Abstract
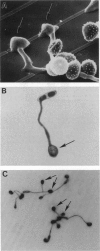
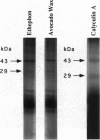
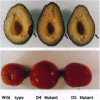
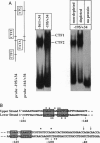
Surface signaling plays a major role in fungal infection. Topographical features of the plant surface and chemicals on the surface can trigger germination of fungal spores and differentiation of the germ tubes into appressoria. Ethylene, the fruit-ripening hormone, triggers germination of conidia, branching of hyphae, and multiple appressoria formation in Colletotrichum, thus allowing fungi to time their infection to coincide with ripening of the host. Genes uniquely expressed during appressoria formation induced by topography and surface chemicals have been isolated. Disruption of some of them has been shown to decrease virulence on the hosts. Penetration of the cuticle by the fungus is assisted by fungal cutinase secreted at the penetration structure of the fungus. Disruption of cutinase gene in Fusarium solani pisi drastically decreased its virulence. Small amounts of cutinase carried by spores of virulent pathogens, upon contact with plant surface, release small amounts of cutin monomers that trigger cutinase gene expression. The promoter elements involved in this process in F. solani pisi were identified, and transcription factors that bind these elements were cloned. One of them, cutinase transcription factor 1, expressed in Escherichia coli, is phosphorylated. Several protein kinases from F. solani pisi were cloned. The kinase involved in phosphorylation of specific transcription factors and the precise role of phosphorylation in regulating cutinase gene transcription remain to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajar A., Podila G. K., Kolattukudy P. E. Identification of a fungal cutinase promoter that is inducible by a plant signal via a phosphorylated trans-acting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8208–8212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhairi S. M., Staples R. C., Freve P., Yoder O. C. Characterization of an infection structure-specific gene from the rust fungus Uromyces appendiculatus. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biteau N., Fremaux C., Hebrard S., Menara A., Aigle M., Crouzet M. The complete sequence of a 10.8kb fragment to the right of the chromosome III centromere of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1992 Jan;8(1):61–70. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coovadia Y. M., Coovadia H. M., van den Ende J. Meningitis due to beta-lactamase producing, chloramphenicol-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type b, in South Africa. J Infect. 1986 May;12(3):247–249. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)94242-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne W. E., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. S., Cooper T. G. Expression of the DAL80 gene, whose product is homologous to the GATA factors and is a negative regulator of multiple nitrogen catabolic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is sensitive to nitrogen catabolite repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6205–6215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig A. H., Zuckerman S. H., Andonov-Roland M. M. Isolation of a Fusarium solani mutant reduced in cutinase activity and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):911–916. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.911-916.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler H. S., Jacobs T. W. Cell division in higher plants: a cdc2 gene, its 34-kDa product, and histone H1 kinase activity in pea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaishman M. A., Kolattukudy P. E. Timing of fungal invasion using host's ripening hormone as a signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6579–6583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S., Rodriguez R. J. Genetic conversion of a fungal plant pathogen to a nonpathogenic, endophytic mutualist. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5104.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. nit-2, the major positive-acting nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5331–5335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner A., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. Signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1280–1292. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Rigby M. R., Davis R. J. Heterogeneous expression of four MAP kinase isoforms in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80612-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto J., Hirabayashi T., Hayano Y., Hata S., Ohashi Y., Suzuka I., Utsugi T., Toh-e A., Kikuchi Y. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding cdc2 homologues from Oryza sativa: a functional homologue and cognate variants. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00587555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Her J. H., Wu J., Rall T. B., Sturgill T. W., Weber M. J. Sequence of pp42/MAP kinase, a serine/threonine kinase regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3743–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Páy A., Györgyey J., Bakó L., Németh K., Bögre L., Schweyen R. J., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Complementation of a yeast cell cycle mutant by an alfalfa cDNA encoding a protein kinase homologous to p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
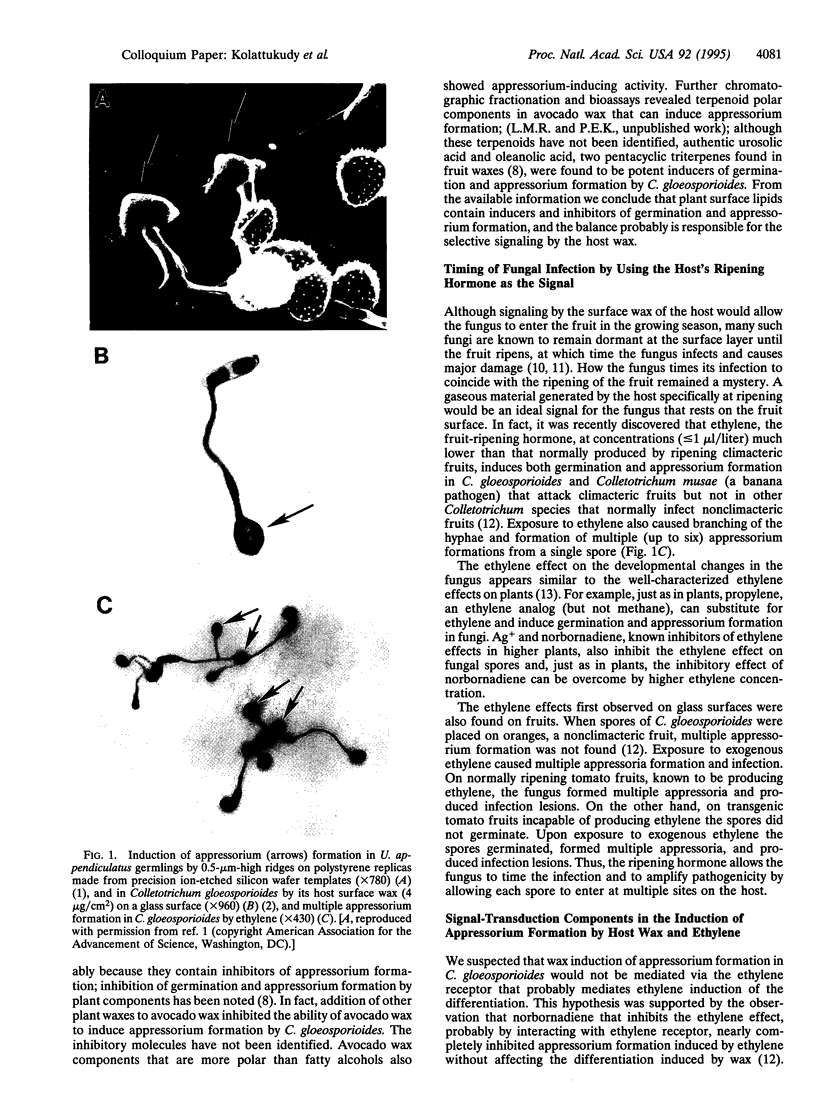
- Hoch H. C., Staples R. C., Whitehead B., Comeau J., Wolf E. D. Signaling for growth orientation and cell differentiation by surface topography in uromyces. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1659–1662. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4796.1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang C. S., Flaishman M. A., Kolattukudy P. E. Cloning of a gene expressed during appressorium formation by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and a marked decrease in virulence by disruption of this gene. Plant Cell. 1995 Feb;7(2):183–193. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara H., Martin B. L., Brautigan D. L., Karaki H., Ozaki H., Kato Y., Fusetani N., Watabe S., Hashimoto K., Uemura D. Calyculin A and okadaic acid: inhibitors of protein phosphatase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):871–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudla B., Caddick M. X., Langdon T., Martinez-Rossi N. M., Bennett C. F., Sibley S., Davies R. W., Arst H. N., Jr The regulatory gene areA mediating nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mutations affecting specificity of gene activation alter a loop residue of a putative zinc finger. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämper J. T., Kämper U., Rogers L. M., Kolattukudy P. E. Identification of regulatory elements in the cutinase promoter from Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi (Nectria haematococca). J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9195–9204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Kolattukudy P. E. Induction of a biopolyester hydrolase (cutinase) by low levels of cutin monomers in Fusarium solani f.sp. pisi. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):942–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.942-951.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiti I. B., Kolattukudy P. E. Prevention of fungal infection of plants by specific inhibition of cutinase. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):507–508. doi: 10.1126/science.205.4405.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Beach D. Homology between the ran1+ gene of fission yeast and protein kinases. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3665–3671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minehart P. L., Magasanik B. Sequence and expression of GLN3, a positive nitrogen regulatory gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoding a protein with a putative zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6216–6228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owaki H., Makar R., Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H., Geppert T. D. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases in T cells: characterization of human ERK1 and ERK2 cDNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1416–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91891-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Le Guellec R., Couturier A., Le Guellec K., Omilli F., Camonis J., MacNeill S., Philippe M. Cloning by differential screening of a Xenopus cDNA coding for a protein highly homologous to cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podila G. K., Rogers L. M., Kolattukudy P. E. Chemical Signals from Avocado Surface Wax Trigger Germination and Appressorium Formation in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Plant Physiol. 1993 Sep;103(1):267–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. E., Kolattukudy P. E. Hydrolysis of plant cuticle by plant pathogens. Properties of cutinase I, cutinase II, and a nonspecific esterase isolated from Fusarium solani pisi. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2832–2840. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. E., Kolattukudy P. E. Hydrolysis of plant cuticle by plant pathogens. Purification, amino acid composition, and molecular weight of two isozymes of cutinase and a nonspecific esterase from Fusarium solani f. pisi. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2824–2831. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz V., Fluhr R. Ethylene Signal Is Transduced via Protein Phosphorylation Events in Plants. Plant Cell. 1993 May;5(5):523–530. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.5.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers L. M., Flaishman M. A., Kolattukudy P. E. Cutinase gene disruption in Fusarium solani f sp pisi decreases its virulence on pea. Plant Cell. 1994 Jul;6(7):935–945. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.7.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaykh M., Soliday C., Kolattukudy P. E. Proof for the Production of Cutinase by Fusarium solani f. pisi during Penetration into Its Host, Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):170–172. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skala J., Purnelle B., Crouzet M., Aigle M., Goffeau A. The open reading frame YCR101 located on chromosome III from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a putative protein kinase. Yeast. 1991 Aug-Sep;7(6):651–655. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soliday C. L., Dickman M. B., Kolattukudy P. E. Structure of the cutinase gene and detection of promoter activity in the 5'-flanking region by fungal transformation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1942–1951. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1942-1951.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot N. J., Ebbole D. J., Hamer J. E. Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1575–1590. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes that confer resistance to staurosporine encode an AP-1-like transcription factor and a protein kinase related to the mammalian ERK1/MAP2 and budding yeast FUS3 and KSS1 kinases. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):60–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Boguski M. S. Structure and evolution of a human erythroid transcription factor. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):92–96. doi: 10.1038/343092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisard C., Wang J., McEvoy J. L., Xu P., Leong S. A. urbs1, a gene regulating siderophore biosynthesis in Ustilago maydis, encodes a protein similar to the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7091–7100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y. Dominant negative selection of heterologous genes: isolation of Candida albicans genes that interfere with Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating factor-induced cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9410–9414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloshuk C. P., Kolattukudy P. E. Mechanism by which contact with plant cuticle triggers cutinase gene expression in the spores of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1704–1708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Han M. Suppression of activated Let-60 ras protein defines a role of Caenorhabditis elegans Sur-1 MAP kinase in vulval differentiation. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):147–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xuei X., Bhairi S., Staples R. C., Yoder O. C. Characterization of INF56, a gene expressed during infection structure development of Uromyces appendiculatus. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90443-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xuei X., Bhairi S., Staples R. C., Yoder O. C. INF56 represents a family of differentiation-specific genes from Uromyces appendiculatus. Curr Genet. 1993 Jul-Aug;24(1-2):84–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00324669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. L., Stumpf M. A., Hoch H. C., Kung C. A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.1716786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Mather C., Burgess S., Bolce M. E., Harland R. M., Orkin S. H. Expression of GATA-binding proteins during embryonic development in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10642–10646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]