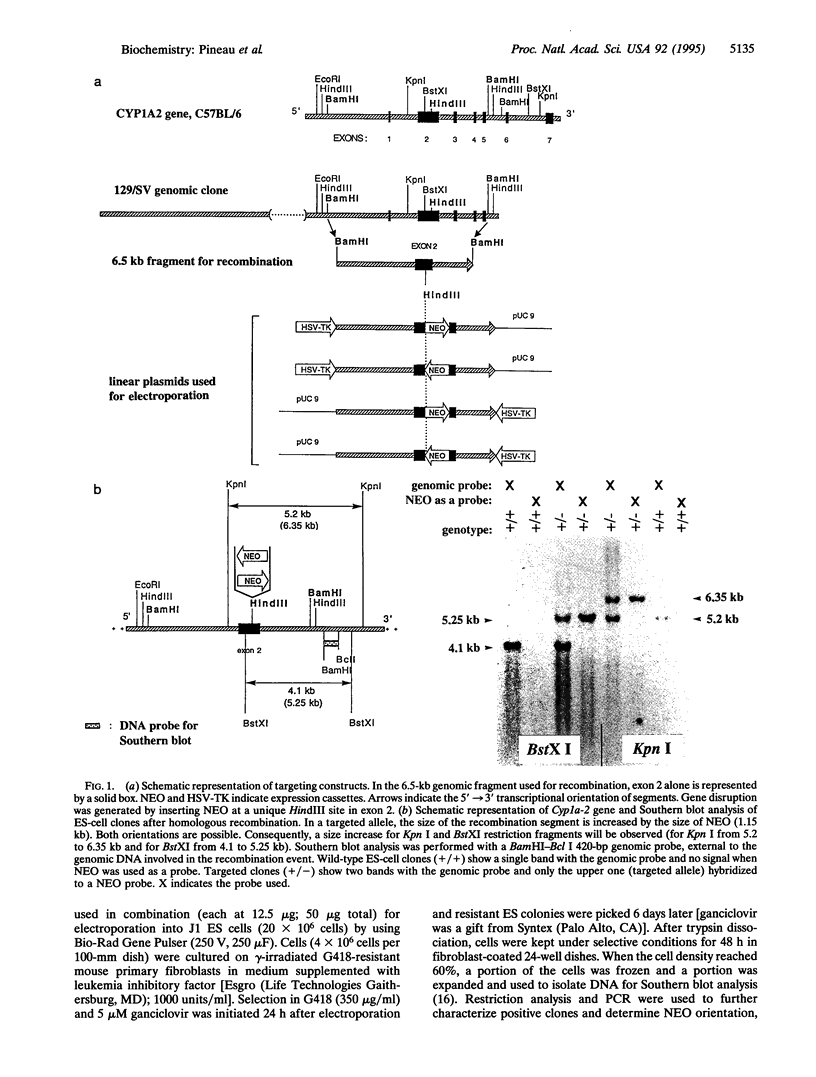
Abstract
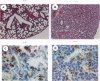
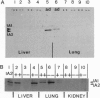
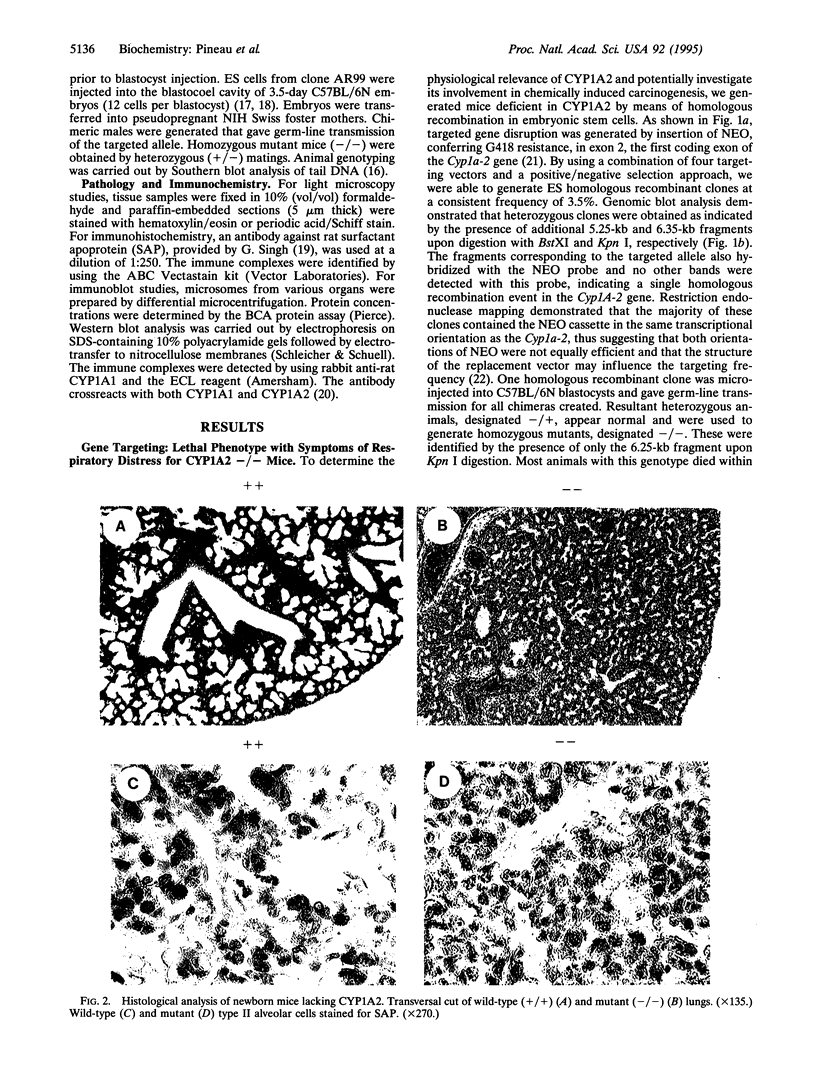
Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) is a constitutively expressed hepatic enzyme that is highly conserved among mammals. This protein is primarily involved in oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics and is capable of metabolically activating numerous procarcinogens including aflatoxin B1, arylamines, heterocyclic amine food mutagens, and polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons. Expression of CYP1A2 is induced after exposure to certain aromatic hydrocarbons (i.e., 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin). Direct evidence for a role of CYP1A2 in any physiological or developmental pathway has not been documented. We now demonstrate that mice homozygous for a targeted mutation in the Cyp1a-2 gene are nonviable. Lethality occurs shortly after birth with symptoms of severe respiratory distress. Mutant neonates display impaired respiratory function associated with histological signs of lung immaturity, lack of air in alveoli at birth, and changes in expression of surfactant apoprotein in alveolar type II cells. The penetrance of the phenotype is not complete (19 mutants survived to adulthood out of 599 mice). Surviving animals, although lacking expression of CYP1A2, appear to be normal and are able to reproduce. These findings establish that CYP1A2 is critical for neonatal survival by influencing the physiology of respiration in neonates, thus offering etiological insights for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Gonzalez F. J., Gelboin H. V. Mutagen activation by cDNA-expressed P(1)450, P(3)450, and P450a. Mol Carcinog. 1989;1(4):253–259. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama T., Korzekwa K., Nagata K., Gillette J., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Estradiol metabolism by complementary deoxyribonucleic acid-expressed human cytochrome P450s. Endocrinology. 1990 Jun;126(6):3101–3106. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-6-3101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borlakoglu J. T., Scott A., Henderson C. J., Jenke H. J., Wolf C. R. Transplacental transfer of polychlorinated biphenyls induces simultaneously the expression of P450 isoenzymes and the protooncogenes c-Ha-ras and c-raf. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Apr 6;45(7):1373–1386. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90035-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon M. J., Ding X. X., Pernecky S. J., Vaz A. D. Cytochrome P450: progress and predictions. FASEB J. 1992 Jan 6;6(2):669–673. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.2.1537454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M. D., Hollingsworth D. R., Belin R. P. Impaired surfactant production in cretin lambs. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Apr;55(4):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding X., Peng H. M., Coon M. J. Cytochromes P450 NMa, NMb (2G1), and LM4 (1A2) are differentially expressed during development in rabbit olfactory mucosa and liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):1027–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S., Nebert D. W. Comparison of the flanking regions and introns of the mouse 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5040–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Evolution of the P450 gene superfamily: animal-plant 'warfare', molecular drive and human genetic differences in drug oxidation. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. The 1992 Bernard B. Brodie Award Lecture. Bioactivation and detoxication of toxic and carcinogenic chemicals. Drug Metab Dispos. 1993 Jan-Feb;21(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitulnik J., Gonzalez F. J. Marked endogenous activation of the CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 genes in the congenitally jaundiced Gunn rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):722–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. The murine Ah locus. Comparison of the complete cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 cDNA nucleotide and amino acid sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10705–10713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Tissue-specific expression of the mouse dioxin-inducible P(1)450 and P(3)450 genes: differential transcriptional activation and mRNA stability in liver and extrahepatic tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1471–1477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Casazza J. P. Identification of ethanol-inducible P-450 isozyme 3a as the acetone and acetol monooxygenase of rabbit microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13607–13612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Bestor T. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):915–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Witte D. P., Branford W. W., Aronow B. J., Weinstein M., Kaur S., Wert S., Singh G., Schreiner C. M., Whitsett J. A. Gsh-4 encodes a LIM-type homeodomain, is expressed in the developing central nervous system and is required for early postnatal survival. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2876–2885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Strobel H. W. Evolution of cytochrome P-450 proteins. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Nov;4(6):572–593. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding R. A., Pereira C. Thyroid function in respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1974 Oct;54(4):423–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Yun C. H., Yamazaki H., Gautier J. C., Beaune P. H., Guengerich F. P. Characterization of human lung microsomal cytochrome P-450 1A1 and its role in the oxidation of chemical carcinogens. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 May;41(5):856–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Katyal S. L., Ward J. M., Gottron S. A., Wong-Chong M. L., Riley E. J. Secretory proteins of the lung in rodents: immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jun;33(6):564–568. doi: 10.1177/33.6.3889141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Tremblay M. L., LaMarca M. E., Willemsen R., Stubblefield B. K., Winfield S., Zablocka B., Sidransky E., Martin B. M., Huang S. P. Animal model of Gaucher's disease from targeted disruption of the mouse glucocerebrosidase gene. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):407–410. doi: 10.1038/357407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Hasty P., Bradley A. Targeting frequency for deletion vectors in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2404–2410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]