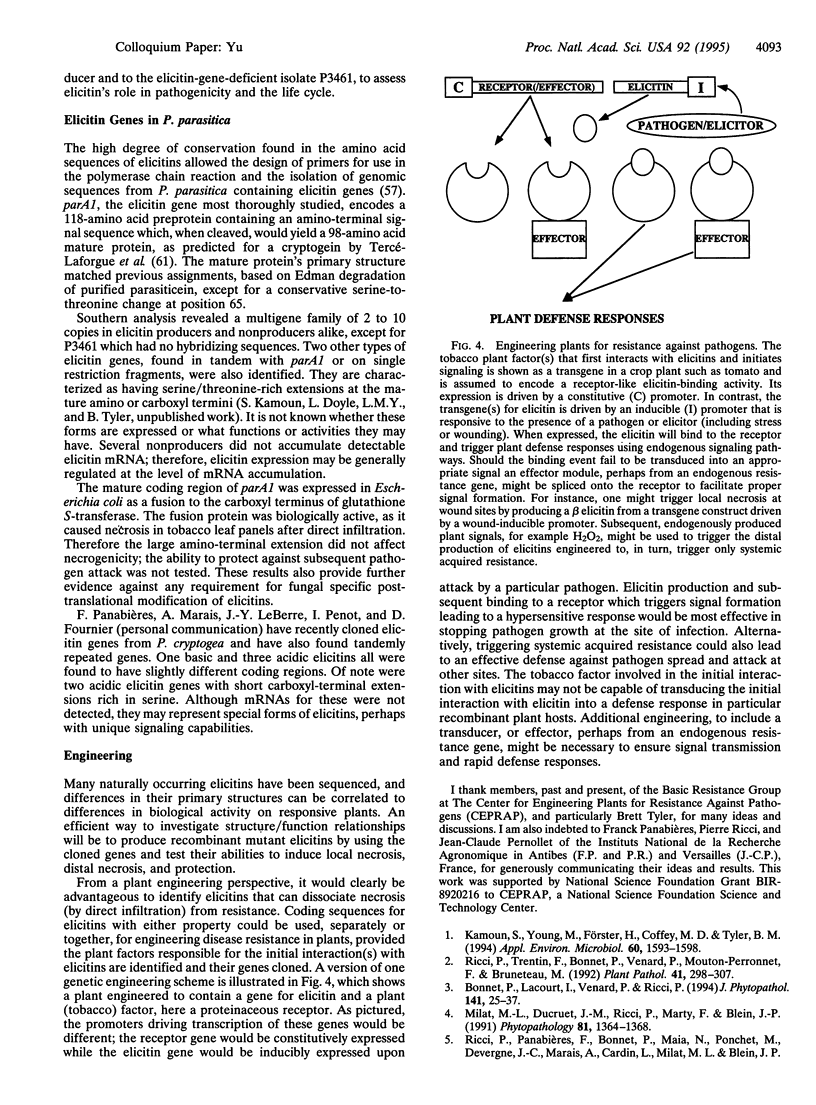
Abstract
Elicitins are a family of small proteins secreted by species of Phytophthora. They are thought to be major determinants of the resistance response of tobacco against these oomycetes, since purified elicitins, alone and at low concentrations, can induce vigorous defense responses in tobacco (i.e., hypersensitive cell death and resistance against subsequent pathogen attack), and in vitro elicitin production by Phytophthora isolates is strongly negatively correlated with their pathogenicity on tobacco plants. A number of elicitins have been purified and their amino acid sequences have been determined and found to be conserved. A three-dimensional structure for elicitin is emerging from nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Two structural classes, alpha and beta, are distinguished by their biological effects when applied to decapitated stems or petioles; the beta class causes more necrosis on leaves and provides better subsequent protection against pathogen attack. However, both these classes of elicitins will similarly cause necrosis when each is, instead, directly infiltrated into tobacco leaf panels. Effects of elicitins on tobacco cells include rapid electrolyte leakage, changes in protein phosphorylation and amounts of active oxygen species, and later production of ethylene and capsidiol. The sites of initial interaction with tobacco cells are unknown, but the interaction appears to induce general defense-related responses.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beever R. E., Dempsey G. P. Function of rodlets on the surface of fungal spores. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):608–610. doi: 10.1038/272608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Dunlap J. C., Loros J. J. The Neurospora circadian clock-controlled gene, ccg-2, is allelic to eas and encodes a fungal hydrophobin required for formation of the conidial rodlet layer. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2382–2394. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya D., Stickel S. K. Sequence analysis of duplicated actin genes in Lagenidium giganteum and Pythium irregulare (Oomycota). J Mol Evol. 1994 Jul;39(1):56–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00178249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
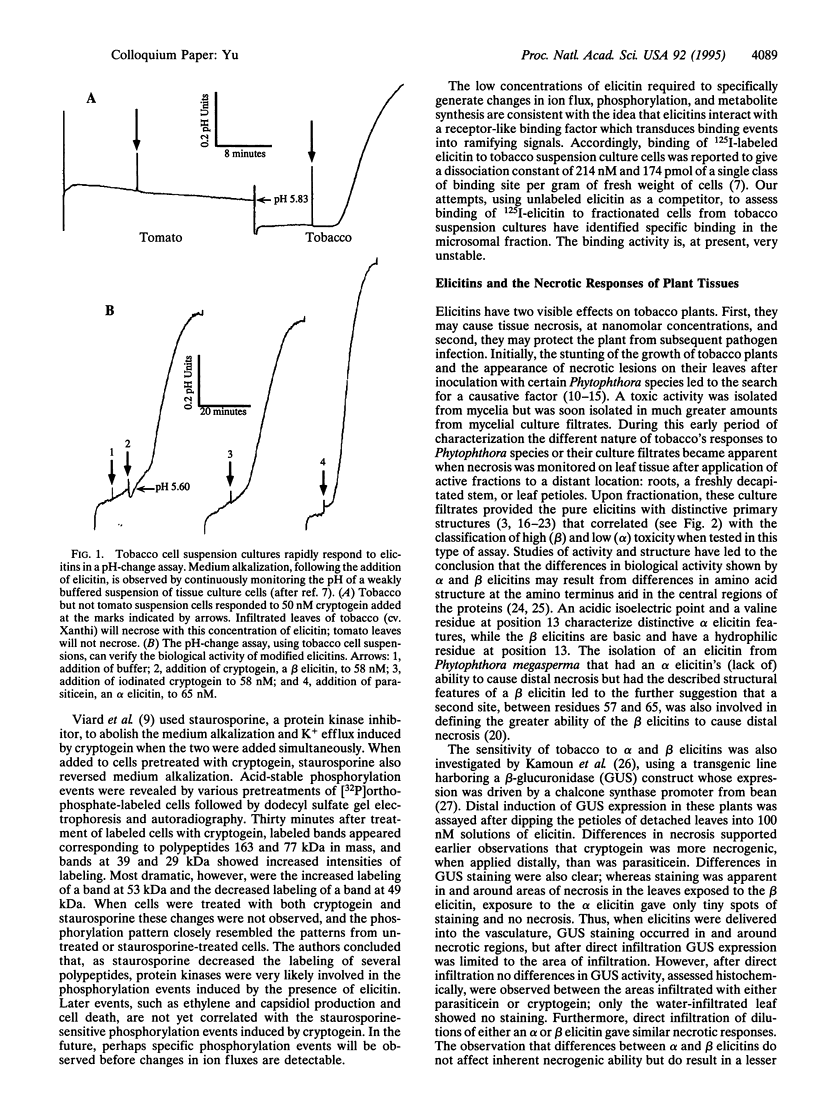
- Blein J. P., Milat M. L., Ricci P. Responses of Cultured Tobacco Cells to Cryptogein, a Proteinaceous Elicitor from Phytophthora cryptogea: Possible Plasmalemma Involvement. Plant Physiol. 1991 Feb;95(2):486–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolyard M. G., Sticklen M. B. Expression of a modified Dutch elm disease toxin in Escherichia coli. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Nov-Dec;5(6):520–524. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz S., van Heijenoort C., Guittet E., Huet J. C., Pernollet J. C. Resonance assignment, cysteine-pairing elucidation and secondary-structure determination of capsicein, an alpha-elicitin, by three-dimensional 1H NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 1;220(2):427–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz S., van Heijenoort C., Huet J. C., Pernollet J. C., Guittet E. 1H and 15N resonance assignment and secondary structure of capsicein, an alpha-elicitin, determined by three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR. Biochemistry. 1994 Jul 12;33(27):8188–8197. doi: 10.1021/bi00193a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. E., Mueller R. J., Kazmierczak P., Zhang L., Villalon D. K., Van Alfen N. K. Effect of a virus on accumulation of a tissue-specific cell-surface protein of the fungus Cryphonectria (Endothia) parasitica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Jan-Feb;5(1):55–61. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devergne J. C., Bonnet P., Panabières F., Blein J. P., Ricci P. Migration of the Fungal Protein Cryptogein within Tobacco Plants. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jul;99(3):843–847. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7713–7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney T., Friedrich L., Vernooij B., Negrotto D., Nye G., Uknes S., Ward E., Kessmann H., Ryals J. Requirement of salicylic Acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.261.5122.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilloteau J. P., Nespoulous C., Huet J. C., Beauvais F., Pernollet J. C., Brunie S. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of beta-cryptogein, a toxic elicitin secreted by the phytopathogenic fungus Phytophthora cryptogea. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):564–565. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J. C., Mansion M., Pernollet J. C. Amino acid sequence of the alpha-elicitin secreted by Phytophthora cactorum. Phytochemistry. 1993 Nov;34(5):1261–1264. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(91)80012-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J. C., Nespoulous C., Pernollet J. C. Structures of elicitin isoforms secreted by Phytophthora drechsleri. Phytochemistry. 1992 May;31(5):1471–1476. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(92)83089-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J. C., Pernollet J. C. Sequences of acidic and basic elicitin isoforms secreted by Phytophthora megasperma megasperma. Phytochemistry. 1993 Jul;33(4):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(93)85277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J. C., Sallé-Tourne M., Pernollet J. C. Amino acid sequence and toxicity of the alpha elicitin secreted with ubiquitin by Phytophthora infestans. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1994 Mar-Apr;7(2):302–304. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-7-0302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun S., Klucher K. M., Coffey M. D., Tyler B. M. A gene encoding a host-specific elicitor protein of Phytophthora parasitica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1993 Sep-Oct;6(5):573–581. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-6-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun S., Young M., Förster H., Coffey M. D., Tyler B. M. Potential Role of Elicitins in the Interaction between Phytophthora Species and Tobacco. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 May;60(5):1593–1598. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.5.1593-1598.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legendre L., Yueh Y. G., Crain R., Haddock N., Heinstein P. F., Low P. S. Phospholipase C activation during elicitation of the oxidative burst in cultured plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24559–24563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci P., Bonnet P., Huet J. C., Sallantin M., Beauvais-Cante F., Bruneteau M., Billard V., Michel G., Pernollet J. C. Structure and activity of proteins from pathogenic fungi Phytophthora eliciting necrosis and acquired resistance in tobacco. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):555–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci P., Bonnet P., Huet J. C., Sallantin M., Beauvais-Cante F., Bruneteau M., Billard V., Michel G., Pernollet J. C. Structure and activity of proteins from pathogenic fungi Phytophthora eliciting necrosis and acquired resistance in tobacco. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):555–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Doerner P. W., Clouse S. D., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Developmental and environmental regulation of a bean chalcone synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):619–631. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Leger R. J., Staples R. C., Roberts D. W. Cloning and regulatory analysis of starvation-stress gene, ssgA, encoding a hydrophobin-like protein from the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene. 1992 Oct 12;120(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90019-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Dean R. A., Sewall T. C., Timberlake W. E. Rodletless, a new Aspergillus developmental mutant induced by directed gene inactivation. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1161–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Timberlake W. E. Cerato-ulmin, a toxin involved in Dutch elm disease, is a fungal hydrophobin. Plant Cell. 1993 Feb;5(2):145–146. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot N. J., Ebbole D. J., Hamer J. E. Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1575–1590. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tercé-Laforgue T., Huet J. C., Ill J. C. Biosynthesis and Secretion of Cryptogein, a Protein Elicitor Secreted by Phytophthora cryptogea. Plant Physiol. 1992 Mar;98(3):936–941. doi: 10.1104/pp.98.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viard M. P., Martin F., Pugin A., Ricci P., Blein J. P. Protein Phosphorylation Is Induced in Tobacco Cells by the Elicitor Cryptogein. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1245–1249. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Z. M., Laby R. J., Zumoff C. H., Bauer D. W., He S. Y., Collmer A., Beer S. V. Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.1621099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels J. G., de Vries O. M., Asgeirsdóttir S. A., Springer J. The thn mutation of Schizophyllum commune, which suppresses formation of aerial hyphae, affects expression of the Sc3 hydrophobin gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2439–2445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels JGH., De Vries OMH., Asgeirsdottir S. A., Schuren FHJ. Hydrophobin Genes Involved in Formation of Aerial Hyphae and Fruit Bodies in Schizophyllum. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):793–799. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosten HAB., De Vries OMH., Wessels JGH. Interfacial Self-Assembly of a Fungal Hydrophobin into a Hydrophobic Rodlet Layer. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1567–1574. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wösten H. A., Asgeirsdóttir S. A., Krook J. H., Drenth J. H., Wessels J. G. The fungal hydrophobin Sc3p self-assembles at the surface of aerial hyphae as a protein membrane constituting the hydrophobic rodlet layer. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;63(1):122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



