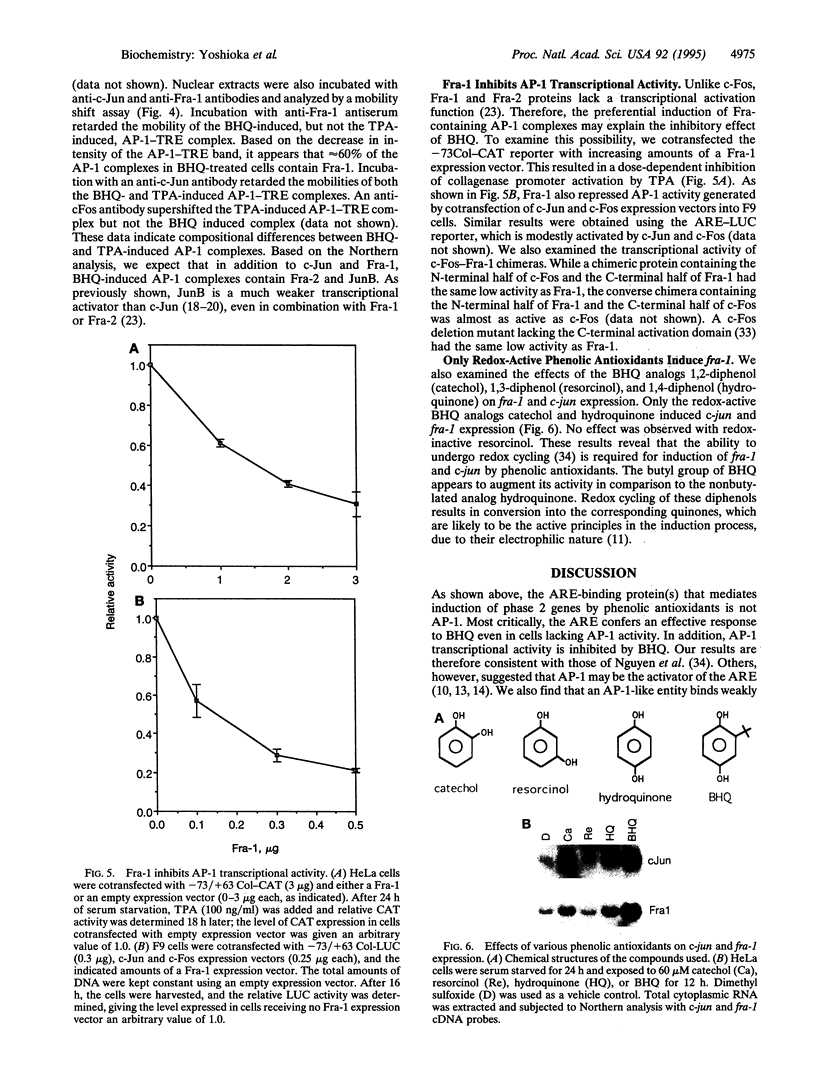
Induction of phase 2 detoxification enzymes by phenolic antioxidants can account for prevention of tumor initiation but cannot explain why these compounds inhibit tumor promotion. Phase 2 genes are induced through an antioxidant response element (ARE). Although the ARE resembles an AP-1 binding site, we show that the major ARE binding and activating protein is not AP-1. Interestingly, AP-1 DNA binding activity was induced by the phenolic antioxidant tert-butylhydroquinone (BHQ), but the induction of AP-1 transcriptional activity by the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) was inhibited by this compound. BHQ induced expression of c-jun, junB, fra-1, and fra-2, which encode AP-1 components, but was a poor inducer of c-fos and had no effect on fosB. Like c-Fos and FosB, the Fra proteins heterodimerize with Jun proteins to form stable AP-1 complexes. However, Fra-containing AP-1 complexes have low transactivation potential. Furthermore, Fra-1 repressed AP-1 activity induced by either TPA or expression of c-Jun and c-Fos. We therefore conclude that inhibitory AP-1 complexes composed of Jun-Fra heterodimers, induced by BHQ, antagonize the transcriptional effects of the tumor promoter TPA, which are mediated by Jun-Fos heterodimers. Since AP-1 is an important mediator of tumor promoter action, these findings may explain the anti-tumor-promoting activity of phenolic antioxidants.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. JunB differs from c-Jun in its DNA-binding and dimerization domains, and represses c-Jun by formation of inactive heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):479–490. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. c-Fos transcriptional activity stimulated by H-Ras-activated protein kinase distinct from JNK and ERK. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):171–175. doi: 10.1038/371171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favreau L. V., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat NAD(P)H:quinone reductase gene. Identification of regulatory elements controlling basal level expression and inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds and phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4556–4561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferriola P. C., Cody V., Middleton E., Jr Protein kinase C inhibition by plant flavonoids. Kinetic mechanisms and structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1617–1624. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bensimon A., Tichauer Y., Daniel V. Xenobiotic-inducible expression of murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene is controlled by an electrophile-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6258–6262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bergelson S., Daniel V. Two adjacent AP-1-like binding sites form the electrophile-responsive element of the murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Fukushima S., Ito N. Effects of subsequent antioxidant treatment on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-initiated carcinogenesis of the mammary gland, ear duct and forestomach in Sprague-Dawley rats. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jan;9(1):101–104. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahl R. Synthetic antioxidants: biochemical actions and interference with radiation, toxic compounds, chemical mutagens and chemical carcinogens. Toxicology. 1984 Dec;33(3-4):185–228. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(84)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Jaiswal A. K. Regulation of human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase gene. Role of AP1 binding site contained within human antioxidant response element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15097–15104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A., Yancheva N., Wasylyk B. Transformation suppressor activity of a Jun transcription factor lacking its activation domain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):635–638. doi: 10.1038/352635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Tokuhara M., Konuma Y., Nomura N., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human fos-related genes and their expression during monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto K., Ito S., Kitazawa S., Tsutsumi M., Denda A., Konishi Y. Inhibitory effect of butylated hydroxyanisole administration on pancreatic carcinogenesis in Syrian hamsters initiated with N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)amine. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Aug;10(8):1491–1494. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.8.1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. A naturally occurring truncated form of FosB that inhibits Fos/Jun transcriptional activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90504-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T., Pickett C. B. Regulation of rat glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene expression. DNA-protein interaction at the antioxidant responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13535–13539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T., Rushmore T. H., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of a rat liver glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Analysis of the antioxidant response element and its activation by the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13656–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus R., Bergelson S., Daniel V. Phenobarbital induction of AP-1 binding activity mediates activation of glutathione S-transferase and quinone reductase gene expression. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):637–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2900637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestera T., Holtzclaw W. D., Zhang Y., Talalay P. Chemical and molecular regulation of enzymes that detoxify carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., De Long M. J., Talalay P. On the mechanisms of induction of cancer-protective enzymes: a unifying proposal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., King R. G., Paulson K. E., Pickett C. B. Regulation of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene expression: identification of a unique xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Characterization of a xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14648–14653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Angel P., Meek J., Karin M. Different requirements for formation of Jun: Jun and Jun: Fos complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2091–2100. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Okuno H., Yoshida T., Endo T., Nishina H., Iba H. Difference in transcriptional regulatory function between c-Fos and Fra-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5537–5542. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talalay P. Mechanisms of induction of enzymes that protect against chemical carcinogenesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1989;28:237–250. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(89)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejo J., Chambard J. C., Karin M., Brown J. H. Biphasic increase in c-jun mRNA is required for induction of AP-1-mediated gene transcription: differential effects of muscarinic and thrombin receptor activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4742–4750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya H., Fujii M., Niki T., Tokuhara M., Matsui M., Seiki M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax activates transcription of the human fra-1 gene through multiple cis elements responsive to transmembrane signals. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7001–7007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7001-7007.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chiu R., Karin M. Elevation of AP1 activity during F9 cell differentiation is due to increased c-jun transcription. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]