Key Points
CDK6 is a critical effector of MLL fusions in myeloid leukemogenesis.
Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of CDK6 overcome the differentiation block associated with MLL-rearranged AML.
Abstract
Chromosomal rearrangements involving the H3K4 methyltransferase mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) trigger aberrant gene expression in hematopoietic progenitors and give rise to an aggressive subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Insights into MLL fusion-mediated leukemogenesis have not yet translated into better therapies because MLL is difficult to target directly, and the identity of the genes downstream of MLL whose altered transcription mediates leukemic transformation are poorly annotated. We used a functional genetic approach to uncover that AML cells driven by MLL-AF9 are exceptionally reliant on the cell-cycle regulator CDK6, but not its functional homolog CDK4, and that the preferential growth inhibition induced by CDK6 depletion is mediated through enhanced myeloid differentiation. CDK6 essentiality is also evident in AML cells harboring alternate MLL fusions and a mouse model of MLL-AF9–driven leukemia and can be ascribed to transcriptional activation of CDK6 by mutant MLL. Importantly, the context-dependent effects of lowering CDK6 expression are closely phenocopied by a small-molecule CDK6 inhibitor currently in clinical development. These data identify CDK6 as critical effector of MLL fusions in leukemogenesis that might be targeted to overcome the differentiation block associated with MLL-rearranged AML, and underscore that cell-cycle regulators may have distinct, noncanonical, and nonredundant functions in different contexts.
Introduction
A substantial proportion of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases harbor balanced translocations of chromosome 11q23, and AML with t(9;11)(p22;q23) is recognized as a distinct entity by the World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.1,2 On the molecular level, t(11q23) results in fusion of the MLL gene, which encodes an H3K4 methyltransferase, to a broad spectrum of partner genes, such as MLLT3 (also called AF9), MLLT4 (AF6), MLLT1 (ENL), and MLLT10 (AF10) on chromosomes 9p22, 6q27, 19p13.3, and 10p12, respectively.3,4 A key functional feature of mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) rearrangements is their ability to confer leukemia-initiating activity to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC).5,6
MLL fusions are characterized by loss of the C-terminal H3K4 methyltransferase domain, and their leukemogenic activity is dependent on both features of the remaining N-terminal portion, such as a binding motif for the menin tumor suppressor that mediates the contact between MLL and chromatin as well as aberrant transactivation of target genes through heterologous domains contributed by the various partner proteins.7 For example, MLL fusions involving AF9, ENL, and AF10, which account for the majority of MLL-rearranged AML, recruit multiprotein complexes essential for transcriptional activation/elongation, such as that comprising the H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L.8,9 Other factors required for establishing leukemogenic gene expression programs in MLL-rearranged AML include the polycomb group protein CBX8, the bromodomain protein BRD4, the H3K4/K9 demethylase KDM1A, and signaling through the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway.10-15 Certain MLL target genes, such as HOXA9 and MEIS1, have established roles in MLL-mediated leukemogenesis,16 whereas the relevance of others remains elusive.
Current treatment of MLL-rearranged AML consists of chemotherapy and, in select cases, allogeneic stem cell transplantation, and results in long-term survival rates of less than 10% to approximately 50% depending on the MLL fusion partner and additional risk factors.4,17 Insights into MLL-mediated leukemogenesis have spurred efforts to develop novel, molecular mechanism-based therapeutic strategies, such as targeting the menin–MLL interaction, DOT1L, or BRD4.12,13,18,19 However, these and other targeted approaches20-22 have not yet been translated into the clinic, and treatment of MLL-rearranged AML remains challenging.
Functional genetic screens provide a means to search for essential signaling pathways in preclinical models of cancer in an unbiased fashion.23,24 From a translational perspective, such an approach can be particularly valuable in the context of oncogenic mutations that are difficult to target directly, such as MLL rearrangements. Here, we have used a functional genetic approach based on large-scale RNA interference (RNAi) to identify dependence on a noncanonical and nonredundant function of CDK6 as specific liability of MLL-rearranged AML that could be exploited for therapeutic benefit.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
AML cell lines, 293T cells, and Ba/F3 cells were maintained under standard conditions. Cell lines derived from mouse HSPC were maintained in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum and 20% WEHI-conditioned medium as a source of interleukin-3. Cell line identity and purity were verified using the Multiplex Cell Authentication and Contamination Tests (Multiplexion). PD-0332991 was obtained from Selleck.
RNAi screening
Large-scale arrayed screening was conducted with a subset of the Broad Institute TRC short hairpin RNA (shRNA) library as described previously.25,26 Screens were performed in a 384-well format. Each well contained a single shRNA species, and each transcript was covered, on average, by 5 different shRNAs. Assay conditions (cell number per well, viral dose, puromycin concentration) were optimized for each cell line before high-throughput screening. Cells were seeded, incubated for 24 hours, infected with lentivirus, and incubated for 6 days. All lentiviral infections were performed in quadruplicate; 2 replicates were selected with puromycin during the final 5 days of incubation, whereas the other 2 replicates were left untreated. Cell viability and proliferation were measured 6 days after lentiviral infection using the CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay (Promega). Raw data for each shRNA were corrected using the B-score, an analog of the Z-score that uses a 2-way median polish to minimize row/column effects, and normalization to the median absolute deviation to account for plate-to-plate variation. A gene was defined as “hit” if 1 shRNA was associated with a B-score of less than −1.2 and at least 1 additional shRNA was associated with a B-score of less than −0.85.
Plasmids and viral transduction
RNAi experiments were performed using pLKO.1 shRNAs obtained from the TRC-Hs 1.0 (human) and TRC-Mm 1.0 (mouse) shRNA libraries through Open Biosystems or Sigma-Aldrich, or a custom shRNA against the MLL-AF9 fusion breakpoint. See supplemental Methods on the Blood Web site for details. The CDK6 and CDK4 complementary DNAs (cDNAs) were obtained from Open Biosystems and polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified from an AML cell line, respectively, and cloned into the pLenti6.2/V5-DEST or pLenti7.3/V5-DEST lentiviral vectors (Invitrogen) for expression in human cells. The CDK6K43M mutant was generated using the QuikChange XL Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene). The MLL-AF9 cDNA was cloned into pLenti6.2/V5-DEST or the pMSCV-PGK-neo and pMSCV-IRES-GFP retroviral vectors for expression in murine cells. For knockdown of Cdk6 in vivo, shRNA TRCN23153 was cloned into the LeGO-C2 lentiviral gene ontology vector.27 Generation of viral supernatants and viral transduction were performed as described previously.28 Vector particles were titrated based on virion RNA by measuring the abundance of the HIV-1 Rev response element using quantitative reverse-transcription PCR (qRT-PCR),29 and cells were infected with equivalent amounts of recombinant viruses to ensure comparability between different knockdown experiments.
In vitro studies
Determination of viable cell numbers, RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis, qRT-PCR, immunoblotting, flow cytometry, and colony assays were performed using standard procedures. See supplemental Methods for details. Chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing (ChIP-seq) was performed as described.30
Murine bone marrow transplantation assays
Transplantation experiments were performed as described previously.28 Eight- to 10-week-old C57BL/6J mice (Jackson Laboratory) were housed in individually ventilated cages and preconditioned with 6 Gy total body irradiation (135Cs source) before administration of transduced hematopoietic cells via IV injection.
Statistics
Experiments were performed at least 3 times; unless otherwise indicated, 1 representative experiment is shown. Error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis was performed using paired or unpaired 2-tailed Student t test, Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, or log-rank test as appropriate. Computations were performed using GraphPad Prism.
Study approval
Human AML samples and normal CD34pos cells were obtained under institutional review board–approved protocols following written informed consent. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Animal experiments were performed after approval and in accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee at the Regierungspräsidium Karlsruhe.
Results
RNAi screens for essential genes in MLL-AF9–expressing AML cells
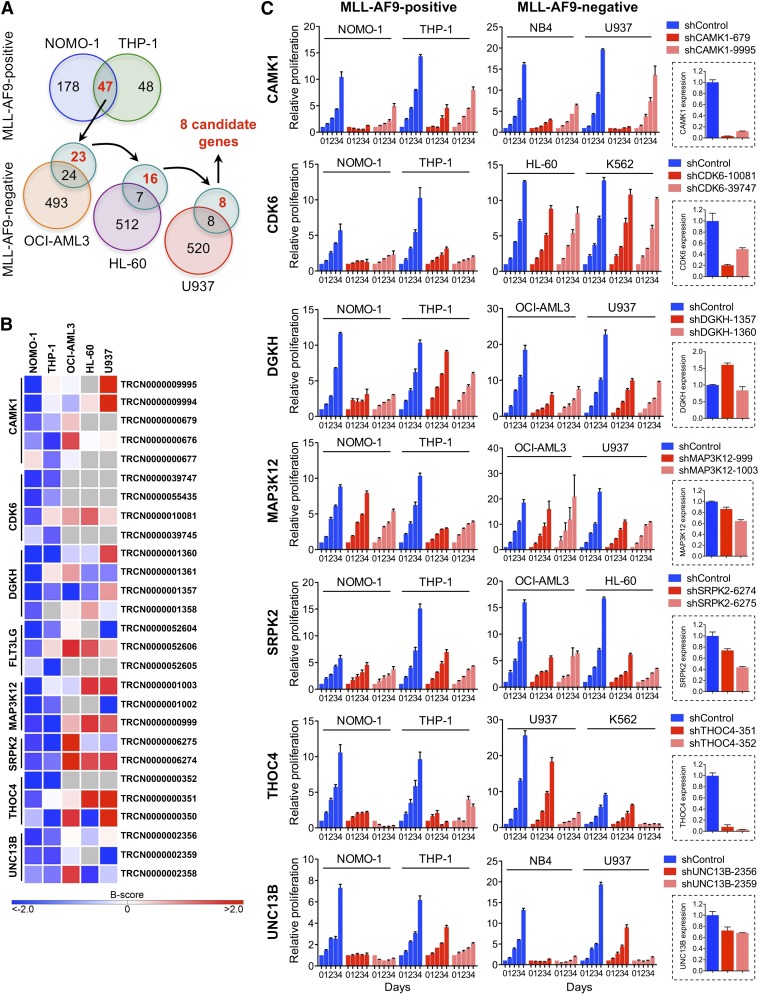
We performed loss-of-function RNAi screens in 5 AML cell lines (supplemental Table 1) using a lentivirally delivered shRNA library targeting genes encoding most protein kinases, selected protein phosphatase genes, and known cancer-related genes.25,26 To nominate candidates that are required specifically in the context of rearranged MLL, we identified genes whose depletion by at least 2 shRNAs inhibited MLL-AF9pos NOMO-1 and THP-1 cells, followed by elimination of genes that also scored in any of the 3 remaining, wild-type (WT) MLL-expressing cell lines with 2 or more shRNAs (Figure 1A). This approach yielded 8 genes potentially involved in MLL-rearranged AML (Figure 1B).
Figure 1.
RNAi screens for genes required by MLL-AF9pos AML cell lines. (A) Schematic of RNAi screens. Numbers in circles indicate genes scoring as positive. Genes scoring exclusively in MLL-AF9pos AML cell lines are indicated in red. (B) Candidate genes preferentially required in MLL-AF9pos AML cell lines. For each of the top-ranking genes, the shRNAs scoring in NOMO-1 and/or THP-1 are shown. Negative B-scores indicate reduced viable cell numbers. (C) Validation of candidate genes. Shown are the effects of 2 shRNAs per candidate gene on cell viability and proliferation of AML cell lines with and without an MLL-AF9 fusion and the knockdown efficiency of each shRNA in NOMO-1 cells, as determined by qRT-PCR.
We next validated the top-ranking genes by knockdown in NOMO-1, THP-1, and 2 MLL-AF9neg cell lines using shRNAs that scored exclusively in MLL-AF9pos cell lines in the RNAi screens, followed by monitoring of viable cell numbers. The knockdown efficiency of each shRNA was determined by qRT-PCR. Of the 7 genes tested, 2 (DGKH, MAP3K12) were not efficiently suppressed, whereas knockdown of 4 genes (CAMK1, SRPK2, THOC4, UNC13B) was growth inhibitory regardless of genotype. In contrast, depletion of CDK6, a serine/threonine kinase essential for passage through the cell-cycle G1/S phase restriction point, selectively impaired MLL-AF9pos cell lines (Figure 1C).
Requirement for CDK6 in MLL-transformed hematopoietic cells
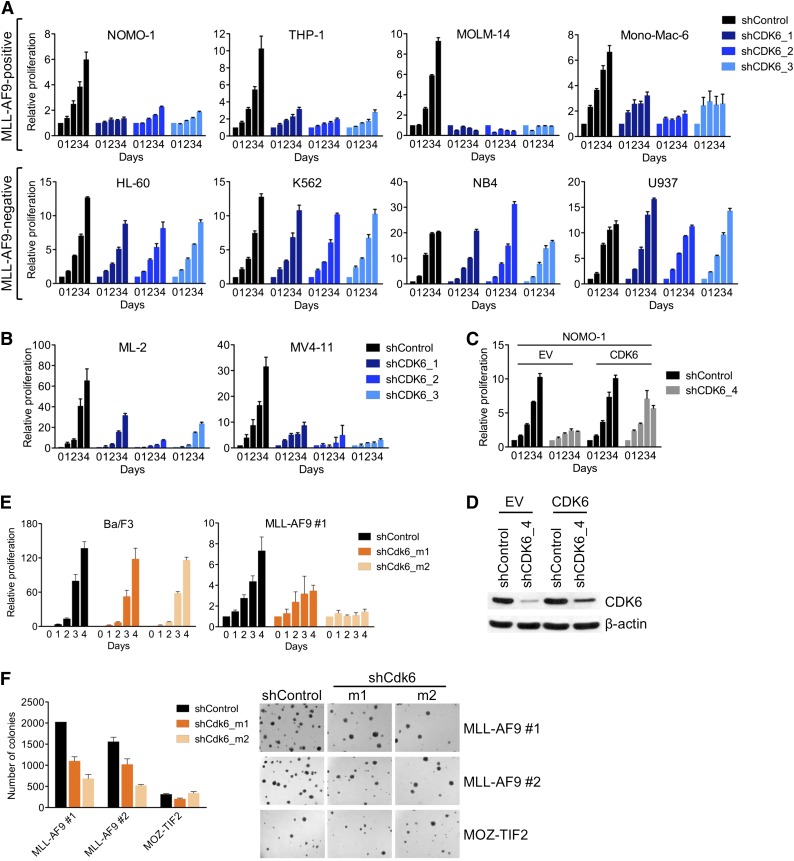
To confirm the differential requirement for CDK6, we suppressed CDK6 in an expanded panel of AML cell lines using 3 different shRNAs. CDK6 knockdown, as determined by qRT-PCR and immunoblotting (supplemental Figure 1A), strongly inhibited MLL-AF9pos cells, whereas there was little to no effect in MLL-AF9neg cells (Figure 2A). CDK6 was also required by AML cell lines (MV4-11, ML-2) harboring other MLL fusions (MLL-AF4/AFF1, MLL-AF6; Figure 2B; supplemental Figure 1B).
Figure 2.
Requirement for CDK6 in MLL-rearranged hematopoietic cells. (A) Effects of CDK6 suppression in MLL-AF9pos and MLL-AF9neg AML cell lines. (B) Effects of CDK6 suppression in MLL-AF4pos MV4-11 and MLL-AF6pos ML-2 cells. (C) Rescue of viable cell number by expression of the CDK6 coding sequence in NOMO-1 cells transduced with an shRNA targeting the CDK6 3′ UTR. (D) CDK6 protein expression of cells used in panel C. (E) Effects of Cdk6 suppression in suspension cultures of Ba/F3 cells and murine HSPC transduced with MLL-AF9. (F) Effects of Cdk6 suppression in methylcellulose cultures of murine HSPC transduced with MLL-AF9 or MOZ-TIF2. Original magnification, ×25.
To further ensure the specificity of these results, we performed rescue experiments with an shRNA targeting the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the CDK6 messenger RNA (mRNA). We first transduced MLL-AF9pos NOMO-1 cells with an empty control vector or the CDK6 coding sequence, which lacks the 3′ UTR. Subsequent knockdown of endogenous CDK6 inhibited the growth of empty control vector–transduced cells, whereas the RNAi-induced phenotype was countered by expression of the shRNA-resistant CDK6 cDNA (Figure 2C,D). Together, these data indicate that MLL-rearranged human AML cells are dependent on CDK6 expression.
To corroborate our results in genetically defined systems based on primary HSPC, we employed 2 cell lines generated through retroviral transduction of 5-fluorouracil-mobilized murine bone marrow (BM) with MLL-AF9 and selection for stable transgene expression during serial replating in methylcellulose. Consistent with the results obtained in human AML cell lines, Cdk6 suppression decreased the growth of MLL-AF9–transformed HSPC in suspension culture, whereas highly proliferative, WT MLL-expressing Ba/F3 murine pro-B cells were unaffected (Figure 2E; supplemental Figure 1C). Similarly, Cdk6 knockdown substantially inhibited colony formation in methylcellulose of MLL-AF9–transduced murine BM compared with cells expressing another leukemogenic fusion, MYST3-NCOA2 (also called MOZ-TIF2; Figure 2F; supplemental Figure 1C). Thus, MLL-AF9 is dependent on Cdk6 to transform primary HSPC in vitro.
Induction of myeloid differentiation by CDK6 suppression in MLL-rearranged AML cells
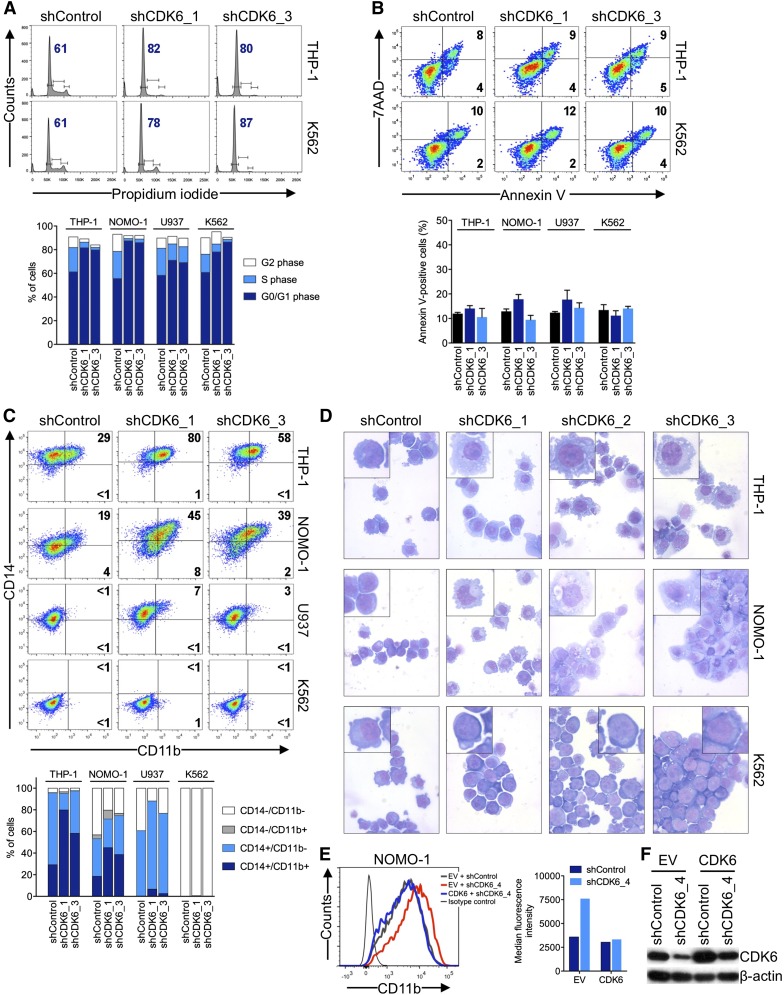
To examine the basis for the disparate effects of CDK6 depletion according to MLL status, we analyzed cell cycle and apoptosis in AML cell lines 6 days after shRNA knockdown of CDK6. Propidium iodide staining and measurement of 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine incorporation showed that MLL-AF9pos cells slightly accumulated in the G0/G1 phase after CDK6 suppression; however, this was also observed in MLL-AF9neg cells (Figure 3A; supplemental Figure 2A-C). CDK6 suppression caused no significant increase in apoptosis regardless of genotype (Figure 3B; supplemental Figure 2D). We next considered whether CDK6 depletion might induce differentiation preferentially in MLL-AF9pos cells. Consistent with this idea, MLL-AF9pos cells upregulated CD11b expression and assumed a more mature, macrophage-like morphology upon CDK6 knockdown, whereas these effects were not observed in WT MLL-expressing cells (Figure 3C,D). These phenotypic changes were paralleled by increases in the expression of CEPBA, SPI1 (also called PU.1), and, to a lesser extent, IRF8, which encode transcription factors involved in myelomonocytic differentiation (supplemental Figure 2E). The inhibitory function of CDK6 on differentiation was rescued by expression of the CDK6 coding sequence in MLL-rearranged cells transduced with an shRNA targeting the 3′ UTR of the CDK6 mRNA (Figure 3E,F; supplemental Figure 2F,G). In contrast, expression of a CDK6K43M mutant with disrupted kinase function or CDK4 was unable to block the differentiation induced by shRNA-mediated depletion of CDK6 (supplemental Figure 2F-G). These data indicate that MLL-rearranged AML cells are disproportionately reliant on CDK6 to maintain an immature phenotype and support the conclusion that the catalytic activity of CDK6 is crucial for the dependence of MLL-rearranged AML cells on CDK6 expression.
Figure 3.
Effects of CDK6 suppression in AML cells. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of cell-cycle progression. Numbers indicate percentages of cells in G0/G1. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis. Numbers indicate percentages of cells. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of myeloid differentiation in AML cell lines. Numbers indicate percentages of cells. (D) Microscopic analysis of May-Grünwald-Giemsa–stained cytospin preparations of AML cell lines. Original magnification, ×400. Insets show twofold magnified details of the corresponding photographs. (E) Inhibition of myeloid differentiation by expression of the CDK6 coding sequence in NOMO-1 cells transduced with an shRNA targeting the CDK6 3′ UTR. (F) Immunoblot analysis of cells shown in panel E.
Targeting of CDK6 by rearranged MLL
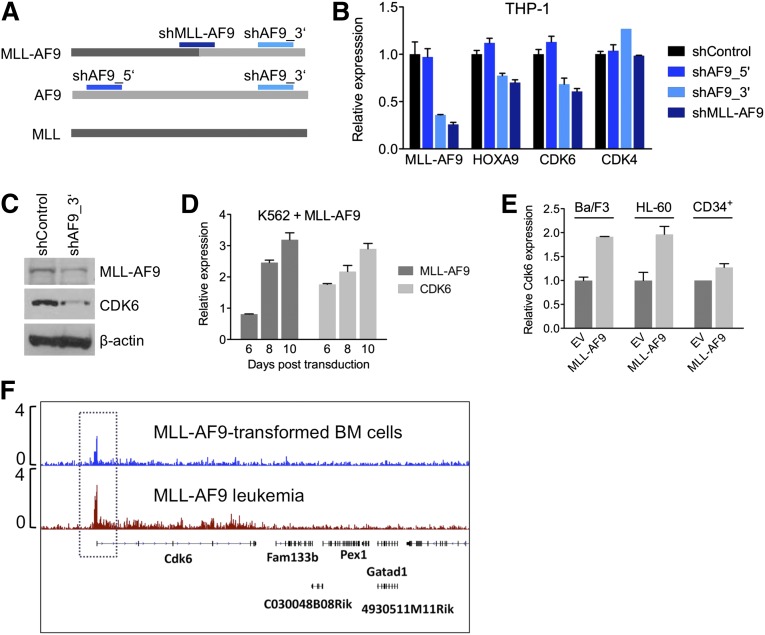
To investigate whether the context-dependent requirement for CDK6 reflects a transcriptional link between rearranged MLL and CDK6, we measured CDK6 mRNA and protein in response to modulation of MLL-AF9 expression in AML cell lines. We transduced THP-1, an MLL-AF9pos cell line with low endogenous AF9 levels (supplemental Figure 2H), with shRNAs against the MLL-AF9 fusion breakpoint or AF9 exon 7, which is retained in the MLL-AF9 fusion transcript. A nontargeting shRNA and an shRNA targeting AF9 exon 5, which is absent in the MLL-AF9 fusion, served as controls (Figure 4A). Suppression of MLL-AF9 caused a decrease in CDK6 mRNA and protein, resembling the effects on HOXA9, a known MLL-AF9 target gene. In contrast, expression of CDK4, a closely related kinase that cooperates with CDK6 to promote cell-cycle progression, was not altered (Figure 4B,C). Conversely, introduction of MLL-AF9 into WT MLL-expressing AML cells, normal human CD34pos cells, and Ba/F3 cells increased CDK6 mRNA levels (Figure 4D,E). Furthermore, ChIP-seq demonstrated that MLL-AF9 binds to the Cdk6 locus in mouse BM cells transduced with MLL-AF9 and in MLL-AF9–driven murine AML (Figure 4F). These findings indicate that CDK6 is rendered essential via direct targeting by truncated MLL.
Figure 4.
Transcriptional activation of CDK6 by MLL-AF9. (A) Schematic of the regions in MLL-AF9 and AF9 targeted by the shRNAs used in panels B and C. (B) Expression of HOXA9, CDK6, and CDK4 mRNA in THP-1 cells after MLL-AF9 suppression. (C) Expression of CDK6 protein in THP-1 cells after MLL-AF9 suppression. (D) Expression over time of MLL-AF9 and CDK6 in K562 cells transduced with MLL-AF9. (E) Expression of CDK6 in HL-60 cells, normal human CD34pos cells, and murine Ba/F3 cells transduced with MLL-AF9. (F) ChIP-seq analysis identifying Cdk6 as direct MLL-AF9 target gene in mouse BM cells transformed with MLL-AF9. The top track is derived from cells before injection into recipient mice; the bottom track is derived from a fully developed mouse leukemia.
Sensitivity of MLL-rearranged AML cells to pharmacologic CDK6 inhibition
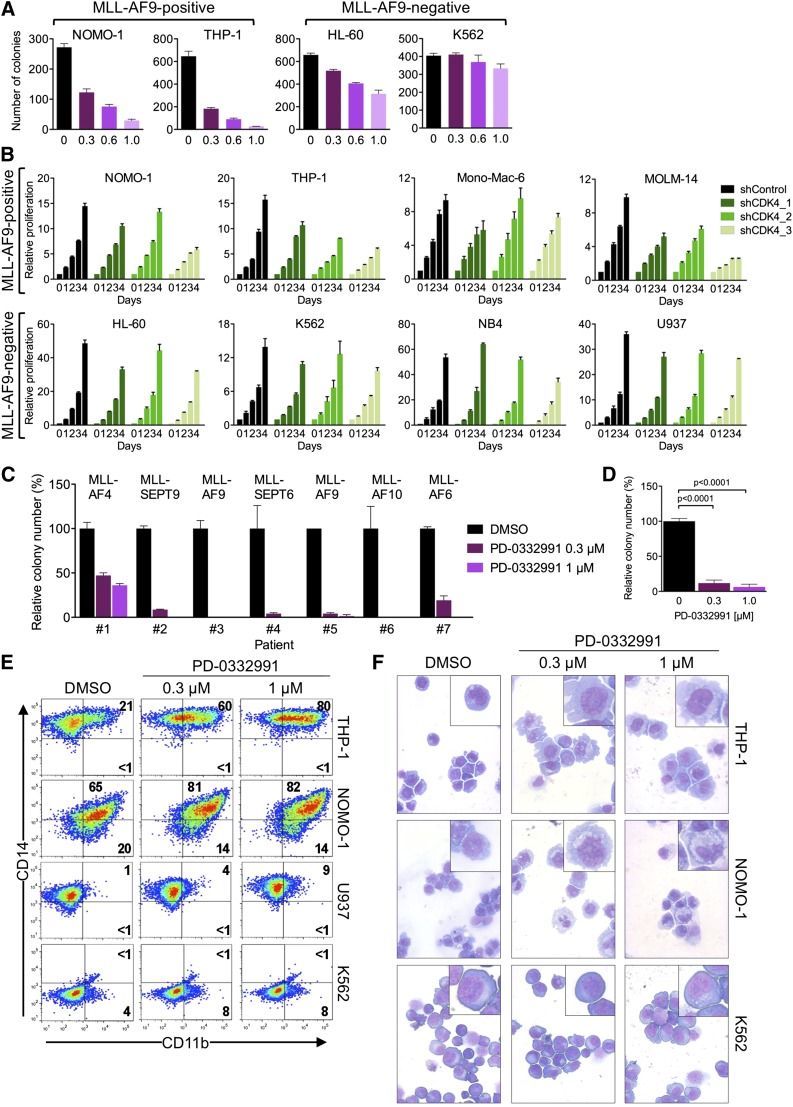
Our genetic data suggested that CDK6 might be a therapeutic target in MLL-rearranged leukemias. We therefore evaluated colony formation of AML cells in the presence of palbociclib (also called PD-0332991), an orally available inhibitor of CDK4/CDK6 kinase activity that is in clinical development as an anticancer agent.31 For the MLL-AF9pos cell lines NOMO-1 and THP-1, we observed a strong, dose-dependent reduction in the number of colonies, whereas MLL-AF9neg HL-60 and K562 cells were affected to a substantially lesser extent (Figure 5A; supplemental Figure 3A).
Figure 5.
Pharmacologic inhibition of CDK6 in human AML cells. (A) Colony formation of AML cell lines treated with PD-0332991. (B) Effects of CDK4 suppression in AML cell lines. (C) Relative colony numbers of primary human MLL-rearranged AML specimens cultured in the presence of PD-0332991. (D) Cumulative analysis of normalized colony data shown in panel C. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of myeloid differentiation in AML cell lines treated with PD-0332991. Numbers indicate percentages of cells. (F) Microscopic analysis of May-Grünwald-Giemsa–stained cytospin preparations of AML cell lines treated with PD-0332991. Original magnification, ×400. Insets show twofold magnified details of the corresponding photographs.
Because PD-0332991 also inhibits CDK4, which acts redundantly with CDK6 to promote cell-cycle progression, it seemed possible that CDK4 blockade contributes to the effect of this compound in MLL-rearranged AML. We therefore suppressed CDK4 in 8 AML cell lines. Consistent with our initial RNAi screens, which did not identify CDK4 as essential gene in MLL-AF9pos cell lines, CDK4 knockdown had no or only a marginal effect on viable cell numbers in all cell lines investigated (Figure 5B; supplemental Figure 3B), implying that the effect of PD-033299 in MLL-rearranged cells is mainly attributable to CDK6 inhibition.
We next sought confirmation of CDK6 inhibitor activity in primary human MLL-rearranged AML. Consistent with the cell line results, PD-0332991 strongly inhibited colony formation in methylcellulose of mononuclear cells from 7 AML patients harboring 5 different MLL rearrangements (Figure 5C-D; supplemental Figure 3C-D).
Given that CDK6 knockdown induces maturation of MLL-rearranged AML cells, we evaluated whether the effect of pharmacologic CDK6 inhibition was also the result of myeloid differentiation. Consistent with the RNAi results, PD-0332991 induced CD11b expression, changes in cell morphology, and dose-dependent increases in the expression of CEPBA, SPI1, and more modestly IRF8, preferentially in MLL-rearranged cells (Figure 5E-F; supplemental Figure 3E). Collectively, these data show that MLL-rearranged AML cells are sensitive to pharmacologic CDK6 inhibition, indicating that their overreliance on CDK6 may provide a therapeutic opportunity. Furthermore, the results demonstrate that the catalytic activity of CDK6 contributes to the myeloid differentiation arrest in MLL-rearranged AML.
Requirement for CDK6 in MLL-AF9–driven murine AML
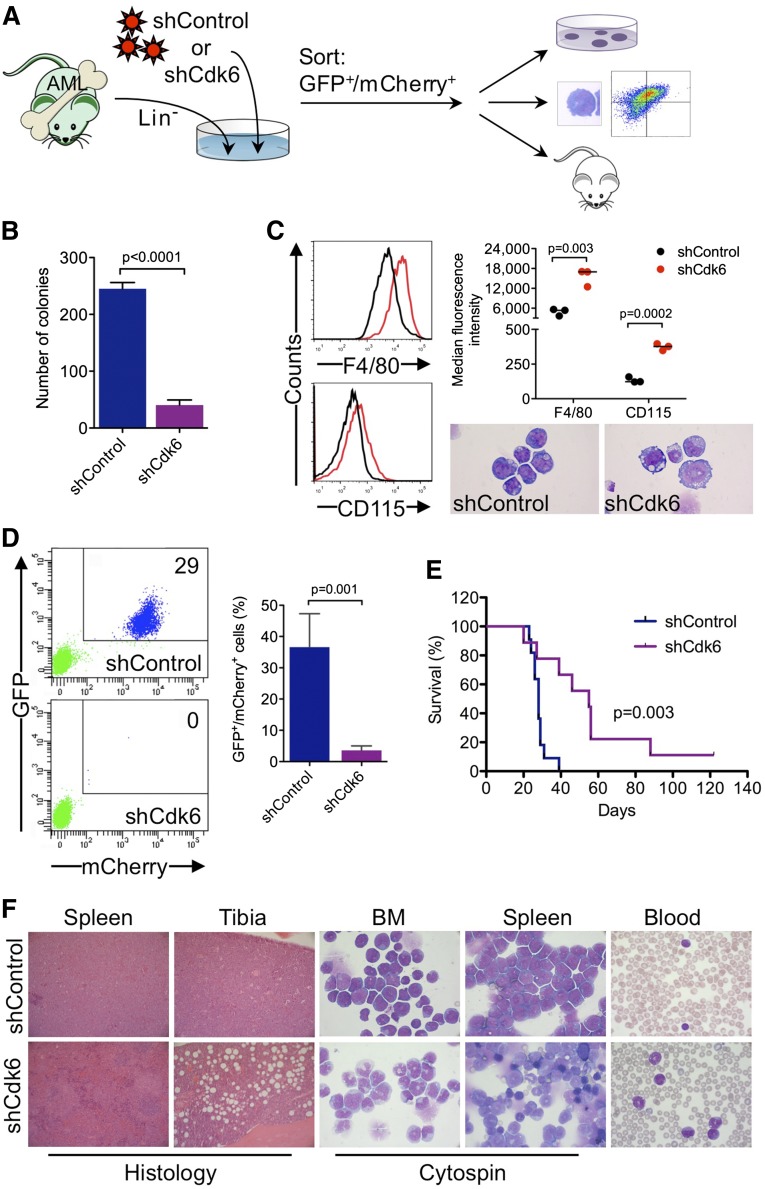
To investigate whether Cdk6 is required for AML development and propagation in vivo, we generated highly aggressive GFPpos MLL-AF9–induced leukemias in a murine BM transplantation model and transduced leukemic cells from secondary transplant recipients with an shRNA against Cdk6 linked to mCherry (Figure 6A). Cells with high mCherry expression were sorted by flow cytometry 40 hours after transduction (supplemental Figure 4) (ie, at an early time point when the shRNA was already expressed but Cdk6 knockdown most likely had not yet occurred) and transplanted into tertiary recipients, which were monitored for development of disease and survival. In addition, we evaluated the effects of Cdk6 knockdown on clonogenic activity and myeloid differentiation (Figure 6A).
Figure 6.
Requirement for Cdk6 in MLL-AF9–driven murine AML. (A) Schematic of in vivo and ex vivo experiments. (B) Effects of Cdk6 suppression in methylcellulose cultures of sorted GFPpos/mCherrypos leukemic cells from mice with secondary MLL-AF9–induced AML. (C) Effects of Cdk6 suppression on myeloid differentiation of leukemic cells from mice with secondary MLL-AF9–induced AML. Original magnification of cytospin preparations, ×1000. (D) Flow cytometric quantification of GFP and mCherry expression after 4 weeks in the blood of tertiary recipient mice transplanted with Cdk6 knockdown cells or control cells. Shown are representative plots from 2 mice (left) and the percentage of GFPpos/mCherrypos cells from all mice (right; shCdk6, n = 13; shControl, n = 8). (E) Survival of tertiary recipient mice transplanted with Cdk6 knockdown cells or control cells (shCdk6, n = 9; shControl, n = 11). (F) Microscopic analysis of hematopoietic tissues from mice with tertiary MLL-AF9-induced AML. Shown are hematoxylin and eosin–stained tissue sections and May-Grünwald-Giemsa–stained cytospin preparations and blood smears from representative mice transplanted with Cdk6 knockdown cells or control cells. Original magnification, ×100 (spleen histology), ×200 (tibia histology), ×1000 (cytospin, blood).
Ex vivo experiments demonstrated that Cdk6 knockdown impaired colony formation of leukemic cells from mice with secondary MLL-AF9–induced AML (Figure 6B). Microscopic and flow cytometric analysis of sorted GFPpos/mCherryhigh cells cultured for 4 days demonstrated that the differentiation block of MLL-AF9pos leukemic cells was reversed by Cdk6 depletion, which induced morphological maturation and increased expression of myeloid differentiation antigens F4/80 and CD115 (Figure 6C).
Flow cytometry 4 weeks after transplantation demonstrated expansion of GFPpos/mCherrypos leukemic cells in the blood of control mice, whereas GFPpos/mCherrypos cells were barely detectable in mice transplanted with Cdk6 knockdown cells (Figure 6D). The decrease in leukemic burden translated into a significant survival advantage because mice transplanted with control cells died after a median of 28 days compared with 55 days in mice transplanted with Cdk6 knockdown cells (Figure 6E). Control mice developed acute leukemia with frequent blasts in the blood and extensive infiltration of BM and spleen by a prominent population of immature myeloid cells and blast forms (Figure 6F, top panels). In Cdk6 knockdown mice, the disease was characterized by expanded granulocyte and monocyte populations as well as maturing myeloid forms in the blood, BM, and spleen, reminiscent of human myeloproliferative neoplasm; furthermore, histopathology demonstrated less BM and spleen infiltration with partially preserved splenic architecture (Figure 6F, bottom panels). These data demonstrate that depletion of Cdk6 overcomes the differentiation block of MLL-AF9–driven AML and prolongs survival in vivo, further supporting CDK6 inhibition as novel strategy to target MLL-rearranged AML cells.
Discussion
Only a minority of patients with MLL-rearranged AML attain long-term disease-free survival, indicating that more effective, molecular mechanism-based therapies are needed.1,2,4 Because interfering with rearranged MLL itself has proved challenging, many studies have focused on downstream events that may be therapeutically tractable. However, although it is firmly established that MLL fusion proteins cause a characteristic pattern of transcriptional changes,32 it is less well defined which of the many deregulated genes are critical to the leukemic phenotype and would need to be blocked for therapeutic benefit. Furthermore, individual MLL target genes that are known to be required for AML development and maintenance, such as HOXA9 and MEIS1,33-35 are not amenable to pharmacologic inhibition. Thus, treatment of MLL-rearranged AML remains a challenge in clinical practice.
We used a functional genetic approach based on a series of shRNA screens to identify that the serine/threonine kinase CDK6 represents a targetable effector of MLL fusion proteins. In particular, we found that CDK6 activity is preferentially required by MLL-rearranged AML cells compared with other AML subtypes, and that this association is due to direct transcriptional regulation of CDK6 by mutant MLL because the Cdk6 locus is bound by MLL-AF9 in vitro and in vivo and modulation of MLL-AF9 levels resulted in concordant changes in CDK6 expression in different human and murine experimental models. The latter conclusion is also supported by data from previous ChIP-chip and ChIP-seq screens showing that CDK6 is bound by MLL fusion proteins and displays abnormal H3K79 methylation patterns in human MLL-rearranged leukemic cell lines and a mouse model of MLL-AF9–driven AML.30,36,37 Remarkably, the data support a link between CDK6 and different MLL fusions, pointing to CDK6 essentiality as unifying feature of MLL-rearranged leukemias.
CDK6 acts redundantly with CDK4 to promote cell-cycle progression. Accordingly, impaired cell-cycle control in hematopoietic malignancies has been linked to combined deregulation of CDK4 and CDK6 through mechanisms such as inactivation of CDKN2 (also called Ink4) CDK inhibitors and aberrant cyclin D expression.38,39 In contrast, our findings indicate that MLL-rearranged leukemias require CDK6, whereas CDK4 is dispensable, substantiating that individual cancers may require particular CDKs depending on their developmental origin and/or pattern of acquired mutations. For example, CDK6 is an oncogene that is amplified in subsets of patients with glioblastoma and medulloblastoma,40,41 and overexpression of CDK6 has been observed in lymphoid malignancies,42-44 whereas CDK4 is affected by DNA copy number gain or a rare activating mutation in patients with melanoma,45,46 and was selectively essential in mouse models of RAS-driven melanoma and lung adenocarcinoma.47,48
Supporting the idea that MLL-mediated leukemogenesis involves noncanonical functions of CDK6 not shared by CDK4, the preferential growth inhibition of MLL-rearranged cells by CDK6 depletion is not due to increased cell-cycle arrest but myelomonocytic differentiation, as evidenced by changes in cell morphology, immunophenotype, and lineage-specific gene expression that are not observed in other AML subtypes. Cdk6 has been shown to block maturation of normal murine myeloid progenitors through a noncatalytic mechanism.49 We now extend these findings by demonstrating that CDK6 possesses antidifferentiation activity in an aggressive subtype of human AML and demonstrate that this function requires its catalytic activity. More generally, our data underscore that an increasing repertoire of “atypical” and nonredundant CDK6 functions contribute to tumorigenesis in a context-specific manner. For example, recent studies indicate that cytokine-triggered chromatin association of CDK6 can modulate NF-κB–dependent gene expression in various cell types, including epithelial cancer and glioblastoma cell lines, and that Cdk6 is part of a transcription complex that induces the expression of Cdkn2A and the proangiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor A in a murine model of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.50,51
The effects of CDK6 knockdown are closely phenocopied by a small-molecule CDK4/6 inhibitor, PD-0332991. This observation not only links CDK6 kinase activity to arrested myeloid differentiation in MLL-rearranged AML, but also identifies CDK6 blockade as a therapeutic strategy with immediate translational potential, as PD-0332991 is already being evaluated clinically in other cancers and has received Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of breast cancer.31 Importantly, Cdk6 knockout mice and mice expressing a kinase-dead Cdk6 allele are viable and develop normally with only a minor defect in erythropoiesis and decreased thymic cellularity,52,53 indicating that CDK6 is not essential under physiological conditions. In line with this, PD-0332991 was associated with manageable toxicity in clinical trials that enrolled patients with solid-organ and hematologic malignancies.54-56 Thus, targeting CDK6 may provide a clinically applicable therapeutic window in MLL-rearranged leukemia. Notably, estrogen receptor positivity, and not cyclin D1 amplification and/or loss of CDKN2A, is the best predictor of response to PD-0332991 in breast cancer (R.S. Finn, J.P. Crown, I. Lang, K. Boer, I.M. Bondarenko, S.O. Kulyk, J. Ettl, R. Patel, T. Pinter, M. Schmidt, Y. Shparyk, A.R. Thummala, N.L. Voytko, A. Breazna, S.T. Kim, S. Randolph, D.J. Slamon, unpublished data, Cancer Therapy & Research Center-American Association for Cancer Research San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, December 4-8, 2012), underscoring the importance of biomarkers beyond cell-cycle regulation. Our data indicate that rearranged MLL represents such an alternative determinant of response to CDK6 inhibition.
Although our studies demonstrate that targeting Cdk6 significantly prolongs survival of mice with highly aggressive MLL-AF9–driven AML, it is likely that the context-specific properties of CDK6 inhibition may be best exploited when coupled with chemotherapy or other targeted agents, similar to the combination of PD-0332991 and letrozole in breast cancer or the combination of the differentiation agent all-trans retinoic acid and chemotherapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia.31,57 Of particular interest in this regard are approaches targeting general components of MLL-mediated transcription, such as the interaction between MLL and menin, H3K79 methylation by DOT1L, and the recognition of acetylated histones by BRD4, thereby affecting the expression of multiple MLL target genes.12,13,18,19 Concurrent inhibition of these “proximal” elements of MLL-mediated transformation and “distal” effectors, such as CDK6, may have additive or synergistic effects, because such an approach would interfere with the consequences of rearranged MLL on multiple levels. Furthermore, combining targeted therapies may allow dose reduction of individual agents, thereby minimizing toxicities, such as the perturbation of normal hematopoiesis after inhibition of Dot1l19,30,58,59 while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
In summary, our findings demonstrate that MLL-rearranged leukemias exhibit an overreliance on the activity of CDK6 to maintain an immature phenotype, supporting the view that certain cancers are preferentially dependent on specific CDK family members and functions. The data also indicate that therapies based on CDK inhibition should consider these contextual requirements, and suggest that patients with MLL-rearranged leukemias may benefit from CDK6 blockade, a notion that can readily be tested in the clinic.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Claudia Ball and Hanno Glimm for critical review of the manuscript; Ines Brunner, Sina Huntscha, Christina Miller, Stefanie Reinhart, Gina Walter, and the German Cancer Research Center Animal Laboratory and Flow Cytometry Facilities for excellent technical assistance; and Kristoffer Riecken, Carol Stocking, and Boris Fehse for the LeGO-C2 vector.
This work was supported by grants from the German Research Foundation (FR 2113/3-1 and FR 2113/4-1) (S.F.); a fellowship from the Heidelberg School of Oncology (T.P.); the BioRN Leading-Edge Cluster “Cell-Based and Molecular Medicine” funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the Dietmar Hopp Foundation (M.D.M.); an Emmy Noether Fellowship from the German Research Foundation (C.S.).
Footnotes
Presented in abstract form at the 55th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, New Orleans, LA, December 9, 2013.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: T.P., M.D.M., C.S., and S.F. designed the studies, performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; K.F., A.N., and S.L.P. performed experiments and analyzed data; and H.R.S., F.H.H., A.K., D.E.R., D.A.B., A.V.K., S.A.A., W.C.H., B.J.H., and S.M.S. contributed vital reagents or analytical tools and analyzed data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Stefan Fröhling, National Center for Tumor Diseases and German Cancer Research Center, Im Neuenheimer Feld 460, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany; e-mail: stefan.froehling@nct-heidelberg.de; and Claudia Scholl, Ulm University, Albert-Einstein-Allee 23, 89081, Ulm, Germany; e-mail: claudia.scholl@uni-ulm.de.
References
- 1.Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al. European LeukemiaNet. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115(3):453–474. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working Group. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116(3):354–365. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Meyer C, Hofmann J, Burmeister T, et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia. 2013;27(11):2165–2176. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Krauter J, Wagner K, Schäfer I, et al. Prognostic factors in adult patients up to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and translocations of chromosome band 11q23: individual patient data-based meta-analysis of the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Intergroup. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(18):3000–3006. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.7981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krivtsov AV, Twomey D, Feng Z, et al. Transformation from committed progenitor to leukaemia stem cell initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature. 2006;442(7104):818–822. doi: 10.1038/nature04980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Somervaille TC, Cleary ML. Identification and characterization of leukemia stem cells in murine MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2006;10(4):257–268. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Slany RK. The molecular biology of mixed lineage leukemia. Haematologica. 2009;94(7):984–993. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2008.002436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mohan M, Herz H-M, Takahashi Y-H, et al. Linking H3K79 trimethylation to Wnt signaling through a novel Dot1-containing complex (DotCom). Genes Dev. 2010;24(6):574–589. doi: 10.1101/gad.1898410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Biswas D, Milne TA, Basrur V, et al. Function of leukemogenic mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL) fusion proteins through distinct partner protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(38):15751–15756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111498108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tan J, Jones M, Koseki H, et al. CBX8, a polycomb group protein, is essential for MLL-AF9-induced leukemogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(5):563–575. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mueller D, Bach C, Zeisig D, et al. A role for the MLL fusion partner ENL in transcriptional elongation and chromatin modification. Blood. 2007;110(13):4445–4454. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-090514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittmann A, et al. Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature. 2011;478(7370):529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature10509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zuber J, Shi J, Wang E, et al. RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2011;478(7370):524–528. doi: 10.1038/nature10334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Harris WJ, Huang X, Lynch JT, et al. The histone demethylase KDM1A sustains the oncogenic potential of MLL-AF9 leukemia stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(4):473–487. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuo H-P, Wang Z, Lee D-F, et al. Epigenetic roles of MLL oncoproteins are dependent on NF-κB. Cancer Cell. 2013;24(4):423–437. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Argiropoulos B, Humphries RK. Hox genes in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Oncogene. 2007;26(47):6766–6776. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gröschel S, Schlenk RF, Engelmann J, et al. Deregulated expression of EVI1 defines a poor prognostic subset of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemias: a study of the German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group and the Dutch-Belgian-Swiss HOVON/SAKK Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(1):95–103. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.5505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Grembecka J, He S, Shi A, et al. Menin-MLL inhibitors reverse oncogenic activity of MLL fusion proteins in leukemia. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8(3):277–284. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, et al. Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O, Somervaille TC, Cleary ML. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature. 2008;455(7217):1205–1209. doi: 10.1038/nature07284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, et al. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is required for the development of leukemia stem cells in AML. Science. 2010;327(5973):1650–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.1186624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yeung J, Esposito MT, Gandillet A, et al. β-Catenin mediates the establishment and drug resistance of MLL leukemic stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(6):606–618. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Boehm JS, Hahn WC. Towards systematic functional characterization of cancer genomes. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(7):487–498. doi: 10.1038/nrg3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bernards R. A missing link in genotype-directed cancer therapy. Cell. 2012;151(3):465–468. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Scholl C, Fröhling S, Dunn IF, et al. Synthetic lethal interaction between oncogenic KRAS dependency and STK33 suppression in human cancer cells. Cell. 2009;137(5):821–834. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Barbie DA, Tamayo P, Boehm JS, et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature. 2009;462(7269):108–112. doi: 10.1038/nature08460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Weber K, Thomaschewski M, Warlich M, et al. RGB marking facilitates multicolor clonal cell tracking. Nat Med. 2011;17(4):504–509. doi: 10.1038/nm.2338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Faber K, Bullinger L, Ragu C, et al. CDX2-driven leukemogenesis involves KLF4 repression and deregulated PPARγ signaling. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):299–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI64745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kutner RH, Zhang XY, Reiser J. Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(4):495–505. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bernt KM, Zhu N, Sinha AU, et al. MLL-rearranged leukemia is dependent on aberrant H3K79 methylation by DOT1L. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(1):66–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dolgin E. Cancer’s true breakthroughs. Nat Med. 2013;19(6):660–663. doi: 10.1038/nm.3245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Armstrong SA, Golub TR, Korsmeyer SJ. MLL-rearranged leukemias: insights from gene expression profiling. Semin Hematol. 2003;40(4):268–273. doi: 10.1016/s0037-1963(03)00196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kumar AR, Li Q, Hudson WA, et al. A role for MEIS1 in MLL-fusion gene leukemia. Blood. 2009;113(8):1756–1758. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-163287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Faber J, Krivtsov AV, Stubbs MC, et al. HOXA9 is required for survival in human MLL-rearranged acute leukemias. Blood. 2009;113(11):2375–2385. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kroon EE, Krosl JJ, Thorsteinsdottir UU, Baban S, Buchberg AM, Sauvageau G. Hoxa9 transforms primary bone marrow cells through specific collaboration with Meis1a but not Pbx1b. EMBO J. 1998;17(13):3714–3725. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.13.3714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang QF, Wu G, Mi S, et al. MLL fusion proteins preferentially regulate a subset of wild-type MLL target genes in the leukemic genome. Blood. 2011;117(25):6895–6905. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-324699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guenther MG, Lawton LN, Rozovskaia T, et al. Aberrant chromatin at genes encoding stem cell regulators in human mixed-lineage leukemia. Genes Dev. 2008;22(24):3403–3408. doi: 10.1101/gad.1741408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jares PP, Colomer DD, Campo EE. Molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(10):3416–3423. doi: 10.1172/JCI61272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Canavese MM, Santo LL, Raje NN. Cyclin dependent kinases in cancer: potential for therapeutic intervention. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(7):451–457. doi: 10.4161/cbt.19589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Whiteway SL, Harris PS, Venkataraman S, et al. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 suppresses cell proliferation and enhances radiation sensitivity in medulloblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 2013;111(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-1000-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wiedemeyer WRW, Dunn IFI, Quayle SNS, et al. Pattern of retinoblastoma pathway inactivation dictates response to CDK4/6 inhibition in GBM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(25):11501–11506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001613107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chilosi M, Doglioni C, Yan Z, et al. Differential expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 in cortical thymocytes and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia. Am J Pathol. 1998;152(1):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hu MG, Deshpande A, Enos M, et al. A requirement for cyclin-dependent kinase 6 in thymocyte development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2009;69(3):810–818. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Corcoran MM, Mould SJ, Orchard JA, et al. Dysregulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 expression in splenic marginal zone lymphoma through chromosome 7q translocations. Oncogene. 1999;18(46):6271–6277. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(20):2135–2147. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wölfel TT, Hauer MM, Schneider JJ, et al. A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma. Science. 1995;269(5228):1281–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.7652577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kwong LN, Costello JC, Liu H, et al. Oncogenic NRAS signaling differentially regulates survival and proliferation in melanoma. Nat Med. 2012;18(10):1503–1510. doi: 10.1038/nm.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Puyol M, Martín A, Dubus P, et al. A synthetic lethal interaction between K-Ras oncogenes and Cdk4 unveils a therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fujimoto TT, Anderson KK, Jacobsen SEWS, Nishikawa S-IS, Nerlov CC. Cdk6 blocks myeloid differentiation by interfering with Runx1 DNA binding and Runx1-C/EBPalpha interaction. EMBO J. 2007;26(9):2361–2370. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Handschick K, Beuerlein K, Jurida L, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 is a chromatin-bound cofactor for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell. 2014;53(2):193–208. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C, et al. A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2013;24(2):167–181. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.07.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Malumbres MM, Sotillo RR, Santamaría DD, et al. Mammalian cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell. 2004;118(4):493–504. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hu MGM, Deshpande AA, Schlichting NN, et al. CDK6 kinase activity is required for thymocyte development. Blood. 2011;117(23):6120–6131. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-300517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dickson MA, Tap WD, Keohan ML, et al. Phase II trial of the CDK4 inhibitor PD0332991 in patients with advanced CDK4-amplified well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(16):2024–2028. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.5476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Leonard JP, LaCasce AS, Smith MR, et al. Selective CDK4/6 inhibition with tumor responses by PD0332991 in patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012;119(20):4597–4607. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-388298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Flaherty KT, Lorusso PM, Demichele A, et al. Phase I, dose-escalation trial of the oral cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991, administered using a 21-day schedule in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):568–576. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mi J-Q, Li J-M, Shen ZX, Chen SJ, Chen Z. How to manage acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26(8):1743–1751. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Jo SYS, Granowicz EME, Maillard II, Thomas DD, Hess JLJ. Requirement for Dot1l in murine postnatal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis by MLL translocation. Blood. 2011;117(18):4759–4768. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Nguyen ATA, He JJ, Taranova OO, Zhang YY. Essential role of DOT1L in maintaining normal adult hematopoiesis. Cell Res. 2011;21(9):1370–1373. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]