Abstract
The title compound, C2H3N3OS, is a monoclinic (P21/c) polymorph of the previously reported triclinic structure [Kang et al. (2012 ▶). Acta Cryst. E68, o1198]. The asymmetric unit contains two independent molecules which are essentially planar, with r.m.s. deviations of 0.001 and 0.032 Å from the mean plane defined by the seven non-H atoms. In the crystal, N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a sheet parallel to (111).
Keywords: crystal structure, polymorph, thiadiazolone, hydrogen bonds
Related literature
For structures and reactivity of thiadiazole derivatives, see: Parkanyi et al. (1989 ▶); Cho et al. (1996 ▶). For the triclinic polymorph, see; Kang et al. (2012 ▶).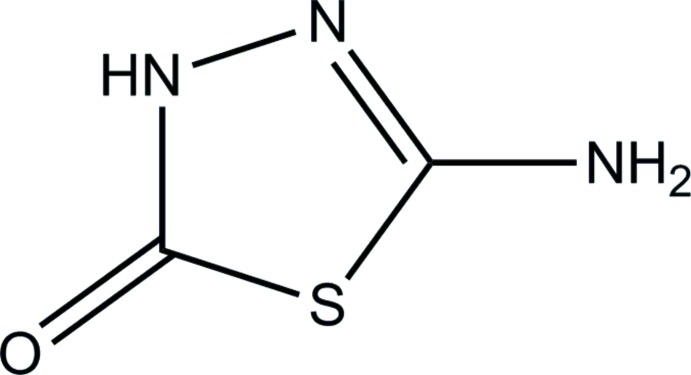
Experimental
Crystal data
C2H3N3OS
M r = 117.13
Monoclinic,

a = 3.8182 (3) Å
b = 10.8166 (7) Å
c = 21.8043 (15) Å
β = 91.015 (4)°
V = 900.37 (11) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.58 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.21 × 0.1 × 0.09 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.911, T max = 0.931
5812 measured reflections
1709 independent reflections
1376 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.08
1709 reflections
151 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and 30% probability ellipsoids. Intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines.
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326fig2.tif
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound, showing molecules linked by intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
CCDC reference: 1013072
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯N11 | 0.77 (3) | 2.12 (3) | 2.891 (4) | 174 (3) |
| N7—H7A⋯O13i | 0.86 (3) | 2.07 (4) | 2.913 (4) | 167 (3) |
| N7—H7B⋯N4ii | 0.85 (4) | 2.21 (4) | 3.048 (4) | 171 (3) |
| N10—H10⋯O13iii | 0.84 (3) | 2.09 (3) | 2.910 (3) | 165 (3) |
| N14—H14A⋯O6iv | 0.91 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 3.005 (4) | 159 (4) |
| N14—H14B⋯O6 | 0.73 (4) | 2.58 (4) | 3.306 (5) | 173 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research fund of Chungnam National University.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Chemical context
S2. Structural commentary
5-Amino-2H-1,2,4-thiadiazolin-3-one heterocycle is an analog of cytosine (Parkanyi et al., 1989). Derivatives of this heterocyclic compound are interesting in the antibacterial activity, potential carcinogenicity, and kinase inhibitor activity (Cho et al., 1996). The title compound, 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-one (I) is an isomer of 5-amino-2H-1,2,4-thiadiazolin-3-one, which has become an attractive moiety due to potential biological activities. These heterocyclic compounds are potentially good ligands because of N, O, and S atoms which are good donor atoms to both transition metals (Cu, Zn, Cd) and lanthanide metals (Tb and Eu). In our interest to metal complexes with these heterocyclic compounds, the title compound was isolated accidently.
In (I), Fig. 1, two independent molecules comprise the asymmetric unit, which are linked by the intermolecular N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds. The 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-one units are almost planar, with r.m.s. deviations of 0.001 – 0.032 Å from the corresponding least-squares plane defined by the seven constituent atoms. The crystal structure is stabilized by the intermolecular N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds, which link the molecules into a two-dimensional sheet parallel to 111 plane (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
S3. Supramolecular features
S4. Database survey
S5. Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound (I) was synthesized by the process of the previous report (Kang et al. 2012). Copper(II) chloride (1.36 g, 8 mmol) dissolved in ethanol, was added drop wise to a stirred ethanolic solution containing 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H-one (1.87 g, 16 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 10 h at room temperature. The resulting solution was filtered and allowed to stand at room temperature. Colourless crystals of (I) were obtained at room temperature over a period of a few weeks.
S6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. H atoms of the NH and NH2 groups were located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely [refined distances = 0.73 (4)–0.91 (4) Å].
Figures
Fig. 1.

Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and 30% probability ellipsoids. Intermolecular N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound, showing molecules linked by intermolecular N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
Crystal data
| C2H3N3OS | F(000) = 480 |
| Mr = 117.13 | Dx = 1.728 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1700 reflections |
| a = 3.8182 (3) Å | θ = 2.7–25.7° |
| b = 10.8166 (7) Å | µ = 0.58 mm−1 |
| c = 21.8043 (15) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 91.015 (4)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 900.37 (11) Å3 | 0.21 × 0.1 × 0.09 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1376 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.8°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −4→4 |
| Tmin = 0.911, Tmax = 0.931 | k = −12→13 |
| 5812 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
| 1709 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0317P)2 + 0.833P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1709 reflections | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 151 parameters | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.5670 (2) | 0.33458 (7) | 0.36148 (3) | 0.0316 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.4389 (8) | 0.4860 (3) | 0.33723 (13) | 0.0297 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.5448 (8) | 0.5631 (3) | 0.38116 (12) | 0.0327 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.487 (9) | 0.631 (3) | 0.3829 (14) | 0.030 (10)* | |
| N4 | 0.7091 (7) | 0.5177 (2) | 0.43328 (11) | 0.0301 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.7362 (8) | 0.3992 (3) | 0.42932 (13) | 0.0259 (7) | |
| O6 | 0.2779 (7) | 0.5107 (2) | 0.28964 (10) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| N7 | 0.8708 (8) | 0.3270 (3) | 0.47486 (13) | 0.0349 (7) | |
| H7A | 0.968 (9) | 0.259 (3) | 0.4641 (14) | 0.035 (10)* | |
| H7B | 0.983 (10) | 0.364 (3) | 0.5033 (17) | 0.049 (11)* | |
| S8 | 0.0629 (2) | 1.02405 (7) | 0.34352 (4) | 0.0334 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.2461 (8) | 1.0171 (3) | 0.41853 (13) | 0.0294 (7) | |
| N10 | 0.3361 (7) | 0.9003 (2) | 0.42943 (12) | 0.0315 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.438 (8) | 0.884 (3) | 0.4630 (14) | 0.024 (8)* | |
| N11 | 0.2747 (8) | 0.8126 (2) | 0.38422 (11) | 0.0359 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.1325 (8) | 0.8645 (3) | 0.33686 (13) | 0.0296 (7) | |
| O13 | 0.2843 (7) | 1.1052 (2) | 0.45367 (10) | 0.0458 (7) | |
| N14 | 0.0397 (10) | 0.8045 (4) | 0.28504 (14) | 0.0502 (9) | |
| H14A | −0.052 (11) | 0.853 (4) | 0.2546 (19) | 0.068 (13)* | |
| H14B | 0.074 (10) | 0.738 (4) | 0.2852 (17) | 0.043 (12)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0410 (5) | 0.0227 (4) | 0.0307 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | −0.0078 (3) | −0.0059 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0324 (18) | 0.0272 (17) | 0.0295 (16) | 0.0007 (14) | −0.0021 (13) | −0.0011 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0497 (19) | 0.0174 (14) | 0.0307 (15) | 0.0063 (13) | −0.0095 (12) | −0.0019 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0401 (16) | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0278 (13) | 0.0087 (12) | −0.0088 (11) | −0.0033 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0287 (17) | 0.0221 (16) | 0.0269 (15) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0001 (12) | −0.0042 (12) |
| O6 | 0.0609 (17) | 0.0390 (14) | 0.0355 (13) | 0.0025 (12) | −0.0201 (12) | 0.0028 (11) |
| N7 | 0.0482 (19) | 0.0240 (16) | 0.0319 (15) | 0.0073 (14) | −0.0118 (13) | −0.0026 (13) |
| S8 | 0.0422 (5) | 0.0250 (4) | 0.0326 (4) | 0.0077 (4) | −0.0091 (3) | 0.0031 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0343 (18) | 0.0242 (16) | 0.0296 (16) | 0.0068 (14) | −0.0037 (13) | 0.0004 (13) |
| N10 | 0.0479 (18) | 0.0233 (14) | 0.0229 (13) | 0.0116 (12) | −0.0093 (12) | −0.0023 (11) |
| N11 | 0.0550 (19) | 0.0239 (14) | 0.0284 (14) | 0.0093 (13) | −0.0091 (12) | −0.0033 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0358 (19) | 0.0242 (16) | 0.0288 (16) | 0.0051 (14) | −0.0027 (13) | −0.0019 (13) |
| O13 | 0.0714 (18) | 0.0255 (13) | 0.0400 (13) | 0.0124 (12) | −0.0154 (12) | −0.0079 (11) |
| N14 | 0.079 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0346 (18) | 0.0114 (18) | −0.0230 (16) | −0.0056 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C5 | 1.749 (3) | S8—C12 | 1.753 (3) |
| S1—C2 | 1.786 (3) | S8—C9 | 1.769 (3) |
| C2—O6 | 1.226 (4) | C9—O13 | 1.230 (3) |
| C2—N3 | 1.328 (4) | C9—N10 | 1.329 (4) |
| N3—N4 | 1.379 (3) | N10—N11 | 1.385 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.77 (3) | N10—H10 | 0.84 (3) |
| N4—C5 | 1.289 (4) | N11—C12 | 1.287 (4) |
| C5—N7 | 1.357 (4) | C12—N14 | 1.345 (4) |
| N7—H7A | 0.86 (3) | N14—H14A | 0.91 (4) |
| N7—H7B | 0.85 (4) | N14—H14B | 0.73 (4) |
| C5—S1—C2 | 88.81 (14) | C12—S8—C9 | 88.66 (14) |
| O6—C2—N3 | 127.9 (3) | O13—C9—N10 | 126.7 (3) |
| O6—C2—S1 | 125.5 (2) | O13—C9—S8 | 125.7 (2) |
| N3—C2—S1 | 106.5 (2) | N10—C9—S8 | 107.6 (2) |
| C2—N3—N4 | 120.0 (3) | C9—N10—N11 | 118.9 (3) |
| C2—N3—H3 | 123 (2) | C9—N10—H10 | 118 (2) |
| N4—N3—H3 | 115 (2) | N11—N10—H10 | 123 (2) |
| C5—N4—N3 | 109.5 (2) | C12—N11—N10 | 109.6 (2) |
| N4—C5—N7 | 123.6 (3) | N11—C12—N14 | 124.4 (3) |
| N4—C5—S1 | 115.1 (2) | N11—C12—S8 | 115.2 (2) |
| N7—C5—S1 | 121.2 (2) | N14—C12—S8 | 120.4 (3) |
| C5—N7—H7A | 117 (2) | C12—N14—H14A | 115 (3) |
| C5—N7—H7B | 116 (2) | C12—N14—H14B | 115 (3) |
| H7A—N7—H7B | 113 (3) | H14A—N14—H14B | 130 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···N11 | 0.77 (3) | 2.12 (3) | 2.891 (4) | 174 (3) |
| N7—H7A···O13i | 0.86 (3) | 2.07 (4) | 2.913 (4) | 167 (3) |
| N7—H7B···N4ii | 0.85 (4) | 2.21 (4) | 3.048 (4) | 171 (3) |
| N10—H10···O13iii | 0.84 (3) | 2.09 (3) | 2.910 (3) | 165 (3) |
| N14—H14A···O6iv | 0.91 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 3.005 (4) | 159 (4) |
| N14—H14B···O6 | 0.73 (4) | 2.58 (4) | 3.306 (5) | 173 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y−1, z; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (iv) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5326).
References
- Bruker (2002). SADABS, SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cho, N. S., Cho, J. J., Ra, D. Y., Moon, J. H., Song, J. S. & Kang, S. K. (1996). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 17, 1170–1174.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Kang, S. K., Cho, N. S. & Jang, S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Parkanyi, C., Yuan, H. L., Cho, N. S., Jaw, J. J., Woodhouse, T. E. & Aung, T. L. (1989). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 26, 1331–1334.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and 30% probability ellipsoids. Intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines.
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016055/tk5326fig2.tif
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound, showing molecules linked by intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
CCDC reference: 1013072
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



