Abstract
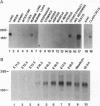
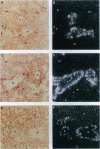
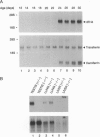
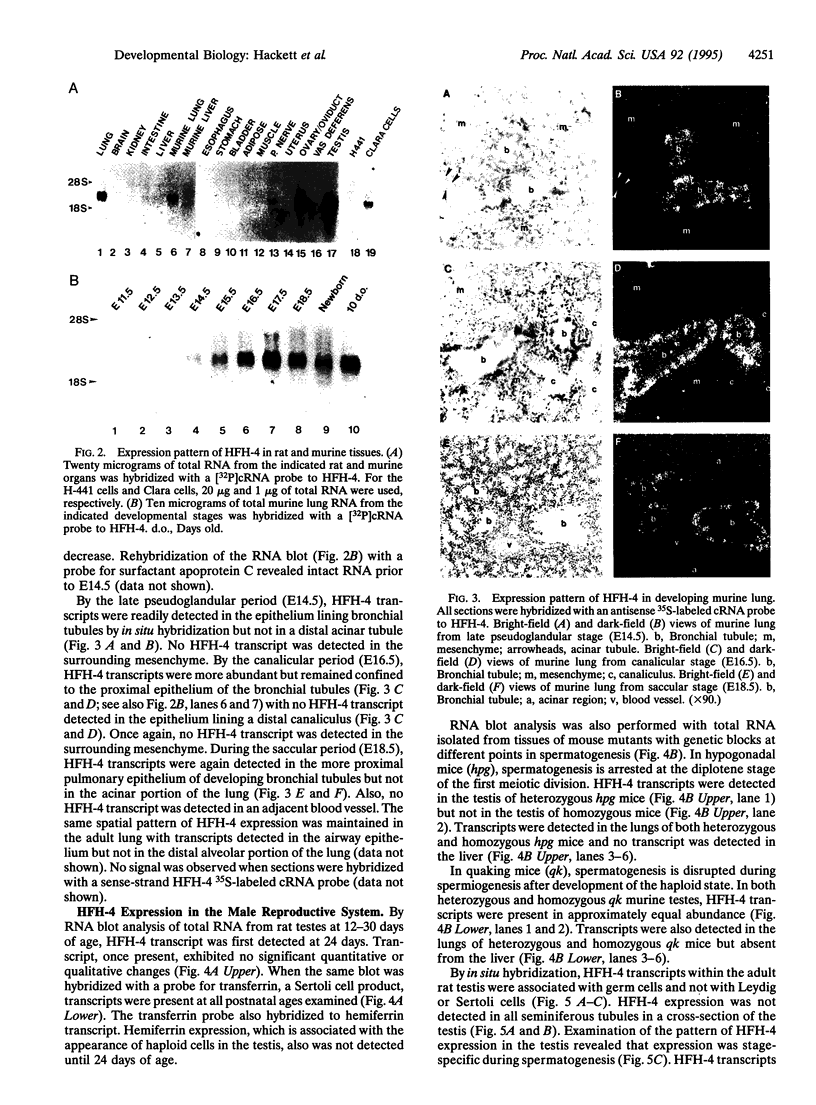
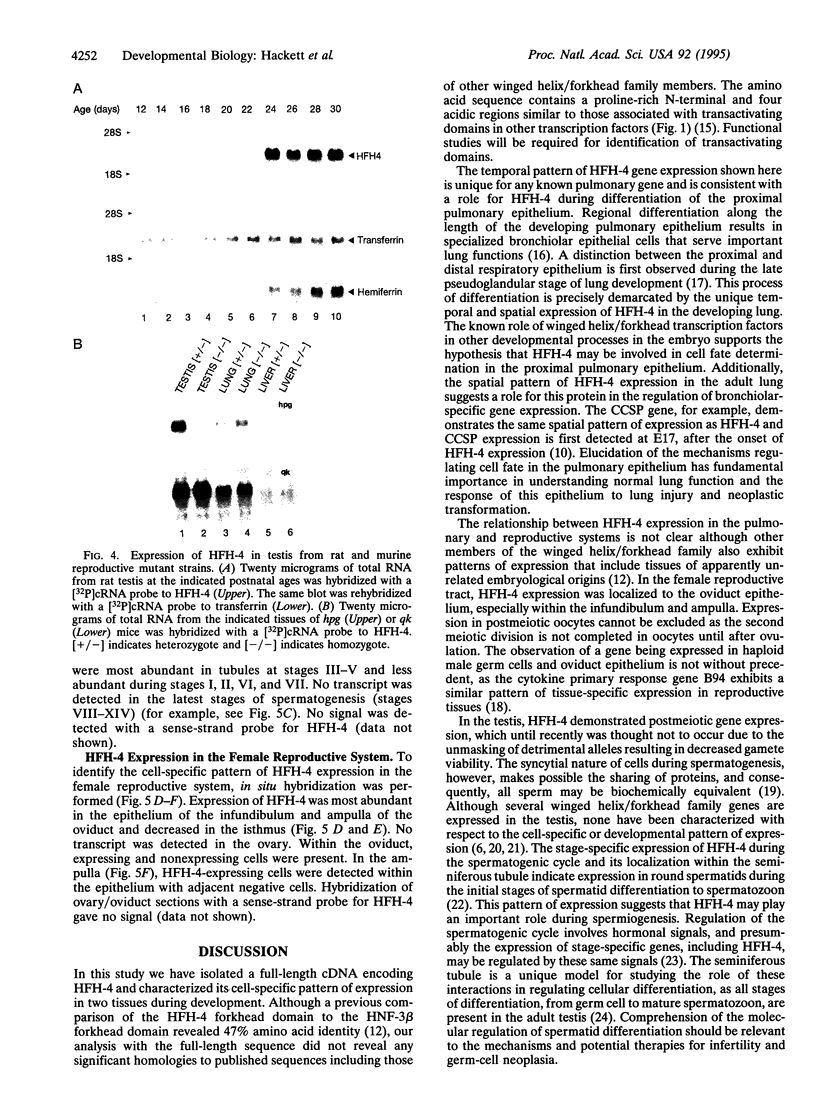
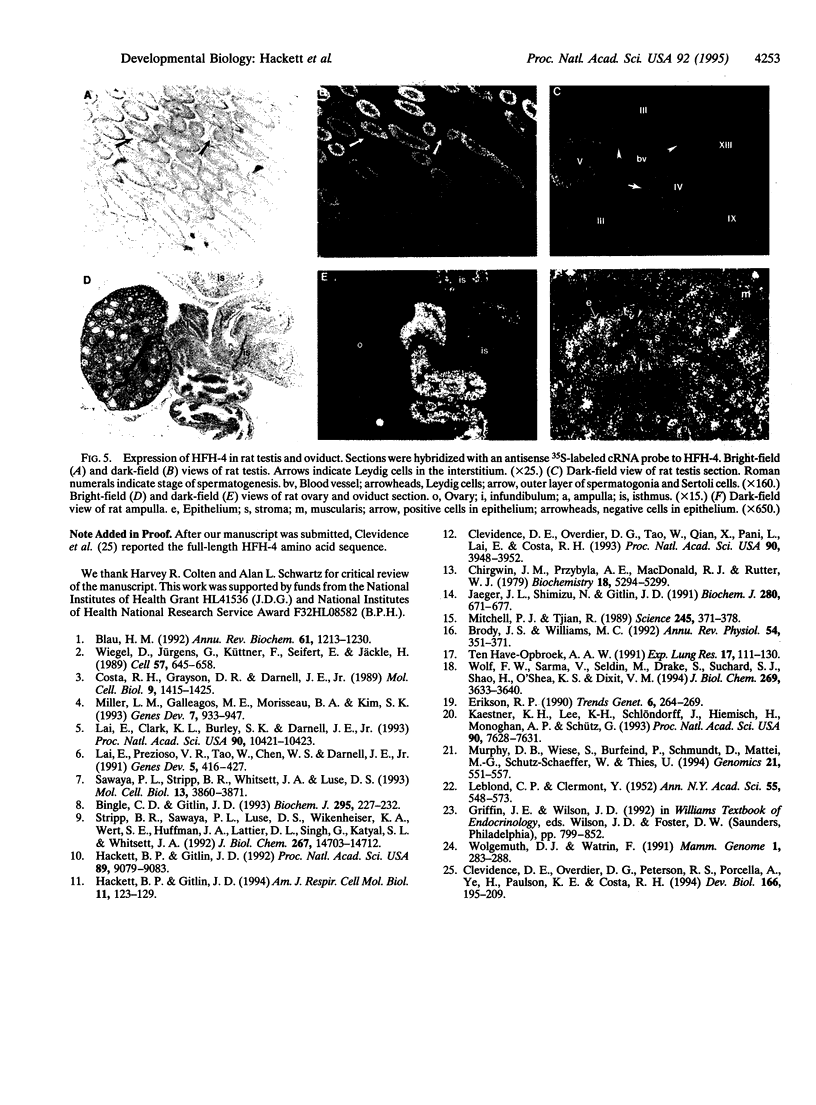
Members of the winged helix/forkhead family of transcription factors are believed to play a role in cell-specific gene expression. A cDNA encoding a member of this family of proteins, termed hepatocyte nuclear factor/forkhead homologue 4 (HFH-4), has been isolated from rat lung and rat testis cDNA libraries. This cDNA contains an open reading frame of 421 amino acids with a conserved DNA binding domain and several potential transactivating regions. During murine lung development, a single species of HFH-4-specific transcript (2.4 kb long) is first detected precisely at the start of the late pseudoglandular stage (embryonic day 14.5) and, by in situ hybridization, is specifically localized to the proximal pulmonary epithelium. The unique temporal and spatial pattern of HFH-4 gene expression in the developing lung defines this protein as a marker for the initiation of bronchial epithelial cell differentiation and suggests that it may play an important role in cell fate determination during lung development. In addition to expression in the pulmonary epithelium, RNA blot analysis reveals 2.4-kb HFH-4 transcripts in the testis and oviduct. By using mice with genetic defects in spermatogenesis, HFH-4 expression in the testis is found to be associated with the appearance of haploid germ cells and in situ hybridization studies indicate that HFH-4 expression is confined to stages I-VII of spermatogenesis. This pattern of HFH-4 gene expression during the early stages of differentiation of haploid germ cells suggests that HFH-4 may play a role in regulating stage-specific gene expression and cell-fate determination during lung development and in spermatogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingle C. D., Gitlin J. D. Identification of hepatocyte nuclear factor-3 binding sites in the Clara cell secretory protein gene. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2950227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M. Differentiation requires continuous active control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1213–1230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.010025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. S., Williams M. C. Pulmonary alveolar epithelial cell differentiation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:351–371. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence D. E., Overdier D. G., Peterson R. S., Porcella A., Ye H., Paulson K. E., Costa R. H. Members of the HNF-3/forkhead family of transcription factors exhibit distinct cellular expression patterns in lung and regulate the surfactant protein B promoter. Dev Biol. 1994 Nov;166(1):195–209. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence D. E., Overdier D. G., Tao W., Qian X., Pani L., Lai E., Costa R. H. Identification of nine tissue-specific transcription factors of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead DNA-binding-domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3948–3952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. Post-meiotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90209-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett B. P., Gitlin J. D. 5' flanking region of the Clara cell secretory protein gene specifies a unique temporal and spatial pattern of gene expression in the developing pulmonary epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Aug;11(2):123–129. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.11.2.8049073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett B. P., Gitlin J. D. Cell-specific expression of a Clara cell secretory protein-human growth hormone gene in the bronchiolar epithelium of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9079–9083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. L., Shimizu N., Gitlin J. D. Tissue-specific ceruloplasmin gene expression in the mammary gland. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):671–677. doi: 10.1042/bj2800671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Lee K. H., Schlöndorff J., Hiemisch H., Monaghan A. P., Schütz G. Six members of the mouse forkhead gene family are developmentally regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7628–7631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P., CLERMONT Y. Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Nov 20;55(4):548–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb26576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Clark K. L., Burley S. K., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head or "winged helix" proteins: a family of transcription factors of diverse biologic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10421–10423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. M., Gallegos M. E., Morisseau B. A., Kim S. K. lin-31, a Caenorhabditis elegans HNF-3/fork head transcription factor homolog, specifies three alternative cell fates in vulval development. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):933–947. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Wiese S., Burfeind P., Schmundt D., Mattei M. G., Schulz-Schaeffer W., Thies U. Human brain factor 1, a new member of the fork head gene family. Genomics. 1994 Jun;21(3):551–557. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaya P. L., Stripp B. R., Whitsett J. A., Luse D. S. The lung-specific CC10 gene is regulated by transcription factors from the AP-1, octamer, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 families. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3860–3871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stripp B. R., Sawaya P. L., Luse D. S., Wikenheiser K. A., Wert S. E., Huffman J. A., Lattier D. L., Singh G., Katyal S. L., Whitsett J. A. cis-acting elements that confer lung epithelial cell expression of the CC10 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14703–14712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Have-Opbroek A. A. Lung development in the mouse embryo. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;17(2):111–130. doi: 10.3109/01902149109064406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf F. W., Sarma V., Seldin M., Drake S., Suchard S. J., Shao H., O'Shea K. S., Dixit V. M. B94, a primary response gene inducible by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, is expressed in developing hematopoietic tissues and the sperm acrosome. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3633–3640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Watrin F. List of cloned mouse genes with unique expression patterns during spermatogenesis. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00352340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]