Abstract
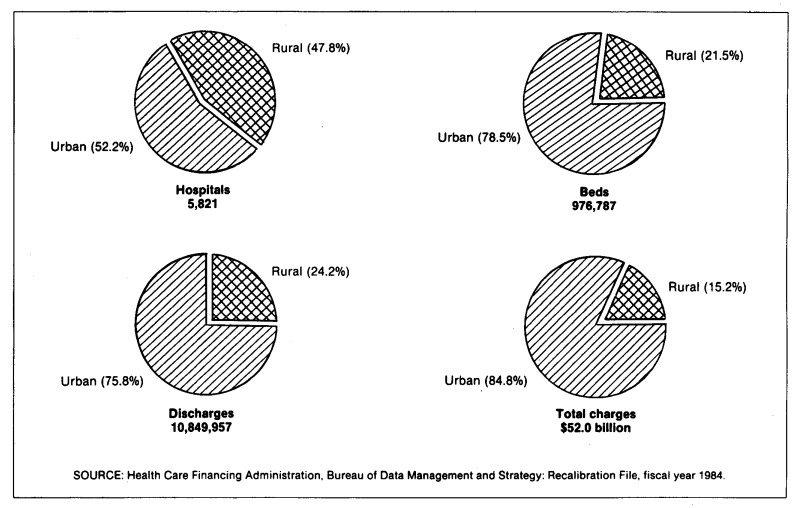
When the Health Care Financing Administration implemented the Medicare prospective payment system (PPS), the payment rates for inpatient hospital operating costs were derived on an urban and rural basis within each region. The rates were also adjusted for area wage levels and other factors affecting hospital costs. The effect of PPS on rural hospitals is of widespread interest. This article provides data on rural and urban hospital facilities, utilization, and charges, as of April 1985. Almost 48 percent of the 5,821 short stay hospitals included in the PPS recalibration file for Federal fiscal year 1984 are located in rural areas. Rural and urban areas are designated by the Executive Office of Management and Budget or, in some instances, by regulation.
Differences
Comparison of facilities and rates
Although about equal in number nationally, rural hospitals differ markedly from urban hospitals in other characteristics and utilization. Rural hospitals are much smaller—less than one-third the size of urban hospitals in average bed size (76 beds to 252 beds per hospital). Rural hospitals have about one-fourth the total number (or 2.6 million) of Medicare discharges. Rural hospitals have a utilization rate (as measured by Medicare discharges per hospital), about one-third that for urban hospitals, 945 versus 2,704. The average length of stay for rural hospitals is two days shorter per Medicare discharge (7.4 days and 9.5 days, respectively). Rural hospitals account for only 15 percent of the more than $52 billion in total inpatient charges for Medicare stays.
Charges per discharge
Total charges per discharge in rural hospitals are only slightly more than one-half (56 percent) of total charges in urban hospitals, ($3,007 versus $5,367). Ancillary charges per discharge in rural hospitals follow a similar pattern ($1,782 versus $3,072). As a percent of total charges, ancillary charges are slightly higher in rural hospitals than in urban hospitals, 59 percent and 57 percent, respectively.
Case-mix index
The average case-mix index (CMI) reflects the relative costliness of treating a mix of cases compared to a national mix of cases. For rural hospitals, the CMI is 1.0229, compared to an average of 1.1423 for urban hospitals.
State differences
Distribution of hospitals
The distribution of rural and urban hospitals by State varies widely. The District of Columbia, New Jersey, and Rhode Island are classified as completely urban and have no rural hospitals. Another 14 States have less than 50 percent of the total hospitals classified as rural hospitals. Arizona and Indiana have an equal number of each. The remaining 32 States have a higher proportion of rural hospitals than urban hospitals, with Idaho, Montana, and South Dakota having more than 90 percent of their hospitals classified as rural.
Discharges
More than 50 percent of all Medicare discharges from rural hospitals occur in just 14 of the 48 States that have rural hospitals. In three of these States— Idaho, Mississippi, and Vermont—rural hospital discharges exceed 75 percent of the total number of discharges. In contrast, fewer than 5 percent of the discharges in California, Connecticut, and Massachusetts are from rural hospitals. The range of variation in the number of Medicare discharges per hospital is large from 134 discharges per rural hospital in Alaska to 4,857 discharges per urban hospital in Delaware.
Average length of stay
Variation in the average length of stay (ALOS) is significant between States, and between rural and urban hospitals within States. New York has the longest ALOS, 13.7 days, comprised of 13.9 days for urban hospitals, and 12.2 days for rural hospitals. Short-stay hospitals in Idaho have the shortest ALOS, 6.3 days. The State of Oregon has the shortest ALOS for urban hospitals, 6.6 days, and Utah has the shortest ALOS for rural hospitals, 5.4 days.
Nationally, the difference in ALOS between urban and rural hospitals is 2.1 days. Of the 48 States that have rural hospitals, 40 States have absolute differences between urban and rural hospital ALOS lower than the absolute difference for the national urban and rural ALOS. The difference in ALOS between urban and rural hospitals in the State of Idaho is a mere one-half day; the differences in the States of Alaska and Hawaii approach 3 days.
Total charges per discharge
Total charges per discharge by State for all hospitals are nearly three times higher in the District of Columbia ($8,659) than in Mississippi ($3,050). Total charges per discharge are higher in urban hospitals than in rural hospitals in every State. The differences in two States, West Virginia and New Hampshire, are minimal, where charges in rural hospitals are 80 and 94 percent of charges in urban hospitals, respectively. At the other extreme, total charges per discharge in rural hospitals in Nevada reached only 40 percent of charges in urban hospitals. The lowest total charges per discharge for urban hospitals, $3,666, are found in the State of Arkansas. The highest average charges per discharge for urban hospitals are in the District of Columbia, $8,659. Minnesota has the lowest charges per discharge, $2,347, for rural hospitals, and California has the highest, $4,734.
Ancillary charges per discharge
Ancillary charges per discharge for all hospitals by State vary by a factor in excess of three. For example, ancillary charges per discharge in Nevada ($5,276) are three times higher than in Vermont ($1,695). For rural hospitals, Minnesota ($1,255) and California ($3,049) are at the extreme ends of the range of ancillary charges per discharge, as was the case for total charges per discharge. For urban hospital ancillary charges per discharge, the range is defined by the States of New Hampshire, $2,037 and Nevada, $5,713. By State, ancillary charges as a percent of total charges for rural hospitals are characterized by less variation, with Vermont beginning the range at 45 percent, and Louisiana limiting the range at 71 percent. The range for urban hospitals extends from 43 percent in New York to 72 percent in Nevada.
Figure 1. Percent distribution of rural and urban hospitals, beds, discharges, and total charges: Federal fiscal year 1984 Recalibration File.
Table 1. Number and percent distribution of urban and rural hospitals, by State: Federal fiscal year 19841.
| State | Total | Urban hospitals | Rural hospitals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | ||
| United States | 5,821 | 3,041 | 52.2 | 2,780 | 47.8 |
| Alabama | 129 | 56 | 43.4 | 73 | 56.6 |
| Alaska | 22 | 3 | 13.6 | 19 | 86.4 |
| Arizona | 72 | 36 | 50.0 | 36 | 50.0 |
| Arkansas | 96 | 19 | 19.8 | 77 | 80.2 |
| California | 486 | 425 | 87.4 | 61 | 12.6 |
| Colorado | 80 | 33 | 41.3 | 47 | 58.8 |
| Connecticut | 35 | 33 | 94.3 | 2 | 5.7 |
| Delaware | 7 | 3 | 42.9 | 4 | 57.1 |
| District of Columbia | 11 | 11 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Florida | 217 | 177 | 81.6 | 40 | 18.4 |
| Georgia | 166 | 68 | 41.0 | 98 | 59.0 |
| Hawaii | 19 | 9 | 47.4 | 10 | 52.6 |
| Idaho | 45 | 2 | 4.4 | 43 | 95.6 |
| Illinois | 240 | 149 | 62.1 | 91 | 37.9 |
| Indiana | 118 | 59 | 50.0 | 59 | 50.0 |
| Iowa | 130 | 26 | 20.0 | 104 | 80.0 |
| Kansas | 145 | 21 | 14.5 | 124 | 85.5 |
| Kentucky | 106 | 30 | 28.3 | 76 | 71.7 |
| Louisiana | 144 | 69 | 47.9 | 75 | 52.1 |
| Maine | 45 | 19 | 42.2 | 26 | 57.8 |
| Maryland | 53 | 46 | 86.8 | 7 | 13.2 |
| Massachusetts | 110 | 104 | 94.5 | 6 | 5.5 |
| Michigan | 204 | 124 | 60.8 | 80 | 39.2 |
| Minnesota | 171 | 55 | 32.2 | 116 | 67.8 |
| Mississippi | 118 | 15 | 12.7 | 103 | 87.3 |
| Missouri | 151 | 73 | 48.3 | 78 | 51.7 |
| Montana | 63 | 4 | 6.3 | 59 | 93.7 |
| Nebraska | 99 | 13 | 13.1 | 86 | 86.9 |
| Nevada | 24 | 13 | 54.2 | 11 | 45.8 |
| New Hampshire | 27 | 13 | 48.1 | 14 | 51.9 |
| New Jersey | 94 | 94 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| New Mexico | 49 | 11 | 22.4 | 38 | 77.6 |
| New York | 260 | 202 | 77.7 | 58 | 22.3 |
| North Carolina | 134 | 51 | 38.1 | 83 | 61.9 |
| North Dakota | 54 | 8 | 14.8 | 46 | 85.2 |
| Ohio | 194 | 126 | 64.9 | 68 | 35.1 |
| Oklahoma | 132 | 44 | 33.3 | 88 | 66.7 |
| Oregon | 75 | 34 | 45.3 | 41 | 54.7 |
| Pennsylvania | 228 | 181 | 79.4 | 47 | 20.6 |
| Rhode Island | 14 | 14 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| South Carolina | 73 | 33 | 45.2 | 40 | 54.8 |
| South Dakota | 63 | 5 | 7.9 | 58 | 92.1 |
| Tennessee | 147 | 69 | 46.9 | 78 | 53.1 |
| Texas | 471 | 241 | 51.2 | 230 | 48.8 |
| Utah | 39 | 16 | 41.0 | 23 | 59.0 |
| Vermont | 16 | 2 | 12.5 | 14 | 87.5 |
| Virginia | 102 | 56 | 54.9 | 46 | 45.1 |
| Washington | 105 | 56 | 53.3 | 49 | 46.7 |
| West Virginia | 66 | 19 | 28.8 | 47 | 71.2 |
| Wisconsin | 145 | 68 | 46.9 | 77 | 53.1 |
| Wyoming | 27 | 3 | 11.1 | 24 | 88.9 |
Prospective payment system recalibration file.
Table 2. Number of beds and average bed size of urban and rural hospitals, by State: Federal fiscal year 19841.
| State | Total | Urban | Rural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||
| Number of beds | Average bed size | Number of beds | Average bed size | Number of beds | Average bed size | |
| United States | 976,787 | 168 | 766,610 | 252 | 210,177 | 76 |
| Alabama | 19,345 | 150 | 13,809 | 247 | 5,536 | 76 |
| Alaska | 1,255 | 57 | 601 | 200 | 654 | 34 |
| Arizona | 10,419 | 145 | 8,309 | 231 | 2,110 | 59 |
| Arkansas | 10,892 | 113 | 4,928 | 259 | 5,964 | 77 |
| California | 82,109 | 169 | 78,967 | 186 | 3,142 | 52 |
| Colorado | 10,978 | 137 | 8,794 | 266 | 2,184 | 46 |
| Connecticut | 10,677 | 305 | 10,374 | 314 | 303 | 152 |
| Delaware | 2,026 | 289 | 1,408 | 469 | 618 | 155 |
| District of Columbia | 4,438 | 403 | 4,438 | 403 | 0 | — |
| Florida | 50,557 | 233 | 47,037 | 266 | 3,520 | 88 |
| Georgia | 24,552 | 148 | 16,227 | 239 | 8,325 | 85 |
| Hawaii | 2,356 | 124 | 1,796 | 200 | 560 | 56 |
| Idaho | 2,884 | 64 | 521 | 261 | 2,363 | 55 |
| Illinois | 55,549 | 231 | 46,525 | 312 | 9,024 | 99 |
| Indiana | 24,465 | 207 | 18,254 | 309 | 6,211 | 105 |
| Iowa | 14,827 | 114 | 7,954 | 306 | 6,873 | 66 |
| Kansas | 12,663 | 87 | 5,901 | 281 | 6,762 | 55 |
| Kentucky | 15,589 | 147 | 8,549 | 285 | 7,040 | 93 |
| Louisiana | 19,824 | 138 | 14,754 | 214 | 5,070 | 68 |
| Maine | 4,681 | 104 | 2,769 | 146 | 1,912 | 74 |
| Maryland | 14,876 | 281 | 13,872 | 302 | 1,004 | 143 |
| Massachusetts | 25,241 | 229 | 24,572 | 236 | 669 | 112 |
| Michigan | 38,183 | 187 | 32,132 | 259 | 6,051 | 76 |
| Minnesota | 18,783 | 110 | 13,117 | 238 | 5,666 | 49 |
| Mississippi | 12,858 | 109 | 3,471 | 231 | 9,387 | 91 |
| Missouri | 28,247 | 187 | 20,857 | 286 | 7,390 | 95 |
| Montana | 3,696 | 59 | 979 | 245 | 2,717 | 46 |
| Nebraska | 8,937 | 90 | 3,858 | 297 | 5,079 | 59 |
| Nevada | 3,409 | 142 | 3,033 | 233 | 376 | 34 |
| New Hampshire | 3,206 | 119 | 1,971 | 152 | 1,235 | 88 |
| New Jersey | 29,135 | 310 | 29,135 | 310 | 0 | — |
| New Mexico | 4,319 | 88 | 2,200 | 200 | 2,119 | 56 |
| New York | 73,493 | 283 | 67,126 | 332 | 6,367 | 110 |
| North Carolina | 23,163 | 173 | 13,483 | 264 | 9,680 | 117 |
| North Dakota | 3,753 | 70 | 1,545 | 193 | 2,208 | 48 |
| Ohio | 49,014 | 253 | 40,563 | 322 | 8,451 | 124 |
| Oklahoma | 14,434 | 109 | 8,932 | 203 | 5,502 | 63 |
| Oregon | 8,998 | 120 | 6,261 | 184 | 2,737 | 67 |
| Pennsylvania | 52,686 | 231 | 45,898 | 254 | 6,788 | 144 |
| Rhode Island | 3,465 | 248 | 3,465 | 248 | 0 | — |
| South Carolina | 11,204 | 153 | 7,079 | 215 | 4,125 | 103 |
| South Dakota | 3,776 | 60 | 1,200 | 240 | 2,576 | 44 |
| Tennessee | 25,149 | 171 | 18,671 | 271 | 6,478 | 83 |
| Texas | 63,724 | 135 | 51,188 | 212 | 12,536 | 55 |
| Utah | 4,351 | 112 | 3,405 | 213 | 946 | 41 |
| Vermont | 2,059 | 129 | 643 | 322 | 1,416 | 101 |
| Virginia | 21,627 | 212 | 15,978 | 285 | 5,649 | 123 |
| Washington | 11,820 | 113 | 9,386 | 168 | 2,434 | 50 |
| West Virginia | 10,069 | 153 | 4,688 | 247 | 5,381 | 114 |
| Wisconsin | 21,292 | 147 | 15,419 | 227 | 5,873 | 76 |
| Wyoming | 1,734 | 64 | 568 | 189 | 1,166 | 49 |
Prospective payment system recalibration file.
Table 3. Number and percent of Medicare discharges from urban and rural hospitals, by State: Federal fiscal year 19841.
| State | Total discharges | Urban hospital discharges | Rural hospital discharges | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | ||
| United States | 10,849,957 | 8,224,020 | 75.8 | 2,625,937 | 24.2 |
| Alabama | 218,616 | 153,048 | 70.0 | 65,568 | 30.0 |
| Alaska | 4,852 | 2,314 | 47.7 | 2,538 | 52.3 |
| Arizona | 122,380 | 102,643 | 83.9 | 19,737 | 16.1 |
| Arkansas | 157,476 | 66,347 | 42.1 | 91,129 | 57.9 |
| California | 912,430 | 870,446 | 95.4 | 41,984 | 4.6 |
| Colorado | 97,127 | 76,589 | 78.9 | 20,538 | 21.1 |
| Connecticut | 128,720 | 124,407 | 96.6 | 4,313 | 3.4 |
| Delaware | 23,427 | 14,571 | 62.2 | 8,856 | 37.8 |
| District of Columbia | 30,676 | 30,676 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Florida | 699,923 | 638,748 | 91.3 | 61,175 | 8.7 |
| Georgia | 271,506 | 163,479 | 60.2 | 108,027 | 39.8 |
| Hawaii | 23,862 | 18,226 | 76.4 | 5,636 | 23.6 |
| Idaho | 36,231 | 7,421 | 20.5 | 28,810 | 79.5 |
| Illinois | 540,106 | 423,031 | 78.3 | 117,075 | 21.7 |
| Indiana | 264,559 | 189,918 | 71.8 | 74,641 | 28.2 |
| Iowa | 154,012 | 77,202 | 50.1 | 76,810 | 49.9 |
| Kansas | 133,083 | 56,997 | 42.8 | 76,086 | 57.2 |
| Kentucky | 186,866 | 91,592 | 49.0 | 95,274 | 51.0 |
| Louisiana | 204,995 | 142,002 | 69.3 | 62,993 | 30.7 |
| Maine | 60,673 | 33,307 | 54.9 | 27,366 | 45.1 |
| Maryland | 160,007 | 144,788 | 90.5 | 15,219 | 9.5 |
| Massachusetts | 300,210 | 288,156 | 96.0 | 12,054 | 4.0 |
| Michigan | 401,317 | 323,615 | 80.6 | 77,702 | 19.4 |
| Minnesota | 194,341 | 124,490 | 64.1 | 69,851 | 35.9 |
| Mississippi | 159,399 | 39,099 | 24.5 | 120,300 | 75.5 |
| Missouri | 305,499 | 213,143 | 69.8 | 92,356 | 30.2 |
| Montana | 38,140 | 12,172 | 31.9 | 25,968 | 68.1 |
| Nebraska | 96,539 | 43,728 | 45.3 | 52,811 | 54.7 |
| Nevada | 33,752 | 29,864 | 88.5 | 3,888 | 11.5 |
| New Hampshire | 37,744 | 22,312 | 59.1 | 15,432 | 40.9 |
| New Jersey | 321,934 | 321,934 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| New Mexico | 44,195 | 21,970 | 49.7 | 22,225 | 50.3 |
| New York | 764,866 | 677,797 | 88.6 | 87,069 | 11.4 |
| North Carolina | 246,532 | 139,861 | 56.7 | 106,671 | 43.3 |
| North Dakota | 47,676 | 21,394 | 44.9 | 26,282 | 55.1 |
| Ohio | 453,186 | 374,353 | 82.6 | 78,833 | 17.4 |
| Oklahoma | 166,403 | 94,170 | 56.6 | 72,233 | 43.4 |
| Oregon | 120,989 | 83,754 | 69.2 | 37,235 | 30.8 |
| Pennsylvania | 678,550 | 582,355 | 85.8 | 96,195 | 14.2 |
| Rhode Island | 46,475 | 46,475 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| South Carolina | 124,892 | 79,602 | 63.7 | 45,290 | 36.3 |
| South Dakota | 44,173 | 15,405 | 34.9 | 28,768 | 65.1 |
| Tennessee | 299,096 | 208,245 | 69.6 | 90,851 | 30.4 |
| Texas | 674,777 | 505,110 | 74.9 | 169,667 | 25.1 |
| Utah | 37,523 | 29,268 | 78.0 | 8,255 | 22.0 |
| Vermont | 21,614 | 5,342 | 24.7 | 16,272 | 75.3 |
| Virginia | 221,233 | 146,549 | 66.2 | 74,684 | 33.8 |
| Washington | 167,003 | 130,642 | 78.2 | 36,361 | 21.8 |
| West Virginia | 123,400 | 52,836 | 42.8 | 70,564 | 57.2 |
| Wisconsin | 231,656 | 157,898 | 68.2 | 73,758 | 31.8 |
| Wyoming | 15,316 | 4,729 | 30.9 | 10,587 | 69.1 |
Prospective payment system recalibration file.
Table 4. Medicare discharges per urban and rural hospital, average length of stay, and case-mix index, by State: Federal fiscal year 19841.
| State | Total | Urban | Rural | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Discharges per hospital | ALOS in days | CMI | Discharges per hospital | ALOS in days | CMI | Discharges per hospital | ALOS in days | CMI | |
| United States | 1,864 | 9.0 | 1.1134 | 2,704 | 9.5 | 1.1423 | 945 | 7.4 | 1.0229 |
| Alabama | 1,695 | 8.1 | 1.0812 | 2,733 | 8.4 | 1.1169 | 898 | 7.2 | 0.9979 |
| Alaska | 221 | 7.8 | 1.0572 | 771 | 9.3 | 1.1358 | 134 | 6.5 | 0.9856 |
| Arizona | 1,700 | 7.8 | 1.1613 | 2,851 | 8.1 | 1.1837 | 548 | 6.5 | 1.0449 |
| Arkansas | 1,640 | 7.2 | 1.0531 | 3,492 | 7.9 | 1.1276 | 1,183 | 6.7 | 0.9988 |
| California | 1,877 | 7.6 | 1.1649 | 2,048 | 7.7 | 1.1684 | 688 | 6.2 | 1.0931 |
| Colorado | 1,214 | 7.7 | 1.1245 | 2,321 | 8.1 | 1.1464 | 437 | 6.4 | 1.0426 |
| Connecticut | 3,678 | 9.7 | 1.1944 | 3,770 | 9.7 | 1.1966 | 2,157 | 8.8 | 1.1302 |
| Delaware | 3,347 | 10.4 | 1.1038 | 4,857 | 11.0 | 1.1285 | 2,214 | 9.5 | 1.0632 |
| District of Columbia | 2,789 | 12.2 | 1.1956 | 2,789 | 12.2 | 1.1956 | 0 | — | — |
| Florida | 3,225 | 8.3 | 1.1346 | 3,609 | 8.5 | 1.1437 | 1,529 | 7.0 | 1.0400 |
| Georgia | 1,636 | 7.5 | 1.0964 | 2,404 | 8.1 | 1.1509 | 1,102 | 6.6 | 1.0139 |
| Hawaii | 1,256 | 8.7 | 1.2053 | 2,025 | 9.4 | 1.2463 | 564 | 6.6 | 1.0730 |
| Idaho | 805 | 6.3 | 1.1131 | 3,711 | 6.7 | 1.3119 | 670 | 6.2 | 1.0619 |
| Illinois | 2,250 | 9.6 | 1.1003 | 2,839 | 10.1 | 1.1271 | 1,287 | 7.8 | 1.0033 |
| Indiana | 2,242 | 8.8 | 1.1014 | 3,219 | 9.2 | 1.1363 | 1,265 | 7.7 | 1.0124 |
| Iowa | 1,185 | 8.0 | 1.1185 | 2,969 | 9.0 | 1.1924 | 739 | 6.9 | 1.0442 |
| Kansas | 918 | 7.7 | 1.1021 | 2,714 | 8.3 | 1.1974 | 614 | 7.2 | 1.0307 |
| Kentucky | 1,763 | 8.4 | 1.0696 | 3,053 | 9.2 | 1.1256 | 1,254 | 7.7 | 1.0158 |
| Louisiana | 1,424 | 7.8 | 1.0727 | 2,058 | 8.2 | 1.1194 | 840 | 6.7 | 0.9676 |
| Maine | 1,348 | 8.4 | 1.1096 | 1,753 | 9.2 | 1.1560 | 1,053 | 7.4 | 1.0531 |
| Maryland | 3,019 | 10.3 | 1.0968 | 3,148 | 10.4 | 1.0971 | 2,174 | 9.3 | 1.0938 |
| Massachusetts | 2,729 | 11.5 | 1.0876 | 2,771 | 11.6 | 1.0890 | 2,009 | 9.3 | 1.0539 |
| Michigan | 1,967 | 9.2 | 1.1085 | 2,610 | 9.5 | 1.1249 | 971 | 7.6 | 1.0400 |
| Minnesota | 1,136 | 7.5 | 1.1600 | 2,263 | 8.1 | 1.2235 | 602 | 6.5 | 1.0468 |
| Mississippi | 1,351 | 7.7 | 1.0148 | 2,607 | 8.5 | 1.1003 | 1,168 | 7.4 | 0.9870 |
| Missouri | 2,023 | 8.7 | 1.1173 | 2,920 | 9.3 | 1.1611 | 1,184 | 7.4 | 1.0161 |
| Montana | 605 | 6.9 | 1.1147 | 3,043 | 8.1 | 1.2339 | 440 | 6.4 | 1.0588 |
| Nebraska | 975 | 7.8 | 1.0793 | 3,364 | 8.7 | 1.1630 | 614 | 7.0 | 1.0100 |
| Nevada | 1,406 | 7.8 | 1.1737 | 2,297 | 8.0 | 1.1917 | 353 | 5.6 | 1.0353 |
| New Hampshire | 1,398 | 8.5 | 1.0913 | 1,716 | 8.9 | 1.0855 | 1,102 | 7.9 | 1.0998 |
| New Jersey | 3,425 | 12.0 | 1.1278 | 3,425 | 12.0 | 1.1278 | 0 | — | — |
| New Mexico | 902 | 7.2 | 1.1105 | 1,997 | 7.7 | 1.1838 | 585 | 6.8 | 1.0381 |
| New York | 2,942 | 13.7 | 1.0892 | 3,355 | 13.9 | 1.0980 | 1,501 | 12.2 | 1.0206 |
| North Carolina | 1,840 | 8.7 | 1.1218 | 2,742 | 9.2 | 1.1638 | 1,285 | 7.9 | 1.0667 |
| North Dakota | 883 | 7.7 | 1.0750 | 2,674 | 8.8 | 1.2036 | 571 | 6.7 | 0.9704 |
| Ohio | 2,336 | 9.2 | 1.1299 | 2,971 | 9.5 | 1.1509 | 1,159 | 7.8 | 1.0302 |
| Oklahoma | 1,261 | 7.7 | 1.0971 | 2,140 | 8.2 | 1.1635 | 821 | 7.1 | 1.0105 |
| Oregon | 1,613 | 6.4 | 1.1658 | 2,463 | 6.6 | 1.2073 | 908 | 6.0 | 1.0725 |
| Pennsylvania | 2,976 | 9.9 | 1.1197 | 3,217 | 10.1 | 1.1302 | 2,047 | 8.6 | 1.0561 |
| Rhode Island | 3,320 | 10.2 | 1.1638 | 3,320 | 10.2 | 1.1638 | 0 | — | — |
| South Carolina | 1,711 | 8.7 | 1.1144 | 2,412 | 9.0 | 1.1526 | 1,132 | 8.1 | 1.0472 |
| South Dakota | 701 | 7.2 | 1.0611 | 3,081 | 8.3 | 1.1931 | 496 | 6.6 | 0.9905 |
| Tennessee | 2,035 | 8.6 | 1.0677 | 3,018 | 9.1 | 1.1134 | 1,165 | 7.4 | 0.9629 |
| Texas | 1,433 | 8.0 | 1.1002 | 2,096 | 8.4 | 1.1389 | 738 | 6.9 | 0.9848 |
| Utah | 962 | 6.5 | 1.2264 | 1,829 | 6.8 | 1.2793 | 359 | 5.4 | 1.0392 |
| Vermont | 1,351 | 8.8 | 1.1206 | 2,671 | 9.9 | 1.3323 | 1,162 | 8.5 | 1.0511 |
| Virginia | 2,169 | 9.2 | 1.0932 | 2,617 | 9.7 | 1.1339 | 1,624 | 8.3 | 1.0132 |
| Washington | 1,591 | 6.6 | 1.1828 | 2,333 | 7.0 | 1.2110 | 742 | 5.5 | 1.0817 |
| West Virginia | 1,870 | 8.1 | 1.0533 | 2,781 | 8.7 | 1.0984 | 1,501 | 7.6 | 1.0195 |
| Wisconsin | 1,598 | 8.3 | 1.1285 | 2,322 | 8.8 | 1.1576 | 958 | 7.0 | 1.0663 |
| Wyoming | 567 | 7.4 | 1.0373 | 1,576 | 9.2 | 1.1181 | 441 | 6.6 | 1.0012 |
Prospective payment system recalibration file.
NOTES: ALOS is average length of stay. CMI is case-mix index.
Table 5. Total charge per Medicare discharge, ancillary charge, and percent of ancillary charge to total for rural and urban hospitals, by State: Federal fiscal year 19841.
| State | Total | Urban | Rural | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total charge per discharge | Ancillary charge per discharge | Percent | Total charge per discharge | Ancillary charge per discharge | Percent | Total charge per discharge | Ancillary charge per discharge | Percent | |
| United States | $4,796 | $2,760 | 57.5 | $5,367 | $3,072 | 57.2 | $3,007 | $1,782 | 59.3 |
| Alabama | 4,454 | 3,032 | 68.1 | 5,009 | 3,400 | 67.9 | 3,159 | 2,174 | 68.8 |
| Alaska | 5,320 | 2,506 | 47.1 | 6,848 | 3,180 | 46.4 | 3,926 | 1,891 | 48.2 |
| Arizona | 4,907 | 3,037 | 61.9 | 5,227 | 3,220 | 61.6 | 3,246 | 2,085 | 64.2 |
| Arkansas | 3,063 | 1,951 | 63.7 | 3,666 | 2,349 | 64.1 | 2,625 | 1,661 | 63.3 |
| California | 6,533 | 3,930 | 60.2 | 6,620 | 3,973 | 60.0 | 4,734 | 3,049 | 64.4 |
| Colorado | 4,449 | 2,615 | 58.8 | 4,808 | 2,854 | 59.4 | 3,111 | 1,726 | 55.5 |
| Connecticut | 4,939 | 2,713 | 54.9 | 4,985 | 2,745 | 55.1 | 3,633 | 1,778 | 48.9 |
| Delaware | 4,804 | 2,359 | 49.1 | 5,390 | 2,544 | 47.2 | 3,839 | 2,055 | 53.5 |
| District of Columbia | 8,659 | 4,368 | 50.4 | 8,659 | 4,368 | 50.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Florida | 5,327 | 3,638 | 68.3 | 5,468 | 3,734 | 68.3 | 3,854 | 2,635 | 68.4 |
| Georgia | 3,631 | 2,397 | 66.0 | 4,191 | 2,744 | 65.5 | 2,785 | 1,872 | 67.2 |
| Hawaii | 5,193 | 2,959 | 57.0 | 5,818 | 3,353 | 57.6 | 3,171 | 1,685 | 53.2 |
| Idaho | 3,169 | 1,828 | 57.7 | 3,837 | 2,263 | 59.0 | 2,996 | 1,716 | 57.3 |
| Illinois | 5,724 | 3,212 | 56.1 | 6,428 | 3,597 | 56.0 | 3,181 | 1,820 | 57.2 |
| Indiana | 3,712 | 2,054 | 55.3 | 4,156 | 2,323 | 55.9 | 2,583 | 1,371 | 53.1 |
| Iowa | 3,594 | 2,051 | 57.1 | 4,553 | 2,617 | 57.5 | 2,631 | 1,483 | 56.4 |
| Kansas | 3,607 | 2,126 | 58.9 | 4,853 | 3,053 | 62.9 | 2,673 | 1,431 | 53.5 |
| Kentucky | 3,610 | 1,975 | 54.7 | 4,315 | 2,292 | 53.1 | 2,933 | 1,671 | 57.0 |
| Louisiana | 4,146 | 2,810 | 67.8 | 4,690 | 3,138 | 66.9 | 2,922 | 2,069 | 70.8 |
| Maine | 4,321 | 2,405 | 55.7 | 4,895 | 2,744 | 56.0 | 3,621 | 1,993 | 55.0 |
| Maryland | 4,308 | 2,076 | 48.2 | 4,451 | 2,137 | 48.0 | 2,954 | 1,493 | 50.5 |
| Massachusetts | 5,474 | 2,842 | 51.9 | 5,544 | 2,877 | 51.9 | 3,788 | 1,995 | 52.7 |
| Michigan | 5,509 | 2,874 | 52.2 | 6,019 | 3,134 | 52.1 | 3,388 | 1,793 | 52.9 |
| Minnesota | 3,663 | 2,040 | 55.7 | 4,402 | 2,480 | 56.3 | 2,347 | 1,255 | 53.5 |
| Mississippi | 3,050 | 2,121 | 69.5 | 4,042 | 2,908 | 71.9 | 2,728 | 1,865 | 68.4 |
| Missouri | 4,674 | 2,868 | 61.4 | 5,378 | 3,313 | 61.6 | 3,052 | 1,842 | 60.3 |
| Montana | 3,477 | 1,968 | 56.6 | 4,681 | 2,720 | 58.1 | 2,912 | 1,615 | 55.4 |
| Nebraska | 3,493 | 2,216 | 63.4 | 4,824 | 3,229 | 66.9 | 2,390 | 1,377 | 57.6 |
| Nevada | 7,349 | 5,276 | 71.8 | 7,890 | 5,713 | 72.4 | 3,193 | 1,922 | 60.2 |
| New Hampshire | 3,848 | 1,967 | 51.1 | 3,940 | 2,037 | 51.7 | 3,714 | 1,865 | 50.2 |
| New Jersey | 4,570 | 2,141 | 46.8 | 4,570 | 2,141 | 46.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| New Mexico | 4,298 | 2,717 | 63.2 | 5,134 | 3,295 | 64.2 | 3,471 | 2,146 | 61.8 |
| New York | 5,922 | 2,530 | 42.7 | 6,246 | 2,647 | 42.4 | 3,403 | 1,620 | 47.6 |
| North Carolina | 3,543 | 2,129 | 60.1 | 3,983 | 2,393 | 60.1 | 2,966 | 1,784 | 60.2 |
| North Dakota | 3,662 | 2,167 | 59.2 | 4,761 | 2,935 | 61.6 | 2,768 | 1,542 | 55.7 |
| Ohio | 4,742 | 2,460 | 51.9 | 5,068 | 2,618 | 51.7 | 3,197 | 1,711 | 53.5 |
| Oklahoma | 4,013 | 2,646 | 65.9 | 4,785 | 3,227 | 67.4 | 3,005 | 1,887 | 62.8 |
| Oregon | 3,942 | 2,183 | 55.4 | 4,242 | 2,347 | 55.3 | 3,265 | 1,814 | 55.6 |
| Pennsylvania | 6,153 | 3,388 | 55.1 | 6,526 | 3,601 | 55.2 | 3,896 | 2,102 | 53.9 |
| Rhode Island | 4,440 | 2,160 | 48.6 | 4,440 | 2,160 | 48.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 |
| South Carolina | 3,928 | 2,497 | 63.6 | 4,328 | 2,811 | 64.9 | 3,225 | 1,947 | 60.4 |
| South Dakota | 3,159 | 1,850 | 58.6 | 4,160 | 2,518 | 60.5 | 2,623 | 1,492 | 56.9 |
| Tennessee | 4,154 | 2,769 | 66.7 | 4,783 | 3,211 | 67.1 | 2,713 | 1,756 | 64.7 |
| Texas | 3,977 | 2,582 | 64.9 | 4,513 | 2,957 | 65.5 | 2,381 | 1,467 | 61.6 |
| Utah | 3,592 | 2,161 | 60.2 | 3,893 | 2,344 | 60.2 | 2,524 | 1,512 | 59.9 |
| Vermont | 3,631 | 1,695 | 46.7 | 4,981 | 2,524 | 50.7 | 3,188 | 1,423 | 44.6 |
| Virginia | 4,352 | 2,585 | 59.4 | 4,916 | 2,919 | 59.4 | 3,245 | 1,928 | 59.4 |
| Washington | 3,788 | 2,063 | 54.5 | 4,042 | 2,193 | 54.3 | 2,873 | 1,595 | 55.5 |
| West Virginia | 3,715 | 2,236 | 60.2 | 4,202 | 2,493 | 59.3 | 3,350 | 2,043 | 61.0 |
| Wisconsin | 3,791 | 2,261 | 59.6 | 4,287 | 2,528 | 59.0 | 2,727 | 1,688 | 61.9 |
| Wyoming | 3,351 | 2,026 | 60.5 | 4,072 | 2,370 | 58.2 | 3,029 | 1,872 | 61.8 |
Prospective payment system recalibration file.
Footnotes
Reprint requests: James M. Hatten, Room l-F-2 Oak Meadows Building, 6325 Security Boulevard, Baltimore, Maryland 21207.