Capsule Summary
IL-17 and TNFα synergistically induce surface expression of IL-13Rα2 on primary lung fibroblasts, rendering them unresponsive to IL-13. Neutralizing antibodies to IL-13Rα2 restored IL-13-mediated signaling and transcriptome studies confirmed IL-13Rα2 is an IL-13 decoy receptor.
Keywords: Severe asthma, IL-13, IL-13Rα2, IL-17, inflammation
To the Editor:
IL-13 is a pleiotropic cytokine that provokes diverse pathophysiological outcomes. While its effect during gastrointestinal (GI) helminth infection is prototypic of a protective Th2 response (increased peristalsis, goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus secretion, eosinophil recruitment, fibroblast activation and wound repair), temporal or spatial dysregulation of this response is thought to underlie diseases such as asthma, allergic hyperreactivity and organ fibrosis (1). IL-13 signals via the IL-13Rα1/IL-4Rα heterodimer to induce several genes specific to Th2 inflammation including CCL26, CCL11, POSTN, and MUC5AC (2). IL-13Rα2 binds IL-13 with significantly higher affinity, and the secreted form found in mice acts as a decoy receptor, protecting mice from IL-13 induced immunopathology. However humans do not alternatively splice IL13RA2 transcript and therefore IL-13Rα2 is only expressed as a cell surface protein (3). The factors that regulate the expression of IL-13Rα2 are unclear and the biological function of the endogenously expressed IL-13Rα2 remains controversial (4, 5). In this study, we show that the inflammatory cytokines TNFα and IL-17, often associated with severe asthma, synergize to induce IL-13Rα2 in primary human lung fibroblasts and mouse lungs, and evaluate its biological role using a novel IL-13Rα2 blocking antibody.
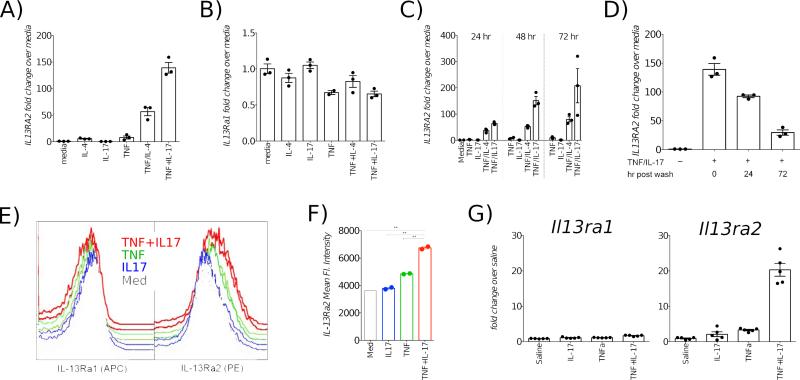
Primary human neonatal lung fibroblasts (NLF) were grown to confluence and incubated with TNFα, IL-4 and IL-17 for 72 hours, at which time cells lysates were analyzed by qPCR with primers specific for IL13RA2 (Methods in Online Repository). While TNFα and IL-4 synergistically induced IL13RA2 as described (6), a combination of TNFα and IL-17 induced higher expression (Fig 1A). In contrast, IL13RA1 decreased in the presence of TNFα (Fig 1B).
Fig 1.
TNFα and IL-17 synergistically induce IL-13Rα2. Primary NLF (A, B) were incubated with specified cytokines for 72 hr. Kinetics of IL13RA2 expression in NLF, assayed at 24, 48 or 72 hr post stimulation (C) and decay post-cytokine withdrawal (D). Flow cytometric measurement of IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2 on ALF surface post cytokine stimulation (E, F). Expression of Il13ra1 and Il13ra2 transcripts in mouse lungs following TNFα and IL-17 administration (G).
IL-13Rα2 mRNA progressively increased over time, peaking at 72 hours (Fig 1C) and longer incubations did not consistently result in any further increase (data not shown); therefore, 72 hrs was chosen as the ideal endpoint for subsequent experiments. To determine whether IL-13Rα2 expression was sustainable, NLF were incubated with a combination of TNF/IL-17 for 72 hours, after which the supernatants were removed and the wells rinsed and replenished with fresh media without added cytokines. Upon removal of TNFα and IL-17, IL-13Rα2 expression declined between 24 hours and 72 hours post-wash, though remained elevated (Fig 1D). We confirmed that primary lung fibroblasts derived from healthy adult donors (ALF) also manifested similar synergy to TNFα and IL-17 (Fig E1). Using flow cytometry, we verified that the transcriptional induction of IL-13Rα2 was associated with augmented surface expression of protein (Fig 1E-F). In order to ascertain if this phenomenon can be recapitulated in vivo, we administered multiple doses of the cytokines into mouse airways. IL-13Rα2 transcripts were strikingly higher in the lungs of mice that received both TNF and IL-17, while IL-13Rα1 message changed negligibly (Fig 1G).
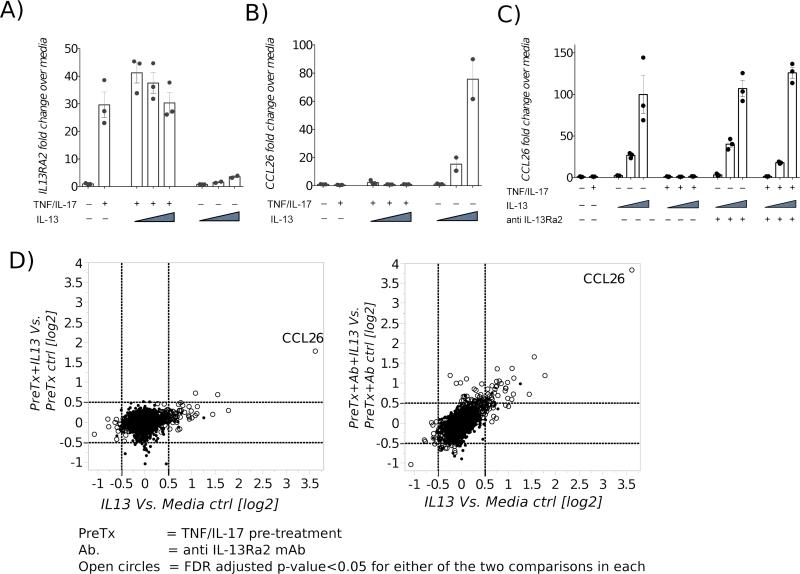
Next, we examined whether TNF/IL-17-induced expression of IL-13Rα2 was capable of altering the biological effects of IL-13. NLFs were incubated with TNF/IL-17 for 72 hours to upregulate IL-13Rα2. Subsequently, the wells were washed with media, and treated with IL-13 in increasing concentrations for 24 hours. Cellular RNA was assayed by real time quantitative PCR for CCL26 (eotaxin-3) expression, as a marker for the canonical IL-13 signaling through IL-13Rα1. Whereas the expression of CCL26 increased in a dose-dependent fashion upon IL-13 stimulation in control wells where IL-13Rα2 was at baseline levels, CCL26 expression was abrogated in conditions where IL-13Rα2 expression was augmented (Fig 2A-B). Similar data were obtained with ALF (Fig E2).
Fig 2.
NLF were treated with TNFα and IL-17 for 72 hr, washed and then treated with IL-13 in increasing concentrations (0.1 to 2.5 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Increased IL13RA2 induction is associated with loss of IL-13 induced CCL26 production (A-B). Recovery of IL-13 induced CCL26 expression by blocking IL-13Rα2 with mAb (C). Pairwise analyses of transcriptome signature of NLF treated with IL-13 ± TNF/IL-17 pretreatment (PreTx), ± anti-IL-13Rα2 mAb (D). Also refer to E Fig 3.
While inhibition of IL-13 activity in the setting of increased IL-13Rα2 was likely due to the IL-13Rα2 receptor functioning as a decoy, a number of other alternative explanations, such as concomitant down-regulation of IL-13Rα1 or dampening of intracellular signaling networks could have also led to the attenuation of IL-13 bioactivity following TNF/IL-17 treatment. To investigate these possibilities, NLF were first incubated with TNF/IL-17 to induce high IL-13Rα2 expression and prior to the addition of IL-13, some wells were treated with a highly selective neutralizing anti-human IL-13Rα2 monoclonal antibody. Subsequently, wells were treated with IL-13 in increasing concentrations for 24 hours and CCL26 expression was assayed by qPCR. As before, in wells expressing basal levels of IL-13Rα2, CCL26 was induced in a dose-dependent fashion following IL-13 stimulation. In wells were IL-13Rα2 was induced with TNF/IL-17, CCL26 expression was suppressed. However, in wells treated with anti-IL-13Rα2 antibody, addition of IL-13 resulted in restoration of CCL26 expression in a dose-dependent fashion, confirming that the diminution of IL-13 activity by TNF/IL-17 was due to increased expression of IL-13Rα2 (Fig 2C).
While the above results confirm potent decoy activity for IL-13Rα2 (7), they fail to explore its signaling activity, which has been proposed in some studies (5). To uncover possible signaling potential for this ligand-receptor pair in fibroblasts, we performed a transcriptome-wide microarray analysis, in which the effect of IL-13 stimulation in NLF with or without TNF/IL17 pretreatment, in the presence or absence of the anti-IL-13Rα2 mAb were compared. With this approach, the effects of IL-13 signaling through IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2 could be distinguished. CCL26 was the most abundant IL-13 induced transcript in this genome-wide screen, upregulated 12.3-fold (i.e. 23.6, q-value=6×10−8) over baseline (Fig 2D and E3). Upon TNF/IL17 pretreatment, this diminished to 3.2-fold (21.7), in accord with the above-described IL-13Rα2 mediated inhibition. Surprisingly however, while IL-13 binding to IL-13Rα2 reduced the transcript abundance of CCL26, it did not result in any additional statistically significant changes in the transcriptome profile of fibroblasts (Fig 2D and E3) that were distinguishable from the pretreatment controls . Blocking IL-13Rα2 with the Ab restored IL-13-induced CCL26 expression (Fig 2D and E3). These data indicate that in NLF, IL-13 binding to the high affinity IL-13Rα2 serves to dampen canonical IL-13 signaling, as opposed to inducing other signaling pathways.
Asthma syndrome is a heterogeneous mixture of distinct phenotypic subtypes and only cohorts that have a ‘IL-13 high’ signature, are indeed likely to benefit from therapeutic modalities that block IL-13/IL-13Rα1 interactions (8). Steroid-resistant and severe asthma subtypes are often associated with neutrophilia, TNFα and IL-17 activity (9) and therefore may not benefit from blockade of IL-13, and perhaps the mechanisms we describe above already operate in these patients to quench endogenous IL-13 activity via IL-13Rα2. Indeed, due caution must be exercised, as blocking IL-13/IL-13Rα1 interactions in these patients might actually lead to disease aggravation, as IL-13 has been shown to down modulate inflammation induced by TNFα and IL-17 (10).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Wynn lab members for helpful suggestions.
Declaration of all sources of funding: The study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. T.O. is an employee of Johnson and Johnson. LAB is funded by a European Union FP7 Marie Curie fellowship.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Other authors have no relevant financial relationships to declare.
References
- 1.Wynn TA. IL-13 effector functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:425–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ramalingam TR, Pesce JT, Sheikh F, Cheever AW, Mentink-Kane MM, Wilson MS, et al. Unique functions of the type II interleukin 4 receptor identified in mice lacking the interleukin 13 receptor alpha1 chain. Nature immunology. 2008 Jan;9(1):25–33. doi: 10.1038/ni1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tabata Y, Khurana Hershey GK. IL-13 receptor isoforms: breaking through the complexity. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007 Sep;7(5):338–45. doi: 10.1007/s11882-007-0051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O'Toole M, Legault H, Ramsey R, Wynn TA, Kasaian MT. A novel and sensitive ELISA reveals that the soluble form of IL-13R-alpha2 is not expressed in plasma of healthy or asthmatic subjects. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2008 Apr;38(4):594–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K, Puri RK, Kitani A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006 Jan;12(1):99–106. doi: 10.1038/nm1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yoshikawa M, Nakajima T, Tsukidate T, Matsumoto K, Iida M, Otori N, et al. TNF-alpha and IL-4 regulate expression of IL-13 receptor alpha2 on human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Dec 26;312(4):1248–55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Campbell-Harding G, Sawkins H, Bedke N, Holgate ST, Davies DE, Andrews AL. The innate antiviral response upregulates IL-13 receptor alpha2 in bronchial fibroblasts. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2013 Mar;131(3):849–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.08.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Corren J, Lemanske RF, Hanania NA, Korenblat PE, Parsey MV, Arron JR, et al. Lebrikizumab treatment in adults with asthma. The New England journal of medicine. 2011 Sep 22;365(12):1088–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1106469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seys SF, Grabowski M, Adriaensen W, Decraene A, Dilissen E, Vanoirbeek JA, et al. Sputum cytokine mapping reveals an ‘IL-5, IL-17A, IL-25-high’ pattern associated with poorly controlled asthma. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2013 Sep;43(9):1009–17. doi: 10.1111/cea.12125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Newcomb DC, Boswell MG, Zhou W, Huckabee MM, Goleniewska K, Sevin CM, et al. Human TH17 cells express a functional IL-13 receptor and IL-13 attenuates IL-17A production. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2011 Apr;127(4):1006–13. e1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]