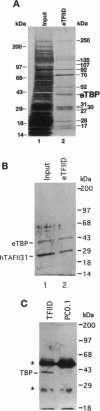
Abstract
The p53 protein activates transcription of a target gene by binding to a specific DNA response element and interacting with the transcriptional apparatus of RNA polymerase II. The amino-terminal domain of p53 interacts with a component of the TFIID basal transcription complex. The human TATA-binding-protein-associated factor TAFII31, a component of TFIID, has been identified as a critical protein required for p53-mediated transcriptional activation. TAFII31 and p53 proteins bind to each other via amino acid residues in the amino-terminal domain of p53 that are essential for transcription. Antibodies directed against TAFII31 protein inhibit p53-activated but not basal transcription in vitro. These results demonstrate that TAFII31 is a coactivator for the p53 protein.
Full text
PDF

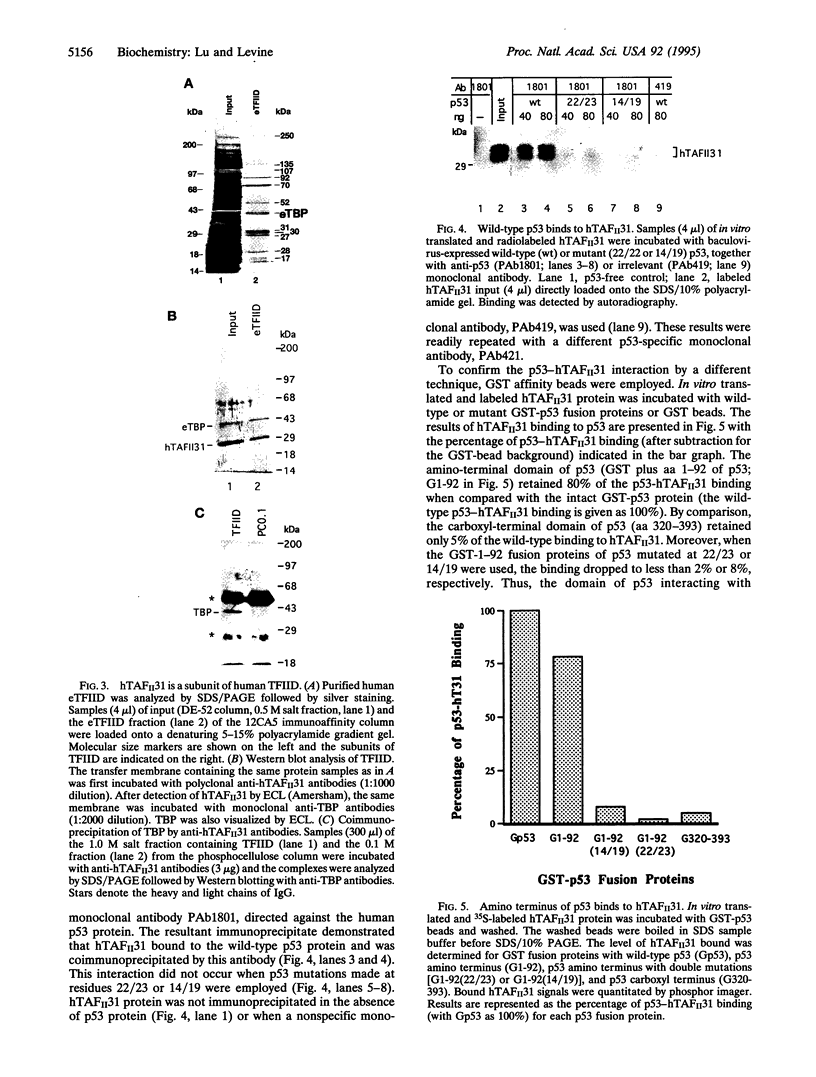
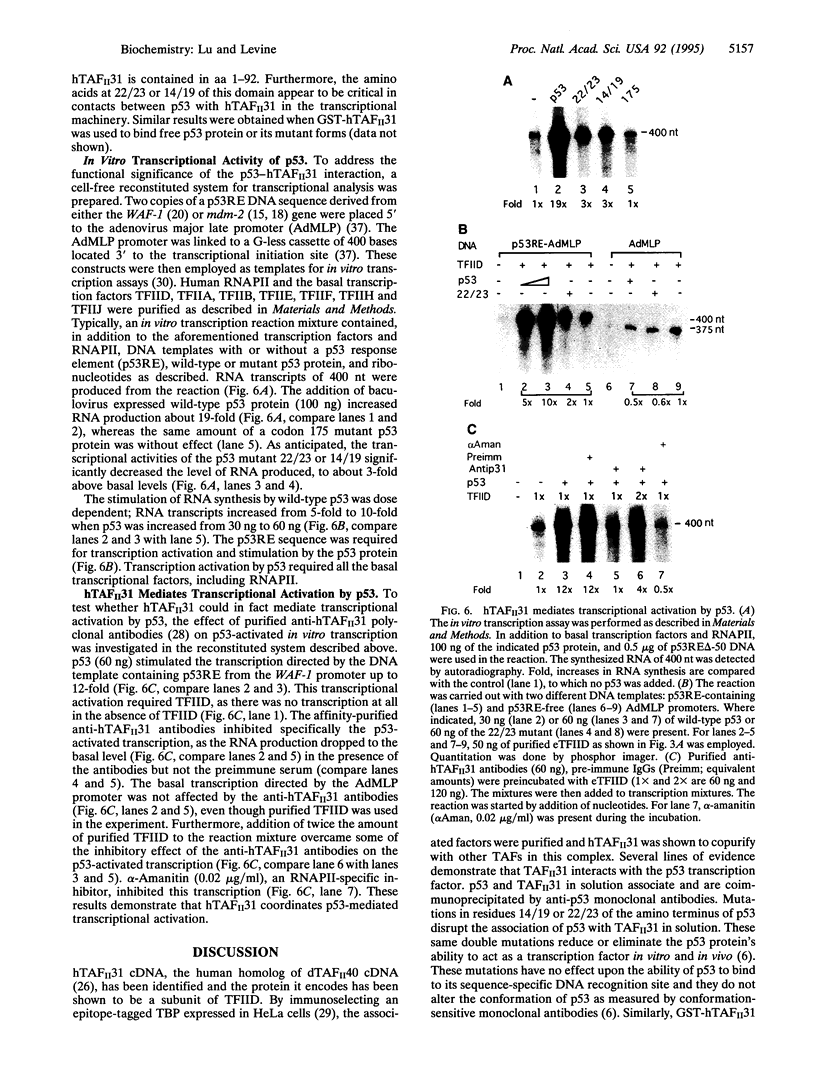

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Soares M. B., Kerlavage A. R., Fields C., Venter J. C. Rapid cDNA sequencing (expressed sequence tags) from a directionally cloned human infant brain cDNA library. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):373–380. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Manfredi J. J., Chen X., Marshak D. R., Prives C. A proteolytic fragment from the central region of p53 has marked sequence-specific DNA-binding activity when generated from wild-type but not from oncogenic mutant p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2565–2574. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Attardi L. D., Verrijzer C. P., Yokomori K., Tjian R. Assembly of recombinant TFIID reveals differential coactivator requirements for distinct transcriptional activators. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):346–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8023157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and analysis of transcription factor IIA and identification of transcription factor IIJ. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):413–421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Hoey T., Thut C. J., Admon A., Tjian R. Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. TBP-TAF complexes: selectivity factors for eukaryotic transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq X., Brou C., Lutz Y., Davidson I., Chambon P., Tora L. Human TAFII30 is present in a distinct TFIID complex and is required for transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90404-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Chang A., Dittmer D., Notterman D. A., Silver A., Thorn K., Welsh D., Wu M. The p53 tumor suppressor gene. J Lab Clin Med. 1994 Jun;123(6):817–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Chen J., Elenbaas B., Levine A. J. Several hydrophobic amino acids in the p53 amino-terminal domain are required for transcriptional activation, binding to mdm-2 and the adenovirus 5 E1B 55-kD protein. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1235–1246. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Chambers K. A., Pabo C. O. The DNA-binding domain of p53 contains the four conserved regions and the major mutation hot spots. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2556–2564. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Inostroza J., Maxon M. E., Flores O., Admon A., Reinberg D., Tjian R. Structure and functional properties of human general transcription factor IIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):369–373. doi: 10.1038/354369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Tosky M. S., Levine A. J., Rotter V. Nuclear localization is essential for the activity of p53 protein. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2055–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thut C. J., Chen J. L., Klemm R., Tjian R. p53 transcriptional activation mediated by coactivators TAFII40 and TAFII60. Science. 1995 Jan 6;267(5194):100–104. doi: 10.1126/science.7809597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Reed M., Wang P., Stenger J. E., Mayr G., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: identification and characterization of two autonomous DNA-binding regions. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2575–2586. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Lieberman P. M., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]