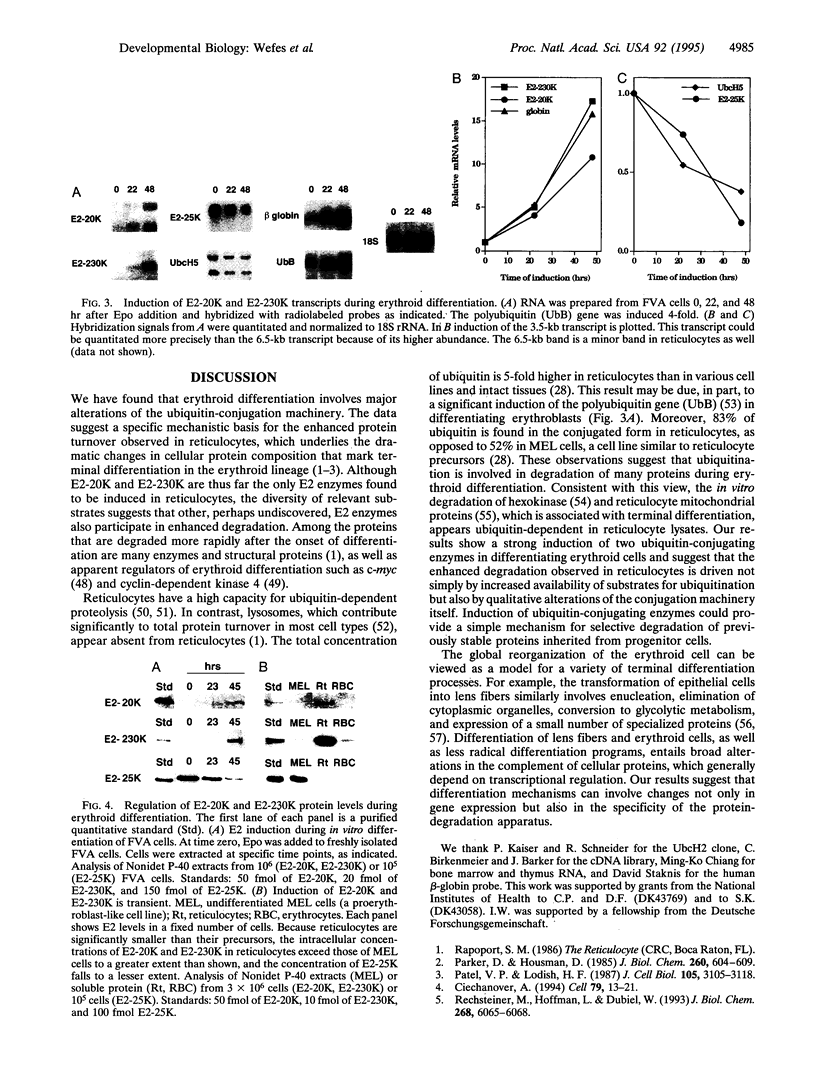
Abstract
A global cellular reorganization occurs during the reticulocyte stage of erythroid differentiation. This reorganization is accomplished partly through programmed protein degradation. The selection of proteins for degradation can be mediated by covalent attachment of ubiquitin. We have cloned cDNAs encoding two ubiquitin-conjugating (E2) enzymes, E2-20K and E2-230K, and found their genes to be strongly induced during the differentiation of erythroblasts into reticulocytes. Induction of the E2-20K and E2-230K genes is specific, as transcript levels for at least two other ubiquitinating enzymes fall during erythroblast differentiation. In contrast to most proteins induced in reticulocytes, E2-20K and E2-230K enzymes are present at strongly reduced levels in erythrocytes and thus decline in abundance as reticulocyte maturation is completed. This result suggests that both enzymes function during the reticulocyte stage, when enhanced protein degradation has been observed. These data implicate regulated components of the ubiquitin conjugation machinery in erythroid differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkenmeier C. S., White R. A., Peters L. L., Hall E. J., Lux S. E., Barker J. E. Complex patterns of sequence variation and multiple 5' and 3' ends are found among transcripts of the erythroid ankyrin gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9533–9540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., de Jong W. W. Lens proteins and their genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:259–281. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boches F. S., Goldberg A. L. Role for the adenosine triphosphate-dependent proteolytic pathway in reticulocyte maturation. Science. 1982 Feb 19;215(4535):978–980. doi: 10.1126/science.7156977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohley P., Seglen P. O. Proteases and proteolysis in the lysosome. Experientia. 1992 Feb 15;48(2):151–157. doi: 10.1007/BF01923508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondurant M. C., Lind R. N., Koury M. J., Ferguson M. E. Control of globin gene transcription by erythropoietin in erythroblasts from friend virus-infected mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):675–683. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Johnson P., Sommer T., Jentsch S., Hochstrasser M. Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90426-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. J., Niles E. G., Pickart C. M. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a mammalian multiubiquitinating enzyme (E225K) and overexpression of the functional enzyme in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15698–15704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Pickart C. M. A 25-kilodalton ubiquitin carrier protein (E2) catalyzes multi-ubiquitin chain synthesis via lysine 48 of ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21835–21842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Chau V., Kirschner M. Ubiquitination of the G1 cyclin Cln2p by a Cdc34p-dependent pathway. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):303–312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deveraux Q., Ustrell V., Pickart C., Rechsteiner M. A 26 S protease subunit that binds ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7059–7061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Khan M. I., Marsh J., Butt T. R., Crooke S. T. Chemical synthesis and expression of a cassette adapted ubiquitin gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3524–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. S., St John T., Krieg P., Bonham K., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Bowden G. T. Overexpression of three ubiquitin genes in mouse epidermal tumors is associated with enhanced cellular proliferation and stress. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):269–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Bright P. M. The immunochemical detection and quantitation of intracellular ubiquitin-protein conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12464–12473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser P., Seufert W., Höfferer L., Kofler B., Sachsenmaier C., Herzog H., Jentsch S., Schweiger M., Schneider R. A human ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme homologous to yeast UBC8. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):8797–8802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley L. L., Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C., Koury S. T., Sawyer S. T., Wickrema A. Survival or death of individual proerythroblasts results from differing erythropoietin sensitivities: a mechanism for controlled rates of erythrocyte production. Blood. 1993 Oct 15;82(8):2340–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley L. L., Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. Regulation of programmed death in erythroid progenitor cells by erythropoietin: effects of calcium and of protein and RNA syntheses. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jun;151(3):487–496. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa H., Richon V. M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Suppression of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 during induced differentiation of erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7195–7203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer N. S., Berleth E. S., Pickart C. M. A novel, arsenite-sensitive E2 of the ubiquitin pathway: purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6035–6041. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornitzer D., Raboy B., Kulka R. G., Fink G. R. Regulated degradation of the transcription factor Gcn4. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6021–6030. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. Erythropoietin retards DNA breakdown and prevents programmed death in erythroid progenitor cells. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):378–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2326648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Kelley L. L., Bondurant M. C. The fate of erythroid progenitor cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Apr 15;718:259–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb55725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Sawyer S. T., Bondurant M. C. Splenic erythroblasts in anemia-inducing Friend disease: a source of cells for studies of erythropoietin-mediated differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):526–532. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury S. T., Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. Morphological changes in erythroblasts during erythropoietin-induced terminal differentiation in vitro. Exp Hematol. 1988 Oct;16(9):758–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Pickart C. M. Inactivation of arginyl-tRNA protein transferase by a bifunctional arsenoxide: identification of residues proximal to the arsenoxide site. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 10;34(1):139–147. doi: 10.1021/bi00001a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani M., Stocchi V., Chiarantini L., Serafini G., Dachà M., Fornaini G. Rabbit red blood cell hexokinase. Decay mechanism during reticulocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8327–8333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Furuno N., Okazaki K., Tanaka H., Ogawa Y., Sagata N. Degradation of Mos by the N-terminal proline (Pro2)-dependent ubiquitin pathway on fertilization of Xenopus eggs: possible significance of natural selection for Pro2 in Mos. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):4021–4027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Cell-specific transcription and cell differentiation in the erythroid lineage. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1003–1012. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D., Housman D. Regulation of protein synthesis and accumulation during murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):604–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel V. P., Lodish H. F. A fibronectin matrix is required for differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells into reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3105–3118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Graziani L. A., Dosch S. F. Murine erythroleukemia cells possess an active ubiquitin- and ATP-dependent proteolytic pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jul;272(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Haldeman M. T., Kasperek E. M., Chen Z. Iodination of tyrosine 59 of ubiquitin selectively blocks ubiquitin's acceptor activity in diubiquitin synthesis catalyzed by E2(25K). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14418–14423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Vella A. T. Levels of active ubiquitin carrier proteins decline during erythroid maturation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12028–12035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. M., Schewe T., Wiesner R., Halangk W., Ludwig P., Janicke-Höhne M., Tannert C., Hiebsch C., Klatt D. The lipoxygenase of reticulocytes. Purification, characterization and biological dynamics of the lipoxygenase; its identity with the respiratory inhibitors of the reticulocyte. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):545–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S., Dubiel W., Müller M. Proteolysis of mitochondria in reticulocytes during maturation is ubiquitin-dependent and is accompanied by a high rate of ATP hydrolysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviv O., Heller H., Hershko A. Alterations in components of the ubiquitin-protein ligase system following maturation of reticulocytes to erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):658–665. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Hoffman L., Dubiel W. The multicatalytic and 26 S proteases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6065–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. Large-scale procurement of erythropoietin-responsive erythroid cells: assay for biological activity of erythropoietin. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:340–352. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. Identification of a human ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that mediates the E6-AP-dependent ubiquitination of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8797–8801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Huibregtse J. M., Vierstra R. D., Howley P. M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob E., Böhm T., Mendenhall M. D., Nasmyth K. The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Futcher B., Jentsch S. Role of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in degradation of S- and M-phase cyclins. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):78–81. doi: 10.1038/373078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spotts G. D., Hann S. R. Enhanced translation and increased turnover of c-myc proteins occur during differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3952–3964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treier M., Staszewski L. M., Bohmann D. Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):787–798. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90285-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaglom J., Linskens M. H., Sadis S., Rubin D. M., Futcher B., Finley D. p34Cdc28-mediated control of Cln3 cyclin degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]