Abstract
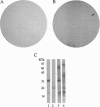
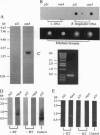
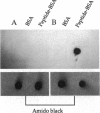
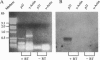
An immunological screening strategy was used to select microbial genes expressed only in the host. Differential screening of a Borrelia burgdorferi (the Lyme disease agent) expression library identified a gene (p21) encoding a 20.7-kDa antigen that reacted with antibodies in serum from actively infected mice but not serum from mice immunized with heat-killed B. burgdorferi. Selective expression of p21 in the infected host was confirmed by Northern blot analysis and RNA PCR. Further differential screening of the expression library identified at least five additional B. burgdorferi genes are selectively expressed in vivo. This screening method can be used to identify genes induced in vivo in a wide variety of pathogenic microorganisms for which a gene transfer system is not currently available.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion C. I., Blanco D. R., Skare J. T., Haake D. A., Giladi M., Foley D., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. A 9.0-kilobase-pair circular plasmid of Borrelia burgdorferi encodes an exported protein: evidence for expression only during infection. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.2653-2661.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erba H. P., Eddy R., Shows T., Kedes L., Gunning P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human gamma-actin gene: differential evolution, location, and expression of the cytoskeletal beta- and gamma-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1775–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam T. T., Nguyen T. P., Montgomery R. R., Kantor F. S., Fikrig E., Flavell R. A. Outer surface proteins E and F of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):290–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.290-298.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan M. J., Slauch J. M., Mekalanos J. J. Selection of bacterial virulence genes that are specifically induced in host tissues. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.8430319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. P., Lam T. T., Barthold S. W., Telford S. R., 3rd, Flavell R. A., Fikrig E. Partial destruction of Borrelia burgdorferi within ticks that engorged on OspE- or OspF-immunized mice. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):2079–2084. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.2079-2084.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probert W. S., LeFebvre R. B. Protection of C3H/HeN mice from challenge with Borrelia burgdorferi through active immunization with OspA, OspB, or OspC, but not with OspD or the 83-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):1920–1926. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.1920-1926.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]