Key Points
VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios define the pathophysiological mechanisms that play a role in VWD and various VWF mutations.
A high VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio indicates increased clearance of VWF and a high FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratio decreased synthesis of VWF.
Abstract
During posttranslational modifications of von Willebrand factor (VWF), the VWF propeptide (VWFpp) is cleaved. The ratio between VWFpp and VWF antigen (VWF:Ag) and the ratio between factor VIII (FVIII:C) and VWF:Ag may be used to assess synthesis and clearance of VWF. We analyzed the contribution of VWFpp and ratios of VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag in the pathophysiological characterization of type 1 von Willebrand disease (VWD) in the Molecular and Clinical Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Type 1 VWD (MCMDM-1VWD) study. The VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios were increased among patients compared with unaffected family members and healthy controls. The VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio was higher in individuals heterozygous for missense mutations than in those heterozygous for null alleles. In contrast, the FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratio was highest among heterozygotes for VWF null alleles. The ratios of VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag indicate that the pathophysiological mechanisms of type 1 VWD include reduced production and accelerated clearance of VWF, but that often a combination of both mechanisms is implicated.
Introduction
von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a bleeding disorder caused by inherited quantitative (types 1 and 3) or qualitative (type 2) defects of von Willebrand factor (VWF).1 VWF supports platelet adhesion and carries factor VIII (FVIII).2 VWF is synthesized as a pre-pro-VWF precursor protein. After cleavage of the signal peptide, the pro-VWF dimerizes in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via disulfide bridges at the carboxy-terminal cysteine knot (CK).2 In the Golgi, pro-VWF dimers multimerize via disulfide bridges between D′D3 domains. Subsequently, the VWF propeptide (VWFpp) is cleaved but stays noncovalently attached to VWF, only to become dissociated after release into the circulation.2 VWF and VWFpp are secreted in equimolar amounts.2,3
Because of the different half-lives of VWFpp (2 hours) and VWF (8-12 hours), the ratio between VWFpp and VWF antigen (VWF:Ag) in plasma can be used to assess synthesis, secretion, and clearance rates of VWF.4-7 We have reported an increased VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio in 19 individuals of the Molecular and Clinical Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Type 1 VWD (MCMDM-1VWD) study in whom the response to desmopressin showed a decreased VWF half-life.8 Some other type 1 VWD patients with increased clearance of VWF could be identified by an increased VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio.9,10
While VWFpp and VWF are cleared independently, FVIII is in complex with VWF and their half-lives are related. The ratio between FVIII coagulant activity (FVIII:C) and VWF:Ag (FVIII:C/VWF:Ag) may be used in addition to the VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio—FVIII:C/VWF:Ag is increased when VWF synthesis is reduced but the ratio remains 1 when VWF is cleared faster.11-13 Opposing results are obtained for VWFpp/VWF:Ag, which will remain unchanged with reduced synthesis, but will increase with reduced half-life of VWF.
Using the VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios, we have investigated the pathophysiological mechanisms involved in type 1 VWD.
Methods
In the European MCMDM-1VWD study, 744 individuals, including index cases (ICs), affected family members (AFMs), and unaffected family members (UFMs), from 154 families previously diagnosed with type 1 VWD as well as healthy controls (HCs) were recruited. Local ethical review committees approved the study. Written informed consent was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The evaluation of phenotype and genotype was reported previously.8,14-20 VWF:Ag, VWF ristocetin cofactor activity (VWF:RCo), FVIII:C, VWF multimers, ABO blood group genotypes, and VWF mutations were determined as described.14-16,19,21 VWFpp antigen was measured in 387 HCs and in all remaining ICs (n = 137), AFMs (n = 264), and UFMs (n = 290) for whom plasma samples were available by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using antibodies from Sanquin (Amsterdam, The Netherlands).4
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics 20.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY). As phenotypic data were not normally distributed, even after logarithmic transformation, median values and interquartile ranges were used as indices of centrality and dispersion. Differences were tested by nonparametric tests (Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis test). Results were plotted using GraphPad Prism 4.00 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA).
Results and discussion
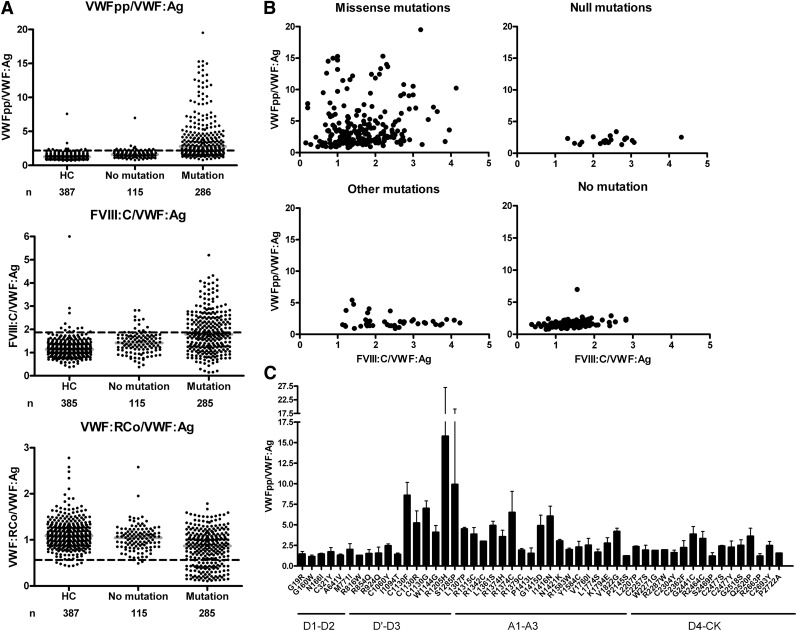
It has been described in a selected subset of VWD patients that the VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio can identify VWF with decreased half-life.8-10 We now report on VWFpp and the ratios of VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag in the entire MCMDM-1VWD study (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website). VWFpp was lower in ICs and AFMs than in HCs (P < .001), although less marked than the VWF:Ag reduction. VWFpp/VWF:Ag was increased for ICs and AFMs compared with HCs and this was also observed for FVIII:C/VWF:Ag (P < .001).
ABO blood group determines VWF and FVIII levels via VWF clearance.22,23 As a reflection of increased clearance FVIII:C, VWF:Ag and VWF:RCo levels were lower (P < .001) in HCs with blood group O compared with non-O (supplemental Table 2). Blood group did not influence FVIII:C/VWF:Ag, supporting the view that VWF and FVIII are cleared as a complex.13 No difference was observed in the VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio between HCs with blood group O and non-O, indicating a proportional decrease of VWF:Ag and VWF:RCo in blood group O and no suggestion of preferential clearance or proteolysis of large multimers in HCs with blood group O. In HCs, the VWFpp levels were not influenced by blood group, whereas VWFpp/VWF:Ag was clearly increased for blood group O in line with more rapid clearance of mature VWF.7
VWFpp and ratios of VWFpp/VWF:Ag, FVIII:C/VWF:Ag and VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag were analyzed after stratification for multimer pattern and mutation status (Table 1, Figure 1). In the MCMDM-1VWD cohort, subtle multimer abnormalities were reported in 38% of the ICs, and these individuals had more severe phenotypes, higher penetrance, a greater extent of linkage to the VWF gene locus, and mutations identified in all cases.14,16,19,21 The increased VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio was particularly raised (median 4.3) in patients with abnormal multimers and mutations (Table 1). An increased VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio was a good predictor of VWD patients with mutations in the VWF gene (Figure 1A): a VWFpp/VWF:Ag >3 had a positive predictive value for the presence of a VWF mutation of 98% with a specificity of 99% in the entire cohort of patients and family members. The VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio was decreased in the group with abnormal multimers (median 0.6, P < .001); however, the large coefficient of variation for VWF:RCo assays reduces the significance of this ratio when VWF levels are low. Among the UFMs, there were 31 individuals classified as unaffected but with a VWF mutation identified (Table 1). Those nonpenetrant cases had slightly higher VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios than UFMs without a mutation (P values .013 and .008 respectively, Table 1). Patients with mutations in families showing complete cosegregation between VWF gene and disease phenotype had higher VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios than patients from families with incomplete cosegregation (Table 1).
Table 1.
Stratification by multimer pattern and mutation status, linkage, and type of mutation
| Multimer pattern19 | Mutation identified | n | VWFpp,U/dL | VWFpp/VWF:Ag | FVIII:C/VWF:Ag | VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC + AFM | Normal | No | 113 | 92 (81-108) | 1.6 (1.3-1.9) | 1.4 (1.1-1.7) | 1.1 (0.9-1.2) |
| Yes | 134 | 81 (64-101) | 2.0 (1.5-2.4) | 1.7 (1.2-2.3)* | 1.0 (0.9-1.2) | ||
| Abnormal | Yes | 150 | 79 (65-100) | 4.3 (2.9-7.0) | 1.8 (1.2-2.5) | 0.6 (0.3-0.9)† | |
| UFM | Normal | No | 255 | 111 (98-128) | 1.2 (1.0-1.5) | 1.2 (0.9-1.4) | 1.0 (0.8-1.2) |
| Yes | 31 | 115 (97-132) | 1.4 (1.1-1.8) | 1.3 (1.1-1.7) | 0.9 (0.8-1.2) | ||
| Linkage of mutation‡ | |||||||
| Cosegregation | 174 | 78 (65-99) | 3.3 (2.0-5.4) | 1.9 (1.3-2.6)§ | 0.8 (0.4-1.1) | ||
| No cosegregation | 57 | 80 (63-103) | 2.4 (1.6-4.0) | 1.6 (1.0-2.0) | 1.0 (0.6-1.2)║ | ||
| P cosegregation vs no cosegregation | 0.786 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.11 | |||
| Type of mutation | |||||||
| Missense mutations | 228 | 89 (73-109) | 2.8 (1.8-5.3) | 1.6 (1.1-2.1)¶ | 0.8 (0.5-1.1)¶ | ||
| “Null” mutations# | 20 | 72 (63-85) | 2.0 (1.7-2.4) | 2.4 (2.0-2.8) | 1.1 (1.0-1.3) | ||
| HC | 387 | 118 (104-136) | 1.2 (1.0-1.5) | 1.1 (1.0-1.3)** | 1.1 (0.9-1.3) | ||
| P missense vs null | 0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |||
Results are indicated as median (25th to 75th percentile).
n = 133.
n = 149.
Linkage was defined as complete cosegregation (pedigrees with no phenocopies and fully penetrant) or incomplete cosegregation (pedigrees with either phenocopies or nonpenetrance).14
n = 173.
n = 56.
n = 227.
Comprise premature stop codons caused by nonsense mutations, frame shifts (small deletions and insertions), and out-of-frame splice site mutations.
n = 385.
Figure 1.
Ratios of VWF, VWFpp, and FVIII:C. (A) Ratios of VWFpp/VWF:Ag, FVIII:C/VWF:Ag, and VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag are shown for HCs, patients without a mutation identified (No mutation), and patients with a mutation identified in the VWF gene (Mutation). Patients represent the combined results of ICs and affected family members (IC + AFM); the ICs and AFMs were combined as there were no significant differences between the groups. The horizontal gray lines indicate median ratios. The dashed lines indicate the upper limit of the normal range for VWFpp/VWF:Ag (97.5th percentile is 2.2) and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag (97.5th percentile is 1.9) and the lower limit of the normal range for VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag (2.5th percentile is 0.6). For a better graphic representation, 4 outliers with very high ratios in the Mutation group for VWFpp/VWF:Ag and 2 in the Mutation group for FVIII:C/VWF:Ag were omitted. All groups differed significantly from each other (all comparisons P < .001 with the exception of VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag HC vs No mutation, P = .0224). (B) Scatter plots of FVIII:C/VWF:Ag vs VWFpp/VWF:Ag for missense mutations (n = 224, 4 outliers were omitted for better graphic representation), null mutations (n = 20), other mutations (n = 42), and for patients with no mutation (n = 115). The group of “other mutations” comprises putative splice site mutations and changes in the 5′ untranslated region that have not yet been proven by molecular studies to result in null alleles; however, the FVIII:C/VWF:Ag suggests indeed a defect of synthesis in many of them. (C) For all individuals heterozygous for a single missense mutation, the mean (+SD) VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio is shown. At a few codons, different substitutions were identified (p.C1130F/R/G, p.R1374H/C, p.C2477S/Y) that are listed separately as the VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio differed for each amino acid substitution. The number of individuals carrying a specific mutation ranged from 1 to 27.
VWFpp in heterozygotes for VWF null mutations was approximately half of that in HCs, reflecting reduced synthesis (Table 1). A high FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratio (median 2.4), identifying reduced VWF synthesis, was seen in carriers of null alleles (Table 1, Figure 1B). The FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratio was above the upper limit of the normal range (1.9) in 80% of these heterozygotes. Missense mutations demonstrated the highest VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio, reflecting faster clearance of abnormal mutant VWF, although not all missense mutations lead to increased clearance (Table 1, Figure 1B). In heterozygotes for VWF missense mutations, there was an intermediate reduction in VWFpp level and increase in FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratio (median 1.6) indicating that missense mutations partly also cause reduced synthesis and/or secretion. Thus, missense mutations can cause a combined defect of reduced synthesis and increased clearance (Figure 1B). The extent of increased clearance was not the same for all missense mutations, and the highest VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratios clustered in the VWF D3 and A1 domains (Figure 1C). Overall, the ratios in most patients with no mutation fell within the normal range (Figure 1A-B) and no clear mechanism could be deduced, but in some of those patients the defect was mainly of reduced synthesis whereas 1 patient had primarily increased clearance (Figure 1B). For a group of other mutations, including putative splice site mutations and changes in the 5′ untranslated region where the pathogenic mechanism had not been fully characterized at the molecular level, a defect in synthesis could be deduced in the majority (Figure 1B).
In conclusion, the VWFpp/VWF:Ag and FVIII:C/VWF:Ag ratios define the pathophysiological mechanisms that play a role in VWD and various types of VWF mutations. Clinical implications of these findings range from identifying increased clearance of VWF, which is important when considering desmopressin treatment, to discrimination between low VWF levels due to blood group O versus VWF null alleles.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sanquin (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for providing the antibodies CLB-Pro 35 and CLB-Pro 14.3 for measurement of VWFpp.
This work was supported in part by the European Community under the Fifth Framework Programme (QLG1-CT-2000-00387).
Appendix: study group members
The members of the MCMDM-1VWD Study Group are:
Ian Peake, Sheffield, UK; Anne Goodeve, Sheffield, UK; Francesco Rodeghiero, Vicenza, Italy; Giancarlo Castaman, Vicenza, Italy; Alberto Tosetto, Vicenza, Italy; Augusto B. Federici, Milano, Italy; Javier Batlle, La Coruna, Spain; Dominique Meyer, Paris, France; Edith Fressinaud, Nantes, France; Claudine Mazurier, Lille, France; Jenny Goudemand, Lille, France; Jeroen Eikenboom, Leiden, The Netherlands; Reinhard Schneppenheim, Hamburg, Germany; Ulrich Budde, Hamburg, Germany; Jørgen Ingerslev, Aarhus, Denmark; Zdena Vorlova, Prague, Czech Republic; David Habart, Prague, Czech Republic; Lars Holmberg, Lund, Sweden; Stefan Lethagen, Malmö, Sweden; John Pasi, Leicester, UK; and Frank Hill, Birmingham, UK.
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: J.E. designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, analyzed and interpreted results, was lead author of the initial manuscript, revised manuscript drafts, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript; A.B.F., R.J.D., U.B., R.S., J.B., M.T.C., and J.G. designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript; G.C. designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, revised manuscript drafts, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript; F.R. initiated, coordinated, and designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript; I.P. initiated, coordinated, and designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, revised manuscript drafts, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript; and A.G. initiated, coordinated, and designed the study, collected data, performed laboratory analyses, analyzed and interpreted results, revised manuscript drafts, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for A.B.F. is Hematology and Transfusion Medicine, L. Sacco University Hospital and Department of Clinical and Community Sciences, University of Milan, Milan, Italy.
A list of the the MCMDM-1VWD Study Group members appears in the “Appendix.”
Correspondence: Jeroen Eikenboom, Einthoven Laboratory for Experimental Vascular Medicine, Department of Thrombosis and Hemostasis, C7-Q, Leiden University Medical Center, PO Box 9600, 2300 RC Leiden, The Netherlands; e-mail: h.c.j.eikenboom@LUMC.nl.
References
- 1.Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JC, et al. Working Party on von Willebrand Disease Classification. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(10):2103–2114. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sadler JE. Biochemistry and genetics of von Willebrand factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:395–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wagner DD, Fay PJ, Sporn LA, et al. Divergent fates of von Willebrand factor and its propolypeptide (von Willebrand antigen II) after secretion from endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84(7):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Borchiellini A, Fijnvandraat K, ten Cate JW, et al. Quantitative analysis of von Willebrand factor propeptide release in vivo: effect of experimental endotoxemia and administration of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin in humans. Blood. 1996;88(8):2951–2958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vischer UM, Ingerslev J, Wollheim CB, et al. Acute von Willebrand factor secretion from the endothelium in vivo: assessment through plasma propeptide (vWf:AgII) Levels. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77(2):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van Mourik JA, Boertjes R, Huisveld IA, et al. von Willebrand factor propeptide in vascular disorders: a tool to distinguish between acute and chronic endothelial cell perturbation. Blood. 1999;94(1):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nossent AY, VAN Marion V, VAN Tilburg NH, et al. von Willebrand factor and its propeptide: the influence of secretion and clearance on protein levels and the risk of venous thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(12):2556–2562. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haberichter SL, Castaman G, Budde U, et al. Identification of type 1 von Willebrand disease patients with reduced von Willebrand factor survival by assay of the VWF propeptide in the European study: molecular and clinical markers for the diagnosis and management of type 1 VWD (MCMDM-1VWD). Blood. 2008;111(10):4979–4985. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-110940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schooten CJ, Tjernberg P, Westein E, et al. Cysteine-mutations in von Willebrand factor associated with increased clearance. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(10):2228–2237. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Haberichter SL, Balistreri M, Christopherson P, et al. Assay of the von Willebrand factor (VWF) propeptide to identify patients with type 1 von Willebrand disease with decreased VWF survival. Blood. 2006;108(10):3344–3351. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-015065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lian EC, Deykin D. Diagnosis of von Willebrand’s disease. A comparative study of diagnostic tests on nine families with von Willebrand’s disease and its differential diagnosis from hemophilia and thrombocytopathy. Am J Med. 1976;60(3):344–356. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90750-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miller CH, Graham JB, Goldin LR, et al. Genetics of classic von Willebrand’s disease. II. Optimal assignment of the heterozygous genotype (diagnosis) by discriminant analysis. Blood. 1979;54(1):137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eikenboom JC, Castaman G, Kamphuisen PW, et al. The factor VIII/von Willebrand factor ratio discriminates between reduced synthesis and increased clearance of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 2002;87(2):252–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eikenboom J, Van Marion V, Putter H, et al. Linkage analysis in families diagnosed with type 1 von Willebrand disease in the European study, molecular and clinical markers for the diagnosis and management of type 1 VWD. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(4):774–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tosetto A, Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, et al. A quantitative analysis of bleeding symptoms in type 1 von Willebrand disease: results from a multicenter European study (MCMDM-1 VWD). J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(4):766–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goodeve A, Eikenboom J, Castaman G, et al. Phenotype and genotype of a cohort of families historically diagnosed with type 1 von Willebrand disease in the European study, Molecular and Clinical Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Type 1 von Willebrand Disease (MCMDM-1VWD). Blood. 2007;109(1):112–121. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-020784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tosetto A, Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, et al. Impact of plasma von Willebrand factor levels in the diagnosis of type 1 von Willebrand disease: results from a multicenter European study (MCMDM-1VWD). J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(4):715–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Castaman G, Lethagen S, Federici AB, et al. Response to desmopressin is influenced by the genotype and phenotype in type 1 von Willebrand disease (VWD): results from the European Study MCMDM-1VWD. Blood. 2008;111(7):3531–3539. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-109231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Budde U, Schneppenheim R, Eikenboom J, et al. Detailed von Willebrand factor multimer analysis in patients with von Willebrand disease in the European study, molecular and clinical markers for the diagnosis and management of type 1 von Willebrand disease (MCMDM-1VWD). J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6(5):762–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.02945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eikenboom J, Hilbert L, Ribba AS, et al. Expression of 14 von Willebrand factor mutations identified in patients with type 1 von Willebrand disease from the MCMDM-1VWD study. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7(8):1304–1312. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hampshire DJ, Burghel GJ, Goudemand J, et al. EU-VWD and ZPMCB-VWD study groups. Polymorphic variation within the VWF gene contributes to the failure to detect mutations in patients historically diagnosed with type 1 von Willebrand disease from the MCMDM-1VWD cohort. Haematologica. 2010;95(12):2163–2165. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.027177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Millar CM, Brown SA. Oligosaccharide structures of von Willebrand factor and their potential role in von Willebrand disease. Blood Rev. 2006;20(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2005.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Morelli VM, de Visser MC, van Tilburg NH, et al. ABO blood group genotypes, plasma von Willebrand factor levels and loading of von Willebrand factor with A and B antigens. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(4):534–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]