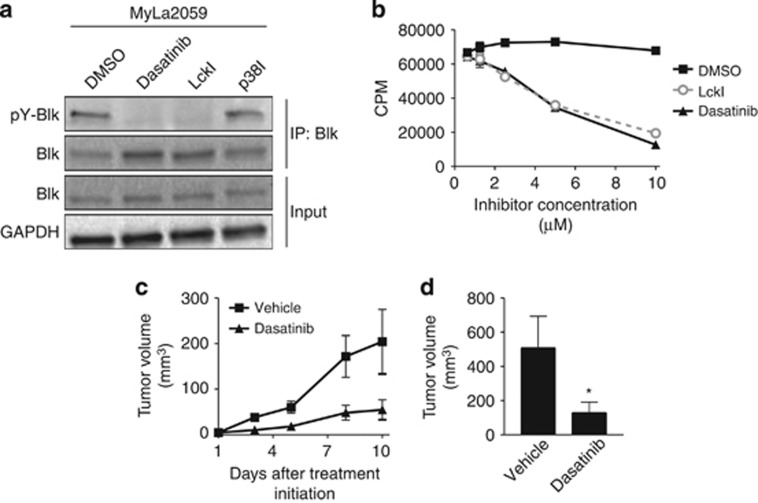
Figure 2.
Dasatinib inhibits proliferation of malignant CTCL cells and tumor growth in a xenograft model of CTCL. (a) Malignant cells obtained from a lesional biopsy of a patient with CTCL (MyLa2059) were treated with 10 μM of either dasatinib, LckI, p38I or vehicle (DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide)) for 1 h before the cells were lysed and Blk immuprecipitated (IP: Blk) followed by western blot (WB) analysis of the level of Blk phosphorylation using anti-phosphotyrosine and anti-Blk antibodies. WB analysis of the input lysates (Input) using anti-Blk and anti-GAPDH antibodies were included for reference. (b) Malignant cells (MyLa2059; 4 × 103) were cultured for 72 h with dasatinib, LckI or vehicle (DMSO) and [3H]-thymidine were added for 20 h before measurement of [3H]-thymidine incorporation. Results are shown as mean counts per minute of triplicate cultures with error bars representing ±s.d. (c, d) Four NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid B2mtm1Unc/J mice per group were inoculated s.c. with 1 × 106 MyLa2059 cells into both flanks as described elsewhere.10 When a mouse developed a palpable tumor (day 1) treatment with either vehicle (10% DMSO, 90% propylene glycol) or 40 mg/kg dasatinib orally 5 days a week was initiated. Mice with palpable tumors were allocated alternately to the group receiving vehicle or the group receiving dasatinib. The length and width of the tumors were measured continuously until the experiment was terminated on day 10 post treatment initiation where the tumors were excised and measured. (c) Graph showing the average tumor volume per mouse ±s.e.m. at different time points after treatment initiation. The tumor volume was calculated using the formula V=(a × b2)/2, where a defines the length (mm) and b the width (mm) of the tumor. (d) Bar graph showing the average tumor volume per mouse ±s.e.m. of the excised tumors at day 10 post treatment initiation. The ellipsoid tumor volume was calculated using the formula (a × b × c) × π/6, where a, b and c designate tumor diameters (mm) for length, width and depth, respectively. *P<0.05 denotes a significant difference using a one-tailed two-sample t-test.