Abstract
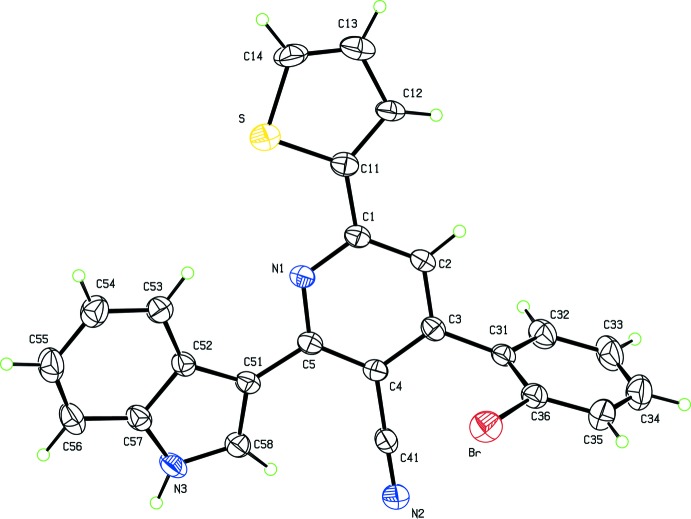
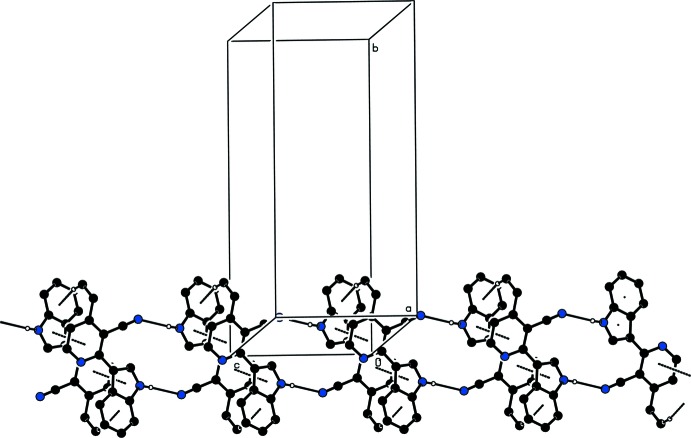
In the title compound, C24H14BrN3S, the dihedral angles between the planes of the pyridine ring and the pendant thiophene ring, the indole ring system (r.m.s. deviation = 0.022 Å) and the bromobenzene ring are 9.37 (17), 21.90 (12) and 69.01 (15)°, respectively. The approximate coplanarity of the central ring and the indole ring system is supported by two intramolecular C—H⋯N interactions. In the crystal, inversion dimers linked by pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds generate R 2 2(16) loops and the dimers are linked by C—H⋯π and aromatic π–π stacking [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.729 (3) Å] into a three-dimensional network.
Keywords: crystal structure, pyridine-3-carbonitrile, hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking
Related literature
For the biological activity of pyridine-3-carbonitrile derivatives, see: Kim et al. (2005 ▶); Ji et al. (2007 ▶); Brandt et al. (2010 ▶); El-Sayed et al. (2011 ▶).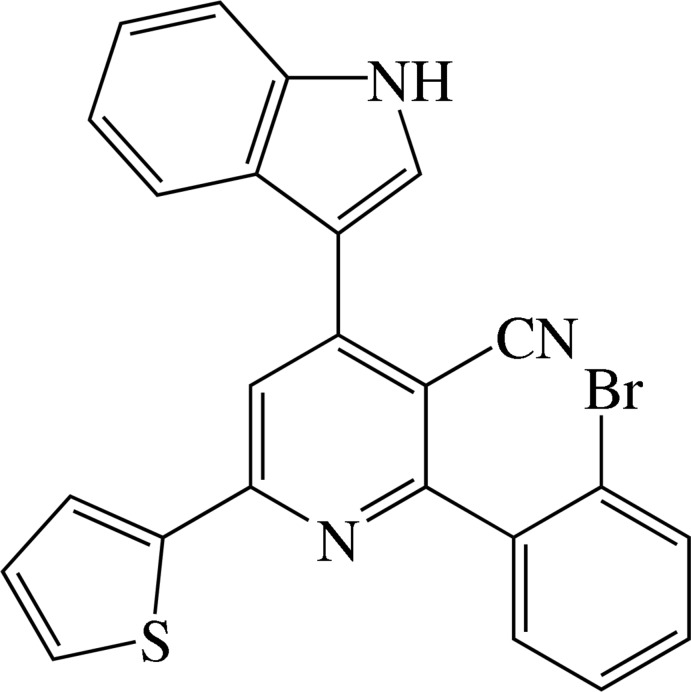
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H14BrN3S
M r = 456.35
Monoclinic,
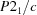
a = 10.470 (5) Å
b = 21.353 (5) Å
c = 9.292 (5) Å
β = 107.710 (5)°
V = 1978.9 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.20 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.52 × 0.23 × 0.17 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.958, T max = 0.986
17079 measured reflections
4305 independent reflections
2837 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.121
S = 1.02
4305 reflections
262 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260fig1.tif
The molecular structure of compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
x y z . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260fig2.tif
Partial packing view of the compound showing molecules interconnected through a C—H⋯π stacking interaction (dotted lines; symmetry code: (i)  − x,
− x,  + y,
+ y,  − z)
− z)
CCDC reference: 1015962
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the benzene ring of the indole moiety.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C53—H53⋯N1 | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.069 (4) | 114 |
| C58—H58⋯N2 | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.278 (4) | 135 |
| N3—H3⋯N2i | 0.86 | 2.17 | 3.008 (4) | 165 |
| C32—H32⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.761 (4) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 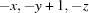 ; (ii)
; (ii) 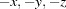 .
.
Acknowledgments
JS and RV thank the management of the Madura College for their encouragement and support. SP thanks the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for a major research project (SR/S1/OC/-50/2011) and the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for the award of a BSR Faculty Fellowship
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
3-Cyanopyridine derivatives have been reported for their wide range of applications such as in antimicrobial, analgesic, anti-hyperglycemic, antiproliferative and antitumor activities (Brandt et al., 2010; El-Sayed et al., 2011; Ji et al., 2007; Kim et al., 2005). As part of our studies in this area, the title compound was investigated.
The deviation of the nitrile atoms (C41,N2) from the mean plane of the pyridine ring system is -0.013 (1) Å and -0.020 (5) Å. The shortening of the C—N distances [1.346 (3) and 1.345 (3) Å] and the opening of the N1–C11–C10 angle [122.83 (2)°] may be attributed to the size of the substituent at C1, correlating well with the values observed in the ortho-substituted derivative.
The crystal structure features a intermolecular N—H···N interaction between inverse related molecules generating a graph set ring motif R22 (16) which are linked into chains through C—H···Cg1 interation (Cg1 is the centroid of the benzene ring of the indole moiety) and by π···π stacking interaction involving adjacent pyridine and pyrrole rings of the symmetry related molecule at (-x, -y, -z), with a centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.729 (3) Å·(Fig 2).
S2. Experimental
A mixture of 3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-3-oxopropanenitrile 1 (1 mmol), 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-(thiophen-2-yl)butane-1,3-dione 2 (1 mmol) and 2-bromo benzaldehyde 3 (1 mmol) in the presence of ammonium acetate (400 mmol) under solvent-free condition was heated at 110 °C for 7 h. After completion of the reaction (TLC), the reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with dichloromethane. After removal of the solvent, the residue was chromatographed over silica gel (230–400 mesh) using petroleum ether-ethyl acetate mixture (7:3 v/v), which afforded the pure compound. Melting point 282°C, yield: 67%.
S3. Refinement
H atoms were placed at calculated positions and allowed to ride on their carrier atoms with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å and with Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C, N) for N, CH2 and CH atoms and Uiso = 1.5Ueq(C) for CH3 atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Partial packing view of the compound showing molecules interconnected through a C—H···π stacking interaction (dotted lines; symmetry code: (i) 1/2 - x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 - z)
Crystal data
| C24H14BrN3S | F(000) = 920 |
| Mr = 456.35 | Dx = 1.532 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2000 reflections |
| a = 10.470 (5) Å | θ = 2–27° |
| b = 21.353 (5) Å | µ = 2.20 mm−1 |
| c = 9.292 (5) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 107.710 (5)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1978.9 (15) Å3 | 0.52 × 0.23 × 0.17 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer | 4305 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2837 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.041 |
| Detector resolution: 0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −12→13 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | k = −27→27 |
| Tmin = 0.958, Tmax = 0.986 | l = −11→11 |
| 17079 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.121 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0618P)2 + 0.4334P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4305 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 262 parameters | Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.2640 (3) | 0.50193 (12) | 0.7417 (3) | 0.0386 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.3077 (3) | 0.44165 (13) | 0.7289 (3) | 0.0425 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.3543 | 0.4194 | 0.8149 | 0.051* | |
| C3 | 0.2818 (3) | 0.41458 (12) | 0.5880 (3) | 0.0390 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.2078 (3) | 0.45002 (12) | 0.4630 (3) | 0.0368 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.1664 (3) | 0.51133 (12) | 0.4822 (3) | 0.0371 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.2890 (3) | 0.53182 (14) | 0.8898 (3) | 0.0432 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.3376 (3) | 0.50426 (15) | 1.0315 (3) | 0.0481 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.3625 | 0.4624 | 1.0484 | 0.058* | |
| C13 | 0.3439 (4) | 0.54874 (19) | 1.1471 (3) | 0.0622 (9) | |
| H13 | 0.3745 | 0.5393 | 1.2496 | 0.075* | |
| C14 | 0.3011 (4) | 0.60608 (18) | 1.0930 (4) | 0.0651 (10) | |
| H14 | 0.2995 | 0.6405 | 1.1538 | 0.078* | |
| C31 | 0.3330 (3) | 0.35097 (13) | 0.5742 (3) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| C32 | 0.2810 (4) | 0.30034 (14) | 0.6331 (3) | 0.0555 (8) | |
| H32 | 0.2108 | 0.3068 | 0.6733 | 0.067* | |
| C33 | 0.3322 (4) | 0.24105 (16) | 0.6326 (4) | 0.0697 (11) | |
| H33 | 0.2958 | 0.2078 | 0.6716 | 0.084* | |
| C34 | 0.4351 (5) | 0.23060 (17) | 0.5759 (4) | 0.0736 (11) | |
| H34 | 0.4695 | 0.1904 | 0.5774 | 0.088* | |
| C35 | 0.4892 (4) | 0.27918 (16) | 0.5159 (4) | 0.0650 (10) | |
| H35 | 0.5597 | 0.2721 | 0.4766 | 0.078* | |
| C36 | 0.4366 (3) | 0.33884 (13) | 0.5151 (3) | 0.0466 (7) | |
| C41 | 0.1792 (3) | 0.42163 (13) | 0.3172 (3) | 0.0451 (7) | |
| C51 | 0.0943 (3) | 0.55225 (13) | 0.3593 (3) | 0.0380 (6) | |
| C52 | 0.0877 (3) | 0.61968 (13) | 0.3648 (3) | 0.0404 (7) | |
| C53 | 0.1419 (3) | 0.66595 (14) | 0.4726 (3) | 0.0497 (8) | |
| H53 | 0.1932 | 0.6550 | 0.5699 | 0.060* | |
| C54 | 0.1186 (4) | 0.72736 (15) | 0.4329 (4) | 0.0614 (9) | |
| H54 | 0.1561 | 0.7581 | 0.5041 | 0.074* | |
| C55 | 0.0405 (4) | 0.74537 (17) | 0.2892 (4) | 0.0657 (10) | |
| H55 | 0.0253 | 0.7877 | 0.2669 | 0.079* | |
| C56 | −0.0136 (4) | 0.70208 (16) | 0.1814 (4) | 0.0581 (9) | |
| H56 | −0.0650 | 0.7140 | 0.0849 | 0.070* | |
| C57 | 0.0104 (3) | 0.63913 (14) | 0.2198 (3) | 0.0451 (7) | |
| C58 | 0.0214 (3) | 0.53562 (14) | 0.2152 (3) | 0.0452 (7) | |
| H58 | 0.0082 | 0.4948 | 0.1791 | 0.054* | |
| N1 | 0.1961 (2) | 0.53636 (10) | 0.6215 (2) | 0.0386 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.1568 (3) | 0.39821 (12) | 0.2015 (3) | 0.0630 (8) | |
| N3 | −0.0283 (3) | 0.58711 (12) | 0.1335 (3) | 0.0500 (7) | |
| H3 | −0.0773 | 0.5870 | 0.0405 | 0.060* | |
| S | 0.25060 (12) | 0.60852 (4) | 0.90204 (10) | 0.0706 (3) | |
| Br | 0.51614 (4) | 0.404354 (16) | 0.43368 (4) | 0.06285 (16) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0378 (18) | 0.0460 (16) | 0.0330 (14) | −0.0027 (13) | 0.0123 (13) | 0.0018 (13) |
| C2 | 0.049 (2) | 0.0473 (17) | 0.0288 (14) | 0.0025 (14) | 0.0084 (13) | 0.0054 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0397 (18) | 0.0415 (15) | 0.0365 (15) | −0.0016 (13) | 0.0128 (13) | 0.0067 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0403 (18) | 0.0393 (14) | 0.0298 (14) | −0.0037 (13) | 0.0094 (12) | 0.0000 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0362 (17) | 0.0420 (15) | 0.0330 (14) | −0.0041 (13) | 0.0103 (12) | 0.0019 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0382 (18) | 0.0517 (17) | 0.0380 (16) | −0.0058 (14) | 0.0093 (13) | −0.0024 (13) |
| C12 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0600 (18) | 0.0271 (14) | −0.0014 (15) | 0.0083 (14) | −0.0045 (14) |
| C13 | 0.059 (2) | 0.088 (3) | 0.0347 (17) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0078 (16) | −0.0043 (17) |
| C14 | 0.076 (3) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0419 (18) | −0.001 (2) | 0.0139 (18) | −0.0232 (17) |
| C31 | 0.0467 (19) | 0.0402 (15) | 0.0285 (14) | 0.0000 (13) | 0.0038 (13) | 0.0009 (12) |
| C32 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.0537 (19) | −0.0032 (16) | 0.0163 (17) | 0.0094 (15) |
| C33 | 0.087 (3) | 0.0421 (19) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0048 (19) | 0.012 (2) | 0.0172 (17) |
| C34 | 0.086 (3) | 0.046 (2) | 0.080 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.0019 (18) |
| C35 | 0.070 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0158 (18) | 0.0176 (19) | −0.0031 (18) |
| C36 | 0.051 (2) | 0.0464 (17) | 0.0392 (16) | −0.0005 (15) | 0.0082 (15) | 0.0002 (13) |
| C41 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0375 (15) | 0.0383 (17) | 0.0044 (14) | 0.0051 (14) | 0.0058 (14) |
| C51 | 0.0384 (18) | 0.0446 (15) | 0.0318 (14) | −0.0001 (13) | 0.0119 (13) | 0.0035 (12) |
| C52 | 0.0407 (18) | 0.0457 (15) | 0.0389 (16) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0182 (14) | 0.0090 (13) |
| C53 | 0.056 (2) | 0.0463 (17) | 0.0477 (18) | 0.0001 (15) | 0.0179 (16) | 0.0005 (14) |
| C54 | 0.072 (3) | 0.0451 (18) | 0.073 (2) | −0.0003 (17) | 0.031 (2) | 0.0008 (17) |
| C55 | 0.076 (3) | 0.0490 (19) | 0.078 (3) | 0.0099 (18) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0204 (19) |
| C56 | 0.057 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0113 (18) | 0.0199 (17) | 0.0262 (18) |
| C57 | 0.0436 (19) | 0.0540 (18) | 0.0409 (16) | 0.0052 (15) | 0.0177 (14) | 0.0119 (14) |
| C58 | 0.045 (2) | 0.0494 (17) | 0.0402 (16) | 0.0037 (14) | 0.0111 (14) | 0.0024 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0424 (15) | 0.0416 (13) | 0.0316 (12) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0107 (11) | 0.0006 (10) |
| N2 | 0.089 (2) | 0.0508 (16) | 0.0405 (15) | 0.0127 (14) | 0.0065 (15) | −0.0049 (12) |
| N3 | 0.0488 (18) | 0.0617 (17) | 0.0330 (13) | 0.0058 (13) | 0.0024 (12) | 0.0085 (12) |
| S | 0.0982 (9) | 0.0602 (5) | 0.0497 (5) | 0.0089 (5) | 0.0167 (5) | −0.0073 (4) |
| Br | 0.0616 (3) | 0.0661 (3) | 0.0687 (3) | −0.00767 (17) | 0.0314 (2) | 0.00167 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.345 (3) | C33—H33 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (4) | C34—C35 | 1.378 (5) |
| C1—C11 | 1.466 (4) | C34—H34 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.380 (4) | C35—C36 | 1.387 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C35—H35 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.405 (4) | C36—Br | 1.899 (3) |
| C3—C31 | 1.480 (4) | C41—N2 | 1.143 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.408 (4) | C51—C58 | 1.371 (4) |
| C4—C41 | 1.431 (4) | C51—C52 | 1.443 (4) |
| C5—N1 | 1.346 (3) | C52—C53 | 1.399 (4) |
| C5—C51 | 1.454 (4) | C52—C57 | 1.407 (4) |
| C11—C12 | 1.390 (4) | C53—C54 | 1.364 (4) |
| C11—S | 1.698 (3) | C53—H53 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.420 (4) | C54—C55 | 1.391 (5) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C54—H54 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.347 (5) | C55—C56 | 1.354 (5) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C55—H55 | 0.9300 |
| C14—S | 1.691 (4) | C56—C57 | 1.394 (4) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9300 | C56—H56 | 0.9300 |
| C31—C36 | 1.381 (4) | C57—N3 | 1.358 (4) |
| C31—C32 | 1.395 (4) | C58—N3 | 1.347 (4) |
| C32—C33 | 1.376 (5) | C58—H58 | 0.9300 |
| C32—H32 | 0.9300 | N3—H3 | 0.8600 |
| C33—C34 | 1.354 (6) | ||
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.8 (2) | C35—C34—H34 | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—C11 | 116.1 (2) | C34—C35—C36 | 118.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—C11 | 121.1 (2) | C34—C35—H35 | 120.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.8 (3) | C36—C35—H35 | 120.6 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C31—C36—C35 | 121.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C31—C36—Br | 120.9 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.3 (3) | C35—C36—Br | 117.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C31 | 119.7 (2) | N2—C41—C4 | 179.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—C31 | 123.1 (2) | C58—C51—C52 | 105.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.6 (2) | C58—C51—C5 | 127.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C41 | 117.3 (2) | C52—C51—C5 | 126.2 (2) |
| C5—C4—C41 | 122.0 (2) | C53—C52—C57 | 117.9 (3) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 120.1 (2) | C53—C52—C51 | 135.8 (3) |
| N1—C5—C51 | 115.4 (2) | C57—C52—C51 | 106.3 (2) |
| C4—C5—C51 | 124.5 (2) | C54—C53—C52 | 119.0 (3) |
| C12—C11—C1 | 127.9 (3) | C54—C53—H53 | 120.5 |
| C12—C11—S | 111.8 (2) | C52—C53—H53 | 120.5 |
| C1—C11—S | 120.3 (2) | C53—C54—C55 | 122.0 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 110.6 (3) | C53—C54—H54 | 119.0 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 124.7 | C55—C54—H54 | 119.0 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 124.7 | C56—C55—C54 | 120.9 (3) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 113.1 (3) | C56—C55—H55 | 119.6 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 123.5 | C54—C55—H55 | 119.6 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 123.5 | C55—C56—C57 | 117.8 (3) |
| C13—C14—S | 112.5 (3) | C55—C56—H56 | 121.1 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 123.8 | C57—C56—H56 | 121.1 |
| S—C14—H14 | 123.8 | N3—C57—C56 | 129.7 (3) |
| C36—C31—C32 | 117.3 (3) | N3—C57—C52 | 107.8 (3) |
| C36—C31—C3 | 123.8 (3) | C56—C57—C52 | 122.4 (3) |
| C32—C31—C3 | 118.8 (3) | N3—C58—C51 | 110.1 (3) |
| C33—C32—C31 | 120.8 (3) | N3—C58—H58 | 124.9 |
| C33—C32—H32 | 119.6 | C51—C58—H58 | 124.9 |
| C31—C32—H32 | 119.6 | C1—N1—C5 | 119.4 (2) |
| C34—C33—C32 | 120.7 (3) | C58—N3—C57 | 109.9 (3) |
| C34—C33—H33 | 119.7 | C58—N3—H3 | 125.1 |
| C32—C33—H33 | 119.7 | C57—N3—H3 | 125.1 |
| C33—C34—C35 | 120.5 (3) | C14—S—C11 | 92.04 (16) |
| C33—C34—H34 | 119.8 | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (5) | C34—C35—C36—C31 | 0.8 (5) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | 179.6 (3) | C34—C35—C36—Br | 179.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.7 (4) | N1—C5—C51—C58 | −161.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C31 | 177.8 (3) | C4—C5—C51—C58 | 20.3 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.1 (4) | N1—C5—C51—C52 | 20.1 (4) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | −177.3 (3) | C4—C5—C51—C52 | −158.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C41 | −179.0 (3) | C58—C51—C52—C53 | −177.4 (3) |
| C31—C3—C4—C41 | 1.6 (4) | C5—C51—C52—C53 | 1.5 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −0.8 (4) | C58—C51—C52—C57 | −0.4 (3) |
| C41—C4—C5—N1 | −179.7 (3) | C5—C51—C52—C57 | 178.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C51 | 177.5 (3) | C57—C52—C53—C54 | −0.4 (4) |
| C41—C4—C5—C51 | −1.4 (4) | C51—C52—C53—C54 | 176.3 (3) |
| N1—C1—C11—C12 | 169.4 (3) | C52—C53—C54—C55 | 1.2 (5) |
| C2—C1—C11—C12 | −10.2 (5) | C53—C54—C55—C56 | −1.3 (5) |
| N1—C1—C11—S | −7.5 (4) | C54—C55—C56—C57 | 0.7 (5) |
| C2—C1—C11—S | 172.9 (2) | C55—C56—C57—N3 | −178.0 (3) |
| C1—C11—C12—C13 | −178.3 (3) | C55—C56—C57—C52 | 0.0 (5) |
| S—C11—C12—C13 | −1.2 (4) | C53—C52—C57—N3 | 178.3 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (4) | C51—C52—C57—N3 | 0.7 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—S | 0.5 (4) | C53—C52—C57—C56 | −0.2 (4) |
| C2—C3—C31—C36 | −108.6 (3) | C51—C52—C57—C56 | −177.8 (3) |
| C4—C3—C31—C36 | 70.8 (4) | C52—C51—C58—N3 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C31—C32 | 66.9 (4) | C5—C51—C58—N3 | −178.8 (3) |
| C4—C3—C31—C32 | −113.7 (3) | C2—C1—N1—C5 | 1.3 (4) |
| C36—C31—C32—C33 | 0.4 (5) | C11—C1—N1—C5 | −178.3 (2) |
| C3—C31—C32—C33 | −175.3 (3) | C4—C5—N1—C1 | −0.9 (4) |
| C31—C32—C33—C34 | 0.5 (5) | C51—C5—N1—C1 | −179.3 (2) |
| C32—C33—C34—C35 | −0.8 (6) | C51—C58—N3—C57 | 0.4 (4) |
| C33—C34—C35—C36 | 0.2 (6) | C56—C57—N3—C58 | 177.6 (3) |
| C32—C31—C36—C35 | −1.1 (4) | C52—C57—N3—C58 | −0.6 (4) |
| C3—C31—C36—C35 | 174.4 (3) | C13—C14—S—C11 | −1.0 (3) |
| C32—C31—C36—Br | −179.4 (2) | C12—C11—S—C14 | 1.3 (3) |
| C3—C31—C36—Br | −3.9 (4) | C1—C11—S—C14 | 178.6 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the benzene ring of the indole moiety.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C53—H53···N1 | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.069 (4) | 114 |
| C58—H58···N2 | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.278 (4) | 135 |
| N3—H3···N2i | 0.86 | 2.17 | 3.008 (4) | 165 |
| C32—H32···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.761 (4) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7260).
References
- Brandt, W., Mologni, L., Preu, L., Lemcke, T., Gambacorti-Passerini, C. & Kunick, C. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 2919–2927. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- El-Sayed, H. A., Moustafa, A. H., Haikal, A. E.-F. Z., Abu-El-Halawa, R. & Ashry, E. S. H. E. (2011). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 2948–2954. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ji, J., Bunnelle, W. H., Anderson, D. J., Faltynek, C., Dyhring, T., Ahring, P. K., Rueter, L. E., Curzon, P., Buckley, M. J., Marsh, K. C., Kempf-Grote, A. & Meyer, M. D. (2007). Biochem. Pharmacol. 74, 1253–1262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-R., Rhee, S.-D., Kim, H. Y., Jung, W. H., Yang, S.-D., Kim, S. S., Ahn, J. H. & Cheon, H. G. (2005). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 518, 63–70. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS, University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260fig1.tif
The molecular structure of compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
x y z . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814017188/hb7260fig2.tif
Partial packing view of the compound showing molecules interconnected through a C—H⋯π stacking interaction (dotted lines; symmetry code: (i)  − x,
− x,  + y,
+ y,  − z)
− z)
CCDC reference: 1015962
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report