Abstract
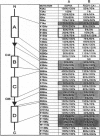
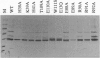
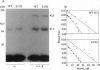
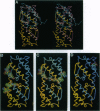
A detailed structure-function analysis of human interleukin 5 (hIL5) has been performed. The hIL5 receptor is composed of two different polypeptide chains, the alpha and beta subunits. The alpha subunit alone is sufficient for ligand binding, but association with the beta subunit leads to a 2- to 3-fold increase in binding affinity. The beta chain is shared with the receptors for IL3 and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor--hence the descriptor beta C (C for common). All hIL5 mutants were analyzed in a solid-phase binding assay for hIL5R alpha interaction and in a proliferation assay using IL5-dependent cell lines for receptor-complex activation. Most residues affecting binding to the receptor alpha subunit were clustered in a loop connecting beta-strand 1 and helix B (mutants H38A, K39A, and H41A), in beta-strand 2 (E89A and R91A; weaker effect for E90A) and close to the C terminus (T109A, E110A, W111S, and I112A). Mutations at one position, E13 (Glu13), caused a reduced activation of the hIL5 receptor complex. In the case of E13Q, only 0.05% bioactivity was detected on a hIL5-responsive subclone of the mouse promyelocytic cell line FDC-P1. Moreover, on hIL5-responsive TF1 cells, the same mutant was completely inactive and proved to have antagonistic properties. Interactions of this mutant with both receptor subunits were nevertheless indistinguishable from those of nonmutated hIL5 by crosslinking and Scatchard plot analysis of transfected COS-1 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma C., Tanabe T., Konishi M., Kinashi T., Noma T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y., Takatsu K., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Cloning of cDNA for human T-cell replacing factor (interleukin-5) and comparison with the murine homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9149–9158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., D'Arcy A., Janes W., Gentz R., Schoenfeld H. J., Broger C., Loetscher H., Lesslauer W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):431–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90132-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budel L. M., Hoogerbrugge H., Pouwels K., van Buitenen C., Delwel R., Löwenberg B., Touw I. P. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptors alter their binding characteristics during myeloid maturation through up-regulation of the affinity converting beta subunit (KH97). J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10154–10159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Ultsch M., De Vos A. M., Mulkerrin M. G., Clauser K. R., Wells J. A. Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):821–825. doi: 10.1126/science.1948064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Guisez Y., Cornelis S., Verhee A., Van der Heyden J., Manneberg M., Lahm H. W., Fiers W., Tavernier J., Plaetinck G. Recombinant soluble human interleukin-5 (hIL-5) receptor molecules. Cross-linking and stoichiometry of binding to IL-5. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6581–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Cornelis S., Vandekerckhove J., Fiers W., Tavernier J. Molecular basis of a high affinity murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2133–2137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Vandekerckhove J., Rolink A., Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W., Tavernier J. Amino acid sequence analysis of a mouse interleukin 5 receptor protein reveals homology with a mouse interleukin 3 receptor protein. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1315–1317. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guisez Y., Oefner C., Winkler F. K., Schlaeger E. J., Zulauf M., Van der Heyden J., Plaetinck G., Cornelis S., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Expression, purification and crystallization of fully active, glycosylated human interleukin-5. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Sato N., Arai K., Miyajima A. Expression cloning of the human IL-3 receptor cDNA reveals a shared beta subunit for the human IL-3 and GM-CSF receptors. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1165–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Tange T., Terasawa T., Chiba S., Kuwaki T., Miyagawa K., Piao Y. F., Miyazono K., Urabe A., Takaku F. Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):323–334. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama S., Tsuruoka N., Tsujimoto M. Role of the C-terminus in the biological activity of human interleukin 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):514–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90137-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Eglinton J. M., Gillis D., Park L. S., Clark S., Vadas M. A. Reciprocal inhibition of binding between interleukin 3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to human eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7022–7026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Shannon M. F., Barry S., Phillips J. A., Cambareri B., Dottore M., Simmons P., Vadas M. A. A human interleukin 3 analog with increased biological and binding activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11842–11846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Shannon M. F., Hercus T., Nicola N. A., Cambareri B., Dottore M., Layton M. J., Eglinton L., Vadas M. A. Residue 21 of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is critical for biological activity and for high but not low affinity binding. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):909–916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie A. N., Barry S. C., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Structure-function analysis of interleukin-5 utilizing mouse/human chimeric molecules. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Hassell A. M., Lambert M. H., Jordan S. R., Proudfoot A. E., Graber P., Wells T. N. A novel dimer configuration revealed by the crystal structure at 2.4 A resolution of human interleukin-5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):172–176. doi: 10.1038/363172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamitake Y., Kodama S., Katayama T., Adachi H., Tanaka S., Tsujimoto M. Structure of recombinant human interleukin 5 produced by Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biochem. 1990 Feb;107(2):292–297. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Takaki S., Migita M., Kikuchi Y., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interleukin 5 receptor. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):341–351. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot A. E., Fattah D., Kawashima E. H., Bernard A., Wingfield P. T. Preparation and characterization of human interleukin-5 expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):357–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2700357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco L. V., Silverman S. L., Wong S. G., Slamon D. J., Park L. S., Gasson J. C. Identification of conserved amino acids in the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor alpha subunit critical for function. Evidence for formation of a heterodimeric receptor complex prior to ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt A. B., Kastelein R. A. High affinity ligand binding is not essential for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25466–25472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt A. B., Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Kastelein R. A. The amino-terminal helix of GM-CSF and IL-5 governs high affinity binding to their receptors. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4105–4112. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Mita S., Kitamura T., Yonehara S., Yamaguchi N., Tominaga A., Miyajima A., Takatsu K. Identification of the second subunit of the murine interleukin-5 receptor: interleukin-3 receptor-like protein, AIC2B is a component of the high affinity interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2833–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Murata Y., Kitamura T., Miyajima A., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Reconstitution of the functional receptors for murine and human interleukin 5. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1523–1529. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Tominaga A., Hitoshi Y., Mita S., Sonoda E., Yamaguchi N., Takatsu K. Molecular cloning and expression of the murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4367–4374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Cornelis S., Tuypens T., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W., Plaetinck G. A human high affinity interleukin-5 receptor (IL5R) is composed of an IL5-specific alpha chain and a beta chain shared with the receptor for GM-CSF. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Hauquier G., Bauden R., Fache I., Kawashima E., Vandekerckhove J., Contreras R., Fiers W. Expression of human and murine interleukin-5 in eukaryotic systems. DNA. 1989 Sep;8(7):491–501. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Tuypens T., Plaetinck G., Verhee A., Fiers W., Devos R. Molecular basis of the membrane-anchored and two soluble isoforms of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Adachi H., Kodama S., Tsuruoka N., Yamada Y., Tanaka S., Mita S., Takatsu K. Purification and characterization of recombinant human interleukin 5 expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biochem. 1989 Jul;106(1):23–28. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuypens T., Plaetinck G., Baker E., Sutherland G., Brusselle G., Fiers W., Devos R., Tavernier J. Organization and chromosomal localization of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha-chain gene. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 Sep-Oct;3(5):451–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ostade X., Tavernier J., Prangé T., Fiers W. Localization of the active site of human tumour necrosis factor (hTNF) by mutational analysis. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):827–836. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Moreau J. F., Koo J. W., Mathey-Prevot B., D'Andrea A. D. The erythropoietin receptor transmembrane region is necessary for activation by the Friend spleen focus-forming virus gp55 glycoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2949–2957. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]