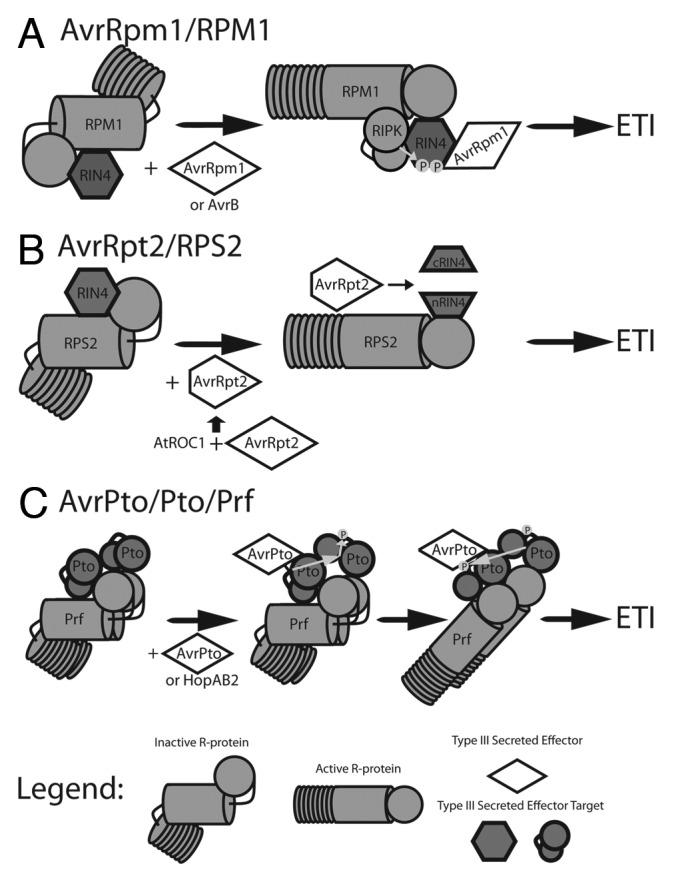
Figure 1. Models of T3SE recognition by NB-LRR proteins to trigger ETI. NB-LRR proteins monitor host proteins targeted by T3SE for modification. Detection of modified host proteins causes NB-LRR conformational change, initiating ETI signaling.14 (A) The NB-LRR RPM1 monitors the host protein RIN4.25,26 Interaction of RIN4 with the T3SE AvrRpm1 or AvrB triggers RIN4 phosphorylation by the host kinase RIPK, activating RPM1.50,83 (B) RIN4 is also monitored by the NB-LRR RPS2. The T3SE AvrRpt2 is activated by the host cyclophillin AtROC1, and causes proteolytic cleavage of RIN4 resulting in activation of RPS2.48 The RIN4 complexes in A and B are membrane associated. (C) Oligomeric complexes of Pto family host kinases80 and the NB-LRR Prf recognize the T3SEs AvrPto35,36 and HopAB2.37 Interaction of AvrPto or HopAB2 with a Pto monomer activates Pto kinase activity, causing transphosphorylation and activation of the second Pto monomer. This causes a second transphosrphorylation event resulting in phosphorylation of both Pto kinases and activation of Prf.81
