Abstract
The 1987 national health expenditure estimates are examined from different perspectives in the following two articles. In the first article, revised expenditure estimates for 1984-87 are presented. A breakdown of the type of services and products purchased is included, as well as the source of funds used to finance health care. In the second article, health care expenditure estimates are used to explore marginal analysis as a policy tool for understanding health spending in relation to our Nation's ability to finance that spending. The concept of marginal analysis is also used to examine selected periods that were relevant to health policy and the timing of public and private changes in health policy in the past.
Highlights
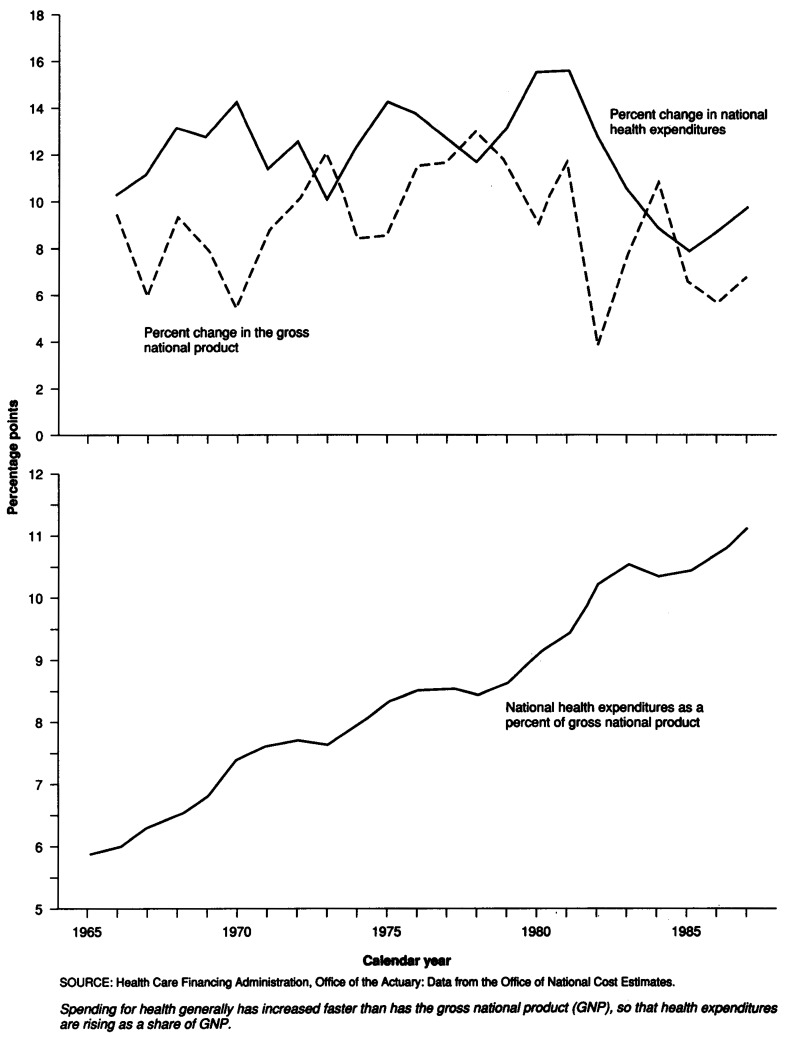
The Nation's health care bill topped $500 billion in 1987, an increase of 9.8 percent from 1986. Per capita spending increased to a level of $1,987, almost ten times the per capita spending of 1965. National health expenditures (NHE), as a share of the gross national product, continued its upward climb to 11.1 percent in 1987, increasing from 10.7 percent in 1986 and nearly double what it was in 1965 (Table 1).
Table 1. National health expenditures aggregate, per capita, percent distribution, and annual percent change, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1965-87.
| Item | 1965 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount in billions | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | $41.9 | $75.0 | $132.7 | $248.1 | $357.2 | $388.5 | $419.0 | $455.7 | $500.3 |
| Private | 30.9 | 47.2 | 76.4 | 142.9 | 209.7 | 228.8 | 244.0 | 266.8 | 293.0 |
| Public | 11.0 | 27.8 | 56.3 | 105.2 | 147.5 | 159.6 | 175.0 | 188.9 | 207.3 |
| Federal | 5.5 | 17.7 | 37.0 | 71.0 | 102.7 | 112.0 | 123.1 | 132.8 | 144.7 |
| State and local | 5.5 | 10.1 | 19.3 | 34.2 | 44.8 | 47.7 | 52.0 | 56.1 | 62.7 |
| Per capita amount | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | $206 | $349 | $591 | $1,055 | $1,473 | $1,587 | $1,696 | $1,827 | $1,987 |
| Private | 152 | 220 | 340 | 608 | 865 | 935 | 987 | 1,069 | 1,164 |
| Public | 54 | 129 | 251 | 447 | 609 | 652 | 708 | 757 | 824 |
| Federal | 27 | 82 | 165 | 302 | 424 | 458 | 498 | 532 | 575 |
| State and local | 27 | 47 | 86 | 145 | 185 | 195 | 210 | 225 | 249 |
| Percent distribution | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Private | 73.8 | 63.0 | 57.5 | 57.6 | 58.7 | 58.9 | 58.2 | 58.5 | 58.6 |
| Public | 26.2 | 37.0 | 42.5 | 42.4 | 41.3 | 41.1 | 41.8 | 41.5 | 41.4 |
| Federal | 13.2 | 23.6 | 27.9 | 28.6 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 29.4 | 29.1 | 28.9 |
| State and local | 13.0 | 13.5 | 14.5 | 13.8 | 12.5 | 12.3 | 12.4 | 12.3 | 12.5 |
| Average annual percent change from previous year shown | |||||||||
| U.S. population | — | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Gross national product | — | 7.6 | 9.5 | 11.3 | 7.6 | 10.8 | 6.4 | 5.6 | 6.8 |
| National health expenditures | — | 12.3 | 12.1 | 13.3 | 12.9 | 8.8 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 9.8 |
| Private | — | 8.8 | 10.1 | 13.4 | 13.6 | 9.1 | 6.6 | 9.3 | 9.8 |
| Public | — | 20.4 | 15.2 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 8.2 | 9.6 | 7.9 | 9.8 |
| Federal | — | 26.1 | 16.0 | 13.9 | 13.1 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 7.9 | 8.9 |
| State and local | — | 13.1 | 13.8 | 12.1 | 9.4 | 6.4 | 9.1 | 8.0 | 11.7 |
| Number in millions | |||||||||
| U.S. population1 | 204.0 | 214.8 | 224.7 | 235.2 | 242.4 | 244.8 | 247.1 | 249.5 | 251.8 |
| Amount in billions | |||||||||
| Gross national product | $705 | $1,015 | $1,598 | $2,732 | $3,406 | $3,772 | $4,015 | $4,240 | $4,527 |
| Percent of gross national product | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | 5.9 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 10.4 | 10.7 | 11.1 |
July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Most of the growth in 1987 NHE was concentrated in spending for professional services. Expenditures for physicians', dental, and other professional services grew at rates faster than overall spending. Spending for the institutional services of hospital and nursing home care grew at slower than overall rates, reflecting the success of public and private hospital cost-control initiatives implemented in the early part of this decade.
National health expenditures
National health expenditures are divided into two parts: health services and supplies (expenditures related to current health care) and research and construction of medical facilities (expenditures related to future health care). Health services and supplies can be disaggregated into personal health care (the direct provision of care), program administration and the net cost of health insurance, and government public health activities.
Personal health care
Personal health care expenditures grew 10.2 percent to reach a level of $443 billion in 1987 (Table 2). This translates to an average of $1,758 per person. Personal health care includes hospital and nursing home care, services of physicians, dentists and other professionals, and miscellaneous other personal health care services, as well as purchases of prescription and nonprescription drugs and durable medical products.
Table 2. National health expenditures aggregate and average annual percent change, by type of expenditure: Selected calendar years 1965-87.
| Type of expenditure | 1965 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount in billions | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | $41.9 | $75.0 | $132.7 | $248.1 | $357.2 | $388.5 | $419.0 | $455.7 | $500.3 |
| Health services and supplies | 38.4 | 69.6 | 124.3 | 236.2 | 341.8 | 372.7 | 403.4 | 439.3 | 483.2 |
| Personal health care | 35.9 | 65.4 | 117.1 | 219.7 | 314.7 | 340.1 | 368.3 | 401.6 | 442.6 |
| Hospital care | 14.0 | 28.0 | 52.4 | 101.6 | 146.8 | 156.1 | 166.7 | 178.4 | 194.7 |
| Physicians' services | 8.5 | 14.3 | 24.9 | 46.8 | 68.4 | 74.4 | 81.4 | 91.6 | 102.7 |
| Dentists' services | 2.8 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 15.4 | 21.7 | 24.6 | 27.1 | 29.6 | 32.8 |
| Other professional services | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 5.7 | 9.3 | 10.8 | 12.4 | 14.1 | 16.2 |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 5.2 | 8.0 | 11.9 | 18.8 | 24.5 | 26.5 | 28.5 | 31.3 | 34.0 |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 1.2 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 8.7 | 9.5 |
| Nursing home care | 2.1 | 4.7 | 10.1 | 20.4 | 29.4 | 31.6 | 34.7 | 37.4 | 40.6 |
| Other personal health care | 1.1 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 5.9 | 8.3 | 9.0 | 9.8 | 10.7 | 12.0 |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 1.7 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 9.2 | 17.1 | 21.7 | 22.6 | 23.9 | 25.9 |
| Government public health activities | 0.8 | 1.4 | 3.2 | 7.3 | 9.9 | 11.0 | 12.5 | 13.8 | 14.7 |
| Research and construction | 3.5 | 5.4 | 8.4 | 11.9 | 15.4 | 15.8 | 15.6 | 16.4 | 17.1 |
| Research1 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| Construction | 2.0 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 6.5 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 8.3 |
| Average annual percent change from previous year shown | |||||||||
| National health expenditures | — | 12.3 | 12.1 | 13.3 | 12.9 | 8.8 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 9.8 |
| Health services and supplies | — | 12.6 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 13.1 | 9.0 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 10.0 |
| Personal health care | — | 12.8 | 12.4 | 13.4 | 12.7 | 8.1 | 8.3 | 9.0 | 10.2 |
| Hospital care | — | 14.9 | 13.4 | 14.2 | 13.0 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 9.1 |
| Physicians' services | — | 11.1 | 11.7 | 13.4 | 13.5 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 12.6 | 12.2 |
| Dentists' services | — | 11.1 | 11.6 | 13.3 | 12.1 | 13.4 | 10.2 | 9.0 | 11.1 |
| Other professional services | — | 9.1 | 10.4 | 16.8 | 17.9 | 16.0 | 14.6 | 13.4 | 15.2 |
| Drugs and medical sundries | — | 9.1 | 8.3 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 8.1 | 7.6 | 9.9 | 8.9 |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | — | 10.7 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 7.1 | 13.0 | 10.3 | 11.6 | 9.3 |
| Nursing home care | — | 17.8 | 16.4 | 15.2 | 13.0 | 7.7 | 9.6 | 7.8 | 8.6 |
| Other personal health care | — | 12.5 | 12.8 | 9.5 | 12.1 | 7.3 | 9.3 | 9.5 | 12.2 |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | — | 10.1 | 7.2 | 18.1 | 23.1 | 26.4 | 4.1 | 6.0 | 8.4 |
| Government public health activities | — | 11.9 | 17.2 | 18.2 | 10.9 | 10.2 | 14.4 | 9.6 | 7.0 |
| Research and construction | — | 9.0 | 9.2 | 7.3 | 8.8 | 2.4 | −1.0 | 4.9 | 4.5 |
| Research1 | — | 5.4 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 4.2 | 12.1 | 9.2 | 10.4 | 6.2 |
| Construction | — | 11.4 | 8.1 | 5.1 | 12.4 | −4.1 | −8.9 | −0.3 | 2.8 |
Research and development expenditures of drug companies and other manufacturers and providers of medical equipment and supplies are excluded from “research expenditures,” but they are included in the expenditure class in which the product falls.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Hospital and nursing home services which combine to represent institutional services, were the slowest growing personal health care expenditure categories during the last 4 years. Growth rates for hospital care spending reached a low of 6.3 percent in 1984, and have steadily increased to a rate of 9.1 percent in 1987. During this period, hospital care spending grew at a slower pace than total spending, reversing the trend of the period 1978-82 when hospital growth exceeded total spending growth.
Hospital care accounted for the largest share of personal health spending—$195 billion in hospital revenues representing 44 percent of personal health expenditures. Estimates of expenditures for hospital care include spending for both inpatient and outpatient hospital services. Spending for drugs and other services and supplies associated with hospital care, including services of hospital-salaried physicians, are also included in the hospital care category.
Nursing home care, the other component of institutional care, showed slower growth than personal health care during 3 of the last 4 years. Expenditures for nursing home care were $41 billion and accounted for 9 percent of personal health care spending. Spending increased only 8.6 percent from 1986, which was the slowest growth rate among all types of service.
While institutional spending showed the slowest growth in 1987, spending for the professional services of physicians, dentists, and other professionals showed the highest growth rates among types of service. In a trend opposite from hospital spending, growth in spending for physicians' services has outpaced that of health care since 1984. Expenditures for physicians' services, representing 23 percent of personal health spending, is the second largest personal health category. In 1987, $103 billion was spent for physicians' services, increasing 12.2 percent from 1986.
Spending for other professional services grew faster than any other type of service in 1987—as it has in every year since 1980. At a level of $16 billion, this category accounted for 4 percent of personal health care spending. Home health agency services are included in other professional services and account for much of the growth in this category. Also included are services rendered by chiropractors, private duty nurses, optometrists, podiatrists, among others.
Spending for dentists' services was $33 billion in 1987, increasing 11.1 percent from 1986. This category accounted for 7 percent of personal health spending.
The remaining 13 percent of the personal health care dollar was spent on drugs and medical sundries, eyeglasses and appliances, and other personal health care. Expenditures for drugs and medical sundries were $34 billion, increasing 8.9 percent from 1986. Expenditures for eyeglasses and appliances were $9 billion, increasing 9.3 percent from 1986. Other personal health care includes health care spending that does not clearly fit in any other category or is unspecified. This category is comprised mostly of public expenditures—the only private expenditures are for the operation of industrial onsite health services (industrial inplant). Other personal health care expenditures were $12 billion in 1987, increasing 12.2 percent from 1986.
Other health services and supplies
Program administration and the net cost of private health insurance (the difference between premiums earned and benefits incurred) amounted to $26 billion. This accounted for 5 percent of total spending, increasing 8.4 percent from 1986. Government public health activities amounted to $15 billion in 1987, increasing 7 percent from 1986. Public health activities are those functions carried out by Federal, State, and local governments to support community health, as opposed to care delivered to individuals.
Other national health expenditures
Expenditures for research were $9 billion in 1987, and include all spending for biomedical research and research in the delivery of health care by both private and public agencies. Research expenditures of drug and medical supply companies are not included in this category, but are included implicitly in the expenditure class in which the product falls. Spending for the construction of medical facilities was $8 billion in 1987, increasing 2.8 percent from 1986. The previous 3 years showed a decline in this category, which was a reaction to falling occupancy rates and overcapacity in community hospitals.
Financing personal health care
Third parties, through private health insurance plans and government programs, financed almost three-quarters of total personal health care in 1987. The remaining 28 percent was paid by direct patient payments in the form of coinsurance and deductibles, as well as out-of-pocket payments for uncovered services.
Within the general category of personal health, the share funded by third parties varied a great deal by type of care. The third-party share ranged from a high of 90 percent for hospital care to a low of 25 percent for drugs and medical sundries. Third parties paid for 74 percent of physician's services, 39 percent of dentists' services, and 51 percent of nursing home care.
Private health insurance plans paid an estimated $139 billion in benefits in 1987, which accounted for 31 percent of all personal health spending (Table 3). A large share of the spending for hospital care and physicians' services was paid for by private health insurance—37 percent of spending for hospital care and 43 percent of spending for physicians' services. The “other private” category of expenditures includes philanthropy and industrial inplant services and amounted to $5 billion in 1987.
Table 3. National health expenditures, by source of funds and type of expenditure: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year and type of expenditure | Total | Private | Government | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| All private funds | Consumer | Other | Total | Federal | State and local | |||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Direct | Private insurance | ||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $248.1 | $142.9 | $135.6 | $63.0 | $72.6 | $7.3 | $105.2 | $71.0 | $34.2 | |
| Health services and supplies | 236.2 | 138.7 | 135.6 | 63.0 | 72.6 | 3.0 | 97.5 | 65.8 | 31.7 | |
| Personal health care | 219.7 | 133.2 | 130.5 | 63.0 | 67.5 | 2.7 | 86.5 | 62.5 | 24.0 | |
| Hospital care | 101.6 | 47.7 | 46.6 | 7.9 | 38.7 | 1.1 | 53.9 | 41.1 | 12.8 | |
| Physicians' services | 46.8 | 34.2 | 34.2 | 14.2 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 12.6 | 9.6 | 3.0 | |
| Dentists' services | 15.4 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 10.1 | 4.7 | — | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 5.7 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 18.8 | 17.1 | 17.1 | 15.0 | 2.2 | — | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 5.1 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.1 | 0.4 | — | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | |
| Nursing home care | 20.4 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 8.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 11.2 | 6.0 | 5.2 | |
| Other personal health care | 5.9 | 1.4 | — | — | — | 1.4 | 4.5 | 3.1 | 1.4 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 9.2 | 5.4 | 5.1 | — | 5.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 2.0 | 1.7 | |
| Government public health activities | 7.3 | — | — | — | — | — | 7.3 | 1.3 | 6.0 | |
| Research and construction | 11.9 | 4.3 | — | — | — | 4.3 | 7.7 | 5.2 | 2.4 | |
| Research | 5.4 | 0.3 | — | — | — | 0.3 | 5.1 | 4.7 | 0.5 | |
| Construction | 6.5 | 4.0 | — | — | — | 4.0 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 2.0 | |
| 1983 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $357.2 | $209.7 | $198.4 | $88.7 | $109.7 | $11.3 | $147.5 | $102.7 | $44.8 | |
| Health services and supplies | 341.8 | 202.8 | 198.4 | 88.7 | 109.7 | 4.5 | 138.9 | 96.9 | 42.1 | |
| Personal health care | 314.7 | 190.6 | 186.7 | 88.7 | 98.0 | 4.0 | 124.1 | 92.9 | 31.1 | |
| Hospital care | 146.8 | 70.0 | 68.2 | 13.3 | 54.9 | 1.8 | 76.8 | 60.4 | 16.4 | |
| Physicians' services | 68.4 | 49.0 | 48.9 | 19.3 | 29.6 | 0.0 | 19.5 | 15.6 | 3.8 | |
| Dentists' services | 21.7 | 21.2 | 21.2 | 13.8 | 7.3 | — | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 9.3 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 4.4 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 0.7 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 24.5 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 19.2 | 3.2 | — | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 6.2 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 0.7 | — | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | |
| Nursing home care | 29.4 | 14.6 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 14.8 | 8.1 | 6.7 | |
| Other personal health care | 8.3 | 1.8 | — | — | — | 1.8 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 2.0 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 17.1 | 12.2 | 11.7 | — | 11.7 | 0.5 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 2.3 | |
| Government public health activities | 9.9 | — | — | — | — | — | 9.9 | 1.3 | 8.7 | |
| Research and construction | 15.4 | 6.8 | — | — | — | 6.8 | 8.6 | 5.9 | 2.7 | |
| Research | 6.2 | 0.4 | — | — | — | 0.4 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 0.6 | |
| Construction | 9.2 | 6.5 | — | — | — | 6.5 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 2.1 | |
| 1984 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $388.5 | $228.8 | $217.6 | $95.7 | $121.9 | $11.2 | $159.6 | $112.0 | $47.7 | |
| Health services and supplies | 372.7 | 222.2 | 217.6 | 95.7 | 121.9 | 4.6 | 150.5 | 105.4 | 45.1 | |
| Personal health care | 340.1 | 205.0 | 201.0 | 95.7 | 105.3 | 4.0 | 135.1 | 101.2 | 33.9 | |
| Hospital care | 156.1 | 72.3 | 70.6 | 14.1 | 56.5 | 1.7 | 83.9 | 66.0 | 17.9 | |
| Physicians' services | 74.4 | 53.3 | 53.2 | 20.0 | 33.3 | 0.0 | 21.2 | 16.9 | 4.3 | |
| Dentists' services | 24.6 | 24.1 | 24.1 | 15.5 | 8.6 | — | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 10.8 | 7.5 | 7.4 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 0.9 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 26.5 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 20.5 | 3.5 | — | 2.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 7.0 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 5.0 | 0.8 | — | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.1 | |
| Nursing home care | 31.6 | 16.0 | 15.8 | 15.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 15.6 | 8.5 | 7.1 | |
| Other personal health care | 9.0 | 2.0 | — | — | — | 2.0 | 6.9 | 4.8 | 2.1 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 21.7 | 17.1 | 16.6 | — | 16.6 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 1.6 | |
| Government public health activities | 11.0 | — | — | — | — | — | 11.0 | 1.4 | 9.6 | |
| Research and construction | 15.8 | 6.7 | — | — | — | 6.7 | 9.1 | 6.6 | 2.5 | |
| Research | 6.9 | 0.5 | — | — | — | 0.5 | 6.4 | 5.8 | 0.6 | |
| Construction | 8.9 | 6.2 | — | — | — | 6.2 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 1.9 | |
| 1985 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $419.0 | $244.0 | $232.8 | $103.7 | $129.1 | $11.1 | $175.0 | $123.1 | $52.0 | |
| Health services and supplies | 403.4 | 238.0 | 232.8 | 103.7 | 129.1 | 5.2 | 165.4 | 115.9 | 49.5 | |
| Personal health care | 368.3 | 220.3 | 215.7 | 103.7 | 112.0 | 4.6 | 148.0 | 111.3 | 36.7 | |
| Hospital care | 166.7 | 76.2 | 74.2 | 15.4 | 58.9 | 2.0 | 90.5 | 71.3 | 19.2 | |
| Physicians' services | 81.4 | 57.2 | 57.2 | 21.6 | 35.6 | 0.0 | 24.1 | 19.3 | 4.8 | |
| Dentists' services | 27.1 | 26.6 | 26.6 | 16.8 | 9.7 | — | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 12.4 | 8.4 | 8.3 | 5.4 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 1.2 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 28.5 | 25.6 | 25.6 | 21.8 | 3.8 | — | 2.9 | 1.4 | 1.5 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 7.8 | 6.3 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 0.9 | — | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | |
| Nursing home care | 34.7 | 17.8 | 17.5 | 17.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 16.9 | 9.5 | 7.4 | |
| Other personal health care | 9.8 | 2.2 | — | — | — | 2.2 | 7.6 | 5.3 | 2.2 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 22.6 | 17.7 | 17.1 | — | 17.1 | 0.6 | 4.8 | 3.2 | 1.6 | |
| Government public health activities | 12.5 | — | — | — | — | — | 12.5 | 1.4 | 11.2 | |
| Research and construction | 15.6 | 6.0 | — | — | — | 6.0 | 9.6 | 7.2 | 2.5 | |
| Research | 7.5 | 0.5 | — | — | — | 0.5 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 0.7 | |
| Construction | 8.1 | 5.5 | — | — | — | 5.5 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 1.7 | |
| 1986 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $455.7 | $266.8 | $255.1 | $112.6 | $142.4 | $11.7 | $188.9 | $132.8 | $56.1 | |
| Health services and supplies | 439.3 | 260.5 | 255.1 | 112.6 | 142.4 | 5.5 | 178.8 | 125.0 | 53.7 | |
| Personal health care | 401.6 | 242.1 | 237.3 | 112.6 | 124.6 | 4.8 | 159.6 | 120.3 | 39.2 | |
| Hospital care | 178.4 | 83.1 | 81.1 | 16.7 | 64.4 | 2.0 | 95.4 | 75.1 | 20.2 | |
| Physicians' services | 91.6 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 23.7 | 40.2 | 0.1 | 27.6 | 22.4 | 5.3 | |
| Dentists' services | 29.6 | 28.9 | 28.9 | 18.2 | 10.8 | — | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 14.1 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 5.7 | 3.7 | 0.1 | 4.6 | 3.2 | 1.4 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 31.3 | 27.9 | 27.9 | 23.7 | 4.2 | — | 3.4 | 1.7 | 1.7 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 8.7 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 5.9 | 1.0 | — | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.2 | |
| Nursing home care | 37.4 | 19.4 | 19.1 | 18.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 18.0 | 10.2 | 7.8 | |
| Other personal health care | 10.7 | 2.4 | — | — | — | 2.4 | 8.3 | 5.9 | 2.4 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 23.9 | 18.5 | 17.8 | — | 17.8 | 0.6 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 2.2 | |
| Government public health activities | 13.8 | — | — | — | — | — | 13.8 | 1.4 | 12.3 | |
| Research and construction | 16.4 | 6.2 | — | — | — | 6.2 | 10.1 | 7.8 | 2.4 | |
| Research | 8.3 | 0.7 | — | — | — | 0.7 | 7.6 | 6.8 | 0.8 | |
| Construction | 8.0 | 5.6 | — | — | — | 5.6 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 1.6 | |
| 1987 | ||||||||||
| National health expenditures | $500.3 | $293.0 | $280.8 | $123.0 | $157.8 | $12.2 | $207.3 | $144.7 | $62.7 | |
| Health services and supplies | 483.2 | 286.7 | 280.8 | 123.0 | 157.8 | 5.9 | 196.5 | 136.3 | 60.2 | |
| Personal health care | 442.6 | 267.3 | 262.1 | 123.0 | 139.1 | 5.3 | 175.3 | 131.2 | 44.1 | |
| Hospital care | 194.7 | 92.6 | 90.4 | 18.5 | 71.9 | 2.2 | 102.2 | 80.0 | 22.2 | |
| Physicians' services | 102.7 | 70.9 | 70.9 | 26.3 | 44.6 | 0.1 | 31.8 | 25.7 | 6.1 | |
| Dentists' services | 32.8 | 32.2 | 32.2 | 20.0 | 12.1 | — | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Other professional services | 16.2 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 5.4 | 3.6 | 1.8 | |
| Drugs and medical sundries | 34.0 | 30.2 | 30.2 | 25.5 | 4.7 | — | 3.9 | 1.9 | 2.0 | |
| Eyeglasses and appliances | 9.5 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 6.3 | 1.1 | — | 2.1 | 1.9 | 0.2 | |
| Nursing home care | 40.6 | 20.6 | 20.4 | 20.0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 19.9 | 11.1 | 8.9 | |
| Other personal health care | 12.0 | 2.6 | — | — | — | 2.6 | 9.4 | 6.7 | 2.7 | |
| Program administration and net cost of private health insurance | 25.9 | 19.4 | 18.7 | — | 18.7 | 0.7 | 6.6 | 3.5 | 3.1 | |
| Government public health activities | 14.7 | — | — | — | — | — | 14.7 | 1.6 | 13.1 | |
| Research and construction | 17.1 | 6.3 | — | — | — | 6.3 | 10.8 | 8.4 | 2.4 | |
| Research | 8.8 | 0.6 | — | — | — | 0.6 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 0.8 | |
| Construction | 8.3 | 5.7 | — | — | — | 5.7 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 1.6 | |
NOTES: Research and development expenditures of drug companies and other manufacturers and providers of medical equipment and supplies are excluded from noncommercial research, being implicitly included in the value of the good or service being produced. “Other private funds” Include spending by philanthropy, industrial inplant health services, and privately financed construction. 0.0 denotes less than $50 million.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Government programs spent $175 billion for personal health care services in 1987 (Table 4). Public programs financed 40 percent of all personal health care expenditures including 52 percent of all hospital care (Table 5), 31 percent of all physicians' services (Table 6), and 49 percent of all nursing home care (Table 7), and 20 percent of all remaining other personal health care services (Table 8).
Table 4. Personal health care expenditures aggregate, per capita, and percent distribution, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year | Total | Direct patient payments | Third parties | Medicare1 | Medicaid2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||
| All third parties | Private health insurance | Other private funds | Government | |||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Federal | State and local | ||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $219.7 | $63.0 | $156.7 | $67.5 | $2.7 | $86.5 | $62.5 | $24.0 | $35.7 | $25.2 |
| 1983 | 314.7 | 88.7 | 226.0 | 98.0 | 4.0 | 124.1 | 92.9 | 31.1 | 57.4 | 33.9 |
| 1984 | 340.1 | 95.7 | 244.4 | 105.3 | 4.0 | 135.1 | 101.2 | 33.9 | 63.0 | 36.4 |
| 1985 | 368.3 | 103.7 | 264.6 | 112.0 | 4.6 | 148.0 | 111.3 | 36.7 | 69.3 | 40.3 |
| 1986 | 401.6 | 112.6 | 289.0 | 124.6 | 4.8 | 159.6 | 120.3 | 39.2 | 74.6 | 43.6 |
| 1987 | 442.6 | 123.0 | 319.6 | 139.1 | 5.3 | 175.3 | 131.2 | 44.1 | 81.2 | 49.4 |
| Per capita amount | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $934 | $268 | $666 | $287 | $11 | $368 | $266 | $102 | (3) | (3) |
| 1983 | 1,298 | 366 | 932 | 404 | 16 | 512 | 383 | 128 | (3) | (3) |
| 1984 | 1,389 | 391 | 998 | 430 | 17 | 552 | 413 | 138 | (3) | (3) |
| 1985 | 1,490 | 420 | 1,071 | 453 | 19 | 599 | 450 | 149 | (3) | (3) |
| 1986 | 1,610 | 452 | 1,159 | 500 | 19 | 640 | 482 | 157 | (3) | (3) |
| 1987 | 1,758 | 488 | 1,270 | 552 | 21 | 696 | 521 | 175 | (3) | (3) |
| Percent distribution | ||||||||||
| 1980 | 100.0 | 28.7 | 71.3 | 30.7 | 1.2 | 39.4 | 28.4 | 10.9 | 16.2 | 11.5 |
| 1983 | 100.0 | 28.2 | 71.8 | 31.1 | 1.3 | 39.4 | 29.5 | 9.9 | 18.3 | 10.8 |
| 1984 | 100.0 | 28.1 | 71.9 | 31.0 | 1.2 | 39.7 | 29.7 | 10.0 | 18.5 | 10.7 |
| 1985 | 100.0 | 28.2 | 71.8 | 30.4 | 1.2 | 40.2 | 30.2 | 10.0 | 18.8 | 10.9 |
| 1986 | 100.0 | 28.0 | 72.0 | 31.0 | 1.2 | 39.7 | 30.0 | 9.8 | 18.6 | 10.9 |
| 1987 | 100.0 | 27.8 | 72.2 | 31.4 | 1.2 | 39.6 | 29.6 | 10.0 | 18.4 | 11.2 |
Subset of Federal funds.
Subset of Federal and State and local funds.
Calculation of per capita estimates is inappropriate.
NOTE: Per capita amounts based on July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Table 5. Hospital care expenditures aggregate, per capita, and percent distribution, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year | Total | Direct patient payments | Third parties | Medicare1 | Medicaid2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||
| All third parties | Private health insurance | Other private funds | Government | |||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Federal | State and local | ||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $101.6 | $7.9 | $93.7 | $38.7 | $1.1 | $53.9 | $41.1 | $12.8 | $25.9 | $9.6 |
| 1983 | 146.8 | 13.3 | 133.6 | 54.9 | 1.8 | 76.8 | 60.4 | 16.4 | 40.5 | 12.9 |
| 1984 | 156.1 | 14.1 | 142.0 | 56.5 | 1.7 | 83.9 | 66.0 | 17.9 | 44.5 | 13.9 |
| 1985 | 166.7 | 15.4 | 151.4 | 58.9 | 2.0 | 90.5 | 71.3 | 19.2 | 48.2 | 14.9 |
| 1986 | 178.4 | 16.7 | 161.7 | 64.4 | 2.0 | 95.4 | 75.1 | 20.2 | 50.4 | 15.8 |
| 1987 | 194.7 | 18.5 | 176.2 | 71.9 | 2.2 | 102.2 | 80.0 | 22.2 | 53.3 | 17.8 |
| Per capita amount | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $432 | $34 | $398 | $165 | $5 | $229 | $175 | $55 | (3) | (3) |
| 1983 | 606 | 55 | 551 | 227 | 7 | 317 | 249 | 68 | (3) | (3) |
| 1984 | 638 | 58 | 580 | 231 | 7 | 343 | 270 | 73 | (3) | (3) |
| 1985 | 675 | 62 | 612 | 238 | 8 | 366 | 288 | 78 | (3) | (3) |
| 1986 | 715 | 67 | 648 | 258 | 8 | 382 | 301 | 81 | (3) | (3) |
| 1987 | 773 | 73 | 700 | 286 | 9 | 406 | 318 | 88 | (3) | (3) |
| Percent distribution | ||||||||||
| 1980 | 100.0 | 7.8 | 92.2 | 38.1 | 1.1 | 53.1 | 40.4 | 12.6 | 25.5 | 9.4 |
| 1983 | 100.0 | 9.0 | 91.0 | 37.4 | 1.2 | 52.3 | 41.2 | 11.2 | 27.6 | 8.8 |
| 1984 | 100.0 | 9.0 | 91.0 | 36.2 | 1.1 | 53.7 | 42.3 | 11.4 | 28.5 | 8.9 |
| 1985 | 100.0 | 9.2 | 90.8 | 35.3 | 1.2 | 54.3 | 42.7 | 11.5 | 28.9 | 9.0 |
| 1986 | 100.0 | 9.4 | 90.6 | 36.1 | 1.1 | 53.4 | 42.1 | 11.3 | 28.2 | 8.9 |
| 1987 | 100.0 | 9.5 | 90.5 | 36.9 | 1.1 | 52.5 | 41.1 | 11.4 | 27.4 | 9.1 |
Subset of Federal funds.
Subset of Federal and State and local funds.
Calculation of per capita estimates is inappropriate.
NOTE: Per capita amounts based on July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Table 6. Physician care expenditures aggregate, per capita, and percent distribution, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year | Total | Direct patient payments | Third parties | Medicare1 | Medicaid2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||
| All third parties | Private health insurance | Other private funds | Government | |||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Federal | State and local | ||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $46.8 | $14.2 | $32.6 | $20.0 | $0.0 | $12.6 | $9.6 | $3.0 | $7.9 | $2.4 |
| 1983 | 68.4 | 19.3 | 49.1 | 29.6 | 0.0 | 19.5 | 15.6 | 3.8 | 13.4 | 2.9 |
| 1984 | 74.4 | 20.0 | 54.5 | 33.3 | 0.0 | 21.2 | 16.9 | 4.3 | 14.5 | 3.1 |
| 1985 | 81.4 | 21.6 | 59.7 | 35.6 | 0.0 | 24.1 | 19.3 | 4.8 | 16.7 | 3.5 |
| 1986 | 91.6 | 23.7 | 67.9 | 40.2 | 0.1 | 27.6 | 22.4 | 5.3 | 19.3 | 3.9 |
| 1987 | 102.7 | 26.3 | 76.4 | 44.6 | 0.1 | 31.8 | 25.7 | 6.1 | 22.3 | 4.4 |
| Per capita amount | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $199 | $61 | $139 | $85 | $0 | $54 | $41 | $13 | (3) | (3) |
| 1983 | 282 | 80 | 202 | 122 | 0 | 80 | 64 | 16 | (3) | (3) |
| 1984 | 304 | 82 | 222 | 136 | 0 | 86 | 69 | 17 | (3) | (3) |
| 1985 | 329 | 88 | 242 | 144 | 0 | 98 | 78 | 19 | (3) | (3) |
| 1986 | 367 | 95 | 272 | 161 | 0 | 111 | 90 | 21 | (3) | (3) |
| 1987 | 408 | 104 | 304 | 177 | 0 | 126 | 102 | 24 | (3) | (3) |
| Percent distribution | ||||||||||
| 1980 | 100.0 | 30.4 | 69.6 | 42.6 | 0.1 | 26.9 | 20.6 | 6.3 | 16.9 | 5.2 |
| 1983 | 100.0 | 28.3 | 71.7 | 43.2 | 0.1 | 28.4 | 22.8 | 5.6 | 19.6 | 4.3 |
| 1984 | 100.0 | 26.8 | 73.2 | 44.7 | 0.1 | 28.4 | 22.7 | 5.7 | 19.5 | 4.2 |
| 1985 | 100.0 | 26.6 | 73.4 | 43.7 | 0.1 | 29.7 | 23.8 | 5.9 | 20.5 | 4.3 |
| 1986 | 100.0 | 25.9 | 74.1 | 43.9 | 0.1 | 30.2 | 24.4 | 5.8 | 21.1 | 4.3 |
| 1987 | 100.0 | 25.6 | 74.4 | 43.4 | 0.1 | 30.9 | 25.1 | 5.9 | 21.7 | 4.3 |
Subset of Federal funds.
Subset of Federal and State and local funds.
Calculation of per capita estimates is inappropriate.
NOTES: 0.0 denotes less than $50 million for aggregate amounts, and 0 denotes less than $.50 for per capita amounts. Per capita amounts based on July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Table 7. Nursing home care expenditures aggregate, per capita, and percent distribution, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year | Total | Direct patient payments | Third parties | Medicare1 | Medicaid2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||
| All third parties | Private health insurance | Other private funds | Government | |||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Federal | State and local | ||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $20.4 | $8.9 | $11.5 | $0.2 | $0.1 | $11.2 | $6.0 | $5.2 | $0.4 | $9.8 |
| 1983 | 29.4 | 14.1 | 15.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 14.8 | 8.1 | 6.7 | 0.5 | 13.0 |
| 1984 | 31.6 | 15.5 | 16.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 15.6 | 8.5 | 7.1 | 0.5 | 13.8 |
| 1985 | 34.7 | 17.2 | 17.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 16.9 | 9.5 | 7.4 | 0.5 | 15.0 |
| 1986 | 37.4 | 18.8 | 18.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 18.0 | 10.2 | 7.8 | 0.6 | 16.0 |
| 1987 | 40.6 | 20.0 | 20.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 19.9 | 11.1 | 8.9 | 0.6 | 17.8 |
| Per capita amount | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $87 | $38 | $49 | $1 | $1 | $48 | $26 | $22 | (3) | (3) |
| 1983 | 121 | 58 | 63 | 1 | 1 | 61 | 33 | 28 | (3) | (3) |
| 1984 | 129 | 63 | 66 | 1 | 1 | 64 | 35 | 29 | (3) | (3) |
| 1985 | 140 | 70 | 71 | 1 | 1 | 68 | 38 | 30 | (3) | (3) |
| 1986 | 150 | 75 | 74 | 1 | 1 | 72 | 41 | 31 | (3) | (3) |
| 1987 | 161 | 79 | 82 | 2 | 1 | 79 | 44 | 35 | (3) | (3) |
| Percent distribution | ||||||||||
| 1980 | 100.0 | 43.6 | 56.4 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 54.9 | 29.6 | 25.3 | 1.9 | 48.0 |
| 1983 | 100.0 | 48.0 | 52.0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 50.4 | 27.5 | 22.9 | 1.8 | 44.4 |
| 1984 | 100.0 | 49.0 | 51.0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 49.4 | 26.9 | 22.4 | 1.7 | 43.7 |
| 1985 | 100.0 | 49.7 | 50.3 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 48.7 | 27.3 | 21.4 | 1.6 | 43.4 |
| 1986 | 100.0 | 50.3 | 49.7 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 48.1 | 27.3 | 20.8 | 1.5 | 42.8 |
| 1987 | 100.0 | 49.3 | 50.7 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 49.1 | 27.3 | 21.8 | 1.4 | 43.9 |
Subset of Federal funds.
Subset of Federal and State and local funds.
Calculation of per capita estimates is inappropriate.
NOTE: Per capita amounts based on July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Table 8. Other personal health care expenditures1 aggregate, per capita, and percent distribution, by source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Year | Total | Direct patient payments | Third parties | Medicare2 | Medicaid3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||
| All third parties | Private health insurance | Other private funds | Government | |||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Total | Federal | State and local | ||||||||
| Amount in billions | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $50.9 | $32.0 | $18.8 | $8.6 | $1.5 | $8.7 | $5.7 | $3.0 | $1.5 | $3.4 |
| 1983 | 70.1 | 42.0 | 28.1 | 13.2 | 1.9 | 13.0 | 8.8 | 4.2 | 3.0 | 5.1 |
| 1984 | 77.9 | 46.1 | 31.8 | 15.2 | 2.1 | 14.4 | 9.8 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 5.6 |
| 1985 | 85.5 | 49.5 | 36.1 | 17.3 | 2.3 | 16.5 | 11.2 | 5.3 | 3.9 | 6.8 |
| 1986 | 94.3 | 53.5 | 40.8 | 19.7 | 2.5 | 18.6 | 12.6 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 7.9 |
| 1987 | 104.6 | 58.2 | 46.4 | 22.2 | 2.8 | 21.4 | 14.5 | 6.9 | 5.1 | 9.4 |
| Per capita amount | ||||||||||
| 1980 | $216 | $136 | $80 | $37 | $6 | $37 | $24 | $13 | (4) | (4) |
| 1983 | 289 | 173 | 116 | 55 | 8 | 54 | 36 | 17 | (4) | (4) |
| 1984 | 318 | 188 | 130 | 62 | 9 | 59 | 40 | 19 | (4) | (4) |
| 1985 | 346 | 200 | 146 | 70 | 9 | 67 | 45 | 22 | (4) | (4) |
| 1986 | 378 | 214 | 164 | 79 | 10 | 74 | 51 | 24 | (4) | (4) |
| 1987 | 415 | 231 | 184 | 88 | 11 | 85 | 57 | 28 | (4) | (4) |
| Percent distribution | ||||||||||
| 1980 | 100.0 | 63.0 | 37.0 | 17.0 | 2.9 | 17.2 | 11.2 | 5.9 | 2.9 | 6.7 |
| 1983 | 100.0 | 59.9 | 40.1 | 18.9 | 2.7 | 18.5 | 12.6 | 6.0 | 4.3 | 7.2 |
| 1984 | 100.0 | 59.2 | 40.8 | 19.5 | 2.7 | 18.5 | 12.5 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 7.2 |
| 1985 | 100.0 | 57.8 | 42.2 | 20.2 | 2.7 | 19.3 | 13.1 | 6.2 | 4.5 | 7.9 |
| 1986 | 100.0 | 56.7 | 43.3 | 20.9 | 2.7 | 19.7 | 13.4 | 6.3 | 4.7 | 8.4 |
| 1987 | 100.0 | 55.7 | 44.3 | 21.2 | 2.6 | 20.5 | 13.8 | 6.6 | 4.9 | 9.0 |
Personal health care expenditures other than those for hospital care, physicians' services, and nursing home care.
Subset of Federal funds.
Subset of Federal and State and local funds.
Calculation of per capita estimates is inappropriate.
NOTE: Per capita amounts based on July 1 social security area population estimates.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
Medicare, the largest public financer of health care, provided $81 billion in health care services to 32.4 million aged and disabled enrollees in 1987 (Table 9). The majority of Medicare benefits, 66 percent, purchased hospital care; another 27 percent bought physicians' services.
Table 9. Personal health care expenditures, by type of expenditure and selected source of funds: Selected calendar years 1980-87.
| Source of payment | Total | Hospital care | Physicians' services | Dentists' services | Other professional services | Drugs and sundries | Eyeglasses and appliances | Nursing home care | Other personal care |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||
| Amount in billions | |||||||||
| 1980 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $219.7 | $101.6 | $46.8 | $15.4 | $5.7 | $18.8 | $5.1 | $20.4 | $5.9 |
| Direct patient payments | 63.0 | 7.9 | 14.2 | 10.1 | 2.8 | 15.0 | 4.1 | 8.9 | — |
| Third-party payments | 156.7 | 93.7 | 32.6 | 5.3 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 11.5 | 5.9 |
| Private health insurance | 67.5 | 38.7 | 20.0 | 4.7 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | — |
| Other private | 2.7 | 1.1 | 0.0 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| Government | 86.5 | 53.9 | 12.6 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 11.2 | 4.5 |
| Federal | 62.5 | 41.1 | 9.6 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 3.1 |
| Medicare | 35.7 | 25.9 | 7.9 | — | 0.7 | — | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Medicaid | 13.6 | 5.2 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | — | 5.3 | 0.5 |
| Other | 13.1 | 10.0 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.1 |
| State and local | 24.0 | 12.8 | 3.0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 5.2 | 1.4 |
| Medicaid | 11.6 | 4.4 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | — | 4.5 | 0.4 |
| Other | 12.4 | 8.4 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| Total Medicaid | 25.2 | 9.6 | 2.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.4 | — | 9.8 | 0.9 |
| 1983 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $314.7 | $146.8 | $68.4 | $21.7 | $9.3 | $24.5 | $6.2 | $29.4 | $8.3 |
| Direct patient payments | 88.7 | 13.3 | 19.3 | 13.8 | 4.4 | 19.2 | 4.5 | 14.1 | — |
| Third-party payments | 226.0 | 133.6 | 49.1 | 7.9 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 1.7 | 15.3 | 8.3 |
| Private health insurance | 98.0 | 54.9 | 29.6 | 7.3 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 0.3 | — |
| Other private | 4.0 | 1.8 | 0.0 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.2 | 1.8 |
| Government | 124.1 | 76.8 | 19.5 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 14.8 | 6.5 |
| Federal | 92.9 | 60.4 | 15.6 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 8.1 | 4.5 |
| Medicare | 57.4 | 40.5 | 13.4 | — | 1.4 | — | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Medicaid | 18.3 | 6.9 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.0 | — | 7.0 | 0.9 |
| Other | 17.2 | 13.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| State and local | 31.1 | 16.4 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 6.7 | 2.0 |
| Medicaid | 15.7 | 6.0 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | — | 6.0 | 0.8 |
| Other | 15.5 | 10.4 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.3 |
| Total Medicaid | 33.9 | 12.9 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.9 | — | 13.0 | 1.7 |
| 1984 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $340.1 | $156.1 | $74.4 | $24.6 | $10.8 | $26.5 | $7.0 | $31.6 | $9.0 |
| Direct patient payments | 95.7 | 14.1 | 20.0 | 15.5 | 5.0 | 20.5 | 5.0 | 15.5 | — |
| Third-party payments | 244.4 | 142.0 | 54.5 | 9.1 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 2.0 | 16.1 | 9.0 |
| Private health insurance | 105.3 | 56.5 | 33.3 | 8.6 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | — |
| Other private | 4.0 | 1.7 | 0.0 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.2 | 2.0 |
| Government | 135.1 | 83.9 | 21.2 | 0.5 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 15.6 | 6.9 |
| Federal | 101.2 | 66.0 | 16.9 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 8.5 | 4.8 |
| Medicare | 63.0 | 44.5 | 14.5 | — | 1.6 | — | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| Medicaid | 19.3 | 7.3 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.1 | — | 7.3 | 0.9 |
| Other | 18.8 | 14.2 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 3.0 |
| State and local | 33.9 | 17.9 | 4.3 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 2.1 |
| Medicaid | 17.1 | 6.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.0 | — | 6.5 | 0.8 |
| Other | 18.1 | 11.3 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| Total Medicaid | 36.4 | 13.9 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 2.1 | — | 13.8 | 1.7 |
| 1985 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $368.3 | $166.7 | $81.4 | $27.1 | $12.4 | $28.5 | $7.8 | $34.7 | $9.8 |
| Direct patient payments | 103.7 | 15.4 | 21.6 | 16.8 | 5.4 | 21.8 | 5.4 | 17.2 | — |
| Third-party payments | 264.6 | 151.4 | 59.7 | 10.3 | 7.0 | 6.7 | 2.3 | 17.4 | 9.8 |
| Private health insurance | 112.0 | 58.9 | 35.6 | 9.7 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | — |
| Other private | 4.6 | 2.0 | 0.0 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| Government | 148.0 | 90.5 | 24.1 | 0.6 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 16.9 | 7.6 |
| Federal | 111.3 | 71.3 | 19.3 | 0.3 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 9.5 | 5.3 |
| Medicare | 69.3 | 48.2 | 16.7 | — | 1.7 | — | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Medicaid | 22.1 | 8.2 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.4 | — | 8.2 | 1.1 |
| Other | 19.9 | 14.9 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 3.3 |
| State and local | 36.7 | 19.2 | 4.8 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 7.4 | 2.2 |
| Medicaid | 18.2 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.1 | — | 6.8 | 0.8 |
| Other | 18.5 | 12.5 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.5 |
| Total Medicaid | 40.3 | 14.9 | 3.5 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | — | 15.0 | 1.8 |
| 1986 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $401.6 | $178.4 | $91.6 | $29.6 | $14.1 | $31.3 | $8.7 | $37.4 | $10.7 |
| Direct patient payments | 112.6 | 16.7 | 23.7 | 18.2 | 5.7 | 23.7 | 5.9 | 18.8 | — |
| Third-party payments | 289.0 | 161.7 | 67.9 | 11.4 | 8.3 | 7.6 | 2.7 | 18.6 | 10.7 |
| Private health insurance | 124.6 | 64.4 | 40.2 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | — |
| Other private | 4.8 | 2.0 | 0.1 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| Government | 159.6 | 95.4 | 27.6 | 0.6 | 4.6 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 18.0 | 8.3 |
| Federal | 120.3 | 75.1 | 22.4 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 10.2 | 5.9 |
| Medicare | 74.6 | 50.4 | 19.3 | — | 1.8 | — | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Medicaid | 24.2 | 8.8 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.6 | — | 8.8 | 1.2 |
| Other | 21.5 | 15.9 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 3.6 |
| State and local | 39.2 | 20.2 | 5.3 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 7.8 | 2.4 |
| Medicaid | 19.4 | 7.0 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 | — | 7.2 | 0.9 |
| Other | 19.9 | 13.2 | 3.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| Total Medicaid | 43.6 | 15.8 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 2.9 | — | 16.0 | 2.1 |
| 1987 | |||||||||
| Personal health care expenditures | $442.6 | $194.7 | $102.7 | $32.8 | $16.2 | $34.0 | $9.5 | $40.6 | $12.0 |
| Direct patient payments | 123.0 | 18.5 | 26.3 | 20.0 | 6.4 | 25.5 | 6.3 | 20.0 | — |
| Third-party payments | 319.6 | 176.2 | 76.4 | 12.8 | 9.8 | 8.6 | 3.2 | 20.6 | 12.0 |
| Private health insurance | 139.1 | 71.9 | 44.6 | 12.1 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | — |
| Other private | 5.3 | 2.2 | 0.1 | — | 0.1 | — | — | 0.3 | 2.6 |
| Government | 175.3 | 102.2 | 31.8 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 3.9 | 2.1 | 19.9 | 9.4 |
| Federal | 131.2 | 80.0 | 25.7 | 0.3 | 3.6 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 11.1 | 6.7 |
| Medicare | 81.2 | 53.3 | 22.3 | — | 2.0 | — | 1.8 | 0.6 | 1.3 |
| Medicaid | 26.8 | 9.7 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 | — | 9.6 | 1.4 |
| Other | 23.2 | 17.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 4.0 |
| State and local | 44.1 | 22.2 | 6.1 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 8.9 | 2.7 |
| Medicaid | 22.6 | 8.1 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 1.6 | — | 8.2 | 1.0 |
| Other | 21.5 | 14.1 | 4.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.7 |
| Total Medicaid | 49.4 | 17.8 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 | — | 17.8 | 2.4 |
NOTES: 0.0 denotes less than $50 million. Medicaid expenditures include Part B premium payments to Medicare by States under “buy-in” agreements to cover premiums for eligible Medicaid recipients.
SOURCE: Health Care Financing Administration, Office of the Actuary: Data from the Office of National Cost Estimates.
During the last 14 years with only one exception, Medicare spending for physicians' care grew 15 to 26 percent per year. Medicare expenditures for hospital care experienced similar growth rates for 1974-82, but that growth has slowed considerably in the last few years because of the implementation of the prospective payment system (PPS). As a result, Medicare's share of expenditures for physicians' services grew from 13 percent in 1974 to 22 percent in 1987; its share of expenditures for hospital care increased from 20 to 27 percent during the same period.
In 1987, the Medicaid program spent $49 billion, 11 percent of all personal health care, on behalf of low-income and medically indigent individuals. This program is jointly funded by Federal and State and local governments. Medicaid is heavily weighted towards institutional care: Program funds are evenly split (36 percent each) between hospital and nursing home care. The share Medicaid paid for nursing home care has decreased from 48 percent in 1980 to 44 percent in 1987; the out-of-pocket share for nursing home care has increased from 44 percent in 1980 to 49 percent in 1987.
Besides Medicare and Medicaid, there are many other public sources of financing for health care services. In 1987, these other programs paid $45 billion in personal health benefits, and represent 10 percent of personal health spending. This category includes such programs as the Veterans' Administration, Department of Defense, Indian Health Service, worker's compensation, and maternal and child health.
Financing other health expenditures
Of the $26 billion spent on program administration and the net cost of private health insurance, 25 percent was for public programs and the remainder for private programs (mainly private health insurance). Government public health activities are financed by Federal (11 percent), and State and local governments (89 percent). An example of Federal government public health would be the Centers for Disease Control in Atlanta that targets diseases rather than beneficiary populations. Activities of State and local health departments comprise most of the State and local public health programs.
The Federal government financed the largest amount for research, with funds totaling $7 billion, most of which was spent by the National Institutes of Health. Of the $8 billion spent on construction of medical facilities in 1987, 32 percent came from public sources, and the remainder was financed by private sources.
Figure 1. Percent change in national health expenditures and gross national product, and national health expenditures as a percent of gross national product: 1965-87.
Figure 2. The Nation's health dollar: 1987.
Acknowledgments
This article was prepared in the Office of National Cost Estimates under the general supervision of Ross H. Arnett, III, Director. The authors are grateful to members of the office staff who assisted in the assembling of data and the preparation of estimates.
Footnotes
Reprint requests: Carol Pearson, LI, 1705 Equitable Building, 6325 Security Boulevard, Baltimore, Maryland 21207.