Abstract
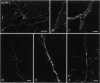
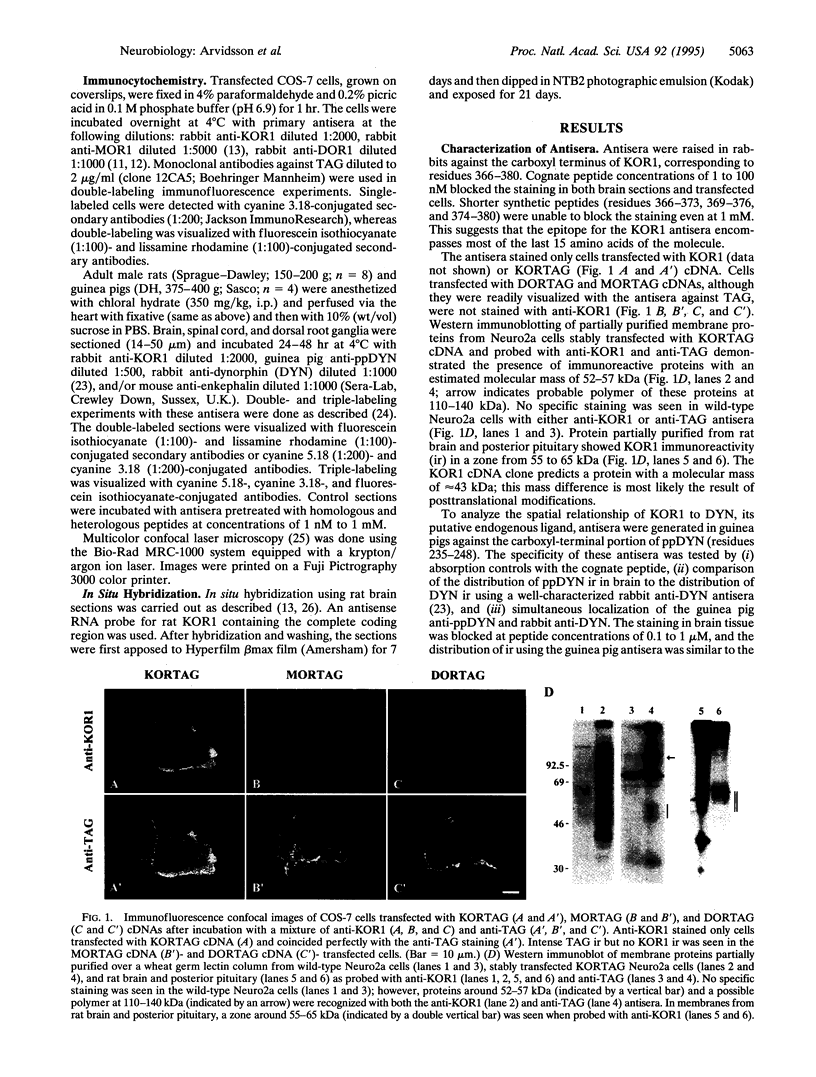
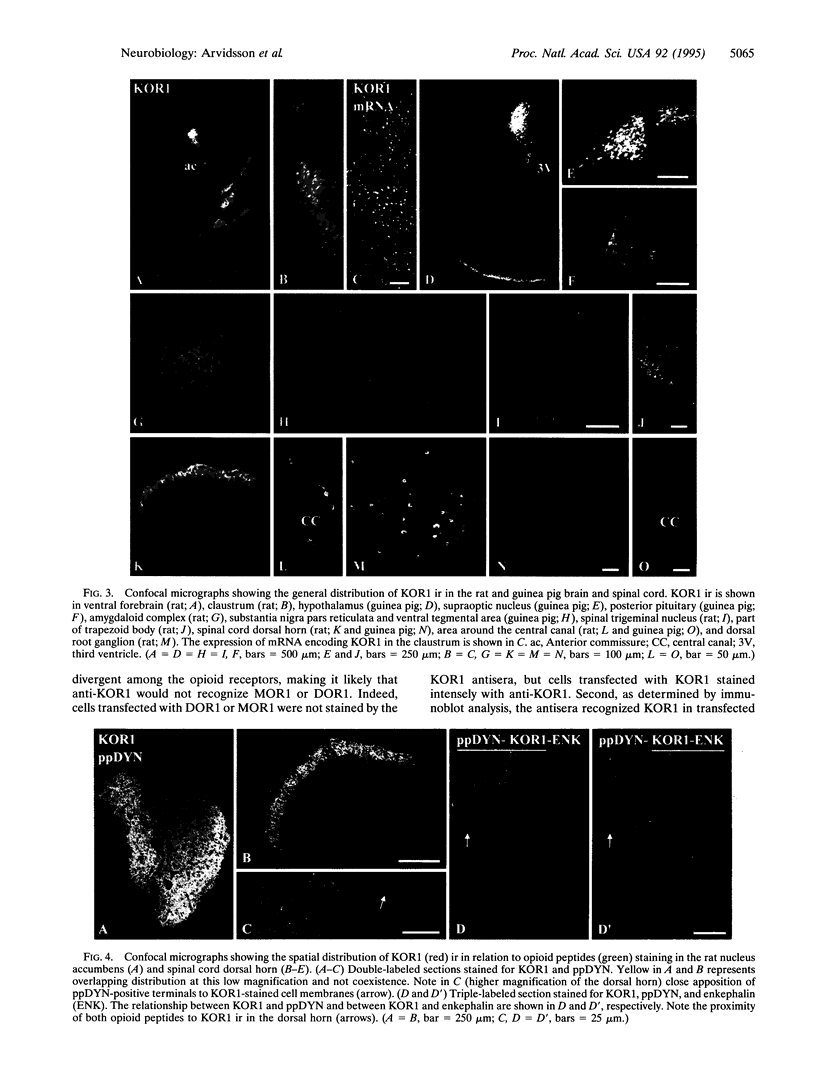
Antisera were raised against a synthetic peptide corresponding to the carboxyl terminus of the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR1). Specificity of the antisera was verified by staining of COS-7 cells transfected with KOR1 and epitope-tagged KOR1 cDNAs, by recognition by the antisera of proteins on Western blots of both transfected cells and brain tissue, by the absence of staining of both brain tissue and transfected cells after preabsorption of the antisera with the cognate peptide, and on the strong correlation between the distribution of KOR1 immunoreactivity and that of earlier ligand binding and in situ hybridization studies. Results indicate that KOR1 in neurons is targeted into both the axonal and somatodendritic compartments, but the majority of immunostaining was seen in the somatodendritic compartment. In sections from rat and guinea pig brain, prominent KOR1 staining was seen in the ventral forebrain, hypothalamus, thalamus, posterior pituitary, and midbrain. While the staining pattern was similar in both species, distinct differences were also observed. The distribution of preprodynorphin and KOR1 immunoreactivity was complementary in many brain regions, suggesting that KOR1 is poised to mediate the physiological actions of dynorphin. However, the distribution of KOR1 and enkephalin immunoreactivity was complementary in some regions as well. These results suggest that the KOR1 protein is primarily, but not exclusively, deployed to postsynaptic membranes where it mediates the effects of products of preprodynorphin and possibly preproenkephalin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidsson U., Dado R. J., Riedl M., Lee J. H., Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Elde R., Wessendorf M. W. delta-Opioid receptor immunoreactivity: distribution in brainstem and spinal cord, and relationship to biogenic amines and enkephalin. J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1215–1235. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01215.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besse D., Lombard M. C., Zajac J. M., Roques B. P., Besson J. M. Pre- and postsynaptic distribution of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in the superficial layers of the cervical dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 25;521(1-2):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91519-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brelje T. C., Wessendorf M. W., Sorenson R. L. Multicolor laser scanning confocal immunofluorescence microscopy: practical application and limitations. Methods Cell Biol. 1993;38:97–181. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr F. E., Reid A. H., Wessendorf M. W. A cryptic peptide from the preprothyrotropin-releasing hormone precursor stimulates thyrotropin gene expression. Endocrinology. 1993 Aug;133(2):809–814. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.2.8344217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Hurley J. A., Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dado R. J., Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Elde R. Immunofluorescent identification of a delta (delta)-opioid receptor on primary afferent nerve terminals. Neuroreport. 1993 Dec 13;5(3):341–344. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199312000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., McMurray C. T., Garrett J. E., Adelman J. P., Calavetta L. Characterization of the rat prodynorphin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):2070–2078. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-2070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Keith D. E., Jr, Morrison H., Magendzo K., Edwards R. H. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1952–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1335167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grudt T. J., Williams J. T. kappa-Opioid receptors also increase potassium conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11429–11432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer B. L., Befort K., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Hirth C. G. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12048–12052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Zhu J., Chen C., Chen Y. W., Deriel J. K., Ashby B., Liu-Chen L. Y. Molecular cloning and expression of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):629–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2950629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Fox C. A., Meng F., Akil H., Watson S. J. Kappa 1 receptor mRNA distribution in the rat CNS: comparison to kappa receptor binding and prodynorphin mRNA. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1994 Apr;5(2):124–144. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Khachaturian H., Lewis M. E., Akil H., Watson S. J. Autoradiographic differentiation of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors in the rat forebrain and midbrain. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2445–2464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Thompson R. C., Akil H., Watson S. J. Delta opioid receptor mRNA distribution in the brain: comparison to delta receptor binding and proenkephalin mRNA. J Chem Neuroanat. 1993 Nov-Dec;6(6):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0891-0618(93)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng F., Xie G. X., Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Goldstein A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami M., Toya T., Katao Y., Maekawa K., Nakamura S., Onogi T., Kaneko S., Satoh M. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the rat kappa-opioid receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 30;329(3):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80240-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Takeshima H., Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K. cDNA cloning and pharmacological characterization of an opioid receptor with high affinities for kappa-subtype-selective ligands. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 6;330(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80923-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerig S. C., Loh H. H., Law P. Y. Identification of three separate guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that interact with the delta-opioid receptor in NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 May;41(5):822–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A., Hunter J. C., Hill R. G., Hughes J. [125I]dynorphin(1-8) produces a similar pattern of kappa-opioid receptor labelling to [3H]dynorphin(1-8) and [3H]etorphine in guinea pig brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 12;86(3):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Akil H., Watson S. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat mu opioid receptor. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90120-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Magnan J. Quantitative analysis of multiple kappa-opioid receptors by selective and nonselective ligand binding in guinea pig spinal cord: resolution of high and low affinity states of the kappa 2 receptors by a computerized model-fitting technique. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):694–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterwald E. M., Knapp C., Zukin R. S. Neuroanatomical localization of kappa 1 and kappa 2 opioid receptors in rat and guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 18;562(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Predominance of the amino-terminal octapeptide fragment of dynorphin in rat brain regions. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):77–79. doi: 10.1038/299077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessendorf M. W., Appel N. M., Molitor T. W., Elde R. P. A method for immunofluorescent demonstration of three coexisting neurotransmitters in rat brain and spinal cord, using the fluorophores fluorescein, lissamine rhodamine, and 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin-3-acetic acid. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Dec;38(12):1859–1877. doi: 10.1177/38.12.1701460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie G. X., Meng F., Mansour A., Thompson R. C., Hoversten M. T., Goldstein A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Primary structure and functional expression of a guinea pig kappa opioid (dynorphin) receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3779–3783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Raynor K., Kong H., Breder C. D., Takeda J., Reisine T., Bell G. I. Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]